Geology - Plate Tectonics
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Earth's layers were formed by
Differentiation and is based on density, composition, temperature, and pressure
Components of the Earth's Crust
Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, and Lithosphere
Lithosphere
made of crust and upper part of mantle; broken into tectonic plates
Astenosphere
Hotter and denser and located below the lithosphere, allows for the movement of plates through mantle convection
Oceanic Crust
Apart of the lithosphere which is thinner, younger, and denser
Continental Cust
Apart of the lithosphere which is thicker, older, and less dense
What is Plate Tectonic Theory?
A unifying theory that provides the framework for understanding processes operating within the Earth's interior and surface.
Alfred Wegener
A German scientist who proposed the theory of continental drift in 1915
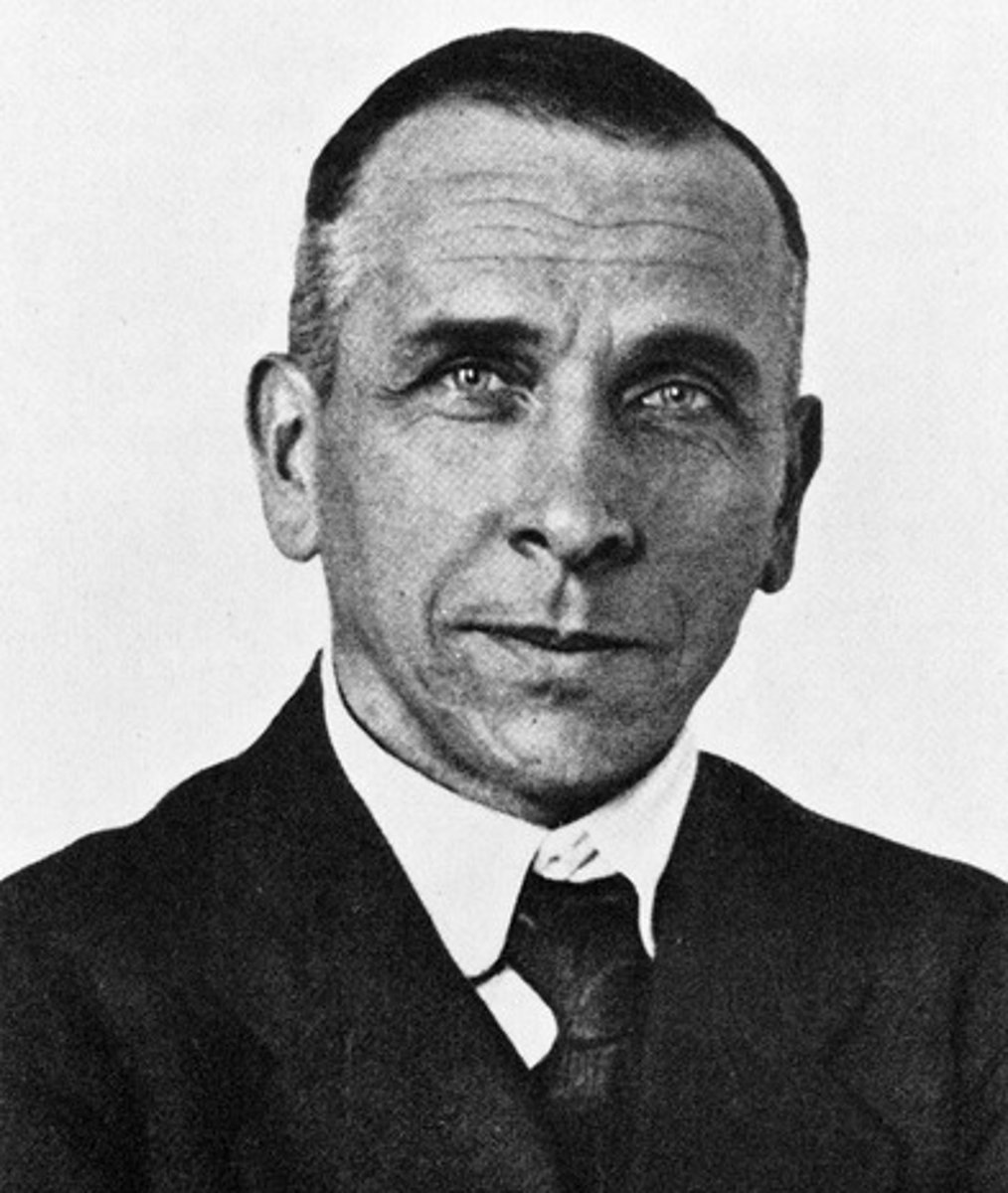

Continental Drift Theory
Alfred Wegener believed landmasses of Earth once fit together to form single landmass called "Pangaea"; landmasses "drifted" to where they are today over 200 million years ago
Name of Wegener's supercontinent
Pangaea
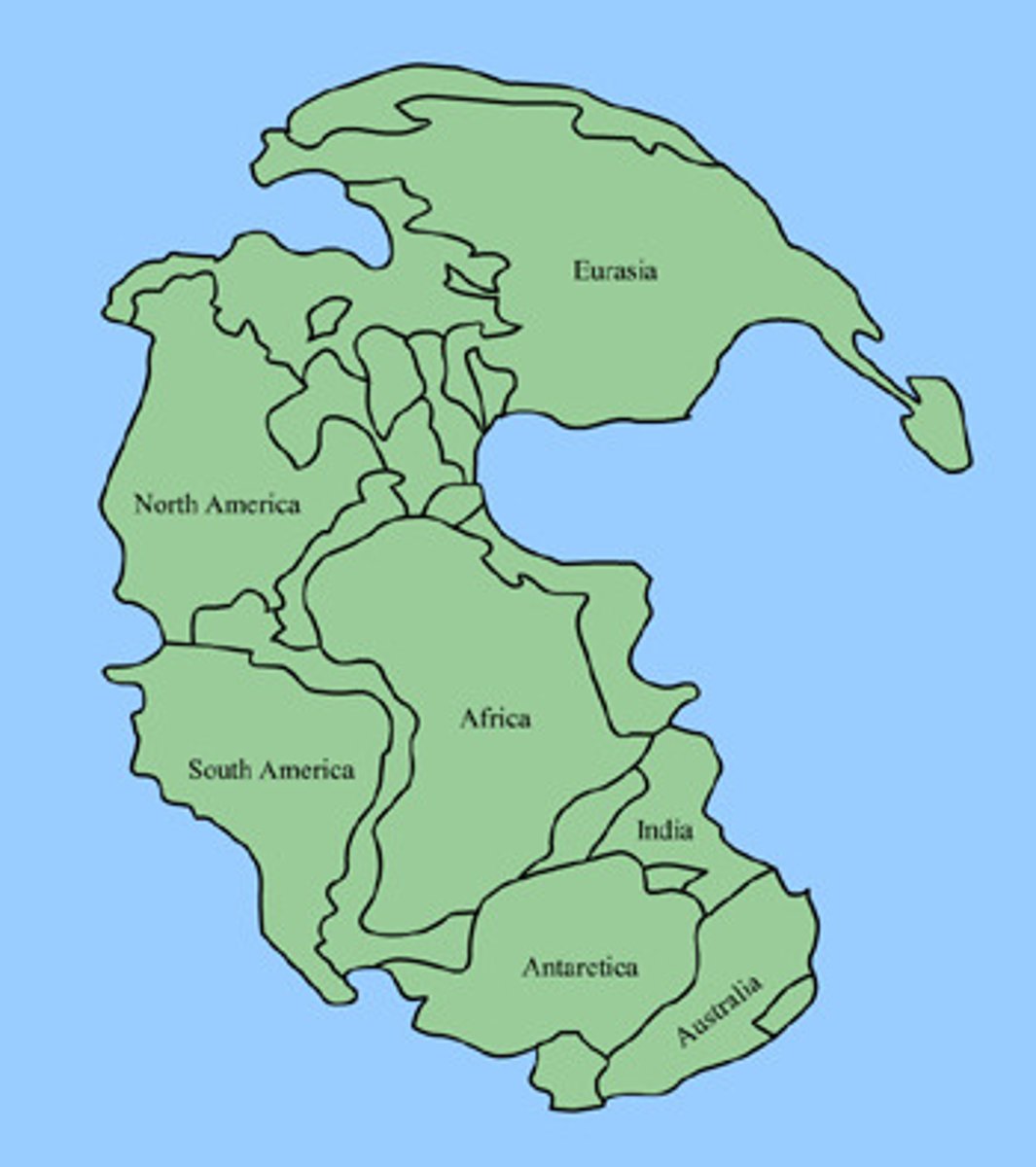
Why was Wegener's theory rejected?
There was no mechanism to prove his theory and he was a meteorologist
Evidence for Continental Drift
1. the continental fit of Africa and South America, 2. Fossils match across the seas, 3. Ancient Climates, 4. Rock type and structure match
