Gas Laws and Kinetic Molecular Theory
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Gas Variables
Four variables: volume, pressure, temperature, moles.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Describes gas behavior based on particle motion.
Volume
Space occupied by gas, measured in mL or L.
Pressure
Force exerted by gas per unit area.
Temperature
Measures kinetic energy of gas particles.
Number of Moles
Amount of substance in a gas sample.
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
Conditions: 1 atm and 273 K (0°C).
Elastic Collisions
No energy loss during gas molecule collisions.
Attractive Forces
Negligible between gas molecules in motion.
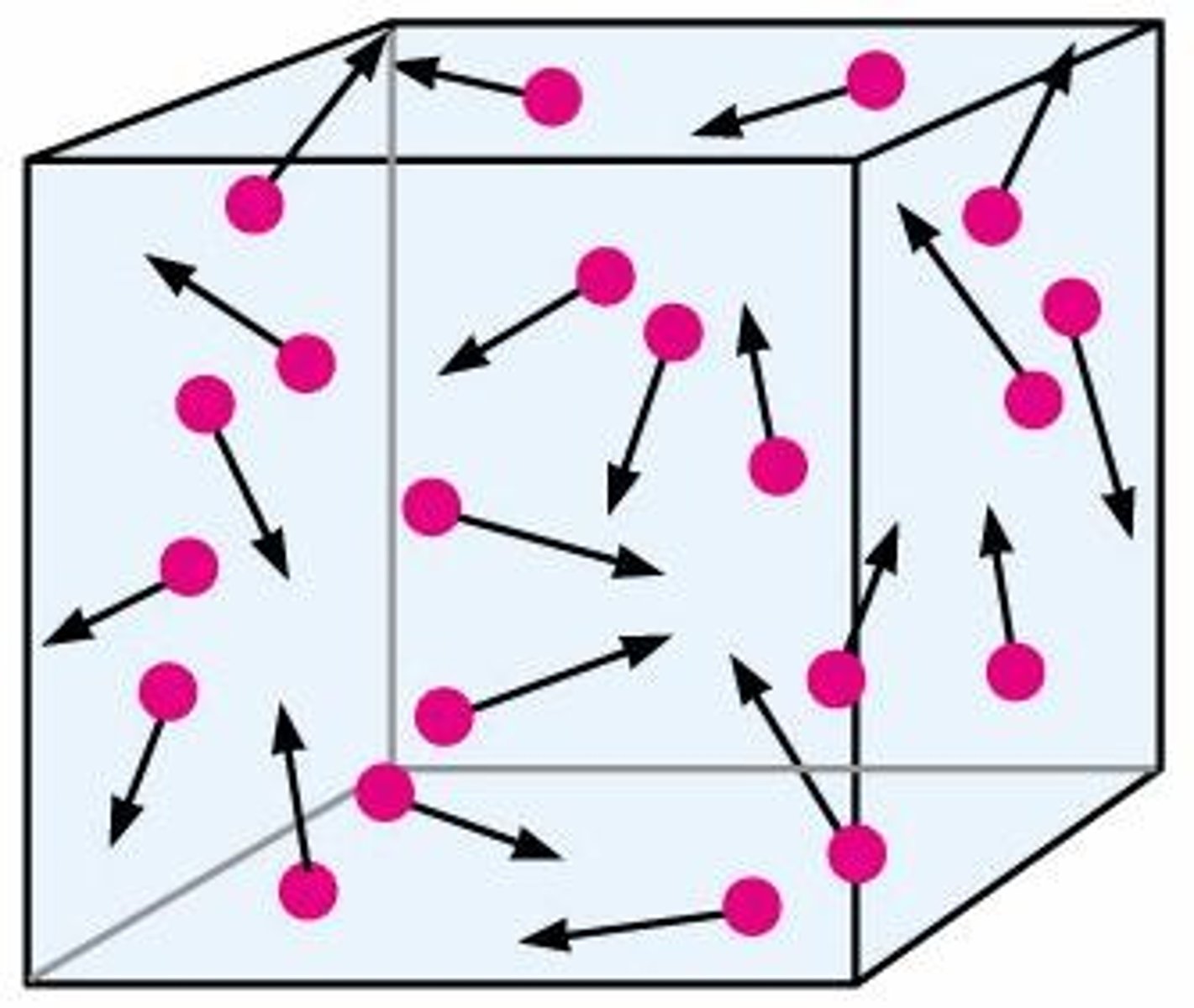
Gas Particle Motion
Particles in constant, random motion.
