Instrumentation
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Desiccator function
air tight dish containing small beads responsible for removing excess moisture from the air
desiccator maintenance requirements and quality control
ensure that it has a tight seal, is cleaned properly, and replace the beads
desiccator clinical application
used for chemicals that absorb moisture from the air, which can cause them to degrade
freezer clinical use
using for storing tissue, concentrated antibodies, precut immunohistochemistry control slides, reagents, and buffer solutions
freezer maintenance and quality control
Do not have a freeze-thaw cycle, temperatures should be closely monitored and alarm systems in place
hydrometer function
measures the specific gravity of a liquid
hydrometer maintenance and quality control
ensure that the equipment is cleaned after each use, and that the mercury or lead shot is where it should be
hydrometer clinical use
Used for measuring the amount of water in the alcohols of the tissue processor
incubator clinical use
Set at body temperature for enzyme reactions, situ hybridization applications, some stains
incubator maintenance and quality control
temperature should be monitored daily and proper cleaning performed
laboratory glassware use
used to hold, mix, and measure reagents
borosilicate glass
high thermal resistance and is resistant to corrosion
low-actinic glass
dark brown to amber, designed to limit amount of light that enters the container
standard flint
less resistant to high temperatures and chemical attacks
graduated cylinders
used for exact measurements
beakers, coplin jars, and flasks
used to hold reagents
lab glassware maintenance and quality control