Describe how mantle convection moves lithospheric plates (continents)
The Earth's heat drives convection currents and mantle plumes extend from mantle-core boundaries as it has less density than solid rock
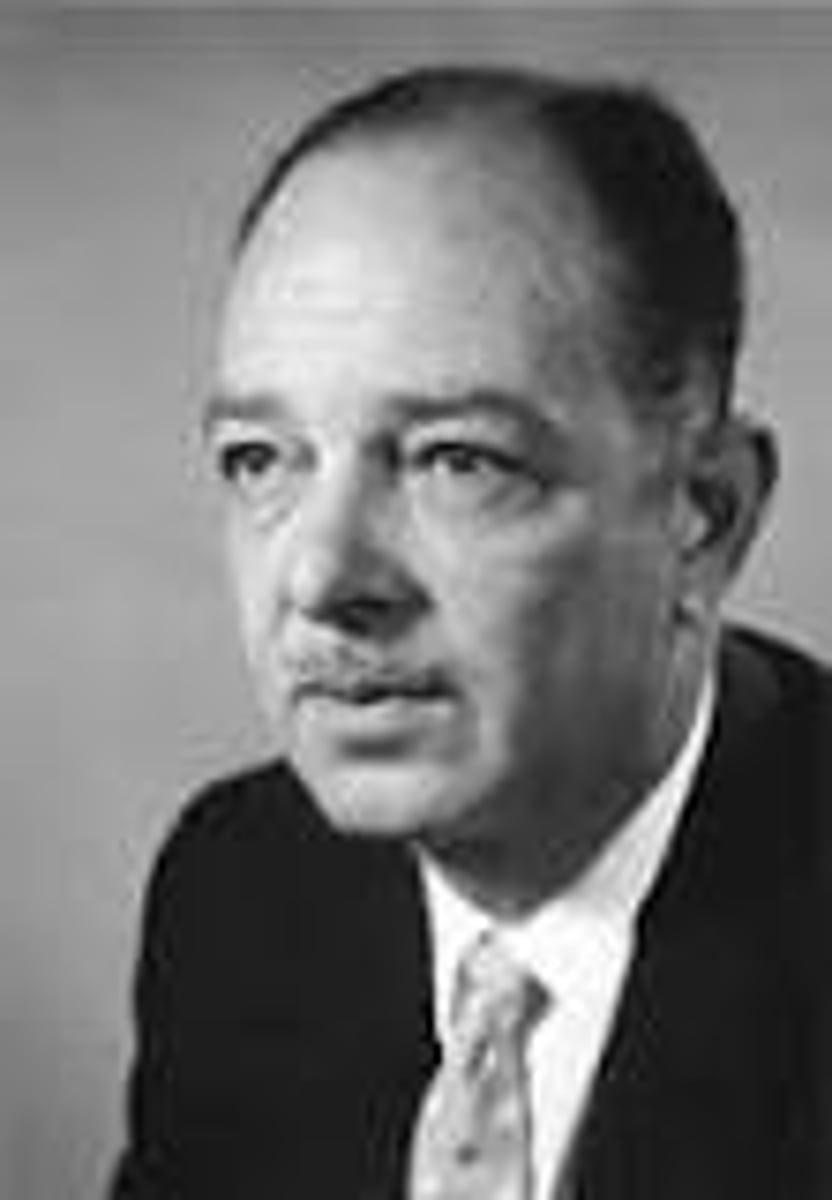
Harry Hess
Proposed the theory of sea-floor spreading in 1960, provided a mechanism which surpassed Wegener's.

Sea-floor spreading
the process by which new oceanic crust forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies. Older rock is pushed away in opposite directions
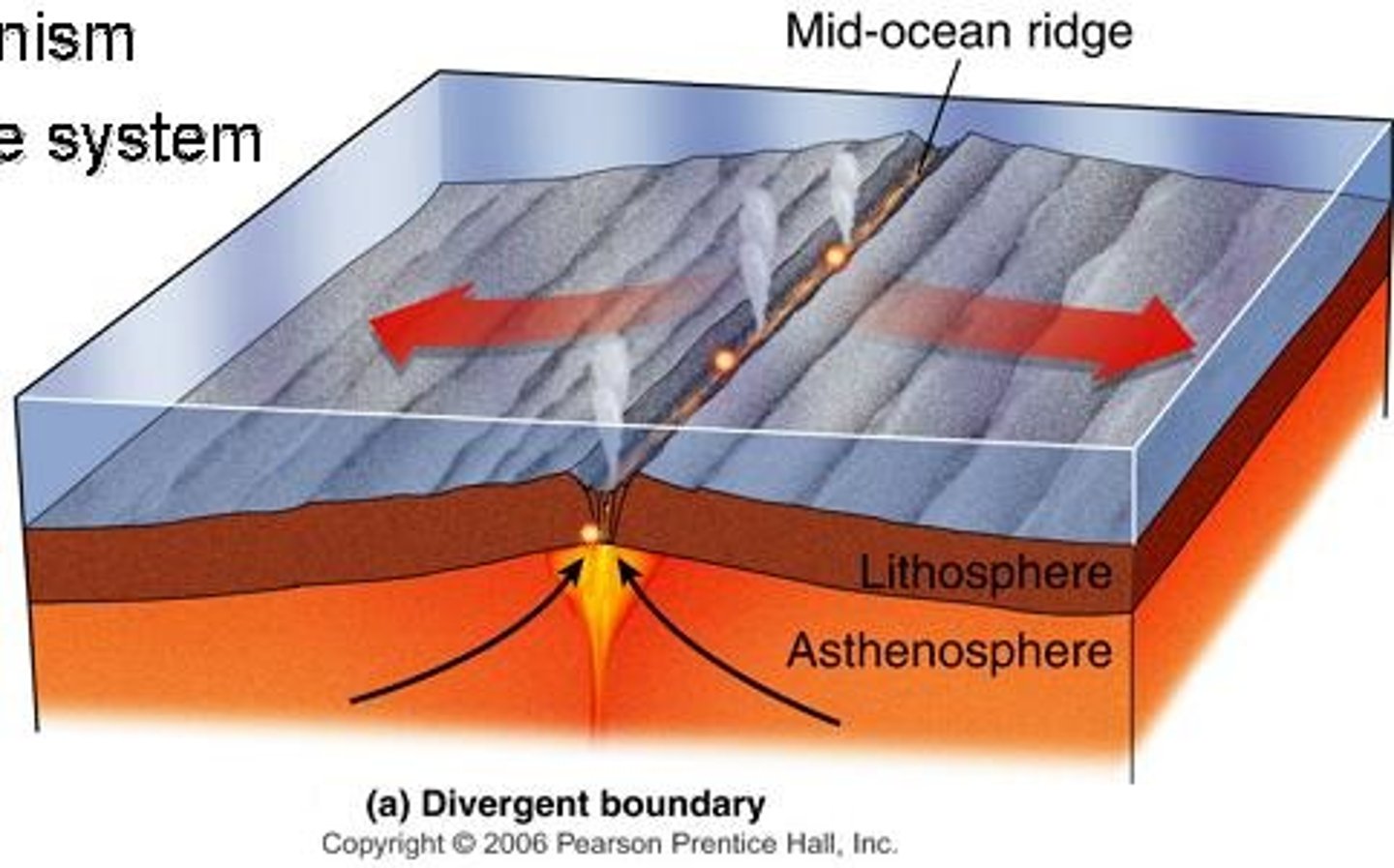
Sea-floor spreading creates
mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and ocean basins
How does Sea-floor spreading relate to mid-oceanic ridge systems
