ch4- Moving charges and magnetism
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Lowrants force
F = qE + q(v x B)
force experienced by moving charge in a magnetic and electric field
v= velocity of charge
electric lowrants force- F = qE
magnetic lowrants force-F= q(v x B)
magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor
I(lxB)
IlBsin theta
A charged particle moving in the direction or opposite direction of magnetic field moves ………………….
undeflected.
A charged particle entering perpendicular to a magnetic field moves in a ………………. path.
Circular.
A charged particle moves at an arbitrary angle 𝛉 with the manetic field. What will be the shape of its path?
It move in a helical path.
Biot- Savart’s law
magnetic field experienced at a point due to a current element is
inversly proportional to the square of the distance between the line joining the current element to the point
directly proportional to sin theta of the angle between the line joining the current element and point
directly proportional to the strength of the current flowing through the current element
directly proportional to the length of the current element
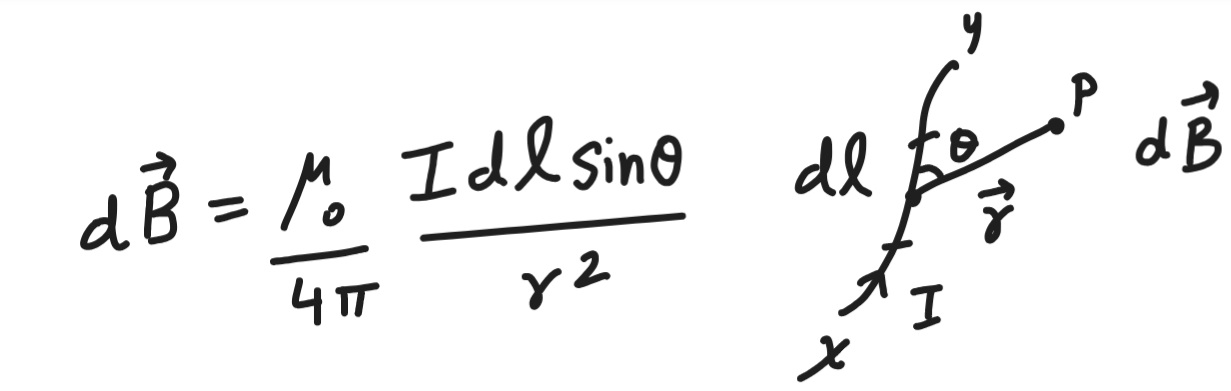
μ0
4π×10-7 Tm/A OR TmA-1
biot savart’s law in vector form
dB = μ0 /4π * (d𝒍 ̅̅̅ x r̅)/ r3
ampere’s cirutal theorem
line integral of magnetic field around any closed path in free space is equal to
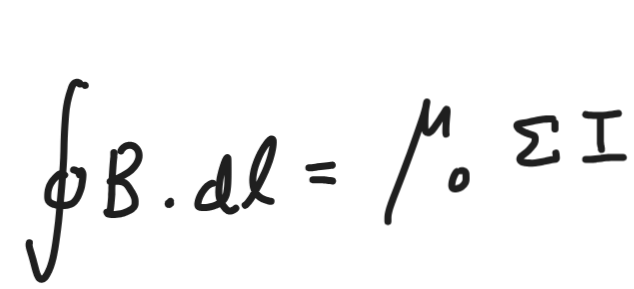
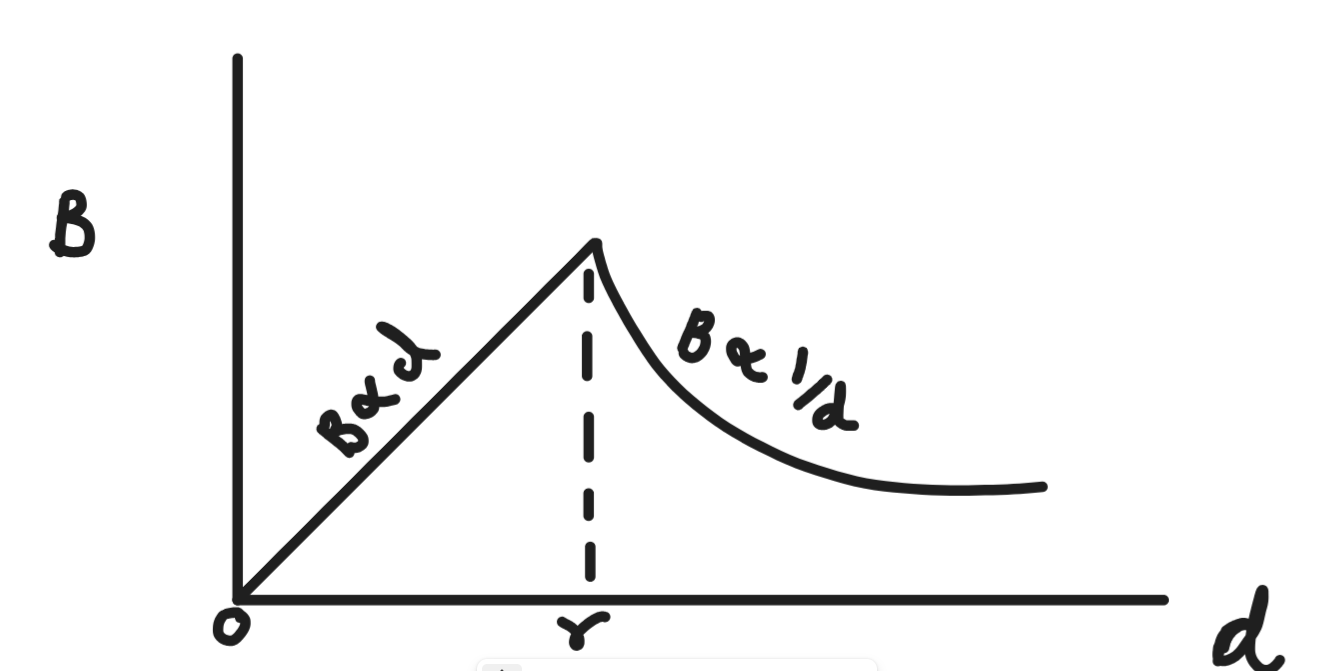
variation of magnetic field with distance from the axis
magnetic field due to long straight conductor
B= μ0I/2π r
magnetic field due to solenoid
B= μ0I n
principle of galvanometer
a rectangular current carrying coil placed in a magnetic field experiences torque and deflects. The deflection produced in the coil is directly proportional to the current passing through the coil.
current sensitivity
Φ/I=BAN/K
K= torrsional constant
deflection per unit current
voltage sensitivity
deflection per unit voltage
Φ/V=BAN/KR
galvanometer to ammeter
galvanometer to voltmeter
S=IgG/(I-Ig)
R=V/Ig -G