Make sure that bottles are tightly closed, glass is not chipped, and when measuring, make sure to measure from the bottom of the meniscus to ensure the proper volume is measured. Clean after use by rinsing 3 times with DI water, and then with cleaning chemicals, rinsed 3 times again, and left to dry upside down
pH meter clinical use
used for enzyme histochemistry techniques because most solutions require a specific pH before use
pH meter maintenance and quality control
Standardized using a standard solution close to the pH of the solution being tested, store electrodes properly according to the type
pipette clinical use
Used in immunochemistry for the dilution of antibodies
pipette maintenance and quality control
Use good micropipetting technique, never set pipette outside of limits (can cause it to uncalibrate), never hold pipette horizontally when it has liquids, and place pipette back in holder when not in use, calibrate pipette annually
Refrigerator clinical use
Used for storing reagents, buffers, tissue, enzyme histochemistry reagents, and diluted antibodies used in immunohistochemistry
refrigerator maintenance and quality control
temperature should be monitored daily and alarm systems should be in place
scale use
used for solution preparation and weighing dyes and chemicals
scale maintenance and quality control
wipe down equipment, tare before use, and make sure has 1-2mg sensitivity, calibrated annually
stir/hot plate use
used to thoroughly mix and heat reagents
stir/hot plate maintenance and quality control
Clean and decontaminate after use, ensure that the plate is warming and stir bars are working as intended
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14, 0 being acidic and 14 being basic
units of measurement for reagent preparation