Air Pressure
Pressure exerted by air surrounding us.
Pressure Units
Measured in atm, mmHg, kPa, or torr.
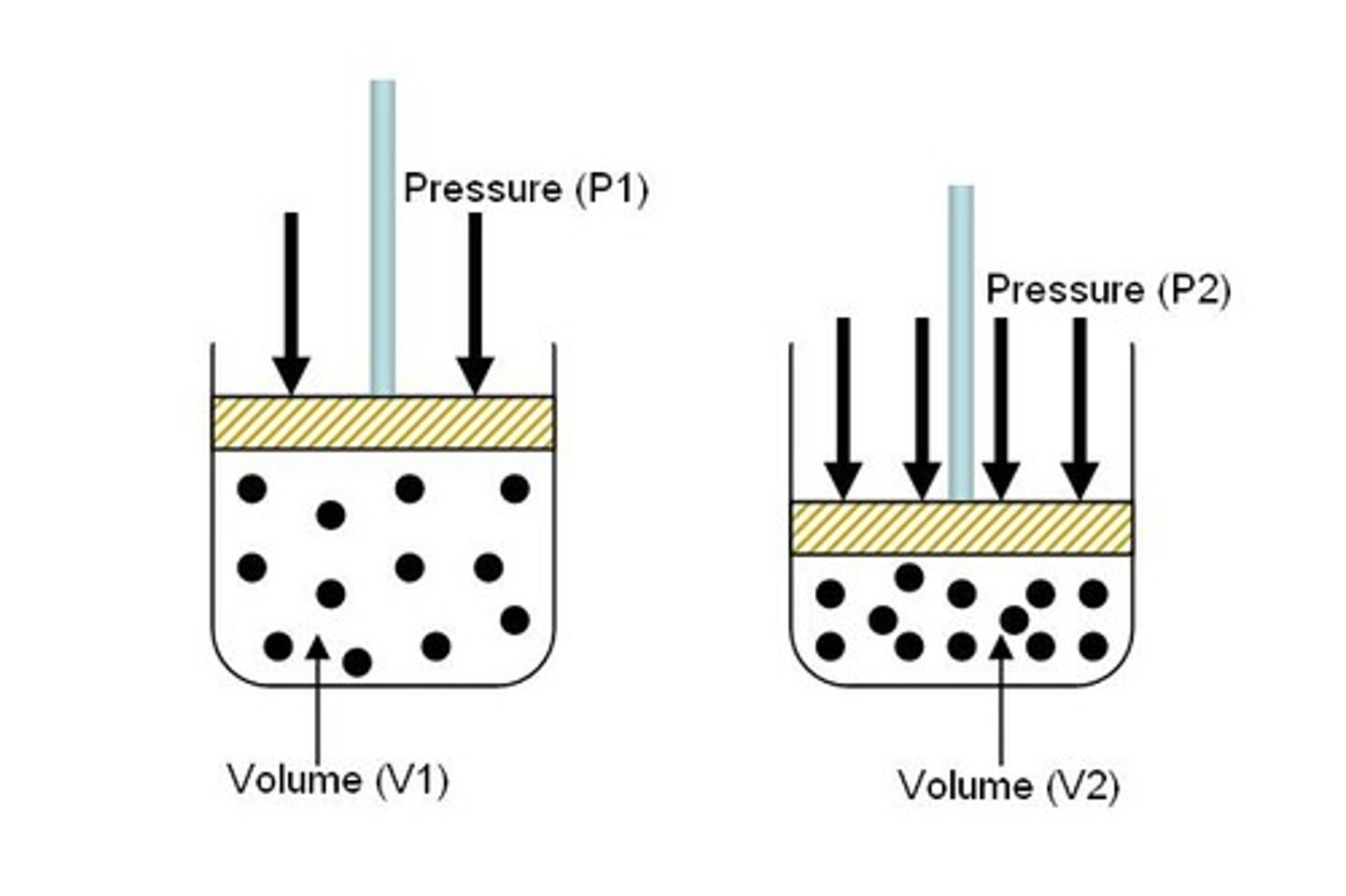
Pressure and Volume Relationship
Inversely related at constant temperature.
