Imaging exam 3
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Last updated 4:54 PM on 2/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
which view of the thoracic reveals all 12 vertebrae, vertebral end plates, pedicles, intervertebral disk
A/P
2
New cards
which view of the thoracic spine reveals all but upper 2 or 3 vertebrae, vertebral bodies, intervertebral disk space
lateral
3
New cards
which view of the thoracic spine reveals the upper thoracic vertebrae
swimmers shoulder
4
New cards
what are some examples of thoracic spine traumatic injuries
anterior compression fx, vertebral fx-dislocatiions, rib fracture
5
New cards
what are some examples of thoracic spine pathologies
* Osteoporosis
* scoliosis
* scheuermann’s disease
* spinal tuberculosis (Pott’s disease)
* scoliosis
* scheuermann’s disease
* spinal tuberculosis (Pott’s disease)
6
New cards
what kind of SCI is detected on radiographs
anterior vertebral body compression fx
7
New cards
what is the MOI for anterior vertebral body fx
flexion
8
New cards
what is common for compression fx to look like
Cod fish
9
New cards
what is used to view bone detail
bone window
10
New cards
what is the gold standard test for osteoporosis
dexa scan
11
New cards
what are some tx for osteoporosis
reduce compression
12
New cards
what can be used to measure the degree of scoliosis
Cobb angle
13
New cards
what is Scheuermann’s disease
* unknown etiology
* common in adolescent boys and girls
* sx of backache and thoracic kyphosis from osteochondrosis
* schmorl nodes are consistent findings
* common in adolescent boys and girls
* sx of backache and thoracic kyphosis from osteochondrosis
* schmorl nodes are consistent findings
14
New cards
what is the diagnostic criteria for Scheuermann’s disease
* at least 3 continuous vertebrae to be involved
* at least 5 degrees of anterior wedging of each affected vertebra
* thoracic kyphosis greater than 40 degrees
* at least 5 degrees of anterior wedging of each affected vertebra
* thoracic kyphosis greater than 40 degrees
15
New cards
what are some PT interventions for Scheuermann’s disease?
* lay supine
* prayer stretch
* supine snow angel with hook lying
* mini pelvic tilts
* work up to light foam rolling
* prayer stretch
* supine snow angel with hook lying
* mini pelvic tilts
* work up to light foam rolling
16
New cards
t/f: Scheuermann’s disease affects the pectoralis major
false
17
New cards
if a patient has Scheuermann’s disease, what muscle would be tight in the low back
erector spinae
18
New cards
what is always secondary to a tuberculosis lesion elsewhere in the body
Tuberculous osteomyelitis (Pott’s disease)
19
New cards
what is the clinical presentation of Tuberculous osteomyelitis (Pott’s disease)
* back pain is earliest and most common sx
* pain usually localized, most common in thoracic spine
* systemic s/s such as weight loss, fever, and fatigue usually present
* lower thoracic vertebra are usually sites, followed by upper lumbar
* pain usually localized, most common in thoracic spine
* systemic s/s such as weight loss, fever, and fatigue usually present
* lower thoracic vertebra are usually sites, followed by upper lumbar
20
New cards
what is a radiologic assessment of Tuberculous osteomyelitis (Pott’s disease)
* progressive destruction leads to collapse of anterior vertebral bodies and an associated increase in kyphosis
* often more than 1 vertebra involved
* osteolysis
* often more than 1 vertebra involved
* osteolysis
21
New cards
which if the preferred view of the chest
P/A
22
New cards
chest x-rays can look at
* pneumonia
* lobar collapse
* pleural effusion
* pneumothorax
* cardiomegaly
* lobar collapse
* pleural effusion
* pneumothorax
* cardiomegaly
23
New cards
For acute LBP clinical findings, what would lead to leading to get radiograph
* cluster of red flags
* no response to 3 weeks of PT intervention; 2-3 visits even
* no response to 3 weeks of PT intervention; 2-3 visits even
24
New cards
what are the recommended screening for lumbar spine imaging
* A/P and lateral radiographs
* erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) → occult neoplasms of spine
* erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) → occult neoplasms of spine
25
New cards
what view of a radiograph of the lumbar spine shows all 5 vertebral bodies
A/P
26
New cards
