Aromatic Chemistry
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
benzene
Alternating single and double carbon carbon bond
1st problem with kekule's model of benzene
The first problem with Kekulé’s model of benzene is that it suggests that benzene should be able to undergo addition reactions with bromine (as it has a C=C). This means that when bromine is added to benzene it should turn colourless. But, it doesn’t!
The Second Problem with Kekulé's Model
The second problem with Kekulé’s model of benzene is that it suggests that benzene should have 2 different carbon-carbon bond lengths (one for the carbon single bonds and one for the carbon carbon double bonds).
However, experimental evidence has shown that these bond lengths are identical.
enthalpy of hydrogenation
The third problem with Kekulé’s model of benzene
The third problem with Kekulé’s model of benzene is that it suggests that benzene’s enthalpy of hydrogenation should be approximately -360 kJ mol−1.
However, experimental evidence has found that it’s less exothermic than expected!
problems with kekukes models summary
valence bond theory
"Why can carbon form 4 covalent bonds?"
Carbon can make 4 bonds because it promotes an electron from its 2s orbital to an empty 2p orbital/ this leaves it with 4 orbitals containing unpaired electrons wich can all form covalent bonds
difference between sigma and pi bond
"Why can't Kekulé’s model of benzene be correct?"
If Kekulé’s model of benzene is correct, we’d assume each carbon atom forms 3 sigma bond(s) and 1 pi bond(s)/ this can't be the case because the carbon carbon lengths are identical
"How are the electrons arranged in benzene?"
each carbon forms 3 sigma bonds.
a p orbital from each carbon overlaps with two neighbouring p orbitals.
the electrons are delocalised across the ring.
how do we draw benzene
The circle represents the ring of delocalised electrons. In the exam you will gets marks for drawing benzene either way
We know that a compound has delocalised electrons when it contains…
single and double carbon-carbon bonds.This means the p orbitals involved in forming the pi bonds can overlap.
what do aromatic compounds contains
benzene ring. Most aromatic compounds have a distinctive smell
Why and how does delocalization of electrons increase the stability of a molecule?
When a compound has delocalised electrons its stability increases (less likely to react with other molecules).
This is because the electrons are spread across a greater distance, so its electron density decreases.
So molecules with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds are more stable
Why does benzene have identical bond lengths
Benzene has identical carbon-carbon bond lengths because each p orbital overlaps both of its neighbouring p orbitals by the same amount above and below the ring.
Addressing the first problem with kekules model - why doesn't benzene undergo additional reactions with bromine?
Benzene does not undergo addition reactions with bromine because it has lower electron density than alkenes.
Why is benzene enthalpy of hydrogenation less exothermic than expected?
The enthalpy of hydrogenation value for benzene is less exothermic than expected because benzene’s delocalised electrons increase its stability
explaining the bond in benzene exam technique
explaining the shape of benzene - exam technique
"How do we name a compound when benzene is the highest priority functional group?"
When benzene is the highest priority functional group, we write the suffix ‘benzene’.
"How do we name a compound when benzene is NOT the highest priority functional group?"
When benzene isn’t the highest priority functional group, we write the prefix ‘phenyl’.
"How do we name benzene compounds when there are multiple substituents?"
When we add the substituents to the prefix we:
include the position number if there’s more than one substituent
include multipliers when there are identical substituents.
What is a nitro group?
NO2
"How do we name benzene compounds with a nitro (-NO₂) group?"
When we name compounds with a nitro group, we write the prefix ‘nitro’. Nitro groups are the lowest functional group
When we name aromatic compounds containing alcohols, we…
write the prefix ‘phenyl’ and treat the benzene ring as a substituent (we don’t include benzene in the longest carbon chain.
"How do you name a aromatic compound with a benzene group and an alcohol (-OH) functional group?"
Identify the longest carbon chain to work out the root (exclude the benzene ring) the longest carbon chain in this compound contains 3 carbons so the root is ‘prop’
Identify the highest priority functional group (which is the alcohol) so we add the suffix ‘anol’
Label the positon numbers of the carbons and identify the position number of the alcohol functional group (in this case it is 1)
Add the prefix phenyl (benzene group)
Add the positon number of the benzene group if the benzene group cna be located on multiple carbons. If the benzene can only be located on one carbon then dont include the positon number
Position number of benzene group ----- phenyl-----number of carbon in longest chain------- an------positon of alcohol functional group -- ol
"How do you name a compound with a benzene group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional group?"
Identify the longest carbon chain to work out the root (exclude the benzene ring) the longest carbon chain in this compound contains 5 carbons so the root is ‘pent’
Identify the highest priority functional group (which is the carboxylic acid) so we add the suffix ‘anoic acid’
Label the positon numbers of the carbons and identify the position number of the carbonyl group functional group (in this case we include positon numbers because COOH groups are always at the end of moelcuels)
Add the prefix phenyl (benzene group)
Add the positon number of the benzene group (2) if the benzene group cna be located on multiple carbons. If the benzene can only be located on one carbon then dont include the positon number
aromatic compounds with carbonyl groups
Position number of benzene group ----- phenyl-----number of carbon in longest chain------- suffix of cabronyl group ------positon of carbonyl functional group -- suffix of carbonyl group
what is a substitution reaction
Under certain conditions, benzene can react with bromine to form bromobenzene and H+.The reaction of bromine with benzene to form bromobenzene is an example of a substitution reaction.