Boyle's Law
P1V1 = P2V2; pressure-volume relationship.
Temperature Effect on Pressure
Higher temperature increases gas pressure.
Temperature Conversion
Celsius to Kelvin: °C + 273 = K.
Gas Particle Collisions
Collisions with container walls create pressure.
Effect of Adding Gas Particles
Increases pressure due to more collisions.
Effect of Reducing Gas Particles
Decreases pressure due to fewer collisions.
Effect of Increasing Temperature
Increases pressure with constant volume.
Effect of Decreasing Temperature
Decreases pressure with constant volume.
Effect of Container Size
Smaller container increases pressure.
Boyle's Law Calculations
Used to find new pressure or volume.
Gas Expansion
Volume increase leads to pressure decrease.
Gas Compression
Volume decrease leads to pressure increase.
Temperature and Kinetic Energy
Higher temperature means faster particle movement.
Air Pressure Variation
Varies with altitude; higher at sea level.
Gas Behavior Prediction
Use gas laws to predict changes.
Pressure
Force exerted by gas particles per unit area.
Volume
Space occupied by a gas.
Temperature
Measure of average kinetic energy of particles.
Direct Relationship
Both variables increase or decrease together.
Inverse Relationship
One variable increases while the other decreases.
Charles's Law
Volume directly varies with temperature at constant pressure.
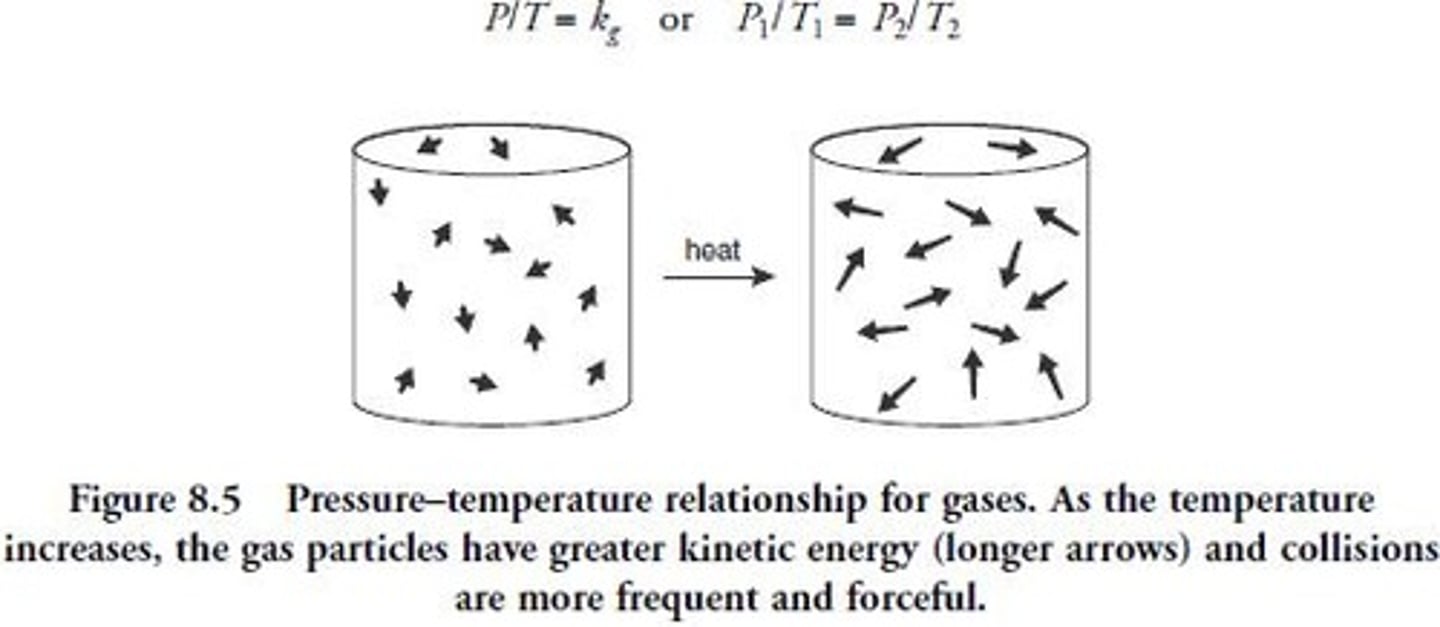
Gay-Lussac's Law
Pressure directly varies with temperature at constant volume.