Magma rises at mid-ocean ridges as tectonic plates rise up to create new crust
Where are the youngest and oldest oceanic crusts along mid-oceanic ridge systems
The youngest is located at the center, and the oldest is spread farthest from the oceanic ridge
Three types of boundaries are
convergent, divergent, transform
convergent boundary
A destructive plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
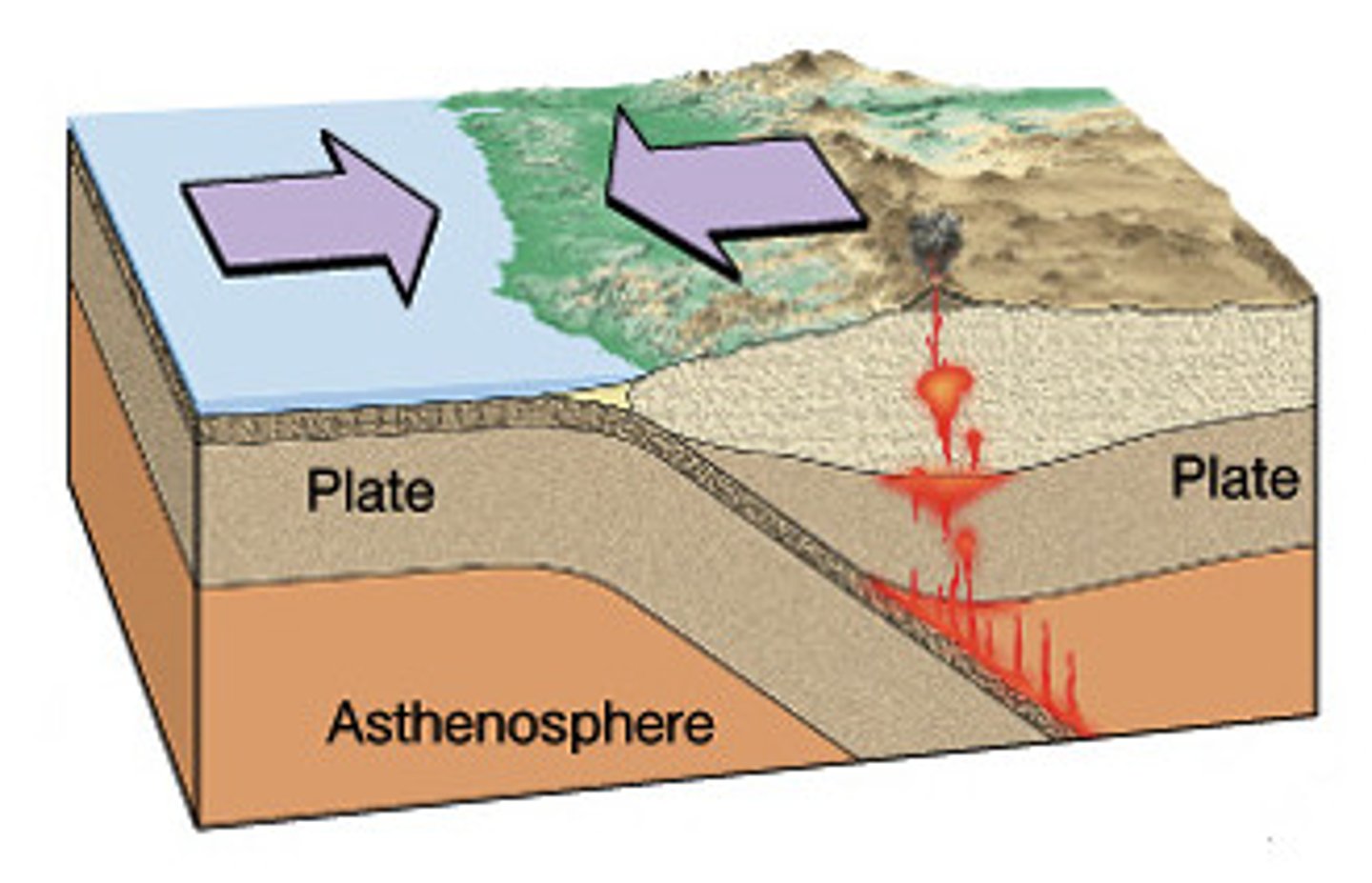
What do convergent boundaries form?
Mountains, Volcanic Arcs, and Trenches
The three types of convergent boundaries
oceanic-oceanic, oceanic-continental, continental-continental
What happens when 2 oceanic plates collide?
Ocean trenches form as the denser oceanic plate subducts.