grams and mL (microliters for histoimmunology)
resolving power
the ability to reveal fin detail or to discriminate between adjacent detail; 0.2 micrometers
parfocal
all objects will have the focal point in the same plane and magnification
micrometry
microscopic measurements
resolution
The optical ability to distinguish 2 objects a minimal distance apart as 2 objects
birefringence
transmitting light unequally in various directions
fluorescence
an optical phenomenon in which light of 1 wavelength is absorbed by a substance and almost instantly reemitted as light of a longer wavelength
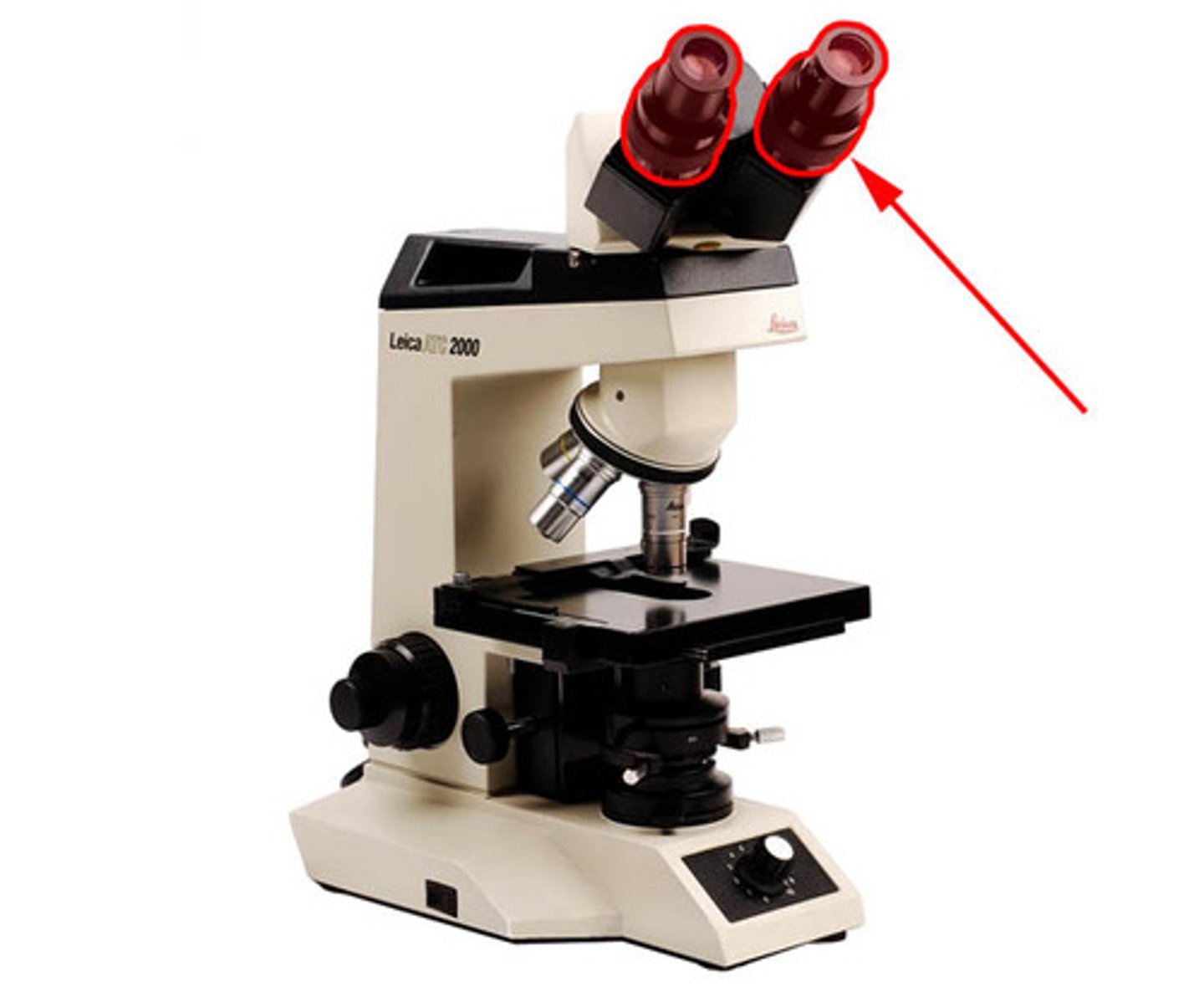
ocular
viewing/magnifies 10x
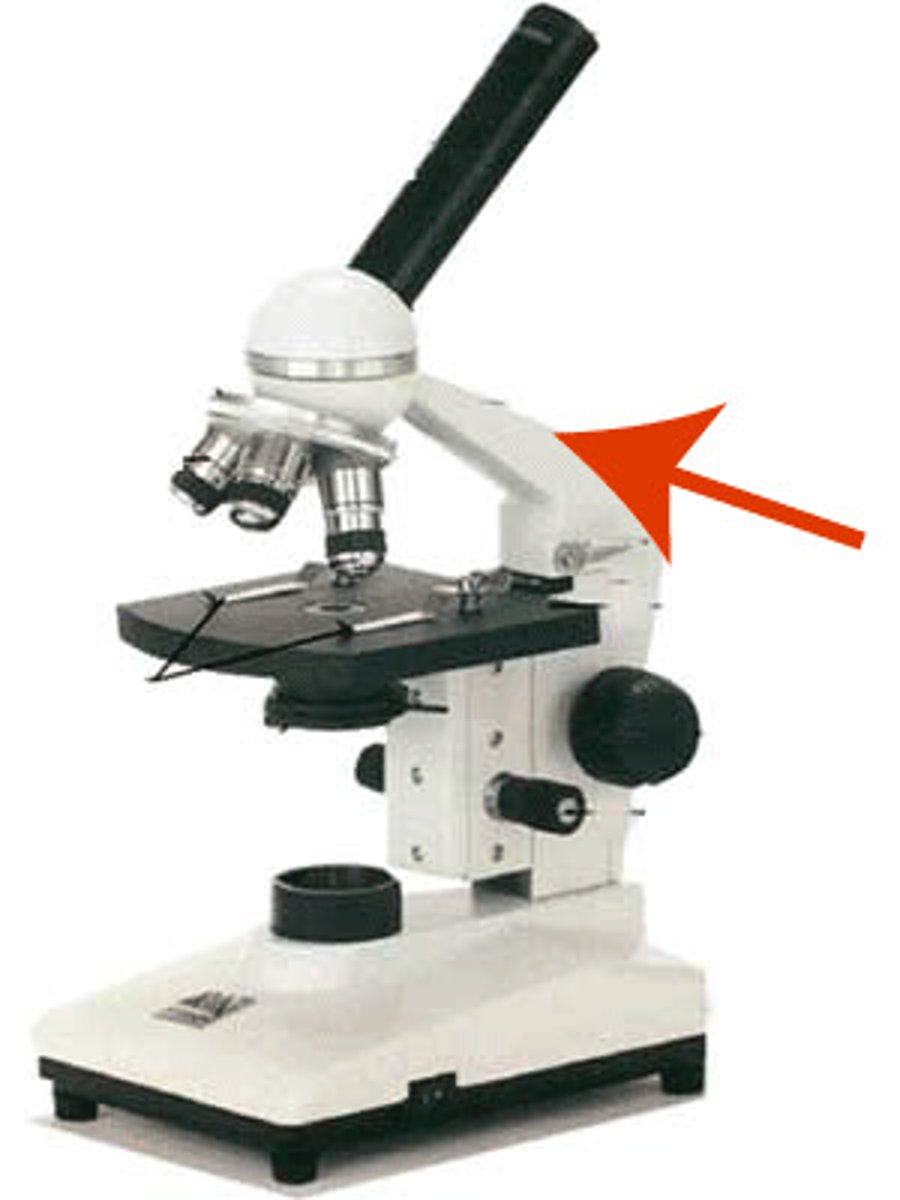
arm
structural piece for carrying
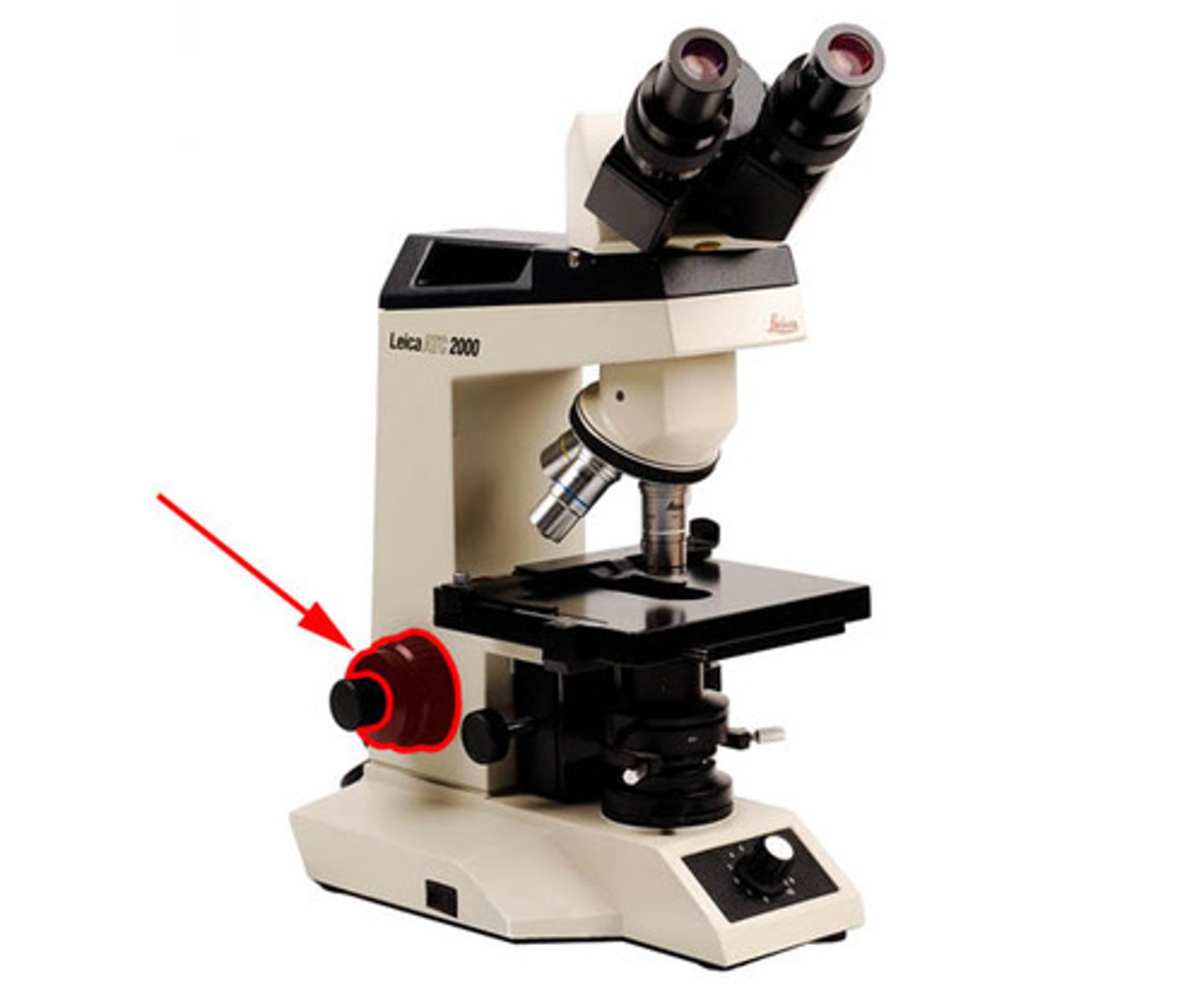
course adjustment knob
course/large focus
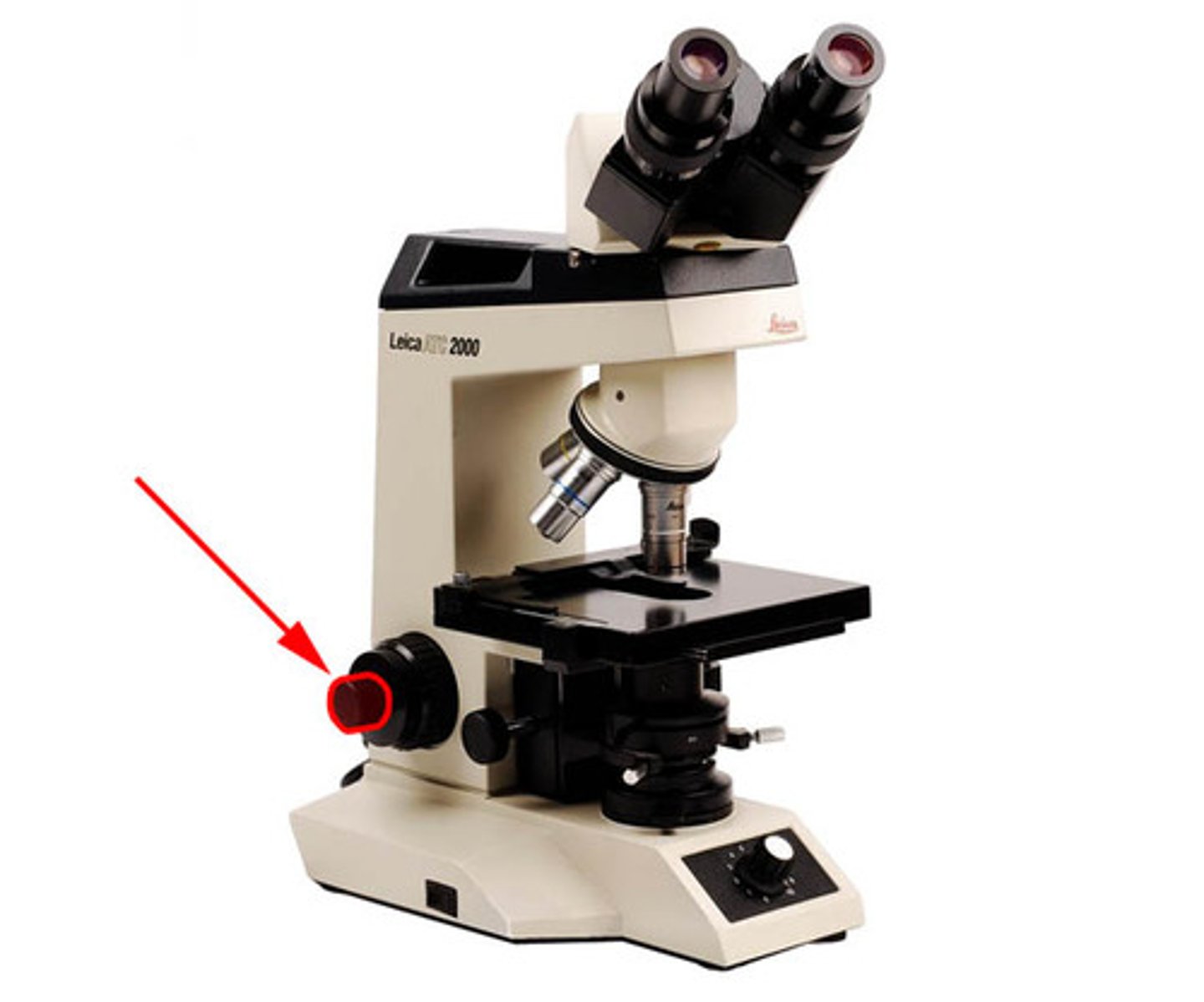
fine adjustment knob
fine/small focus
base
stability/structure
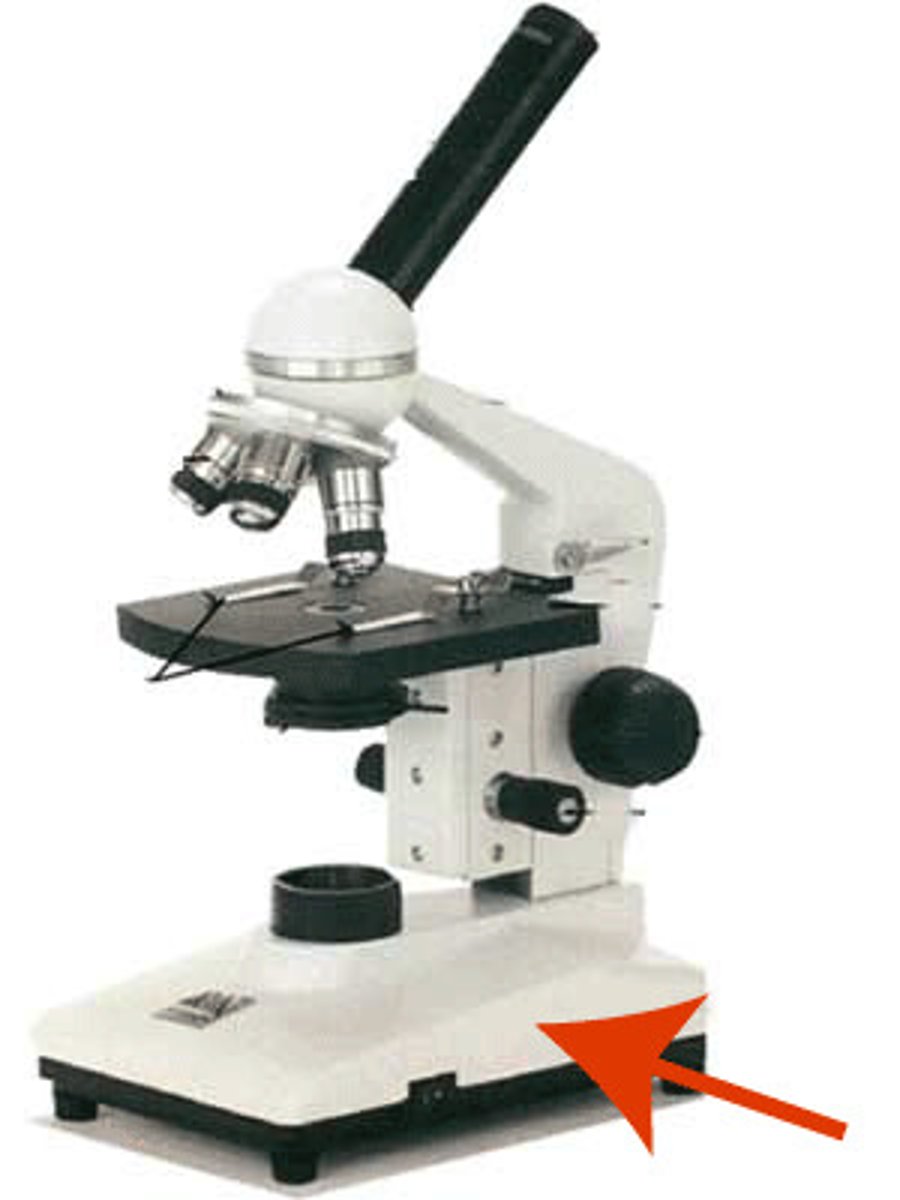

rheostat
light intensity
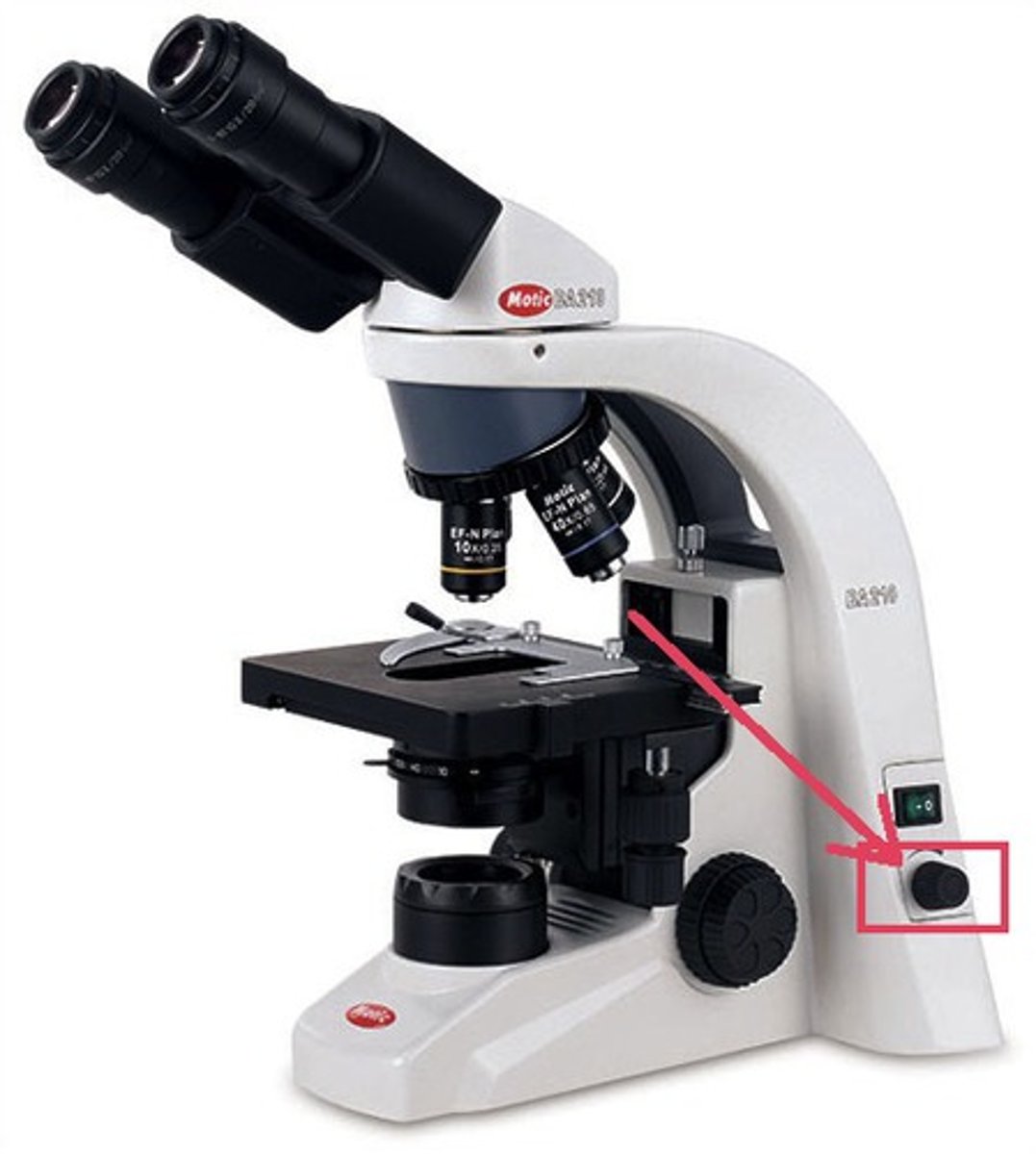
condenser adjustment knob
moves condenser up and down
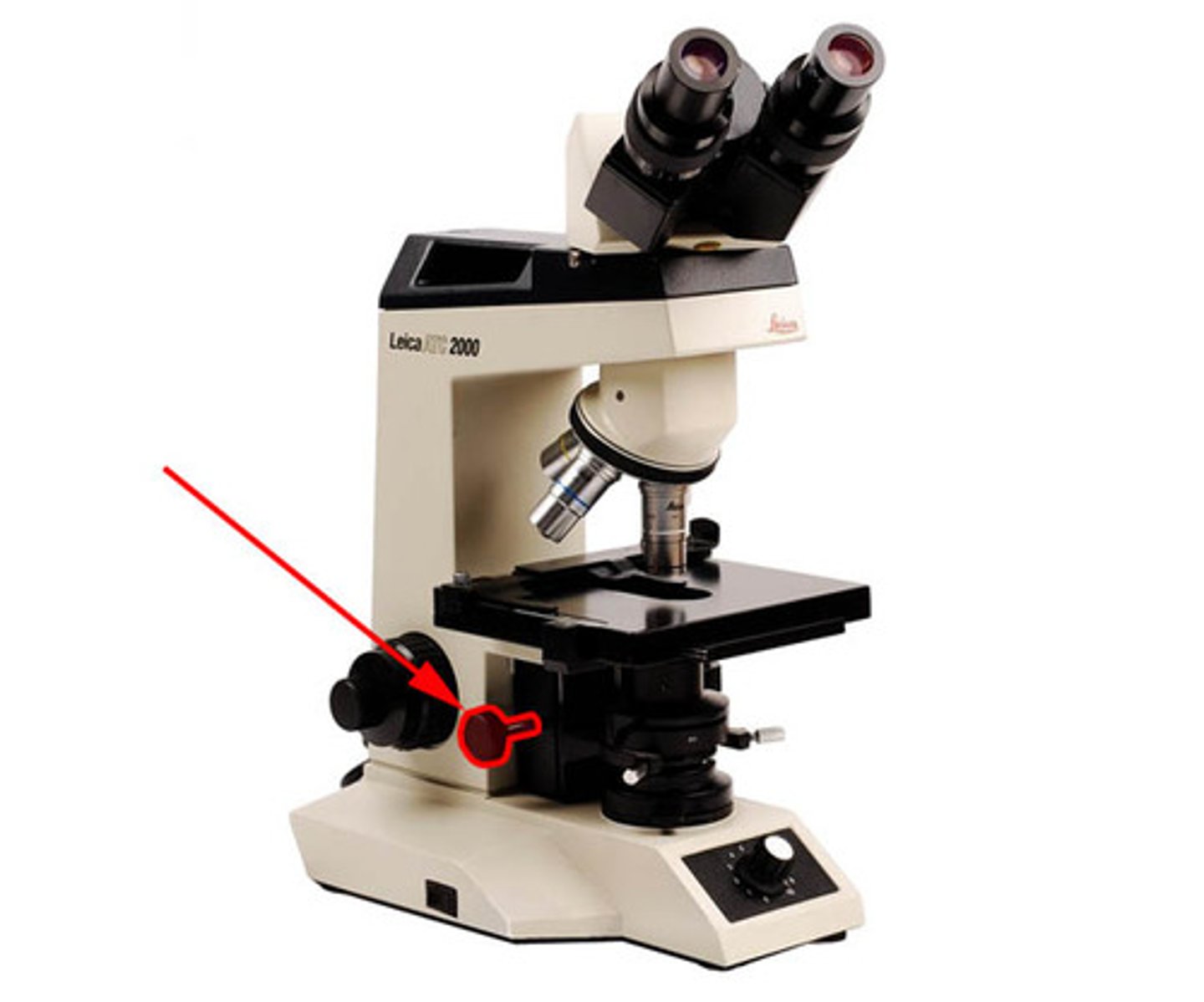
stage adjustment knob
moves the stage forwards/backwards and left to right
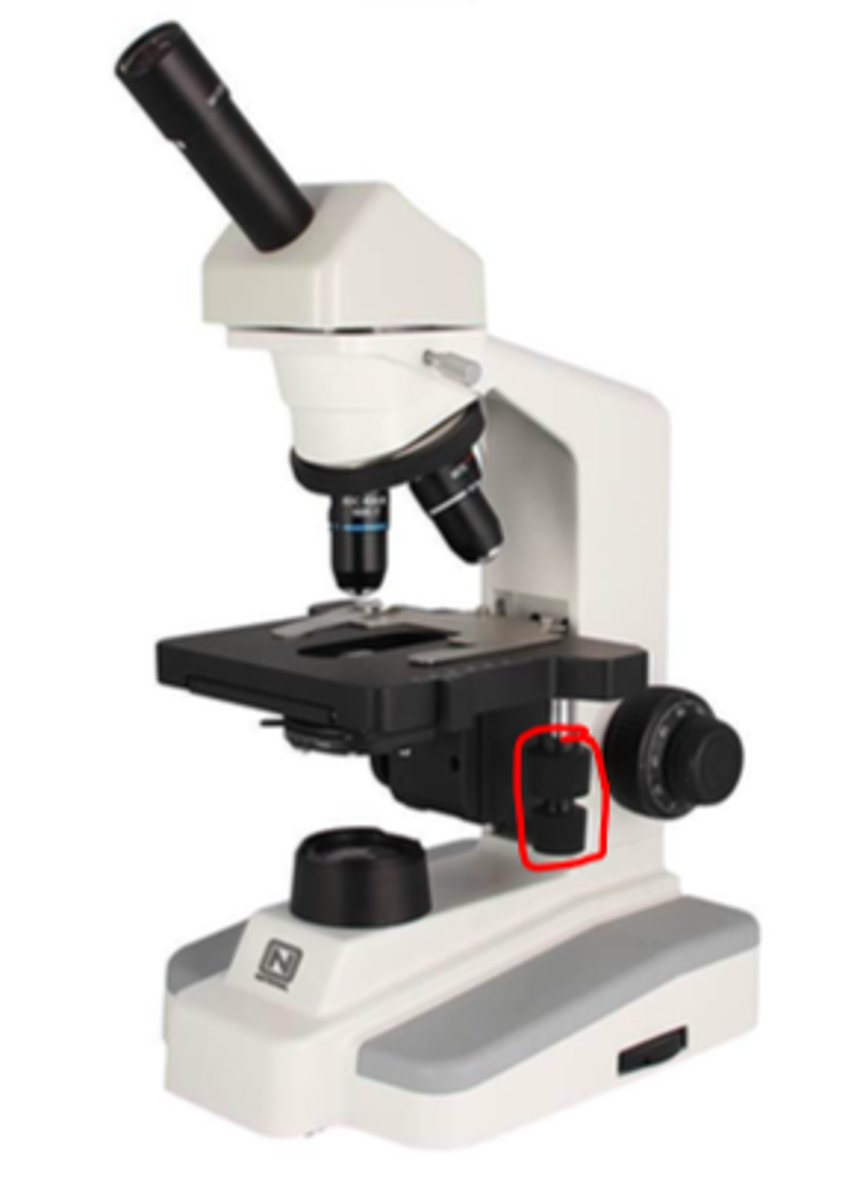
iris diaphragm
opens/closes light source
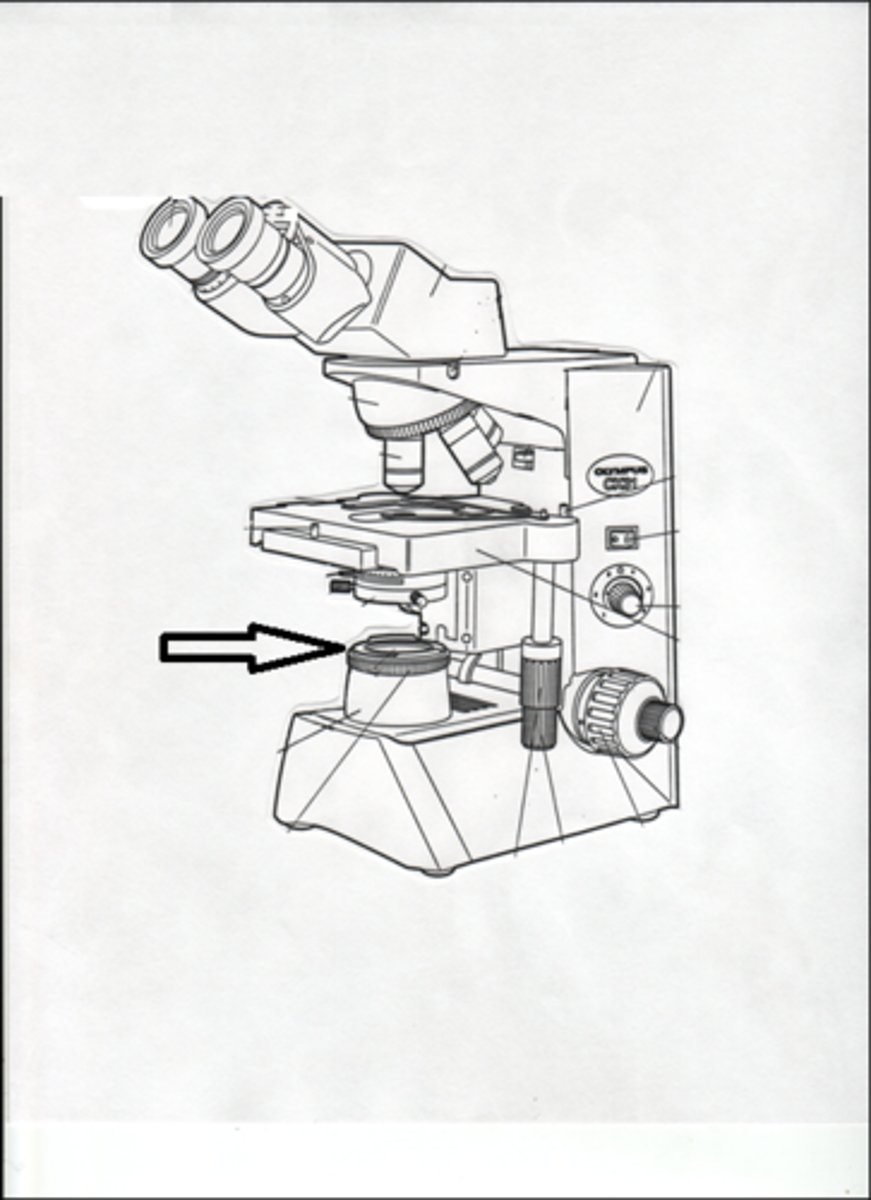
condenser
focuses/blends light onto specimen
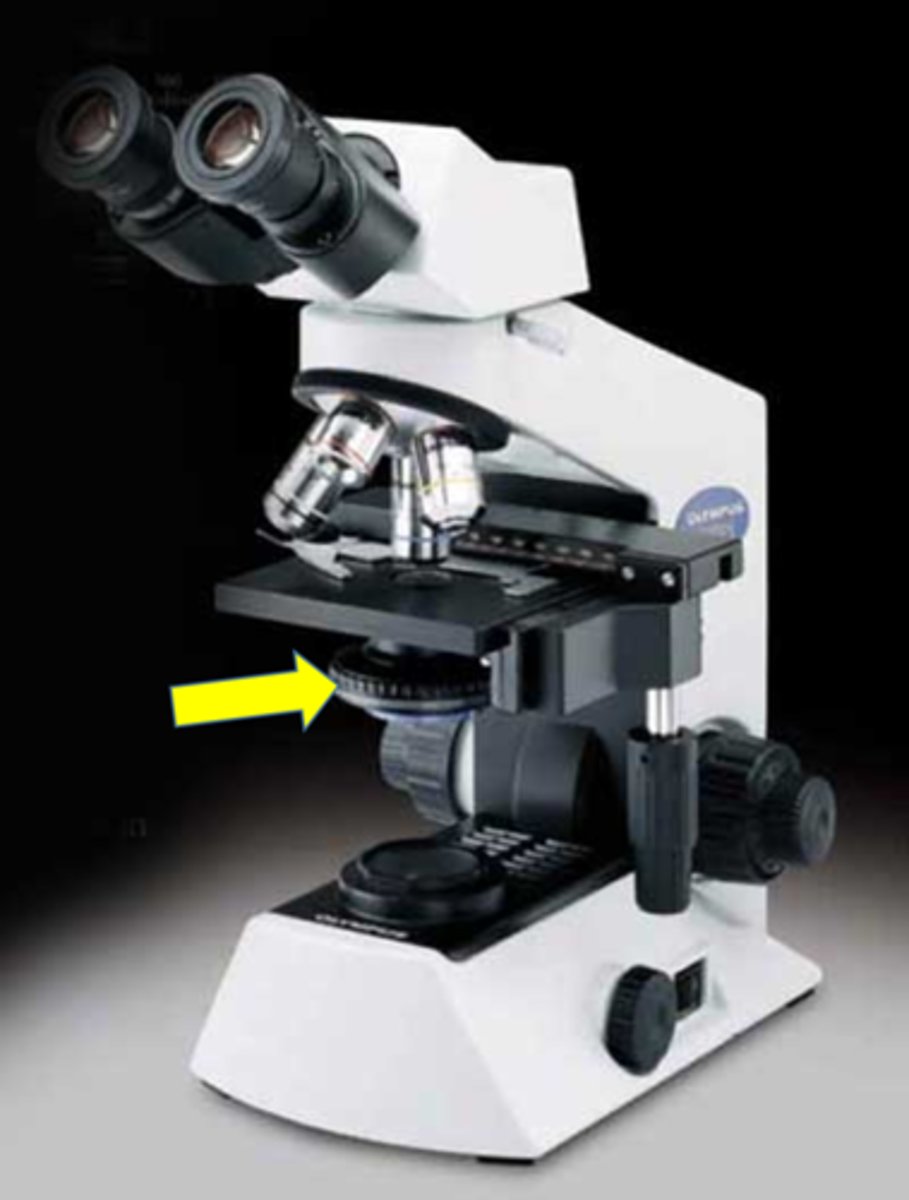
objective
magnifies and resolves specimen
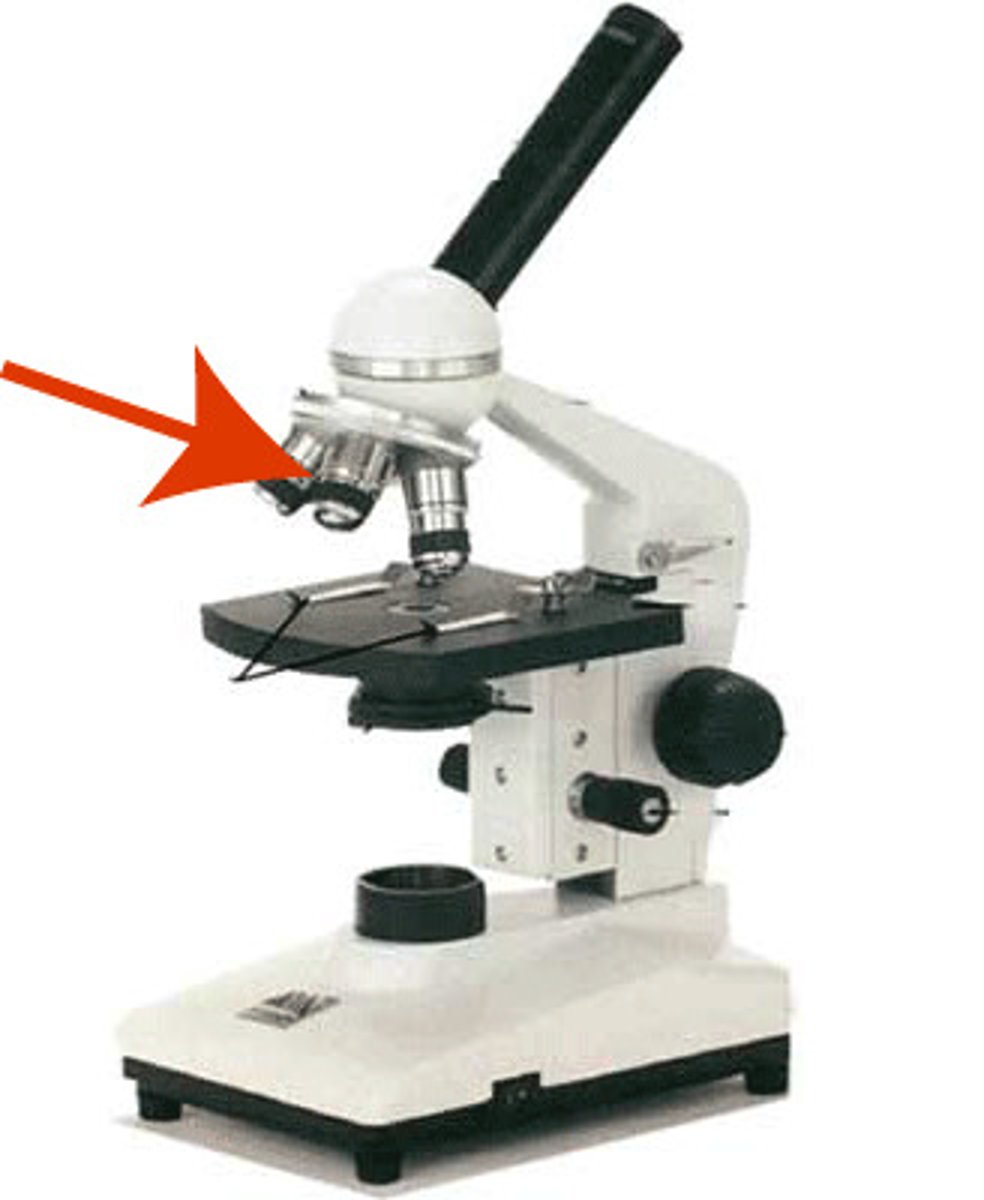

total magnification of a microscope
10 x objective lens magnifying power (10, 40, 60)
achromatic
corrected for 2 colors, red and blue
apochromatic
corrected for 3 colors and for other lens aberrations
light microscope principle
