Week 3 - General Nervous System - Lecture Notes (Q&A Flashcards)
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Q&A flashcards covering CNS divisions, brain landmarks, basal nuclei, brainstem, cerebellum, spinal cord, and labeling tasks.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
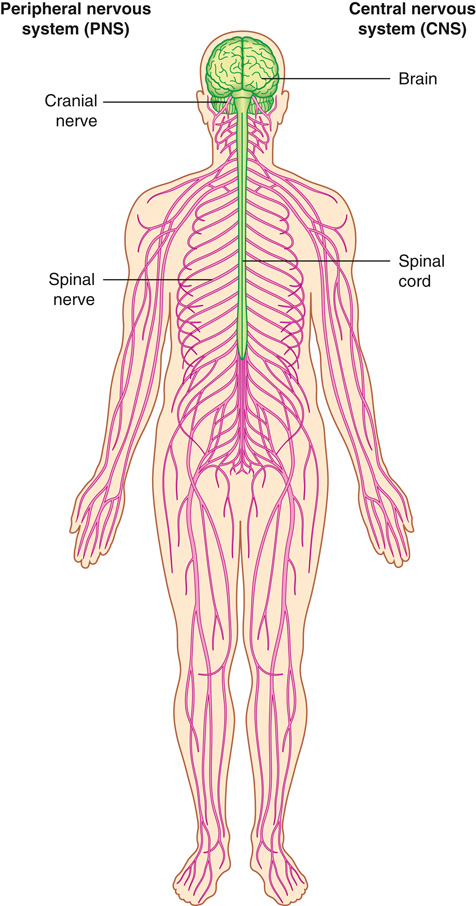
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS: brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (PNS: communication with body/environment).
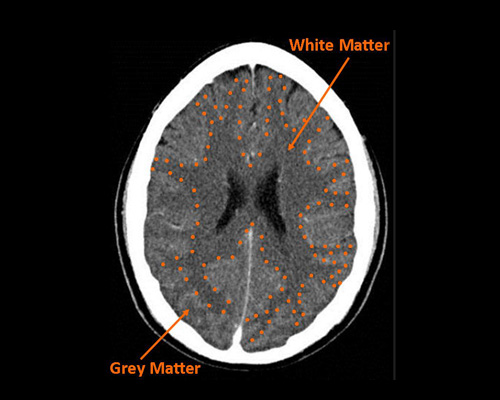
How is gray matter different from white matter?
Gray matter consists of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses; white matter contains myelinated axons.
What does the precentral gyrus control?
Voluntary motor movement (motor strip).
What is the function of the postcentral gyrus?
Processes sensory input (somatosensory cortex).
What does the central sulcus separate?
Frontal lobe (motor) from parietal lobe (sensory).
Which fissure separates temporal lobe from frontal/parietal lobes?
Lateral (Sylvian) fissure.
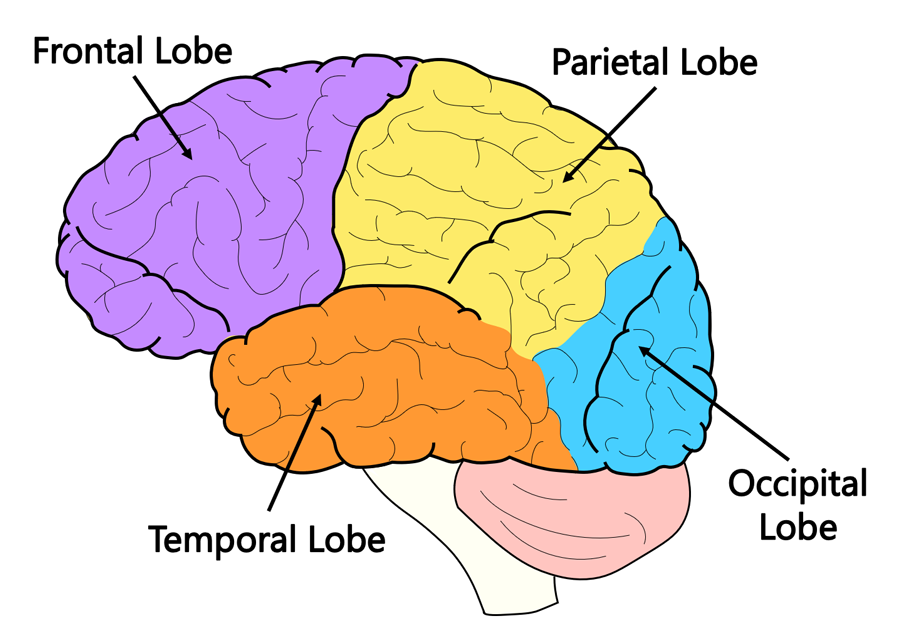
What are the four lobes of the brain?
Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal (insula sometimes described as a fifth).
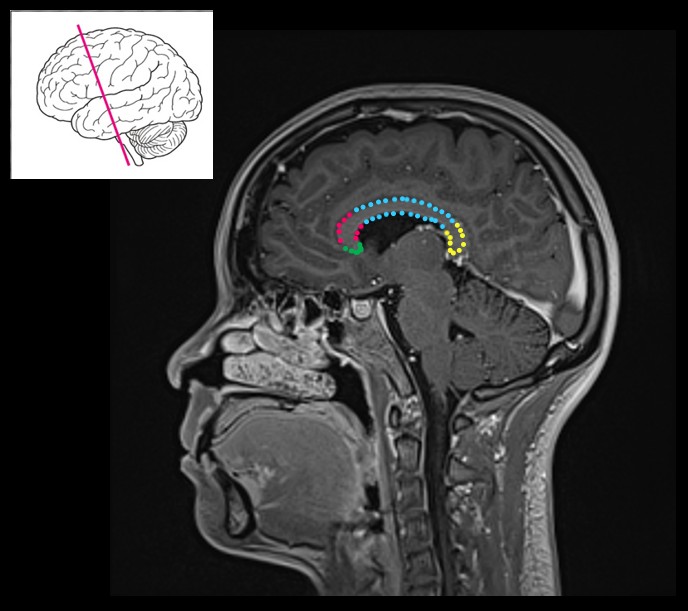
What are the four regions of the corpus callosum?
Rostrum, genu, body, and splenium.
Which sensory pathway does not relay through the thalamus?
Olfactory pathway.
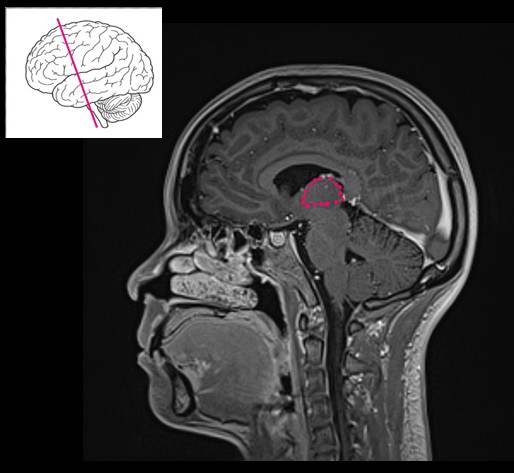
What are the main functions of the hypothalamus?
Maintains homeostasis (temperature, hunger, sleep) and regulates hormones via the pituitary.
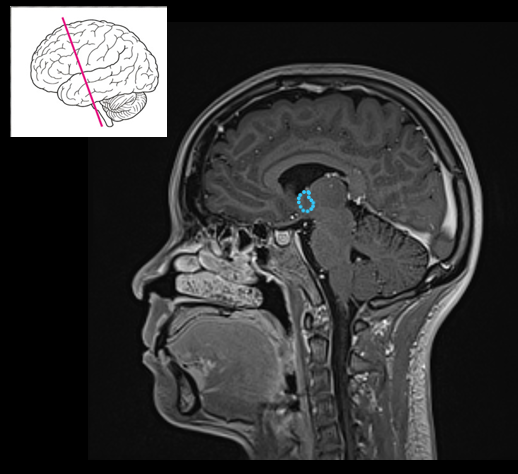
Which gland is part of the epithalamus and regulates circadian rhythm?
Pineal gland.