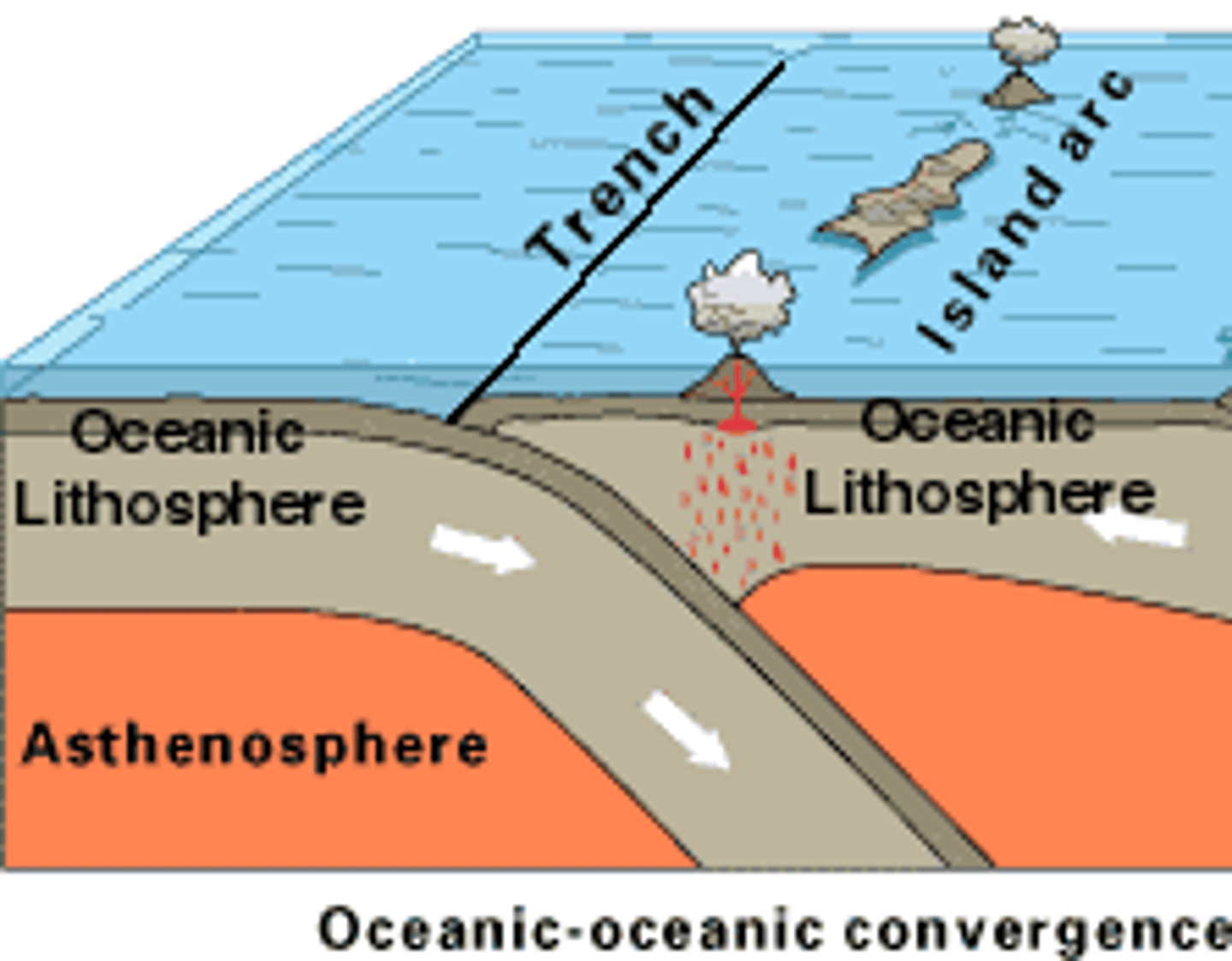
What is formed as a result of oceanic-oceanic plate subduction?
Ocean volcanoes.
How are volcanic islands formed in oceanic-oceanic collisions?
Volcanoes emerge from the sea.