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT; relates pressure, volume, temperature, and moles.
Particles
Small units that compose gases, in constant motion.
Elastic Collisions
Collisions where total kinetic energy is conserved.
Capped Syringe
Demonstrates pressure-volume relationship in gases.
Kelvin Temperature
Absolute temperature scale used in gas laws.
Shock Wave
Pressure wave caused by explosive gas expansion.
Pressure Units
Commonly measured in mmHg or atm.
Constant Variables
Conditions that remain unchanged during an experiment.
Volume Doubling Effect
Pressure halves when volume doubles at constant particles.
Volume Halving Effect
Pressure doubles when volume is halved at constant particles.
Temperature Doubling Effect
Pressure doubles when temperature is doubled at constant volume.
Temperature Halving Effect
Pressure halves when temperature is halved at constant volume.
Gas Behavior
Describes how gases respond to changes in conditions.
Balloon Analogy
Illustrates gas expansion with temperature increase.
Aerosol Can Pressure
Pressure increases when temperature rises in a closed container.
Tire Pressure Change
Pressure increases with temperature during driving.
Gas Expansion
Increase in volume due to temperature rise.
Gas Compression
Decrease in volume due to pressure increase.
Fixed Mass of Gas
Amount of gas that remains constant in calculations.
Gas Laws Calculations
Mathematical applications of gas laws to find unknowns.
Pressure-Volume Relationship
Describes how pressure changes with volume adjustments.
Temperature-Pressure Relationship
Describes how pressure changes with temperature adjustments.
Combined Gas Law
Relates pressure, volume, and temperature of gas.
Boyle's Law
Pressure and volume of gas are inversely related.
Charles's Law
