RP9 - Investigation into the effect of a named variable on the rate of respiration of cultures of single-celled organisms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Describe how a respirometer can be used to measure the rate of aerobic respiration
𝐌𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐎𝟐 𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐚𝐤𝐞:
1. Add a set mass of single-celled organism eg. yeast to a set volume / concentration of substrate eg. glucose
2. Add a buffer to keep pH constant
3. Add a chemical that absorbs CO2 eg. sodium hydroxide
4. Place in water bath at a set temperature and allow to equilibrate
5. Measure distance moved by coloured liquid in a set time
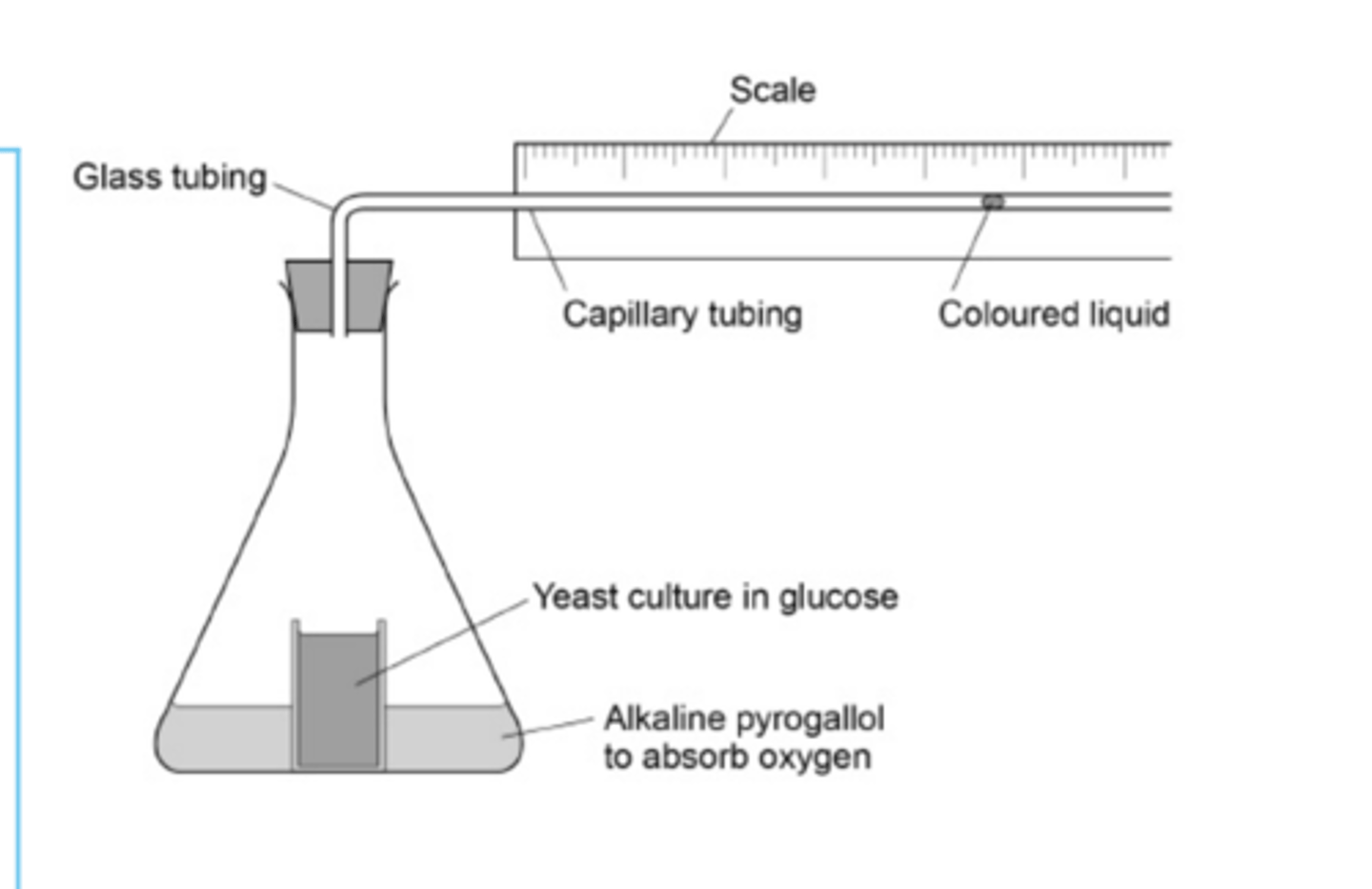
Explain why and to where the liquid moves. (aerobic respiration)
● Organisms aerobically respire → take in O2
● CO2 given out but absorbed by sodium hydroxide solution
● So volume of gas and pressure in container decrease
● So fluid in capillary tube moves down a pressure gradient 𝐭𝐨𝐰𝐚𝐫𝐝𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐨𝐫𝐠𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐬𝐦
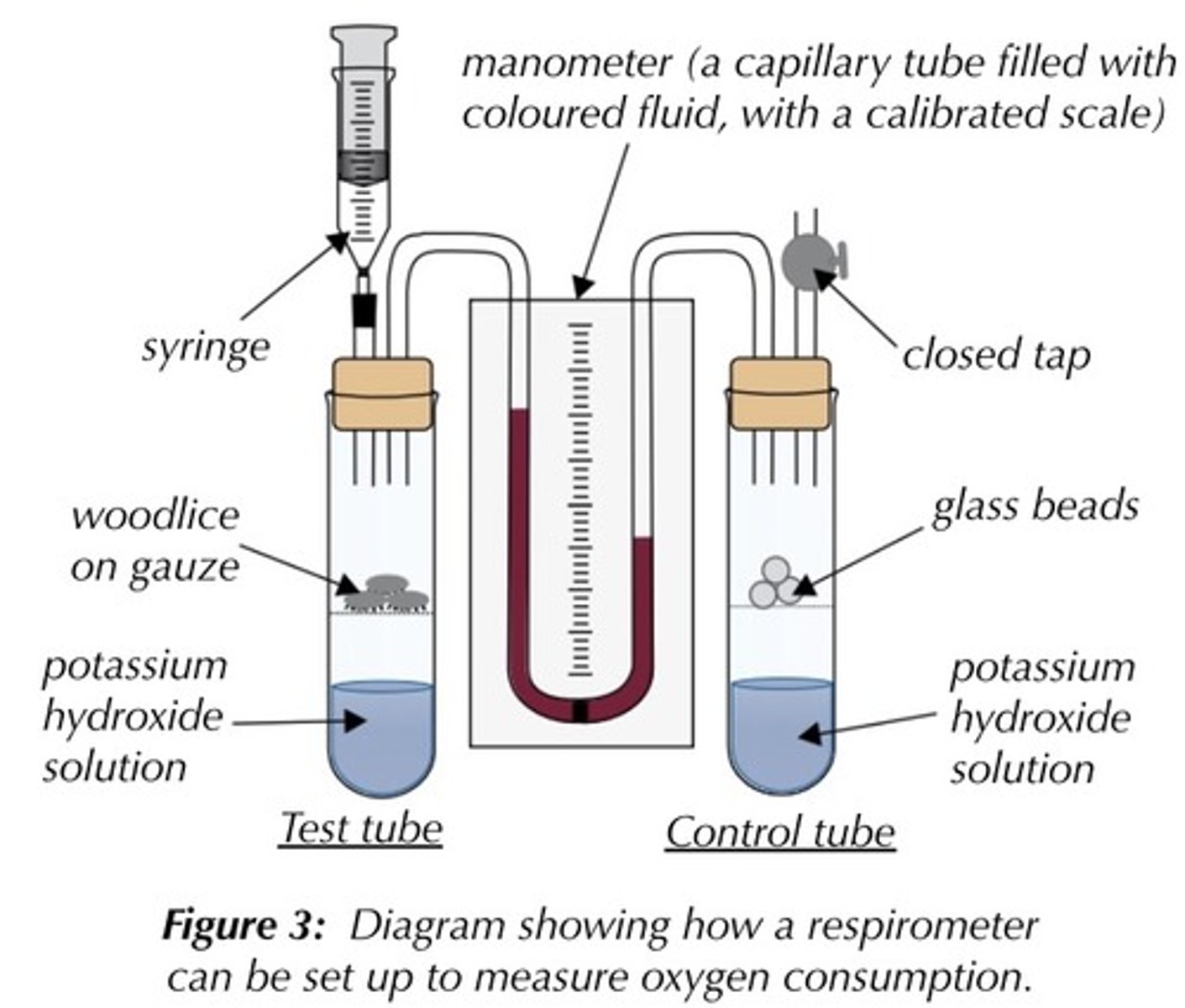
Explain why the respirometer apparatus is left open for 10 minutes.
