Isomers!
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are structural isomers?

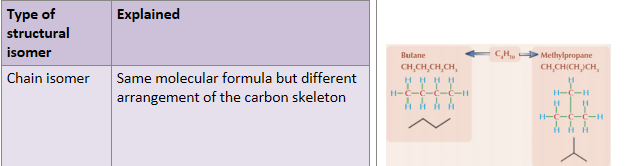
What is a chain isomer?
What is a positional isomer?

What is a functional group isomer?

What is stereoisomerism?
Stereoisomers- isomers which have the same structural and molecular formula but a different arrangement in space
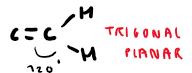
Why does steroisomerism only occur in alkenes?
Atoms can't rotate around the C=C bond (restricted rotation) -
What are examples of stereoisomerism?
E/Z isomerism
Cis/trans isomerism
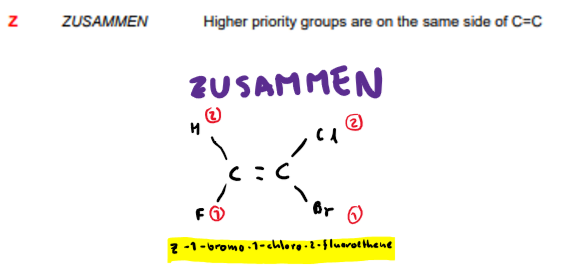
What is Z-isomerism?
What is E-isomerism?
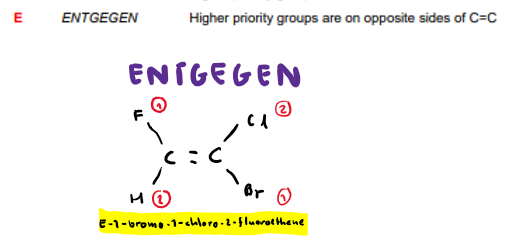
What groups are given higher priorities?
The groups with higher Mr.
When does cis and trans isomerism apply?

What is cis/trans isomerism?
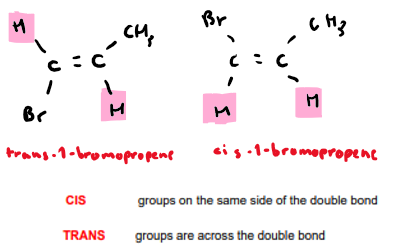
What is optical isomerism?
Optical isomerism- a form of stereoisomerism, they have the same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
What do optical isomers have?
They have a chiral carbon centre (asymmetric carbon attached to 4 different groups)
Have non-superimposable mirror images
Have a tetrahedral shape
What can be said about a chiral molecule?
It is non-superimposable on its mirror image
What do enantiomers do to light?
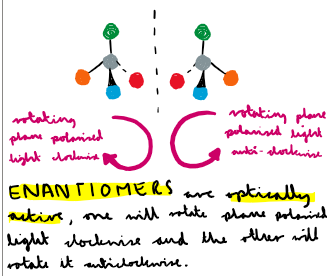
What is a racemic mixture?
When we have an equal amount of each enantiomer
What can be said about racemic mixtures in terms of rotating plane-polarised light?
Racemates do not rotate plane polarised light as the two enantiomers rotate light in opposite directions (clockwise and anticlockwise) and they cancel out.
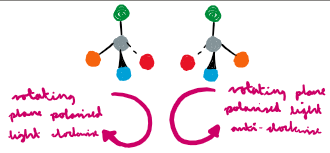
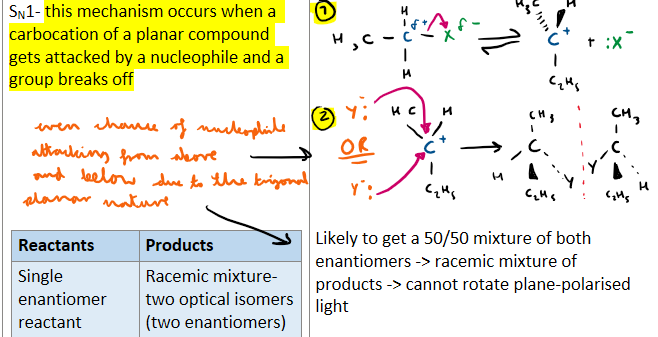
Which mechanism produces a racemic mixture, please include a diagram as well and explain why there is a racemix mixture as product?
SN1
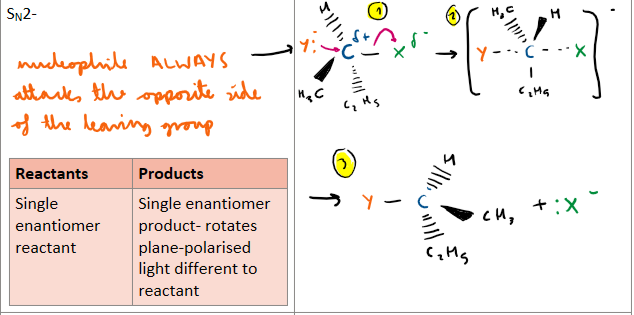
Which mechanism produces optically active products, explain why?
SN2