Examples of Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence
Aleutian Mountains, Mariana Trench, and Tonga Islands
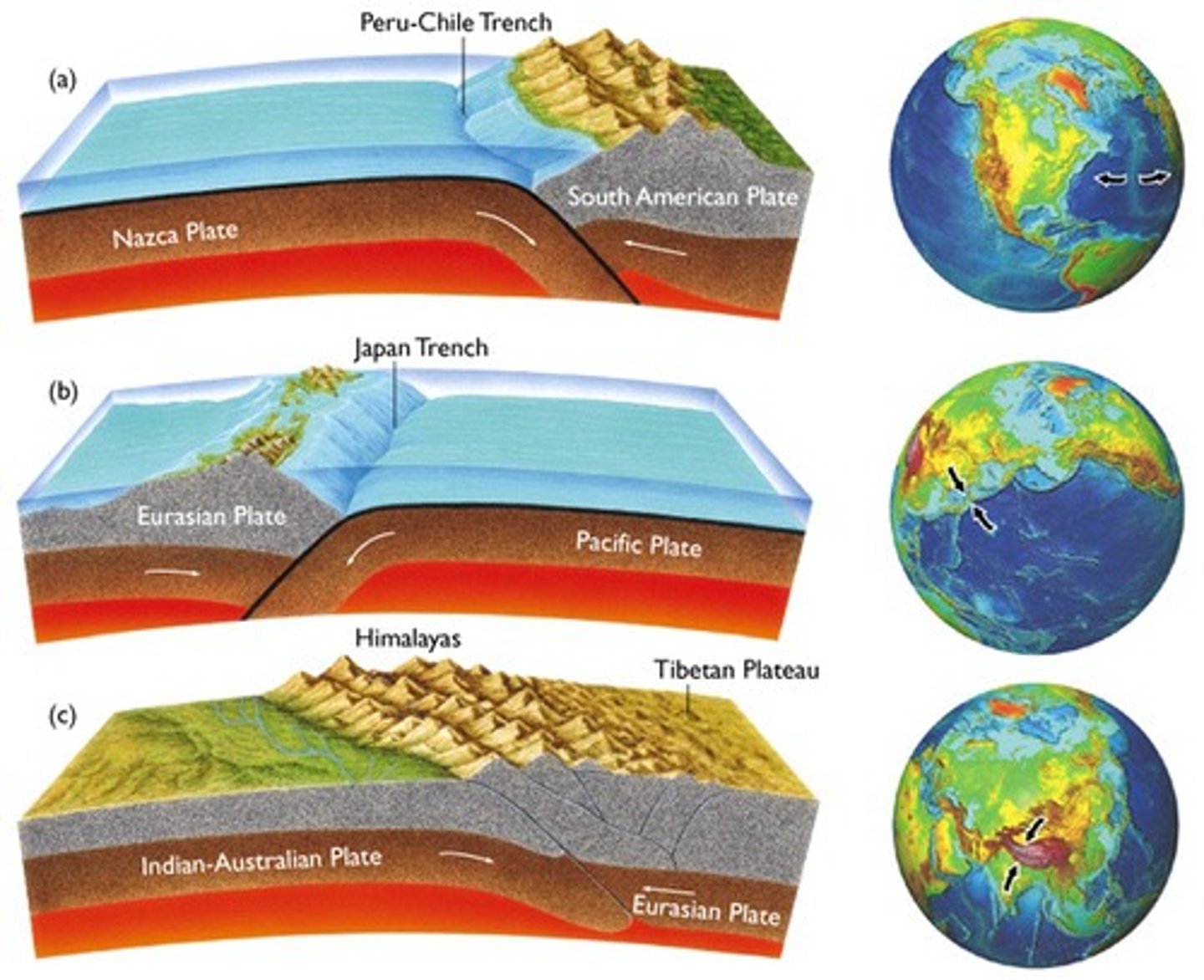
What happens during oceanic-continental subduction?
Oceanic crust subduces below continental crust and partially melts.
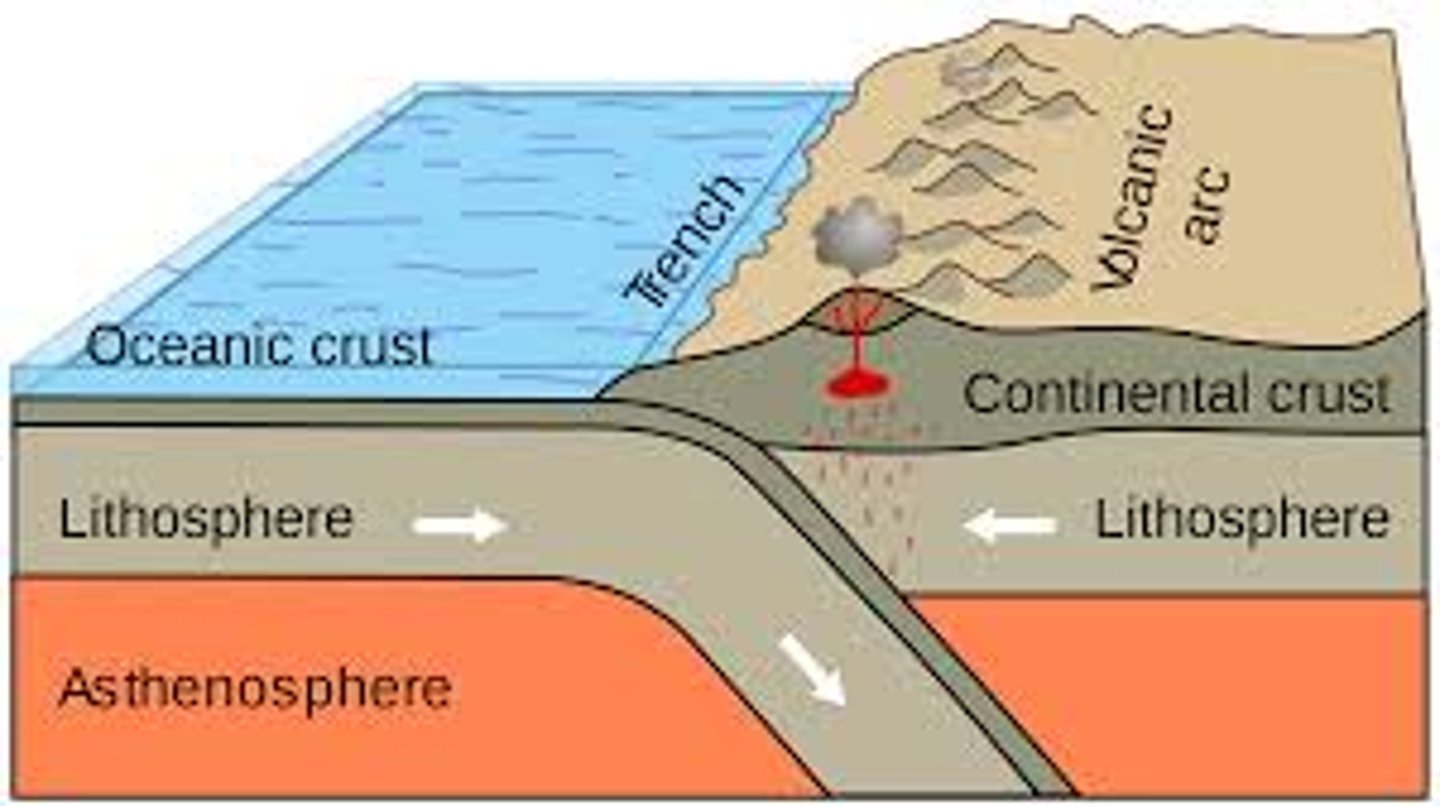
What rises from continental volcanic arcs during oceanic-continental subduction?