● Allow apparatus to equilibrate
● Allow for overall pressure expansion/change throughout ● Allow respiration rate of organisms to stabilise
Explain why the apparatus must be airtight.
● Prevent air entering or leaving
● Would change volume and pressure, affecting
movement of liquid
Describe a more accurate way to measure volume of gas.
● Use a gas syringe
Describe how the rate of respiration can be calculated.
1. Calculate volume of O2 / CO2 consumed / released (calculate area of a cylinder)
a. Calculate cross-sectional area of capillary tube using πr²
b. Multiply by distance liquid has moved
2. Divide by mass of organism and time taken
3. Units - unit for volume per unit time per unit mass eg. cm3min -1g -1
Describe how a respirometer can be used to measure the rate of anaerobic respiration
𝐌𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐂𝐎𝟐 𝐫𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞:
● Repeat experiment as above but remove chemical that absorbs CO2
● Make conditions anaerobic
give ways to make conditions anaerobic
- Layer of oil / liquid paraffin above yeast → stop oxygen diffusing in
- Add a chemical that absorbs O2
- Leave for an hour to allow O2 to be respired and used up
Explain why and to where the liquid moves. (anaerobic respiration)
● Yeast anaerobically respire → release CO2
● So volume of gas and pressure in container increase ● So fluid in capillary tube moves down a pressure gradient away from organism
Explain why the apparatus is left for an hour after the culture has reached a constant temperature.
to allow time for all the oxygen to be used up/respired
what are redox indicators? give an example
- a compound that changes colour when they accept electrons to become reduced
- eg. methylene blue, DCPIP
why can redox indicators such as methylene blue be used to measure rate of respiration?
redox indicators will take up hydrogens and get reduced instead of NAD and FAD
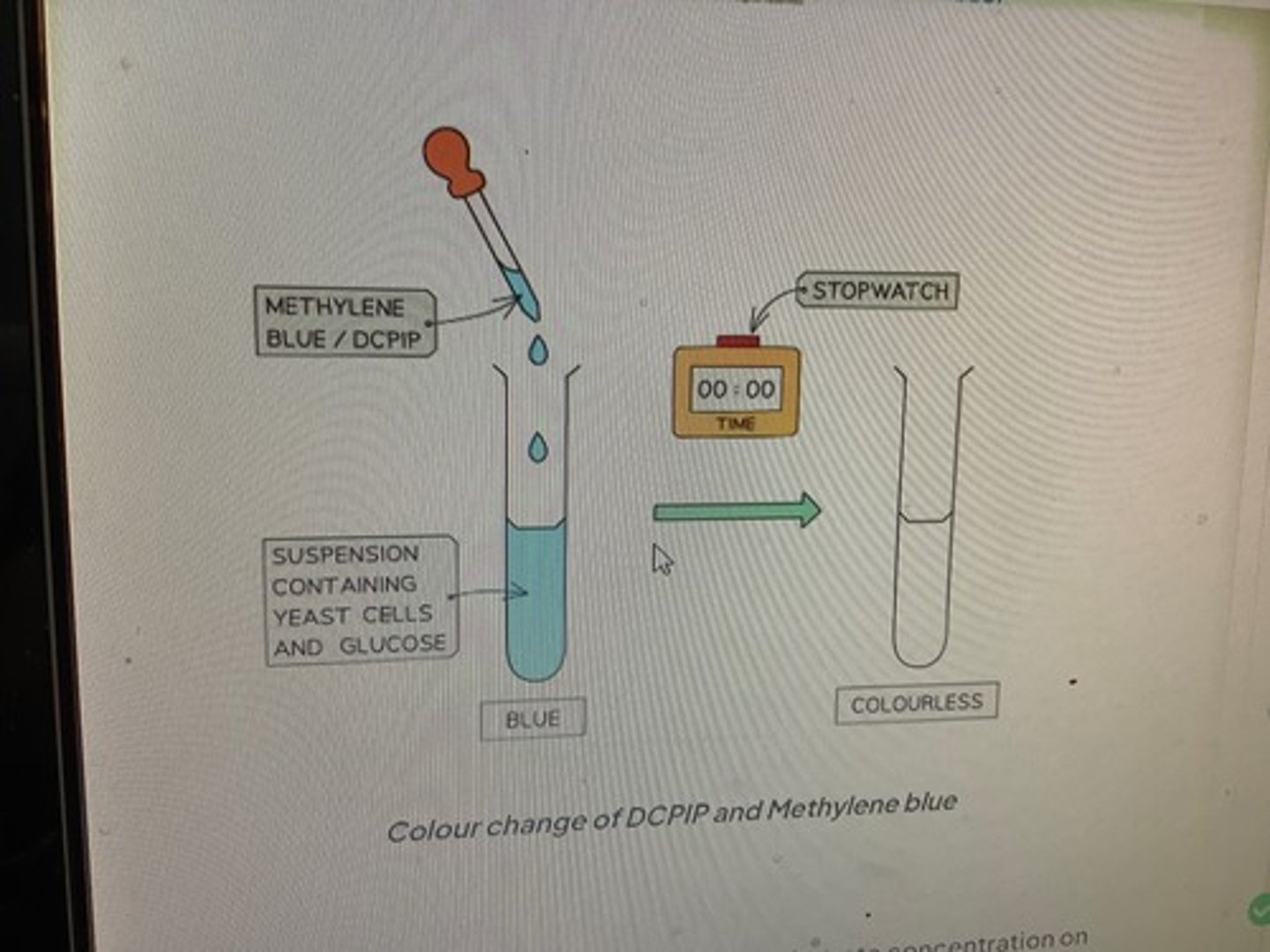
Describe how redox indicator dyes such as Methylene blue can be used to measure rate of respiration
1. Add a set volume of organism eg. yeast and a set volume of respiratory substrate eg. glucose to tubes
2. Add a buffer to keep pH constant
3. Place in water bath at a set temperature and allow to equilibrate for 5 mins
4. Add a set volume of methylene blue, shake for a set time (do not shake again) 5. Record time taken for colour to disappear in tube rate of respiration (s -1 ) = 1 / time (sec)