Light is aimed towards a condenser, which focuses the light through the object
the objective lens collects the light and magnifies the image
light microscope use
Quality monitoring in histology and for diagnostic histopathology practices
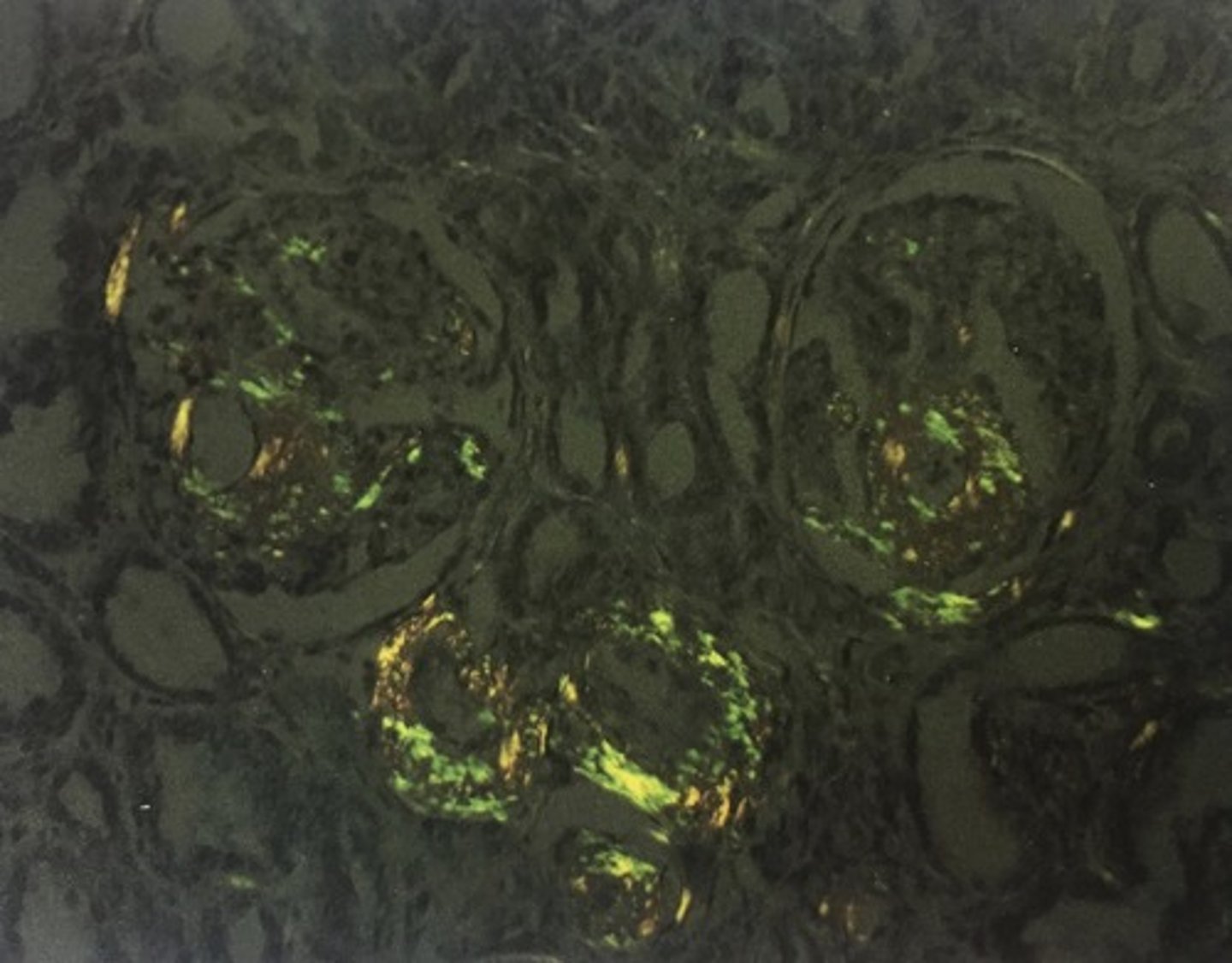
polarizing microscope principle
Uses vibrating light to visualize anisotropic samples with birefringent qualities
Has a polarizer between the light source and specimen, and an analyzer between the specimen and the eye
Birefringent components appear apple green in color
polarizing microscope use
Useful in specialized medical and industrial
Diagnosing amyloid stained with congo red
Identifying crystals such as talc, silica, and urates
phase contrast microscope principle
Light passes through transparent specimen slower that light that is uninfluenced
Wavelength has a phase shift
Transparent phase-plate in microscope intensified and translates the lift in light, causing it to be bright transparent object to stand out in contrast to the background
phase-contrast use
Can be used to study live organisms and other structures that may be destroyed in staining process (cell cycle)
Used to visualize specimen with transparent or colorless properties
dark-field microscope principle
Sample is illuminated with light that is mostly not collected by the objective lens
Light that is directly transmitted through the specimen is excluded due to direct illumination block
Bright object appears in midst of a dark background
dark-field microscope use
Used to visualize live, unstained samples or microorganisms (mostly bacteria)
Tissue culture or single-celled water-borne organism
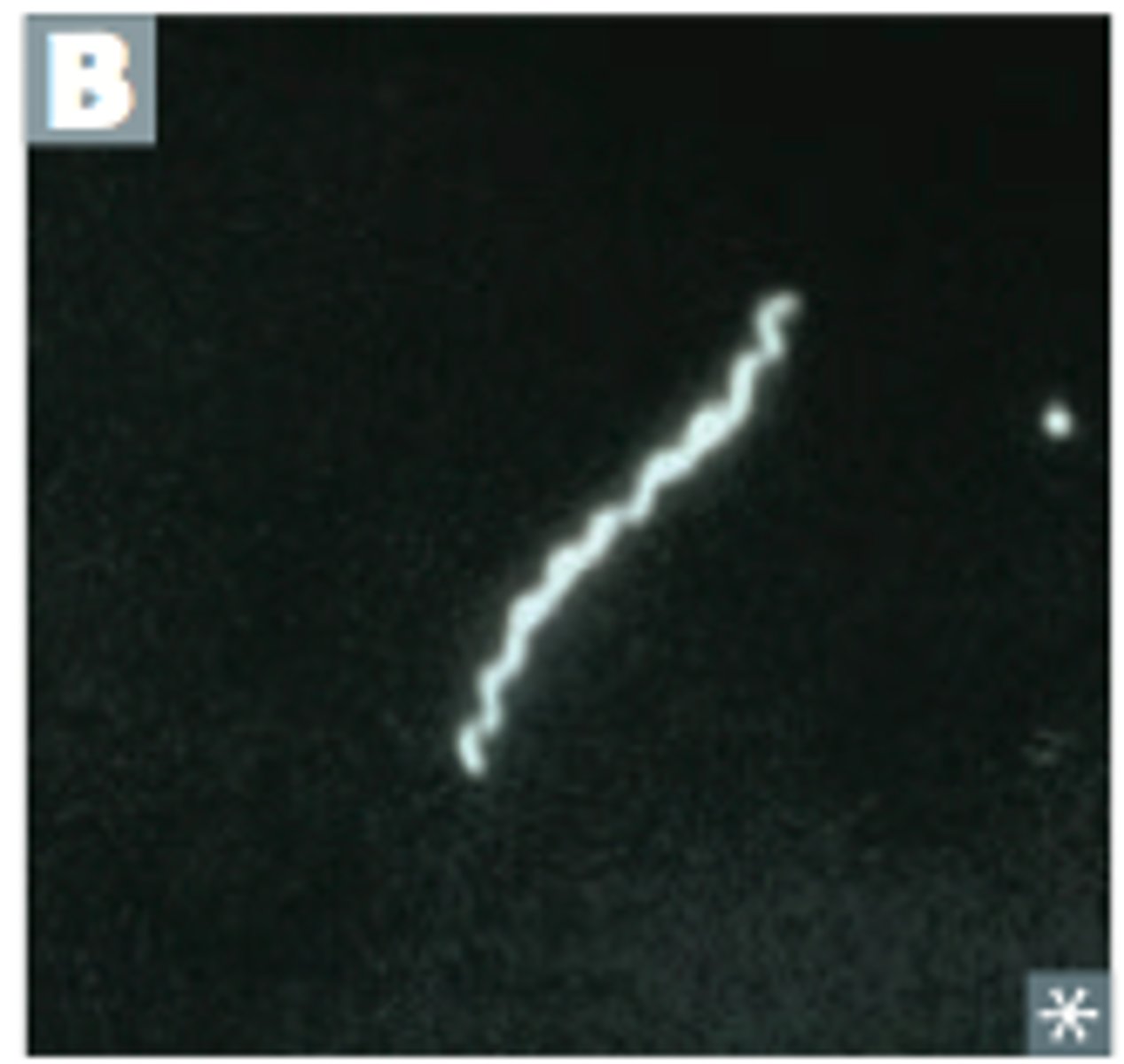
fluorescent microscope
Uses a dual filter system
