BIO 101 Chapter 4 Obj jc
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is Energy
Ability to do work, capacity for change
Potential Energy
Stored energy
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion
3 Types of Work Required by Cells
Chemical
Transport
Mechanical
First law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted to other forms
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy change increases disorder, loses some energy as heat
Entropy
Measure of randomness or disorder
What is Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions that happen inside a cell or organism
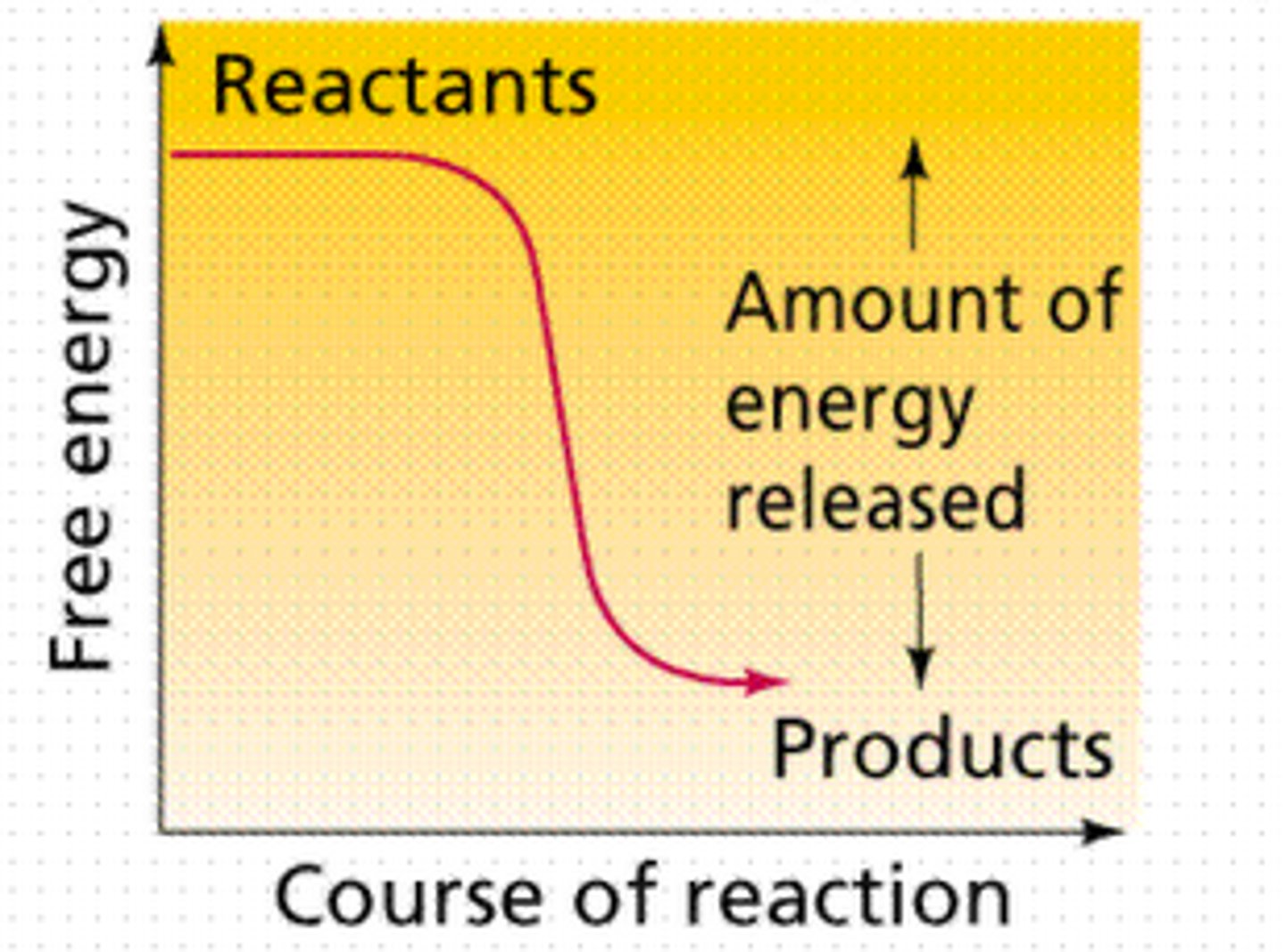
Exergonic Reactions
Release energy (respiration)
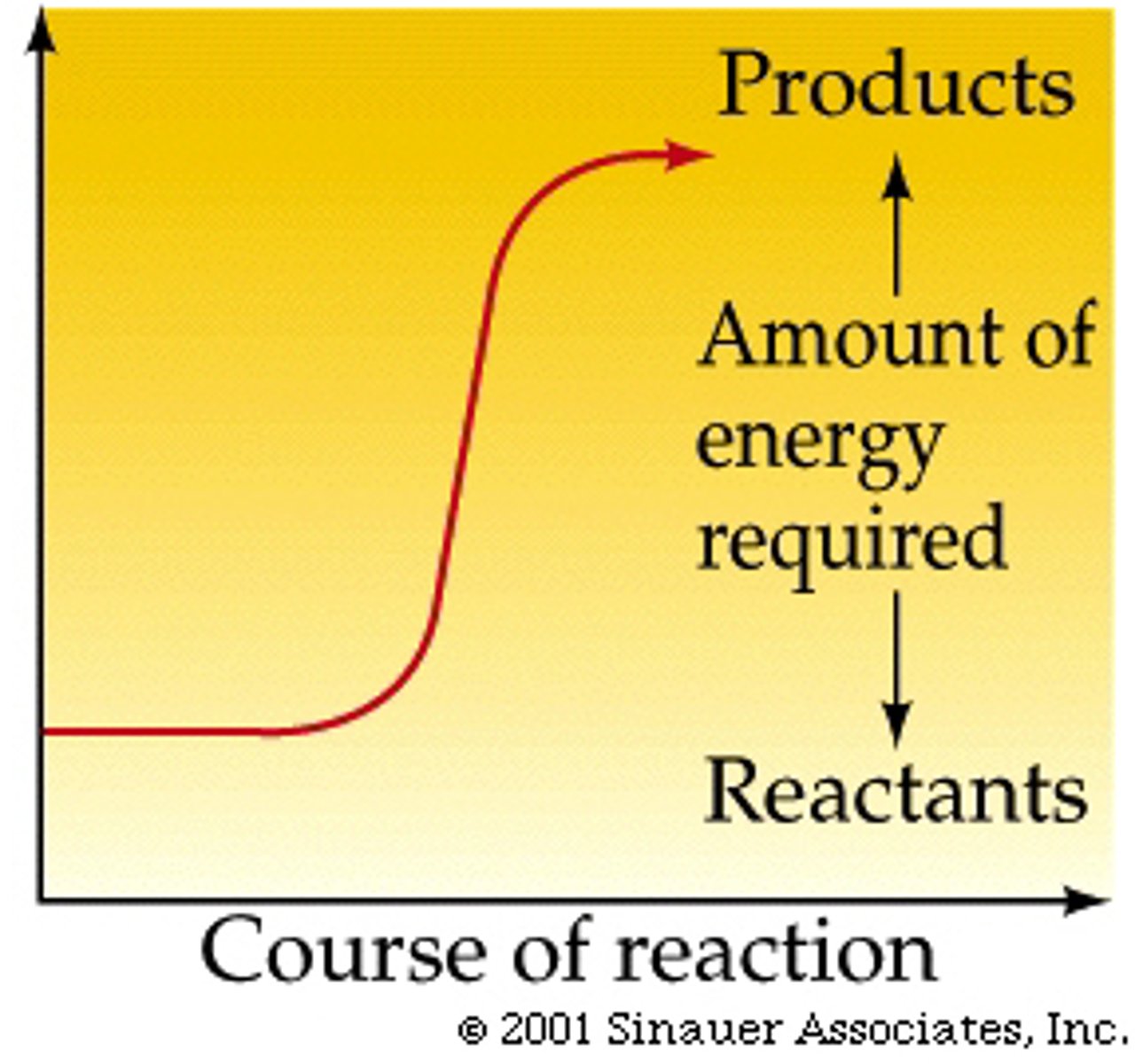