Volume and temperature of gas are directly related.
Gay-Lussac's Law
Pressure and temperature of gas are directly related.
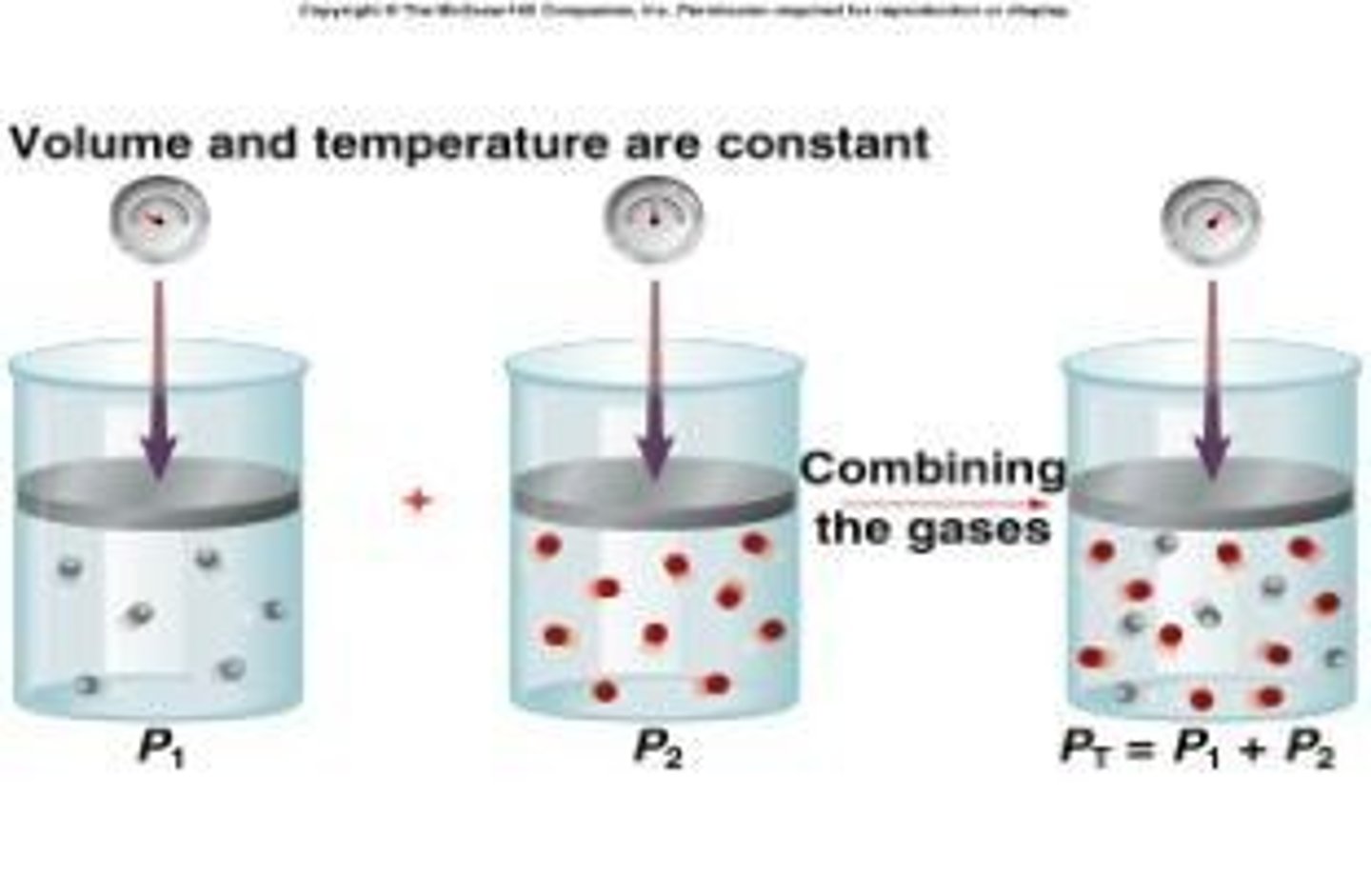
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
Total pressure equals sum of partial pressures.
Effusion
Gas escaping through a tiny hole.
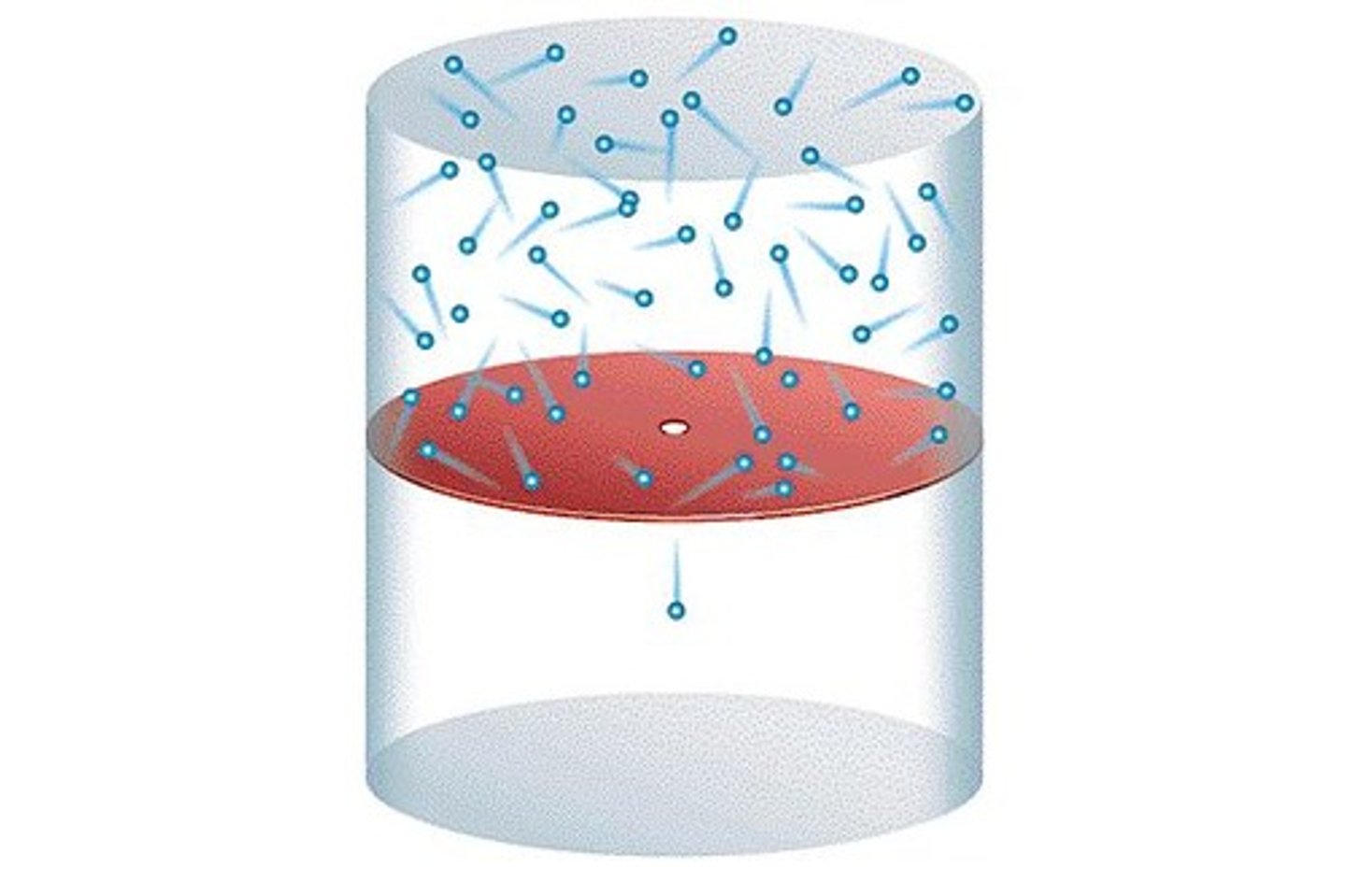
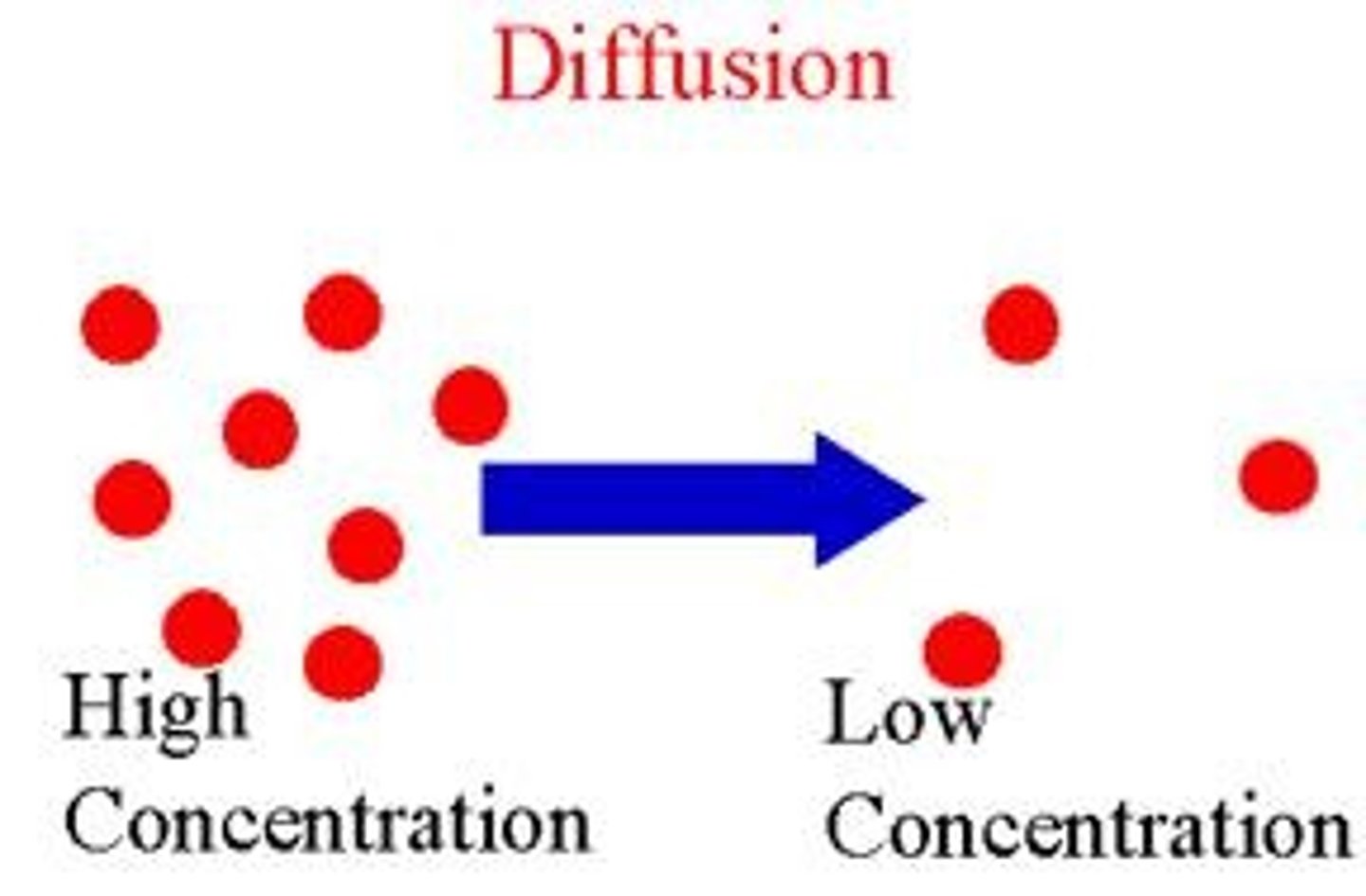
Diffusion
Molecules move from high to low concentration.
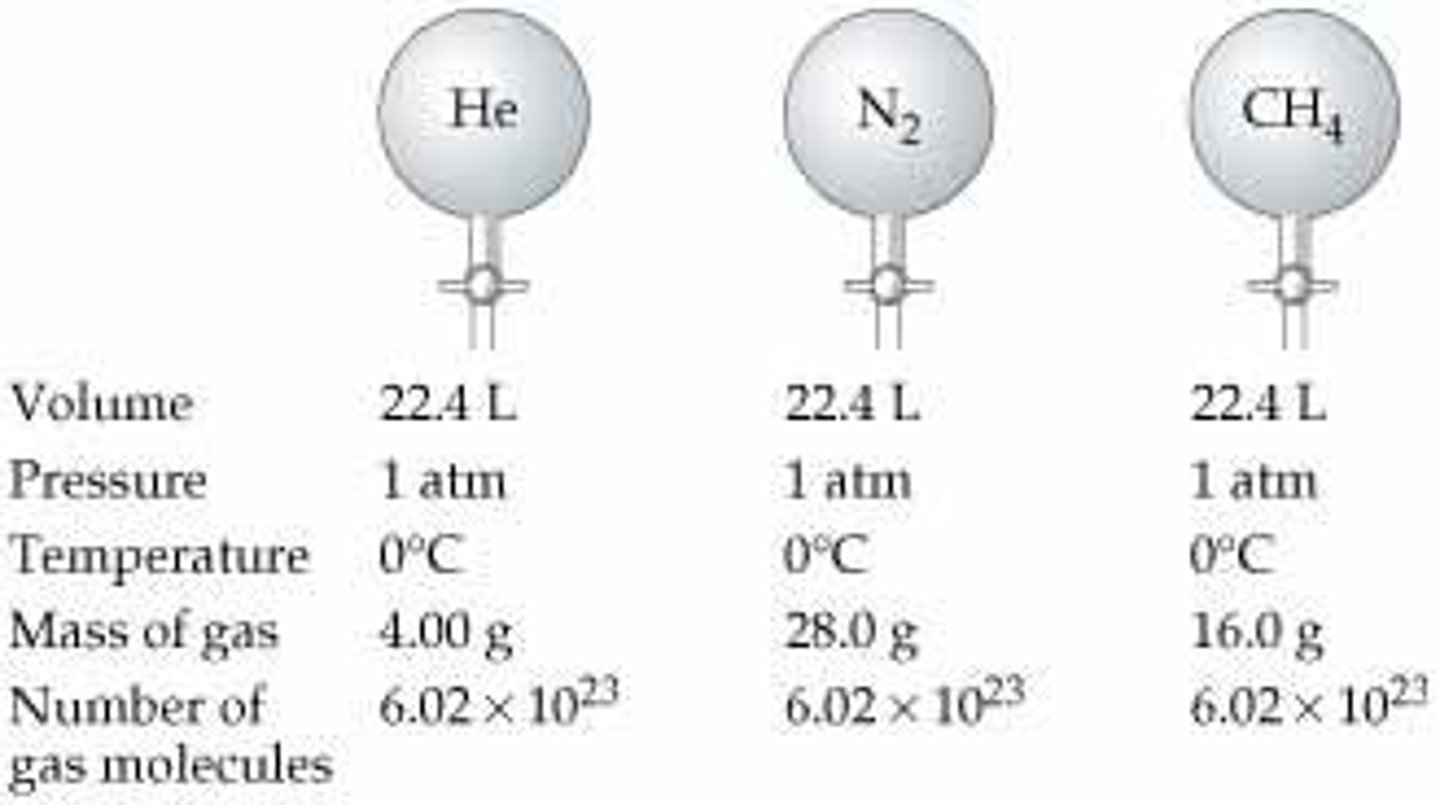
Avogadro's Hypothesis
Equal volumes of gas have equal particles.
Gas Volume Calculation
Volume changes with temperature and pressure.
Pressure Units
Commonly measured in atm, kPa, mmHg.
STP
Standard Temperature and Pressure conditions.
Gas Law Equation
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 for gas calculations.
Initial Conditions
Starting pressure, volume, and temperature of gas.
Final Conditions
Ending pressure, volume, and temperature of gas.