UV passes through excitation filter, excites fluorophores
Fluophores release light and passes through an emission or barrier filter, resulting in a distinct color
A dichromatic mirror also helps direct the appropriate wavelength for light
fluorescent microscope use
Used for situ hybridization that can be used to diagnose malignancy by enabling the quantification of select chromosomes present in a cell
Also visualize fluorescein Isothiocyanate in immunohistochemical staining
Auramine Rhodamine with acid fast bacilli
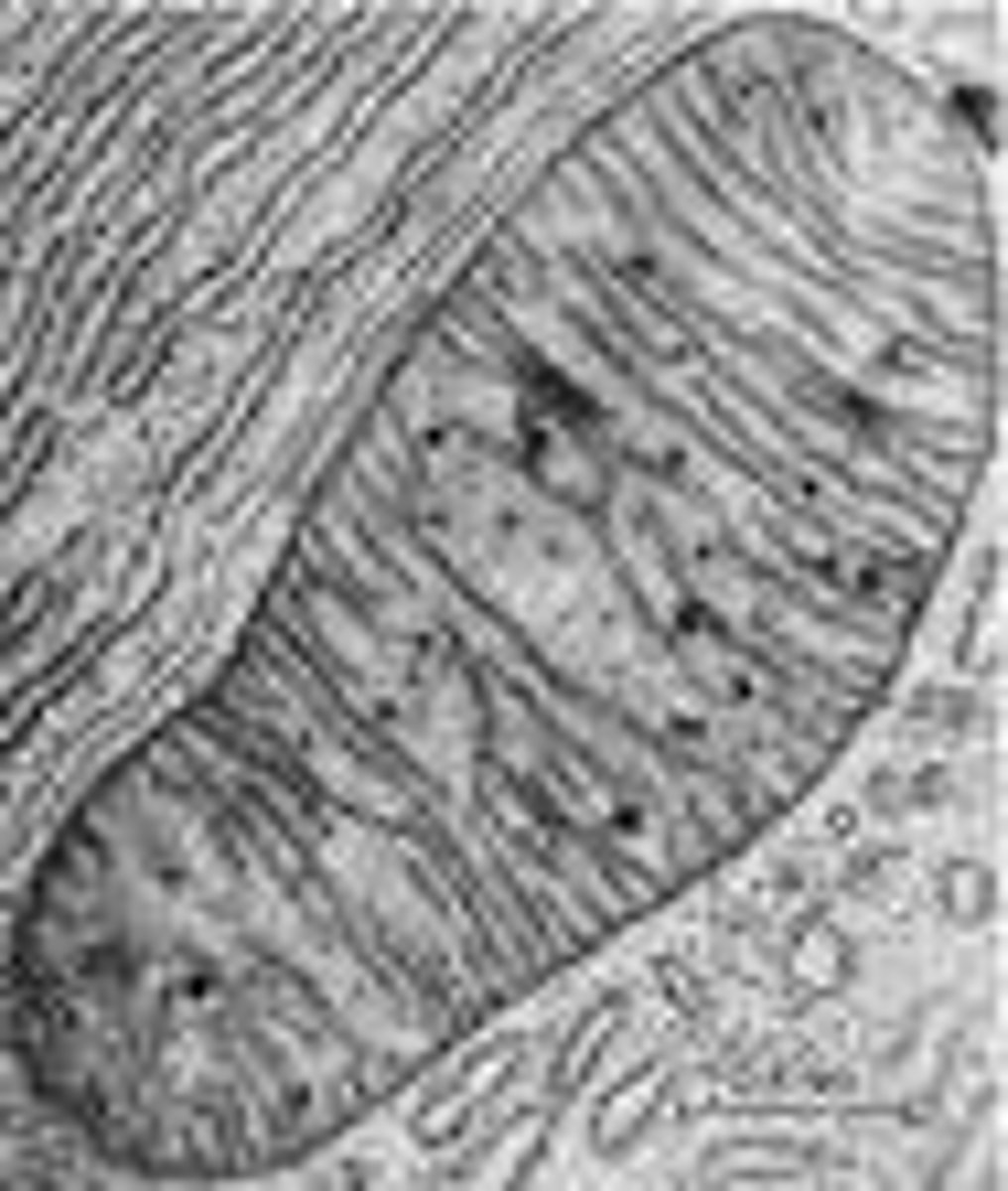
transmission electron microscope (TEM) principle
Electron beam passes through an ultrathin specimen
2D, black and white image with electron lucent (clear) and electron dense (dark) areas
TEM use
Useful for ultrastructure of an organism
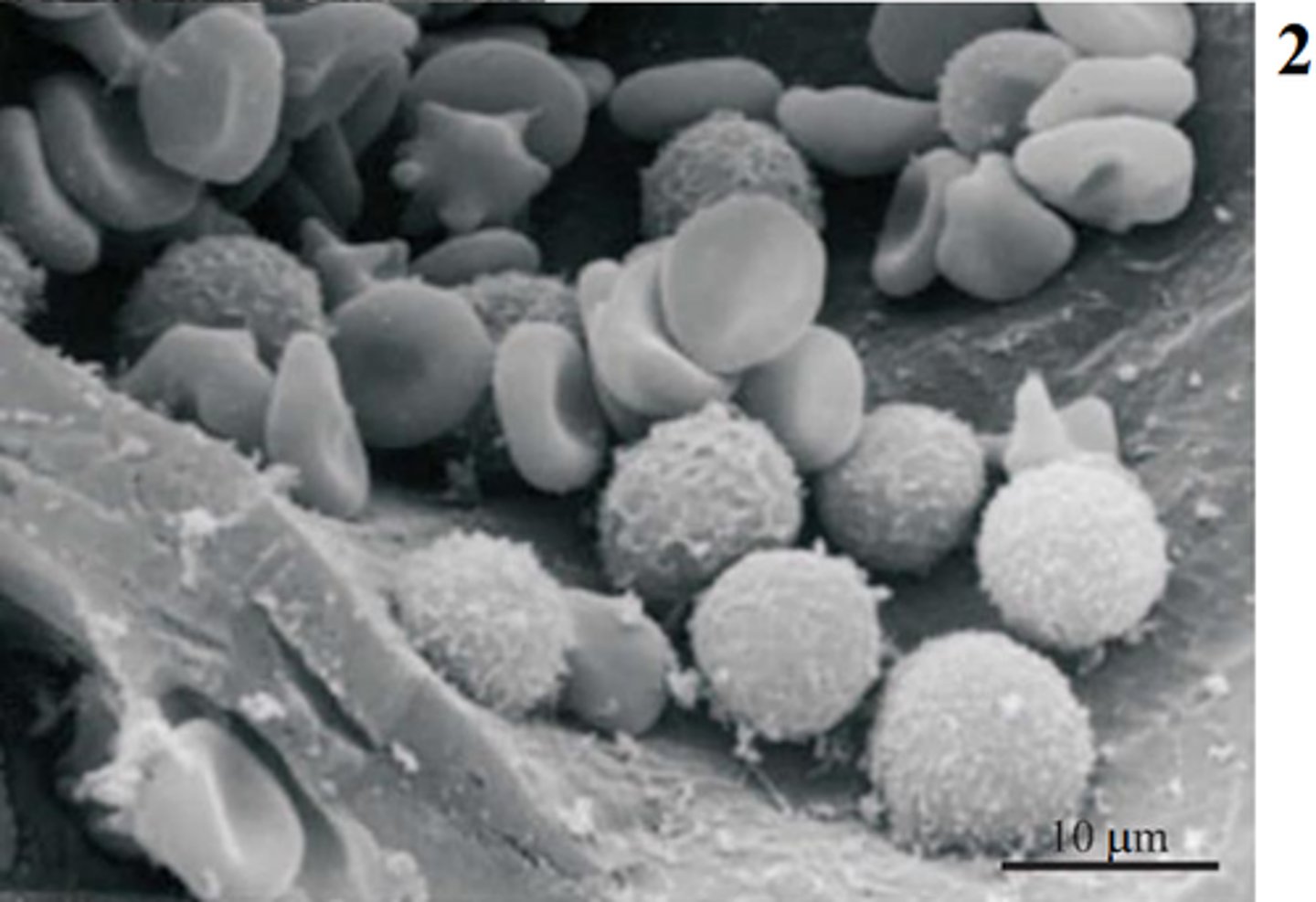
scanning electron microscope (SEM) principle
Electrons from beam interact with sample's atoms producing info in forms of signals about the surface and composition of specimen
3D black and white image
SEM use
Useful for crystal structure or chemical analysis
purpose of oil immersion
decreases diffraction of light as it passes through the object
role of the computer and laboratory information system in histopathology
The LIS receives, processes, and stores information generated by lab process and often interfaces with additional institutional software and histology related equipment. Specimens are tracked by the system as they go through the laboratory.
importance of confidentiality
Confidentiality is important for every role in healthcare and is protected under HIPAA. This means that only those who are part of the care team for the patient should know details about the case. If you must share with someone else, like you need help with something and you need to ask someone, keep the information minimal and unidentifiable