Endergonic Reactions
Require energy (photosynthesis)
Oxidation Reaction
A molecule loses electrons
Reduction Reaction
A molecule gains electrons
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions
One molecule loses electrons, another gains them, helps transfer energy in cells
Electron Transport Chain
Path of proteins that move electrons and make ATP
What is the Cellular Currency
ATP
3 components of ATP
Triphosphate
Ribose
Adenine
Exergonic Hydrolysis of ATP Equation
ATP + H2O => ADP + P + energy
Endergonic Dehydration of ATP Equation
ADP + P + energy => ATP + H2O
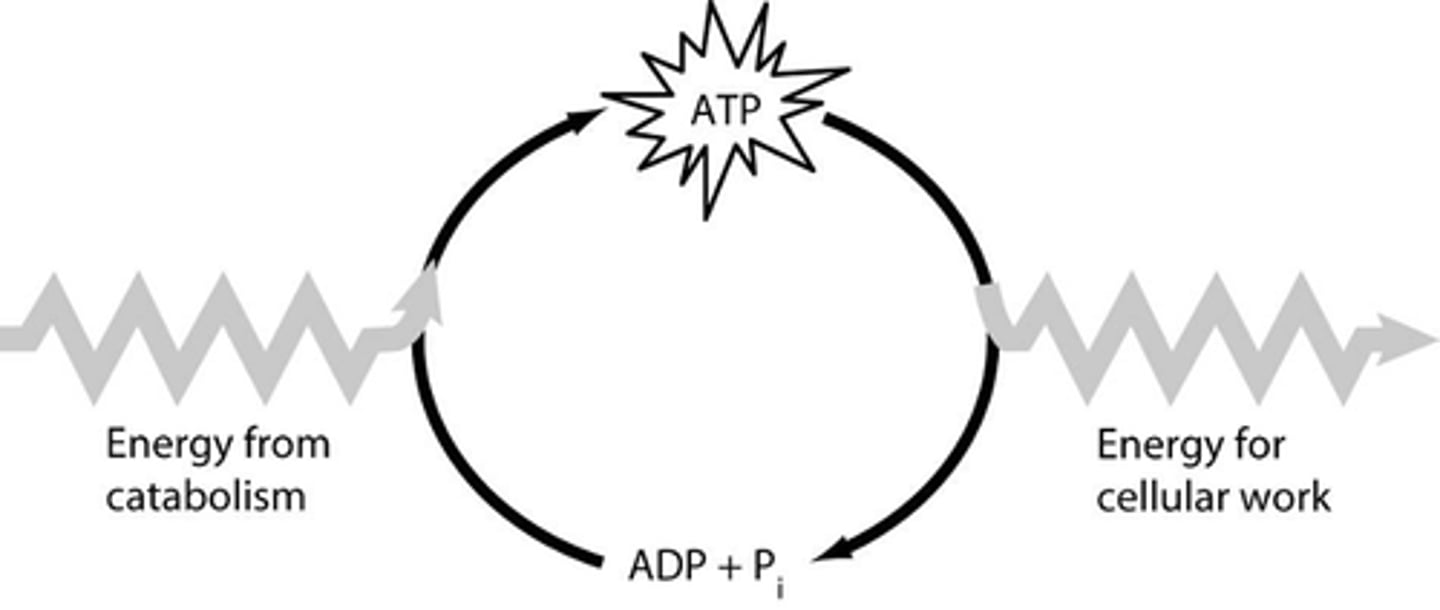
ATP/ADP Cycle
How cells recycle energy. ATP + Energy = lose one phosphate group and become ADP, releases energy. When cells need more energy, add a phosphate back to ADP to make ATP again