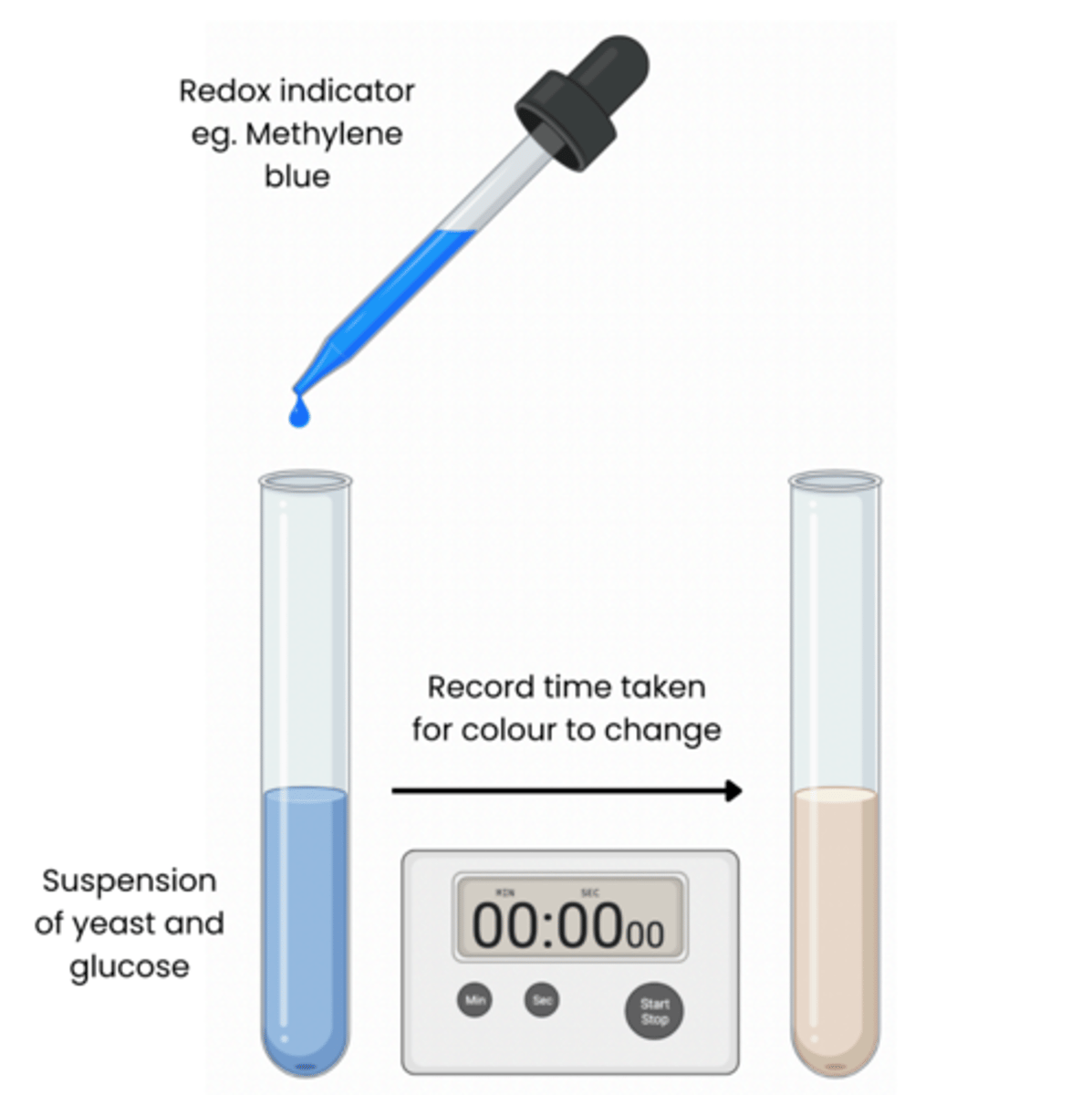

Give examples of variables that could be controlled.
● Volume of single-celled organism
● Volume / conc. / type of respiratory substrate
● Temperature (with a water bath)
● pH (with a buffer)
● Volume of redox indicator (only control)
Why leave tubes in the water bath for 5 minutes?
Allow for solutions to equilibrate and reach the same temperature as the water bath.
Describe a control experiment and why it would be done
● Add methylene blue to boiled / inactive / dead yeast (boiling denatures enzymes)
● All other conditions the same
● To show change in colour is due to respiration in organisms
Explain why you must not shake tubes containing methylene blue.
● Shaking would mix solution with oxygen
● Which would oxidise methylene blue / cause it to lose its electrons
● So methylene blue would turn back to its original blue colour
Suggest one source of error in using methylene blue. Explain how this can be reduced.
● Subjective as to determination of colour change / end point
● Compare results to a colour standard (one that has already changed)
● Or use a colorimeter for quantitative results