define quality control
Creating a culture of quality and continuous improvement to ensure that the results are always high quality, and our patients can be properly cared for - this includes monitoring and maintaining the instruments we work with
cryostat function
A traditional rotary microtome encased in a cooling chamber to check fresh tissue while surgery is ongoing
Rapid results for a quick analysis by the pathologist
cryostat quality control
Temperature and the blade should be monitored
drying oven function
Removes excess water and helps attach the tissue to slide
20-30 minutes at 60 C or 2-4 degrees above paraffin melting point
drying oven quality control
Temperature should be carefully monitored
embedding center function
Used to orient and surround the processed tissue in a liquid embedding medium which is then solidified to create a tissue block
embedding center quality control
Monitor temperature of embedding paraffin, forceps must be kept clean
hood function
Used when working with hazardous chemicals to limit exposure to noxious fumes and vapors
hood quality control
Only effective when used properly, annual quality checks to ensure that air is being moved and filtered properly
Sash maintained at optimal operating high, keep glass panes closed when the sash is open, limit excessive clutter
microtome (rotary) and associated water bath function
Used to cut thin sections of tissue to be placed on a microscope slide for viewing
Water bath used to float ribbons of tissue for mounting onto a glass slide
microtome (rotary) and associated water bath quality control
Ensuring the angle of the blade is correct, checking the temperature of the water bath
paraffin vat function
Used to melt solidified paraffin pellets and store for future use
paraffin vat quality control
Temperature is critical and needs to be monitored
staining microwave function
Used during histochemical staining to heat solutions (acts as a catalyst)
staining microwave quality control
Temperatures should be controlled and radiation leakage monitored
Caution used when removing the heated solution
tissue processor function
Used along with fixation to preserve the morphology of tissue specimens for pathologic review and diagnosis
tissue processor quality control
Monitor temperature and adequate ventilation, ensure the alarm system is working, use a hydrometer to measure the water content of the alcohol
closed tissue processor
tissue remains stationary in retort while chemicals are transferred into the holding chamber
Less chemical exposure, but can't use certain chemicals (chloroform)
open tissue processor
tissue is transferred through a series of stationary chemicals
Allows for special processing techniques (such as a whole eye) and is gentler on the tissue
Higher risk of chemical exposure
microwave tissue processor
microwave technology to create friction, which warms the chemicals and rapidly preserves the tissue sample
Tissue should be closely monitored and safety checks for radiation leakage
how a microwave works to aid in the processing and staining of tissue
A microwave heats the tissue, removing the water through evaporation. It also acts as a catalyst for tissue staining
clinical freezing microtome principle
Tissue is frozen on a metal stage and a large blade is moved across the face of the tissue