Phosphorylation
Adding a phosphate to a molecule to store or use energy
Enzymes
Catalysts that speed up chemical reactions
Active Binding Site
Part of enzyme where substrates fit and the reaction happens
Allosteric Binding Site
A different spot on the enzyme where a molecule can bind to, to change its shape to either help or stop the enzyme from working
Activation energy
Amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
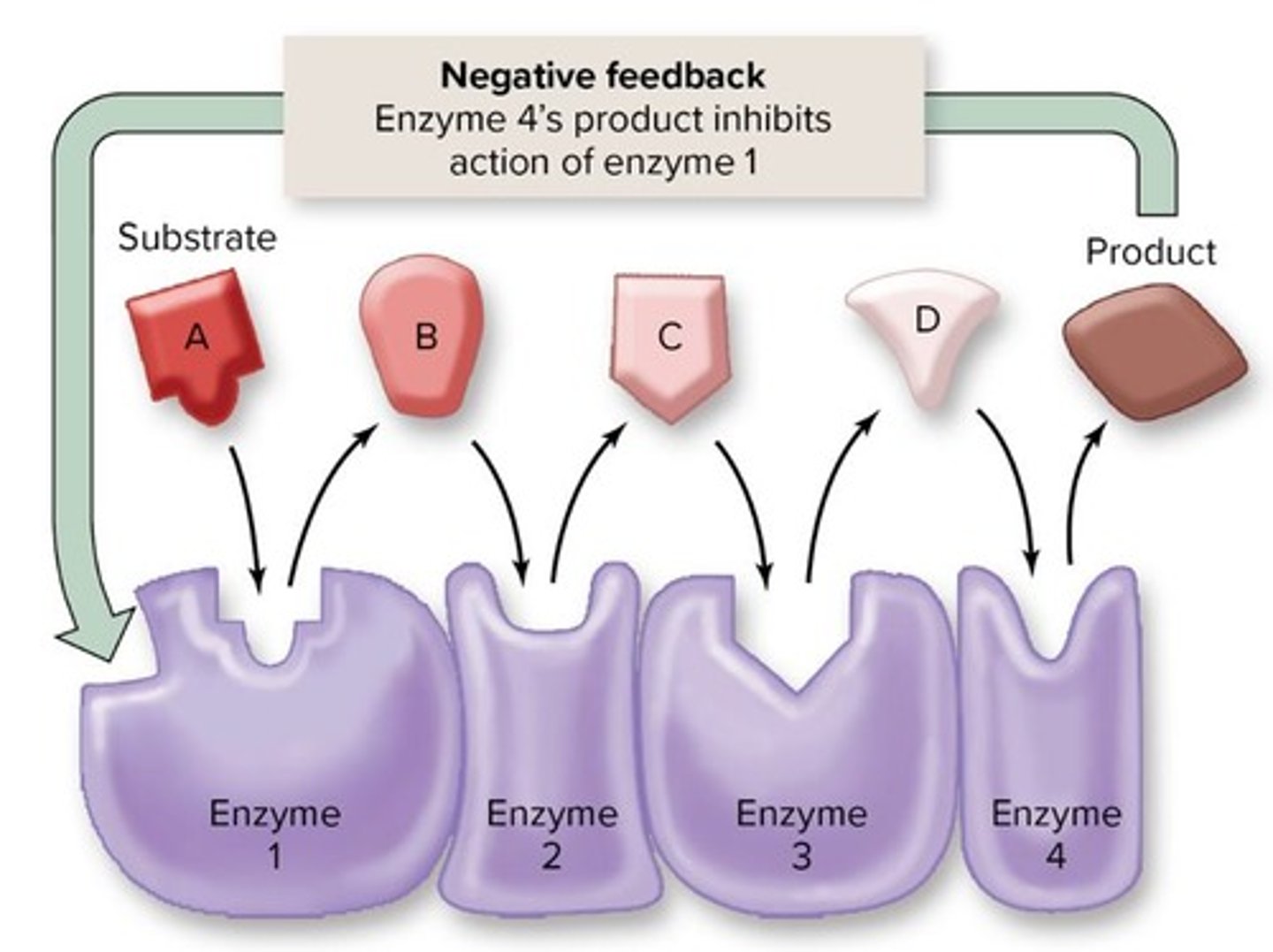
Negative Feedback
Controlling enzymes by slowing or stopping it from doing something
Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor binds to the active site and competes with normal substrate, blocking it