what view of a radiograph of the lumbar spine shows alignment of lumbar vertebrae and intervertebral disk spaces
lateral
27
New cards
what view of a radiograph of the lumbar spine shows facet articulations, pedicles, pars, scotty dog
A/P and P/A oblique
28
New cards
what is the downside of the A/P and P/A oblique
high levels of gonadal radiation
29
New cards
what is the owl sign
deals with the condition of the pedicle- should be able to see the eyes and beak. can see pedicle erosion, compression fx, and fx dislocation
30
New cards
what are different degenerative conditions
* DDD
* DJD
* spondylosis
* spondylolysis
* spondylolisthesis
* spinal stenosis
* DJD
* spondylosis
* spondylolysis
* spondylolisthesis
* spinal stenosis
31
New cards
what condition has breakdown of discs
DDD
32
New cards
what condition has facet breakdown
DJD
33
New cards
what condition has formation of osteophytes in response to DDD- the umbrella term
spondylosis
34
New cards
what condition has a defect in pars interarticularis (scotty dog)
spondylolysis
35
New cards
what condition has forward displacement of vertebrae can result from degenerative changes and or fx
spondylolisthsis
36
New cards
what condition develops in the central canal, intervertebral foramen, or lateral or sub articular recesses
spinal stenosis
37
New cards
what are the segments of the scotty dog fracture/spondylolysis
* transverse process- nose
* pedicle- eye
* pars interarticular - neck
* superior articular facet- ear
* inferior articular facet- front leg
* pedicle- eye
* pars interarticular - neck
* superior articular facet- ear
* inferior articular facet- front leg
38
New cards
what indicates if there is a scotty dog fracture
if the dog has a collar on the parts interarticularis
39
New cards
what are spondylolthesis grades determined by
percentage of motion
40
New cards
what is a protrusion of disk material through annulus
intervertebral disk herniation
41
New cards
t/f: conventional radiographs are poor at showing disk material but will show chronic changes to bone
true
42
New cards
what imaging are good at showing morphological and physiochemical changes in disk
CT myelography & MRI
43
New cards
the vacuum phenomena involving the intervertebral discs are a result of what
accumulation of gas within the crevices of the intervertebral dicks or adjacent vertebrae
44
New cards
what should be looking for with S1
triangle shape
45
New cards
what is the common direction for a primary disc budge
posterior/lateral
46
New cards
why is it common for a disc bulge to be P/L
because the posterior longitudinal ligament is not the entire width of the vertebral body and there is a space
47
New cards
t/f: are fat infiltrated in the lumbar multifidus muscles strongly associated with LBP in adults
true (81% of adult sample)
48
New cards
if an image has the terms melted candle stick on it, what is that indicative of
AS
49
New cards
what view of a radiograph shows entire pevlis, sacrum, coccyx, and lumbrosacral articulation and B hip joint
A/P view of pelvis
50
New cards
what view of a radiograph of the pelvis shows acetabulum, femoral head, neck, and proximal 3rd of shaft, GT, and angle of inclination of femoral neck
A/P view of hip
51
New cards
what view shows femoral head, neck, and proximal 3rd of femoral shaft and greater and lesser trochanter from medial aspect
lateral frog leg of hip
52
New cards
what position is the lateral frog leg of hip image taken in
FABER
53
New cards
what are the 6 important lines of the pelvis
1. radiographic teardrop
2. iliopublic
3. ilioischial
4. anterior acetabular rim
5. posteriior acetabular riim
6. acetabular roof
54
New cards
what does a disruption of the lines of the pelvis indicate
fracture, dislocation or pathology in the hip/pelvis
55
New cards
what are some sex differences on pelvic radiographs
* infrapubic angle is greater than 90 degrees in female
* pelvic inlet shape
* male: heart shaped
* female: round or oval
* wider greater sciatic notch in females
* acetabulum faces more anteriorly in females
* sacrum more triangular and shorter in females
* oval obturator foramen in females
* pelvic inlet shape
* male: heart shaped
* female: round or oval
* wider greater sciatic notch in females
* acetabulum faces more anteriorly in females
* sacrum more triangular and shorter in females
* oval obturator foramen in females
56
New cards
t/f: CT is not the first line imaging evaluating the pelvic viscera except in the setting of trauma