Molten rock rises from continental volcanic arcs near the coastline.
Where are continental volcanic arcs located in relation to oceanic-continental trenches?
Continental volcanic arcs are parallel to ocean trenches. (Ex: Andes Mountains and Peru-Chile Trench)
continental-continental convergence
Begins as subduction, 2 plates collide after ocean basins close. (Ex: Himalayas and Alps Mountains)
divergent boundary
A constructive margin where 2 plates move apart and mantle material rises to form new crust
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions. No new crust is created/destroyed, and no new crust is formed
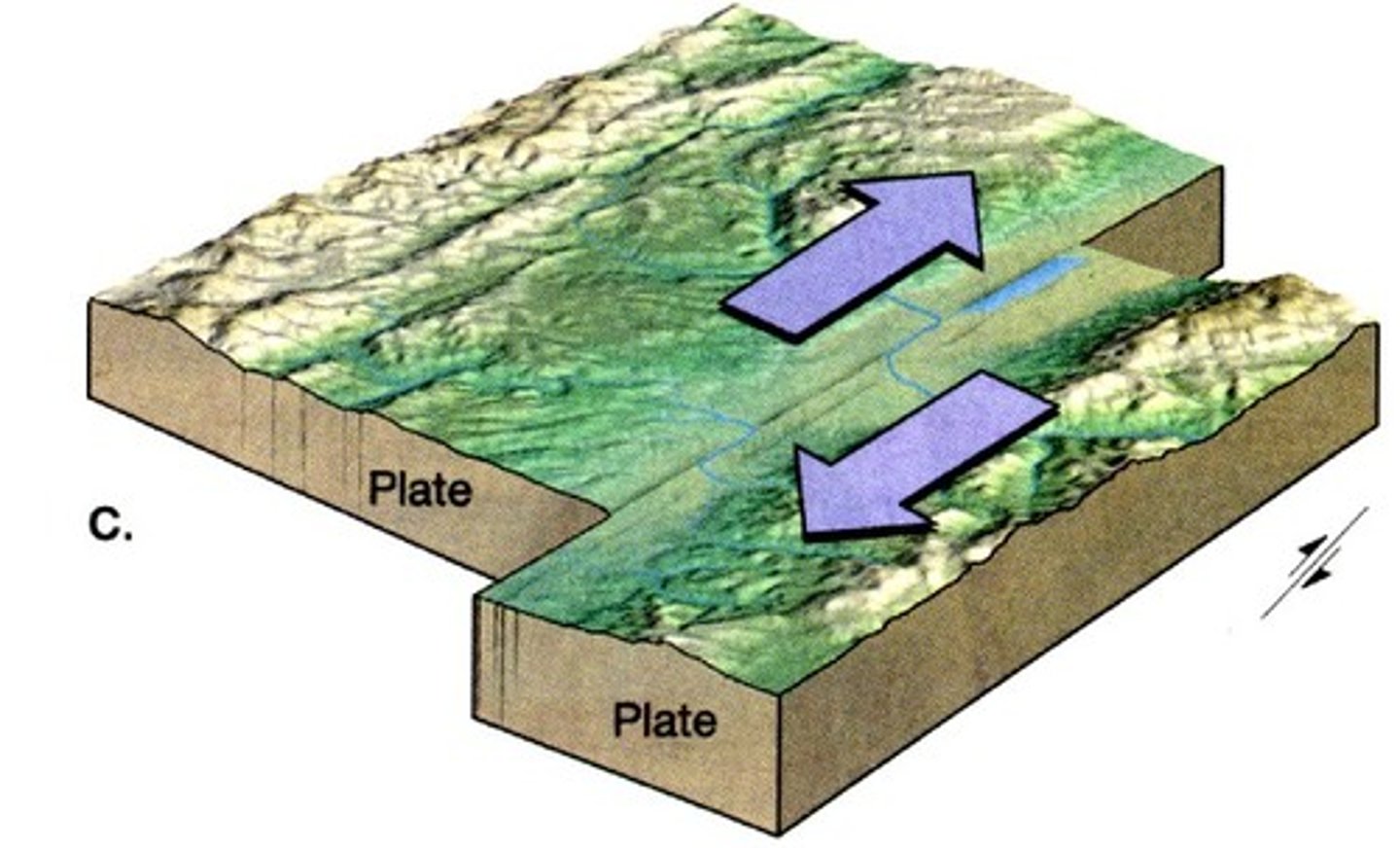
2 types of transform boundaries
oceanic and continental
Japan's plate boundary
Convergent
Cascade Range Plate Boundary
Convergent
San Andreas Fault Boundary
Transform
Himalayas Boundary
Convergent
Aluetion Islands
Convergent
Boundary that was responsible for the breakup of Pangea?