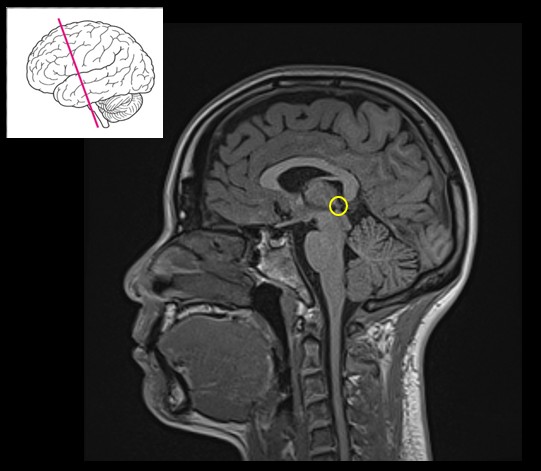
Which basal nucleus regulates voluntary movement by inhibition?
Globus pallidus.
Which basal nucleus is linked with motor control and learning?
Putamen.
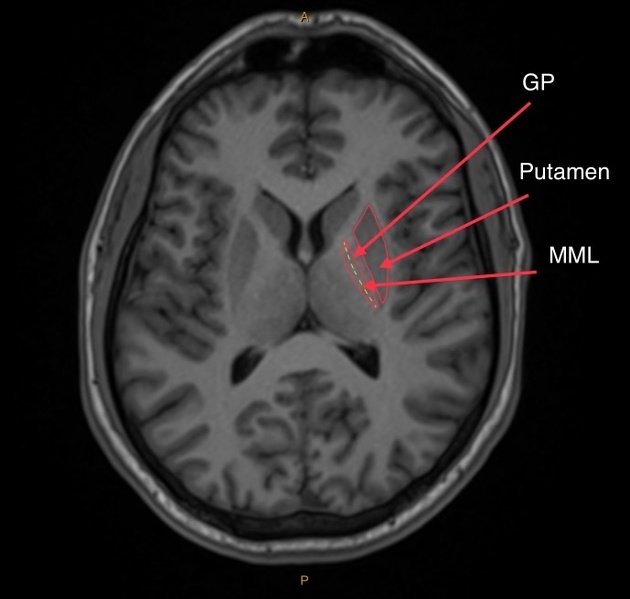
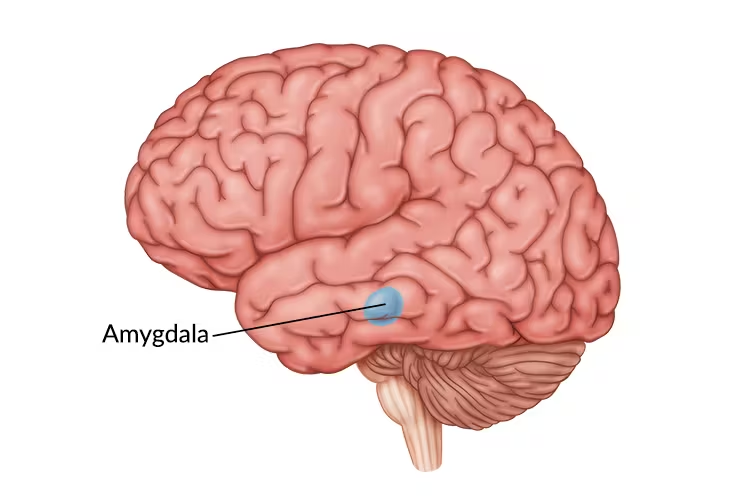
Where does the caudate nucleus tail terminate?
At the amygdala.