true
57
New cards
what are common pelvic and hip fx
* pelvic ring f
* ischiopubic ramus fx
* acetabular fx
* ischiopubic ramus fx
* acetabular fx
58
New cards
what constitutes a pelvic ring fx
1 or more fx to the bones that make up the ring (2 inanimate and sacrum)
59
New cards
what is the most common MOI for a pelvic ring fx
MVA
60
New cards
what kind of proximal femoral fx is complicated by vascular disruption, may lead to avascular necrosis
intracapsular fx
61
New cards
what kind of proximal femoral fx is vascular complication is rare
extracapsular fx
62
New cards
t/f: upper fx to proximal femoral head are better than lower fx
false (vise versa)
63
New cards
what kind of femoral neck stress fracture is the best to have
compression
64
New cards
what kind of femoral neck stress fracture is the worst to have
tension
65
New cards
what are some signs of OA
* joint space narrowing
* sclerotic subchondral bone
* osteophyte formation at joint margins
* cyst or pseudocyst formation
* migration of femoral head
* sclerotic subchondral bone
* osteophyte formation at joint margins
* cyst or pseudocyst formation
* migration of femoral head
66
New cards
what are the types of migration of the femoral head
* superolateral
* non-migratory
* medial-axial
* non-migratory
* medial-axial
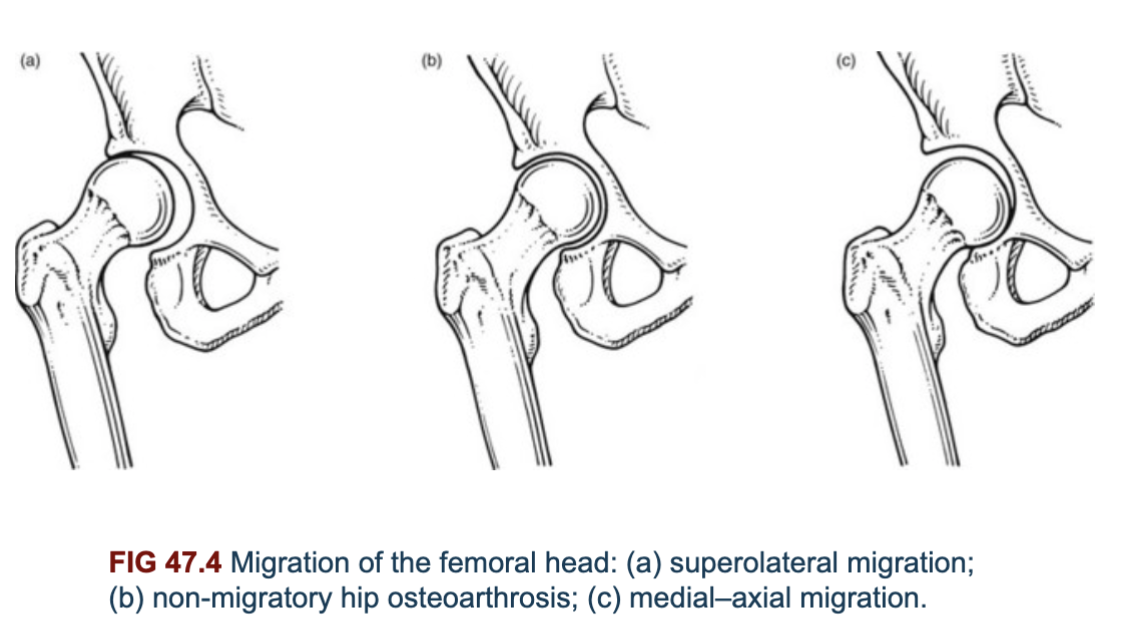
67
New cards
what are some s/sx of RA
* osteoporosis of periarticular area
* symmetrical and concentric joint space narrowing B
* articular erosions
* synovial cysts located within nearby bone
* periarticular swelling and joint effusions
* axial migration of femoral head
* acetabular protrusion
* minimal evidence of bone trying to repair itself → lack of sclerotic bone or osteophytes
* symmetrical and concentric joint space narrowing B
* articular erosions
* synovial cysts located within nearby bone
* periarticular swelling and joint effusions
* axial migration of femoral head
* acetabular protrusion
* minimal evidence of bone trying to repair itself → lack of sclerotic bone or osteophytes
68
New cards
what is the simple complex of RA
synovial fluid turning into battery acid
69
New cards
what is a SCFE
* weakening of epiphyseal plate that leads to slipping and displacement of femoral head
* patterns of pain in hip and knee area, limited hip ROM, antalgic gait, and limb shortening
* 2x more prevalent in boys than girls
* onset usually around growth spurts at puberty
* patterns of pain in hip and knee area, limited hip ROM, antalgic gait, and limb shortening
* 2x more prevalent in boys than girls
* onset usually around growth spurts at puberty
70
New cards
what is legg-calve perthes disease
* epiphyseal ischemic necrosis of femoral head
* associated with subtle trauma, synovitis, infection, or metabolic bone disease
* can be unilateral or B
* Predominately in boys, avg 6y.o
* Findings
* non-specific dull pain in joint, thigh or leg
* limited hip ROM, progressive limp
* associated with subtle trauma, synovitis, infection, or metabolic bone disease
* can be unilateral or B
* Predominately in boys, avg 6y.o
* Findings
* non-specific dull pain in joint, thigh or leg
* limited hip ROM, progressive limp
71
New cards
what does the femoral head look like on legg-calve-perthes
shrunken walnut
72
New cards
what type of femoral acetabular impingement is the femoral head-neck junction is offset and femoral head doesnt fully clear the acetabular rim
Cam
73
New cards
what type of femoral acetabular impingement has over coverage of femoral head caused by acetabulum, caused by deep socket or other malformations
pincer
74
New cards
what test can test for femoral acetabular impingement
straight flexion
75
New cards
what are common findings for femoral acetabular impingement
* snapping
* clicking
* limited hip ROM
* hip flexion contractures
* painful provocation tests
* clicking
* limited hip ROM
* hip flexion contractures
* painful provocation tests
76
New cards
true hip locking is associated with what conditioin
labral tears
77
New cards
t/f: many unsymtomatic people have FAI and labral tears
true
78
New cards
t/f:labral tears of the hip can happen anywhere
true
79
New cards
what is the common MOI for a hip labral tear
forced FADIR- pressure on with twisting
80
New cards
looking for labral tears of the hip is similar to the shoulder and we should be looking for what
black triangles