DNA packaging in the nucleus
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
State 3 reasons as to why DNA needs to be packaged
there’s a lot of it and it needs to be packaged to fit
organised packaging allows it to be easily unpacked
protects DNA from attack
-there’s a lot of DNA and so it has to fit- (2 points)
each of your cells has about 2m of DNA in the nucles
average human nucleus has a diameter of 10μm
-organised packing allows it to be easily unpacked- for.. (2 points)
transcription
repair
-protects DNA from attack- (2 points)
mutagens and other DNA elements can attack uncoiled DNA
packaging it up for safety helps protect it
What is a nucleoside?
a base with deoxyribose
What is a nucleotide?
a nucleoside with 1-3 phosphates
What is a nucleus?
the eukaryotic cellular compartment where DNA is stored
What is a nucleolus?
a dense area within the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled
What is a nucleosome?
histone octamer wrapped in 147 bp DNA and linker DNA
List 3 common DNA replication sequences
DNA replication origin
centromere
telomere
DNA replication origin (2 points)
the location at which DNA duplication begins
eukaryotic chromosomes contain many origins of replication to ensure that the entire chromosome can be replicated rapidly
Centromere (2 points)
link identical sister chromatids after DNA replication
allows one copy of each duplicated chromosome to be pulled into each daughter cell
Telomeres (3 points)
ends of a chromosome
contain repeated nucleotide sequences that enable the ends of chromosomes to be officially replicated
repeated telomere sequences, together with the region adjoining them, form structures that protect the ends of the chromosome from being mistaken by the cell for a broken DNA molecule in need of repair
List the arrangement of chromatin
“beads on a string“
String =
DNA
Bead =
nuclesome core particle
How can we separate a nucleosome from chromatin?
degrading the linker DNA
What do nucleosome core particles consist of?
an octametric histone core
147 nucleotide double stranded DNA (wrapped in a left handed coil of 1.7 turns)
List the structural composition of the histone octamer core
2x (tetramers)
(H2A + H2B + H2A + H2B)
(H3 + H4 + H3 + H4)
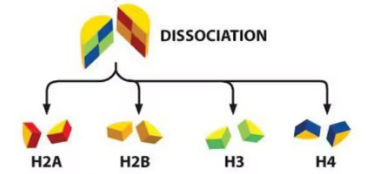
Describe the bonds present between octamer core and DNA (2 points)
there are 142 hydrogen bonds formed between DNA and histone core in each nucleosome
nearly half of these bonds are between amino acid backbone and sugar phosphate backbone of DNA
How long is the linker DNA that separates each nucleosome core particle
80 nucleotide pairs
How often do nucleosomes repeat?
intervals of 200 nucleotide pairs
Discuss amino acid composition in histone cores
>1/5 of amino acids in each histone core are either lysine or arganine, whos positive charges neutralise the negatively charged DNA backbone
Discuss histone amino acid tail composition (2 points)
each histone core has an N terminal amino acid tail
these tails, subject to covalent modification, can determine critical aspects of chromatin structure and function
Describe the dynamic structure of nucleosomes
unwraps from each end 4x per second, remaining exposed for 10-50ms before the structure releases
Describe the dynamic structure of chromatin (2 points)
further loosening of DNA-histone contacts is required because eukaryotic cells contain a large variety of ATP dependent chromatin remodeling complexes
this complex binds to histone core and the DNA, using the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move the DNA relative to the core, making it less tightly bound
State 2 different variations of chromatin sructure
zig zag model of 30nm fiber
nucleosomes form a tetra-nucleosome
solenoid model
six nucleosomes per twist of coil