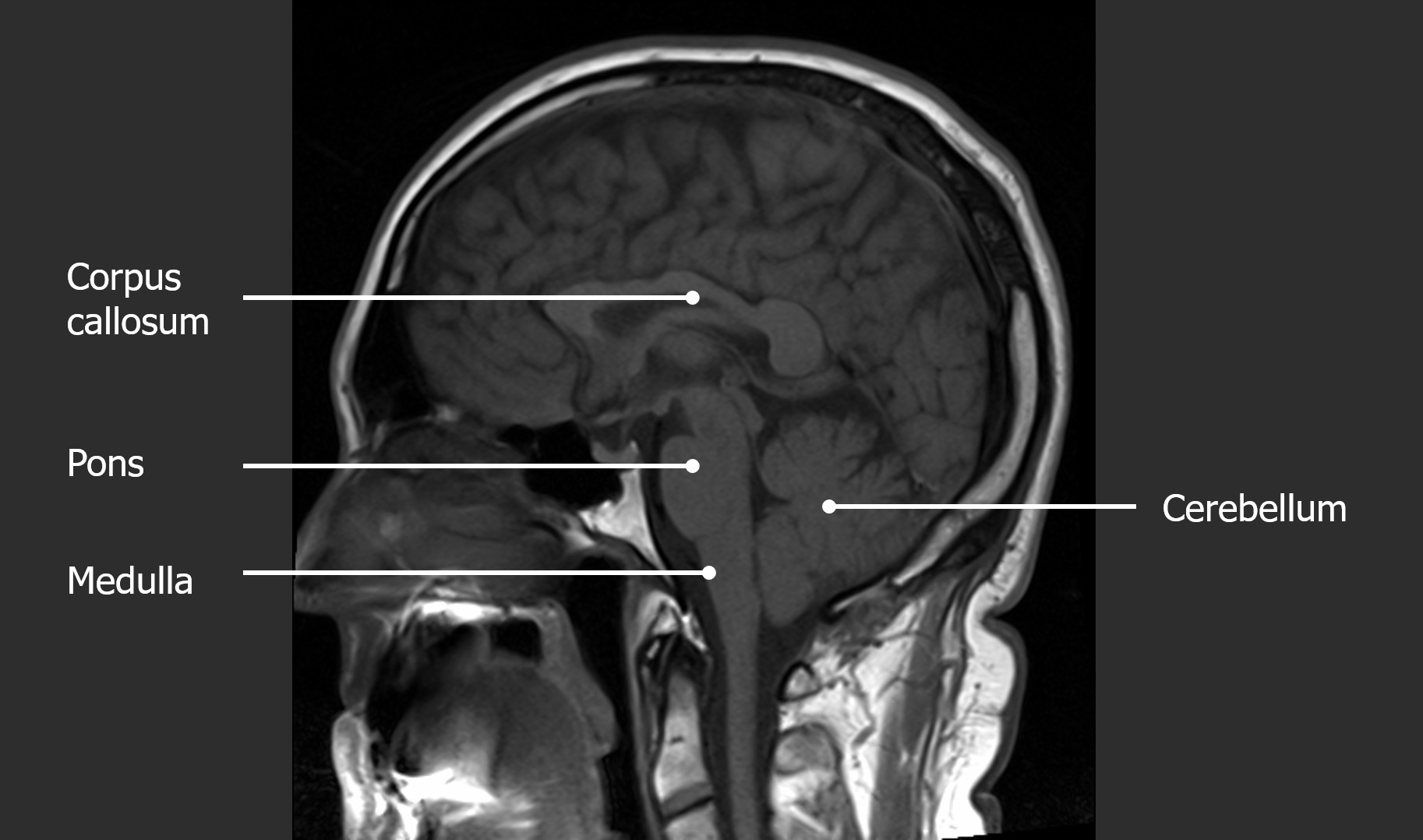
What are the three parts of the brainstem?
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata.
What structures are found in the tectum of the midbrain?
Superior colliculi (visual reflexes) and inferior colliculi (auditory reflexes).
Which part of the medulla contains nuclei for coordination, balance, and sound?
The olives.
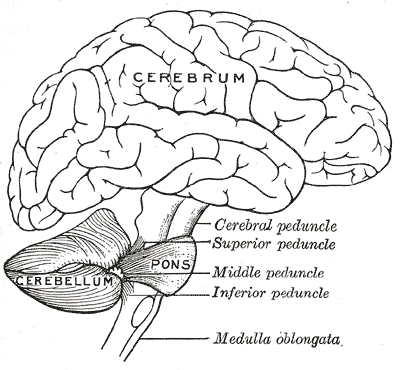
What connects the cerebellum to the brainstem?
Cerebellar peduncles: superior, middle, and inferior.