Sections are then free floated for staining
clinical freezing microtome use
fresh tissue slides generated in 1-2 minutes
rotary microtome principle
Moves block up and down across a steel blade while advancing the block forward slowly with each manual turn
sliding microtome principle
The block is stationary while the blade moves across the surface of the tissue
sliding microtome use
Used to cut large paraffin or celloidin embedded tissue blocks
most commonly used in research
ultramicrotome principle
Embedded in a plastic embedding medium and uses diamond blades to cut ultrathin slices
ultramicrotome use
Used to cut sections for light and/or electron microscopy
vibrating microtome principle
Uses a vibrating blade to cut thin section of fixed or unfixed tissue samples
Vibration of blade requires less pressure than a stationary blade
vibrating microtome use
to cut fresh tissue
role of automation
Automation can be used for both quality control and for high volume laboratories. It is used in staining to ensure the timing and quality of the stains. It is used in coverslipping because of high volumes. It can also be used to decrease physical stress on technicians
preventative maintenance
cleaning machines, storing them properly, using them properly, and calling maintenance when machines are broken so you don't break them further
corrective maintenance
after an instrument is already broken, and is fixed retroactively
maintenance applications for HTs
Perform daily quality checks (especially for temperatures), calibrate instruments often to a known standard, use control samples with known values regularly, perform regulate maintenance on machines (cleaning, software updates, and repairs), and document all that was previously listed