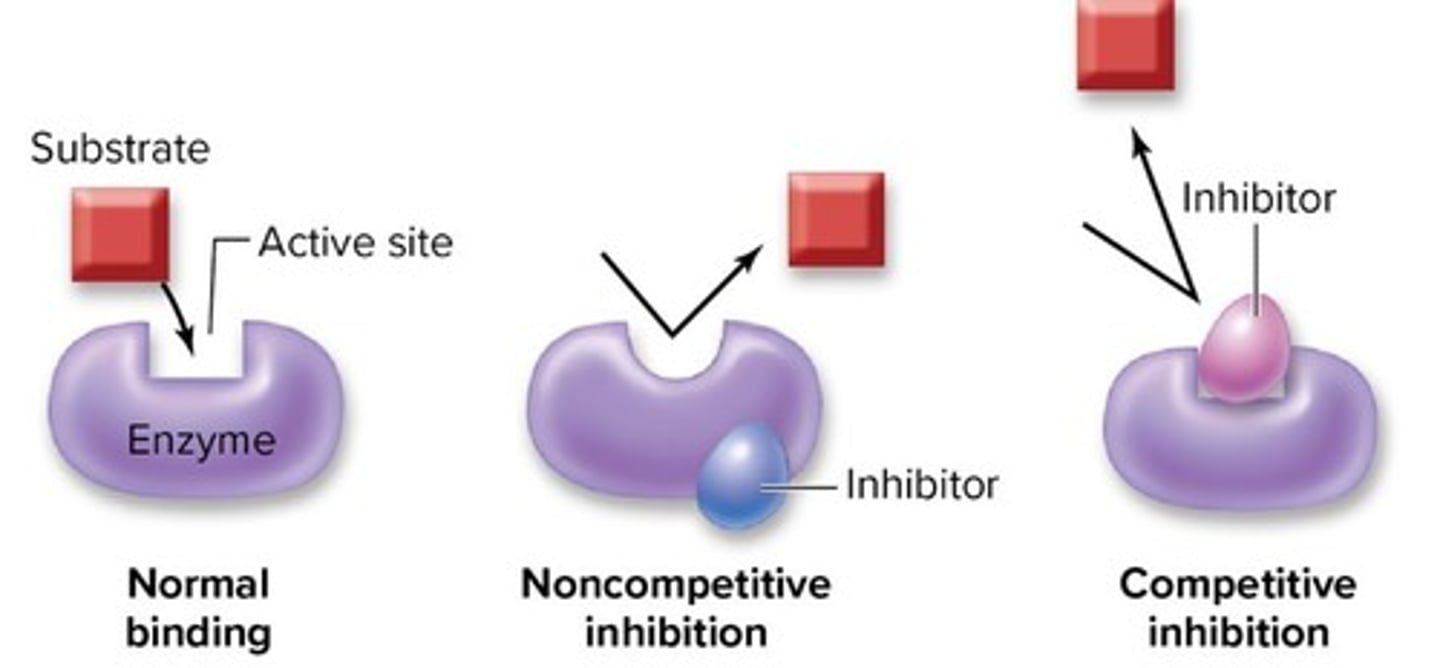
Non-Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor binds to allosteric site, changing the shape of the enzyme so the substrate can’t fit
Selective Permeability
Membrane admits some substances but excludes others
Concentration Gradients
A difference in concentration between adjacent areas
Passive transport
Transport that doesn't require input of energy
Diffusion
Movement of substances from high to low concentration until equilibrium
Simple diffusion
Diffusion that does not require assistance, moves down the concentration gradient (high to low)
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion that requires assistance, moves down the concentration gradient (high to low)
Osmosis
Diffusion of water from high to low concentration across a semi permeable membrane until equilibrium
Terms of tonicity
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Solution has more solutes and less water outside of the membrane (shrink)
Isotonic
Same solutes and water concentration
Hypotonic
Solution has less solutes and more water outside of the membrane (swell)
Active Transport
Cells use energy to move substances from low to high concentration
Endocytosis
Cell takes things in by engulfing them
Exocytosis
Cell moves things out by fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane
Phagocytosis
Form of endocytosis where cell engulfs a large particle by surrounding then eating them