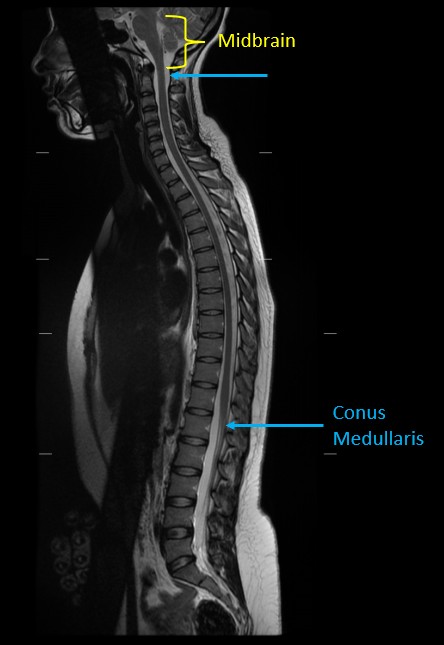
Where does the spinal cord end in adults?
Around L1–L2 at the conus medullaris.
What structure continues beyond the conus medullaris?
Cauda equina.
Through which root does sensory information enter the spinal cord?
Dorsal root.
Through which root does motor information leave the spinal cord?
Ventral root.
On a brain diagram, label the four lobes of the cerebrum (plus the insula).
Frontal lobe: anterior to the forehead; Parietal lobe: superior, posterior to the central sulcus; Occipital lobe: posterior, behind the parieto-occipital fissure; Temporal lobe: lateral, below the lateral fissure; Insula: deep, hidden within the lateral fissure.
Which fissure separates the two cerebral hemispheres?
Longitudinal fissure.
Which fissure separates frontal/parietal lobes from the temporal lobe?
Lateral (Sylvian) fissure.
On a diagram, label: central sulcus, precentral gyrus, and postcentral gyrus.
Central sulcus divides frontal and parietal lobes; Precentral gyrus is anterior to the central sulcus (motor strip); Postcentral gyrus is posterior to the central sulcus (sensory strip).
Label the four parts of the corpus callosum on a mid-sagittal diagram.
Rostrum (inferior), Genu (anterior bend), Body (long midsection), Splenium (posterior thickened part).
On a coronal section, identify thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland.
Thalamus – egg-shaped, flanking the third ventricle; Hypothalamus – inferior to thalamus, floor of the third ventricle; Pineal gland – posterior diencephalon, epithalamus region.
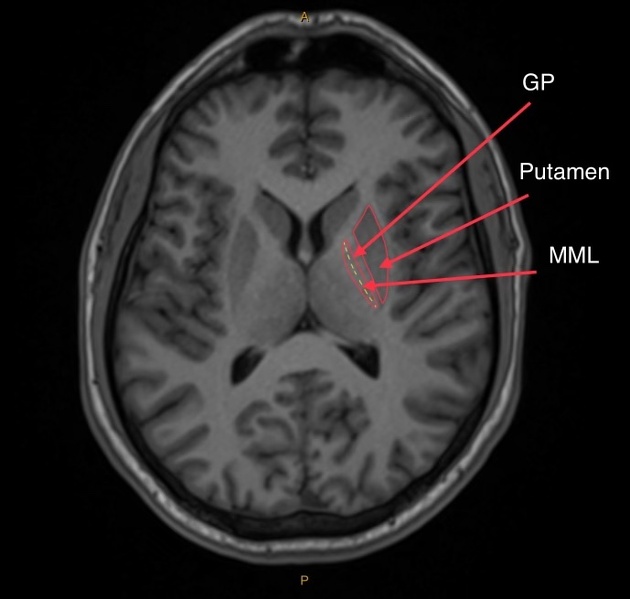
On an axial brain CT/MRI, label: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, claustrum.
Caudate nucleus follows the lateral ventricle; Putamen is lateral and large; Globus pallidus is medial to the putamen; Claustrum is a thin strip lateral to the putamen.
On a sagittal diagram, label: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum.
Midbrain – top of brainstem near the cerebral aqueduct; Pons – middle bulge anterior to the cerebellum; Medulla oblongata – lowest portion, continuous with spinal cord; Cerebellum – posterior, the little brain with vermis between hemispheres.
Label midbrain tectum structures.
Superior colliculi (visual reflexes) and Inferior colliculi (auditory reflexes).
On a spinal cord cross-section, label gray and white matter.
Gray matter – butterfly-shaped center with dorsal and ventral horns; White matter – outer region with ascending and descending tracts.
Which root carries sensory info into the spinal cord?
Dorsal root.
Which root carries motor info out of the spinal cord?
Ventral root.