Psychology Topic 2 - Visual perception
1/66
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Absolute threshold
the min stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
Reception
the stimulus energy is collected by the sense organ
transduction
stimulus energy is converted by the receptor cells into electrochemical nerve impulses
transmission
the sending of neural signals to the primary sensory cortex when the specialized receptor cells respond as the process of perception begins
selection
the process of selecting the important sensory info on which to focus attention from the millions of stimuli we receive
organization
sensory info reaches the brain and is reorganized so we can make sense of it
interpretation
stimulus is given meaning in the brain based on our past experiences, motives, values and context
sensation
the process by which our sensory receptors and the nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment and transmit it to the brain
photoreceptors
a layer of specialized nerve cells that detects the visual stimuli, the make up the retina and convert visual light energy into nerve impulses
rods
photoreceptors that become active under low-light conditions for night vision
cones
photoreceptors connected near the center of the retina that function in daylight or well-lit conditions. These detect fine detail and give rise to colour sensations
optic nerve
the two tracts of neurons that transmit visual info form the eyes to the occipital lobes
receptive field
a particular region of the visual space
retinal ganglion cell
a type of neuron that is located near the surface of the retina; receives visual info form the photoreceptors
visual acuity
clarity/clearness of vision
perception
the process whereby the brain organises and interprets sensory info
feature detectors
cells in the optic nerve that individually respond to lines of a certain length, angle or direction to break up an image for visual perception
light energy
the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum
presbyopia
farsightedness caused by loss of elasticity of the lense of the eye, occurring typically in the middle and old age
floaters
clumps of matter that appear as small specks of spots in central vision
cataracts
cloudy spots in the lens that cause vision to become blurred when proteins in the lens break down
glaucoma
a disease affecting the optic nerve that interferes with the transmission of peripheral visual info to the brain
age-related macular degeneration
a build up of grainy deposits in the center of the retina causing deterioration of central vision
inherited visual disorders
visual disorders passed down from parents to children due to genetic factors
congenital visual disorders
visual disorders present at birth
colour vision deficiency
a genetically inherited disorder affecting how people perceive colour
retinis pigmentosa
a genetic degenerative disease affecting the retina
perceptual set
a predisposition/readiness to perceive something in a particular way
perceptual constancies
allow us to recognise familiar stimuli under varying conditions
size constancy
the tendency to interpret an object as always being the same actual size, regardless of its distance
shape constancy
the tendency to interpret the shape of an object as being constant, even when its shape changes on the retina
Gestalt principles of visual perception
used to organise and interpret perceptual stimuli; including figure-ground organisation, closure, similarity and proximity
figure-ground organisation
Gestalt principle where images are organised into the central object of attention (figure) and a background (ground)
camouflage
the contour of the figure is blended against the ground, making it more difficult to see
closure
when an object is perceived as being whole despite actually being incomplete
similarity
the principle that elements that are similar in appearance will tend to be seen as a unit
depth perception
the ability to accurately judge 3D space and distance, using cues in the environment
proximity
the individual parts of a stimulus patter are close together, allowing those parts to be perceived visually as a whole
binocular depth cues
depth cues that use both eyes to gauge distance and space
monocular depth cues
depth cues that use one eye independently or both eyes together to gauge distance and space
retinal disparity
the binocular depth cues that arises as the brain compares and contrasts the 2 slightly different distance between the two eyes
convergence
a binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object
accommodation
the process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
pictorial depth cues
a monocular depth cue used by artists to create a 3D perception of something that exists on a 2D suface
linear perspective
a monocular depth cue that parallel lines appear to converge as they retreat into the distance
interposition
a monocular depth cue, in which objects further form the observer are partially obscured by those in the foreground
texture gradient
a monocular depth cue in which texture in the foreground is seen in finer detail than that further away
relative size
a monocular depth cue based on our tendency to perceive the object producing the largest retinal image as being the nearest and the object producing the smallest retinal image as being the furthest.
height in the visual field
a monocular depth cue that shows depth by portraying objects further away as being closer to the horizon
Sensation - Perception Acronym
Real (Reception) Alphabetical order (Transmission, Transduction), Special (Selection), Orange (Organization) Ice blocks (Interpretation)
Reception
stimulus is recognized by photoreceptors
Transduction
Stimulus info is processed by receptive fields
Transmission
Optic nerve carries info to the occipital lobe
Selection
Feature detectors focus on particular elements of the stimulus to determine what is and is not attached to.
Organisation
use visual cues to interpret details, which are then passed to temporal lobe for identification and the partial lobe for judgment (location of the stimulus in space)
interpretation
temporal lobe applies meanings to the stimulus based on memories and stored info
electromagnetic spectrum wavelength visible to humans
360-720/40
Social influences on perception
cultural norms and expectations influence how we interpret images. Cross-cultural research (Deregowski 1972) showed that some African tribes were unable to recognise 3D depth cues in human face photos or could not see pictorial clues to estimate depth and distance (relative size and height in the visual field).
Hudson Study
studied Bantu warriors from different tribal backgrounds, educational levels and degrees of urbanisation. All participants were shown 14 unambiguous pictures. Hudson found that there was a difference between 2D and 3D perception between African tribal members and the general population.

visual illusion
occurs when perception consistency differs from objective reality

Pronzo illusion
upper horizontal lines in a series of diagrams are perceived to be longer than the lower horizontal lines because we mistakenly perceive depth cues of linear perspective and heigh in the visual field
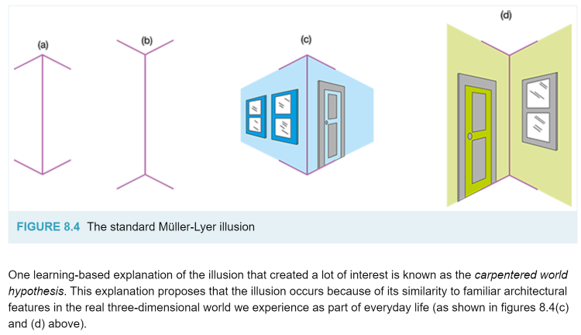
muller-lyer illuison
consists of 2 lines of = length with regular arrowheads on one end and inverted on the other. We percive the line with inverted arrow heads as being longer than the regular arrow headed line due to the Carpentered World Theory
impossible figures
work by exploiting perceptual cues so that we are forced to see images that should not be possible or should not be able to exist
ambiguous figures
examples of optical illusions that work by exploiting similarities int he image, and aspects of the way our visual system interprets between two or more objects in an image
optical illusions
physical properties of light