Divergent
Plate boundaries that cause earthquakes
All (Convergent, Divergent, and Transform)
Plate boundary that causes deep-focus earthquakes
Convergent
Plate boundaries associated with trenches and volcanic arcs
Convergent
The 2 types of volcanic arcs
Continental and Island
How do continental volcanic arcs form?
When oceanic crust subducts below continental plates, creating a subduction zone. Arcs are formed near the coastline
How do volcanic islands form?
oceanic-oceanic convergence, the denser plate subducts and partially melts and produces magma
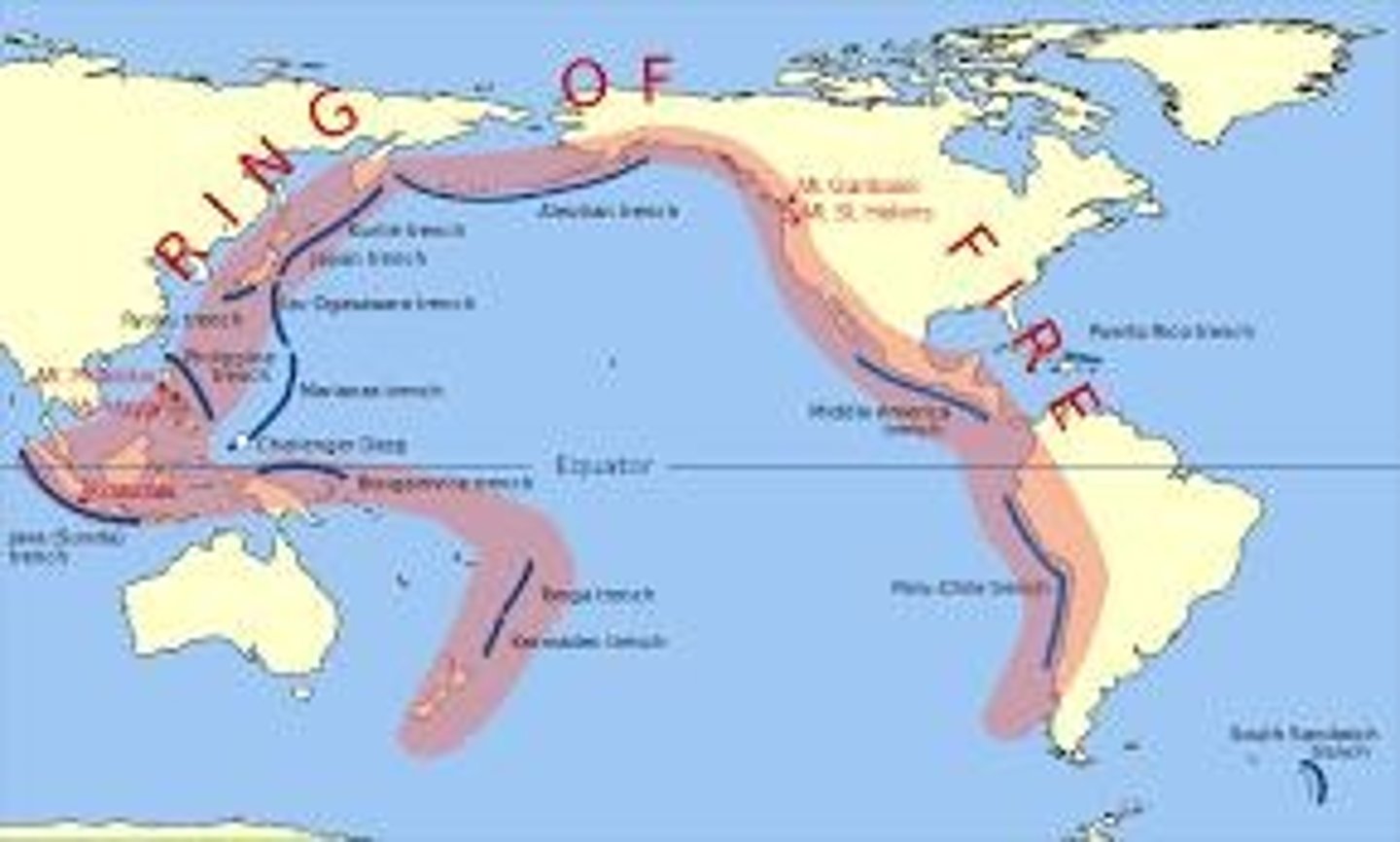
Significance of the ring of fire
The world's most volcanically and seismically active zone, responsible for ~75% of volcanoes and ~90% of all earthquakes, due to the constant movement of tectonic plates
What causes offsets along the mid-oceanic ridge system?
Tectonic plates pulling apart at divergent boundaries in a process called seafloor spreading
What type of plate boundary seldom produces volcanoes?
Transform