"Why do we need a to react bromine with benzene and why?"
To react bromine with benzene we need to use a halogen carrier such as AlBr3/aluminium bromide or FeBr3/iron bromide. The halogen carrier forms a stronger electrophile.
For example when we react aluminium bromide with bromine
The halogen carrier forms stronger electrophile ---- This bromine cation (Br+) is a stronger electrophile
Electrophilic substitution reaction ---Step one of reaction between benzene and bromine
To explain how bromine replaces a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring, chemists proposed that:
A C-Br bond forms
A pi bond breaks
When benzene reacts with bromine and a halogen carrier, they undergo an electrophilic substitution reaction. During the reaction of benzene and bromine
Step 1:
A C-Br bond forms
A pi bond breaks forming an intermediate
Step 2
C-H bond breaks (intermeidate)
The two electron reform the pi bond (final product)
"What is the general mechanism for electrophilic substitution in benzene?"
We can generalise the mechanism to all electrophilic substitution involving benzene. All the mechanisms we see at a level will involve a positively charged electrophile so we can generalize the mechanism by representing the electrophile with E
Exam tips for drawing the electrophilic substitution of benzene
The curly arrow should start from the circle/pi system
Exam tips for drawing the electrophilic substitution of benzene
When you draw the intermediate you need to make sure the horse shoe does not extend before the top 2 carbons and doesn't stop before the bottom 2 cabrons
Exam tips for drawing the electrophilic substitution of benzene
In the intermediate the positive charge should be in line with the 2 carbons not below them
Exam tips for drawing the electrophilic substitution of benzene
The curly arrow in the intermediate which starts from the C-H bond should end inside the hexagon
During Friedel-Crafts acylation…
an electrophilic substitution reaction takes place.
an acyl group is substituted onto benzene. Hydrogen is removed and bonds to the Cl to make HCl
"How do we react acyl chlorides with benzene?
To react acyl chlorides with benzene, we need to use halogen carrier or aluminium chloride. It forms the electrophile by removing chlorine from the acetyl chloride (RCOCl +AlCl3 ------ RCO+ + AlCl4-)
Friedal-Crafts Acylation: the mechnism
when acyl chlorides react with benzene and a halogen carrier…
a carbon-carbon bond forms
a carbon-hydrogen bond breaks.
"How do we write equations for the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene?"
When we write equations for the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene, we write the molecular formula for benzene and the structural formula of everything else.
The 1st equation shows the overall equation for a reaction between acyl chloride and benzene
The 2nd equation shows the regeneration of the catalyst.
Example: the overall reaction between benzene and ethanoyl chloride
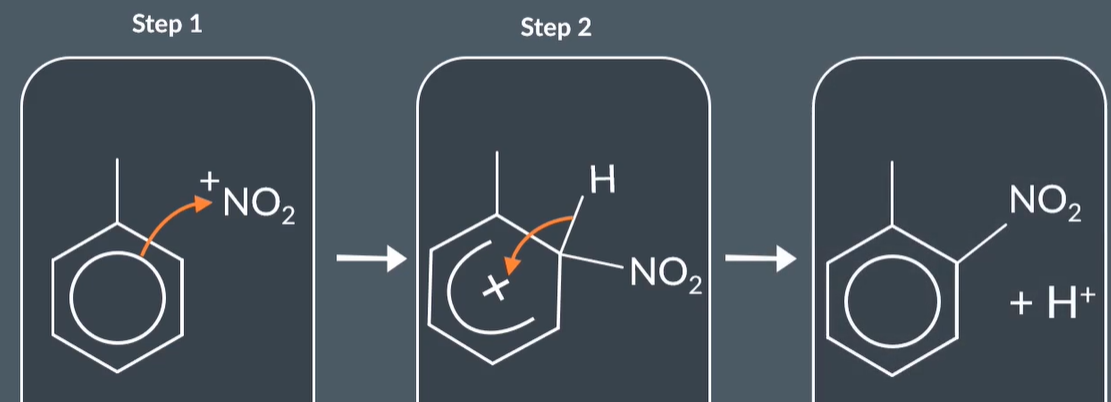
nitration of benzene
"What happens when benzene undergoes a nitration reaction?"
When benzene undergoes a nitration reaction we produce nitrobenzene and water. For this reaction we need to use concentrated HNO3 (conc nitric acid) and concentrated H2SO4 catalyst (conc sulfuric acid catalyst)
In the exam you must specify that the reagents are CONCENTRATED or you won't get the mark.
The equation for the reaction between nitric acid and sulfuric acid looks like this. This is all you need to know for A level
NO2+ is the nitronium ion which is the electrophile we need to produce
Nitration of Benzene: The Mechanism
Why Do Nitric Acid and Sulfuric Acid Need to Be Concentrated?
Well, if these acids are dilute, that means they’re in a solution in water. And as we’ve seen, the mechanism for this reaction is reversible.
This means that if our reaction mixture contains a lot of water, the equilibrium position will move to the left. And so, we’ll end up with a much lower yield of our electrophile!
The electrophiles generated in these reactions are extremely reactive. So, rather than reacting with benzene, they’ll react with water instead!