Temperature Conversion
Convert Celsius to Kelvin by adding 273.15.
Gas Behavior
Gases expand to fill their containers.
Pressure Increase Effect
Higher pressure decreases gas volume.
Volume Decrease Effect
Lower volume increases gas pressure.
Gas Mixture
Combination of different gases in a container.
Total Pressure Calculation
Sum of individual gas pressures in mixture.
Gas Law Quiz
Assessment of understanding gas law principles.
Temperature Increase Effect
Higher temperature increases gas volume.
Volume Expansion
Gas expands when heated at constant pressure.
Pressure Decrease Effect
Lower pressure increases gas volume.
Gas Law Applications
Used in real-world scenarios like weather.
Gas Collection
Collecting gas samples under specific conditions.
Gas Constant
R = 0.0821 L·atm/(K·mol) for ideal gas.
Gas Density
Mass per unit volume of gas.
Graham's Law
Rate of diffusion inversely proportional to molar mass.
Velocity of gas molecules
Inversely related to their mass.
Diffusion
Process of molecules moving to lower concentration.
Molar mass
Mass of one mole of a substance.
Partial pressure
Pressure exerted by a single gas in a mixture.
Ideal Gas
Hypothetical gas conforming to kinetic theory assumptions.
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT; relates pressure, volume, temperature.
Pressure (P)
Force exerted by gas per unit area.
Volume (V)
Space occupied by gas, measured in liters.
Number of moles (n)
Amount of substance measured in moles.
Ideal gas constant (R)
Value varies based on pressure units used.
Temperature (T)
Measured in Kelvin for gas law calculations.
Kinetic molecular theory
Explains gas behavior based on particle motion.
Rate of diffusion
Speed at which gas molecules spread out.
Rate of effusion
Speed at which gas escapes through a hole.