B1.2: Proteins
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How many amino acids do humans have?
20
How many amino acids can be made, and how many need to be taken in?
11 made, 9 taken in
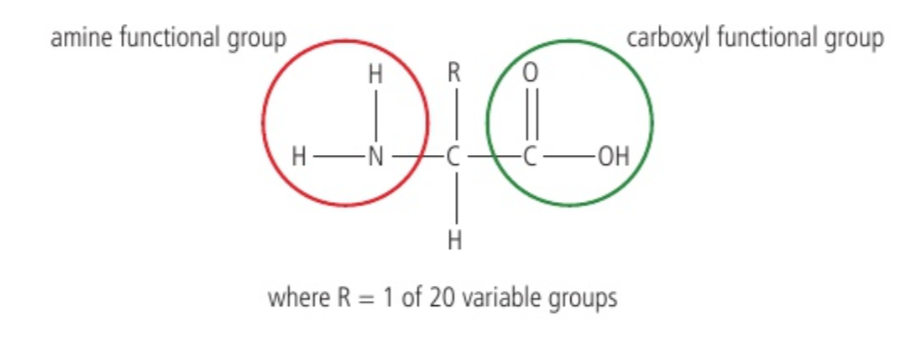
Common structure of amino acids
Central carbon linked to NH2 and COOH groups, one hydrogen atom, variable group (R)
Polypeptide examples
Haemoglobin, keratin, insulin
Peptide bonds
Condensation reaction
Amino acid structure
Central carbon liked to amine group, carboxyl, r-group, hydrogen atom
Essential amino acids
Cannot be synthesised by the organism, must be taken up in the diet
Obtaining essential amino acids
They are all produced by plants during photosynthesis, are passed through the food chain
Peptide/polypeptide def.
An unbranched chain of amino acids, short or long (respective)
Denaturation
Heat or excessive pH change causes intramolecular bonds in peptides to break, changing the shape of the protein, which defines its purpose.
Denaturation reversability
At mild disruption to optimum pH/temperature, only hydrogen bonds are broken causing denaturation. Returning to optimum pH/temperature would allow bonds to be re-established.
With excessive disrpution, covalent bonds are irreversibly broken, and returning to optimum pH/temperature would not allow these bonds to be re-established.
What defines the function of a protein?
Its shape
Outline structure of proteins
Formed from amino acids
Linked together by peptide bonds
May consist of one or more polypeptides
Have a specific shape/conformation/folding
Shape determines function
Outline protein synthesis in the cell
Proteins are produced when genes are expressed, they are coded for in DNA
Genetic codon in DNA = 3-base sequence
1 DNA codon = 1 amino acid
Codons are transcribed by mRNA
mRNA exits the nucleus
mRNA codons are translated by tRNA into polypeptides (chains of amino acids)
Polypeptide/protein synthesis finalised at the ribosome
Sequence of amino acids decided by order of DNA bases
Proteins vary depending on type and order of amino acids
Outline enzyme denaturation
Change in pH or temperature causes denaturation
Intramolecular bonds are broken
Causes change to protein shape
Protein becomes denatured
Function of protein is halted/impaired by damage to shape
Enzyme denaturation consequences
Enzyme loses structure, active site changes shape
Active site damaged/changed = substrate unable to bind to active site (as efficiently)
Impaired/halted rate of reaction
Polypeptide vs protein
Polypeptides = chains of amino acids, proteins = complex structures made of one of more polypeptides.