JMU COB 487 Rutherford Exam #1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Strategos
Word comes from "The art of the army general"
3 Models of Strategy
1) Strategy Process Model
2) Emergent Strategy Model
3) 5 P Model
Draw the Strategy Process Model
Mission
Goals and Objectives
SW OT
Corporate Level
Business Level
Functional
Strategy Implementation
Results
Draw Emergent Strategy Model
4 boxes
List 5 P's Model
Plan Ploy Position Pattern Perspective
Vision
"What the organization hopes to become in the future"
Mission Statement
"The reason for an organization's existence"
ex. To inspire and nuture the human spirit-one person,one cup,one neighborhood at a time. - Starbucks
SMART Goals
S-Specific
M- Measurable
A- Aggressive
R- Realistic
T- Time Bound
Balanced Scorecard
An approach to assessing performance in 4 major areas (think "CLIF")
1) Financial
2) Customer
3) Internal Processes
4) Learning & Growth
Stakeholder Approach
The firm is a coalition of interest groups - it seeks to balance their different objetives
Shareholder Approach
The firm exists to maximize the wealth of the shareholders (owners)
PESTEL Analysis
P) Political
E) Economic
S) Social
T) Technological
E) Environmental
L) Legal
2 Things about Macro Environments
1) Firms vary in their ability to detect changes and respond
2) Firms are not passive, firms can cause environments to change for their benefit
Porter's 5 Forces
Threat of
1) New entrants
2) Substitutes
Bargaining Power of
3) Suppliers
4) Buyers
5) Rivalry
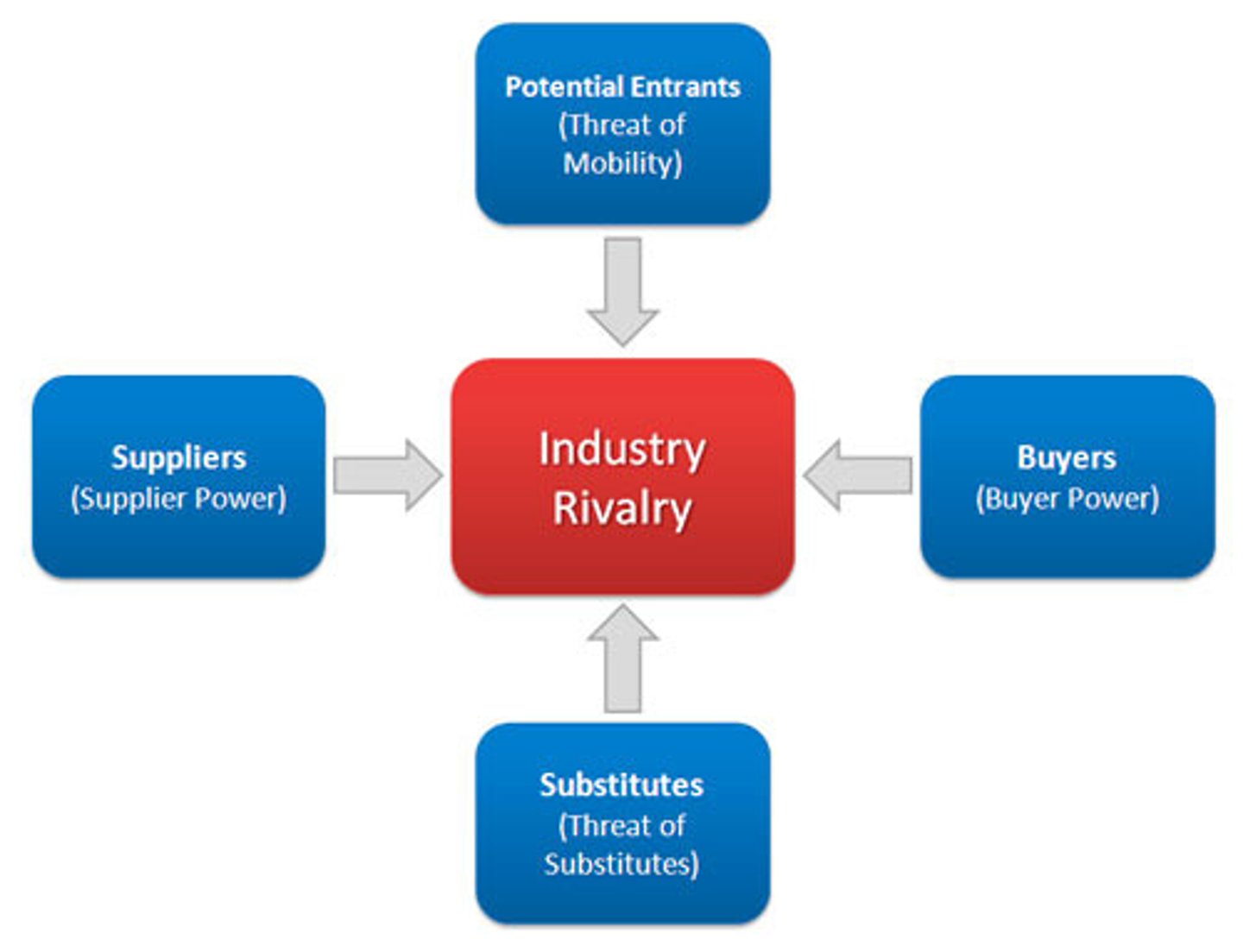
1) Supplier Power
Buyer's Price Sensitivity
Relative Bargaining Power
2) Buyer Power
Buyer's Price Sensitivity
Relative Bargaining Power
3) New Entrants
Economies of Scale
Absolute Cost Advantage
Product Differentiation
Legal/Regulatory
Retaliation
4) Substitute
Buyer's propensity to substitute
Relative prices and value of substitutes
5) Rivalry
Diversity of competitors
Lack of product differentiation
Excess capacity & exit barriers
Slow industry growth
Strategic Group
group of firms in an industry that follow similar or the same strategies
ex. Honda & Toyota
Strategic FIt
Traditional View: Firm Performance is determined by the degree of fit between strategy and external environment
Variation -> Selection -> Retention
Paradox of Fitness (6 Minimal's)
C onsistency
A ffluence
R ationality
F aith
C onsensus
C ontentment
Bottom Line: Firms must stay flexible in order to adapt to changing environments
VRIO Analysis (Internal)
Resource-based-theory (textbook)
V) Valuable
R) Rare
I) Inimitable
O) Organized
Valuable
Resources that help make a firm create strategies that capitalize on opportunities and ward off threats
Rare
Resources that are unique when contrasted with resources of competitors
Inimitable*
Resources that can not be easily duplicated (often protected by legal means...trademark...patent...etc)
Organized
Organization can use/exploit the resource effectively
Sources of Inimitability* (5 things - "NCUPS")
N) Non Substitute - ex. Gatorade and Powerade
C) Casual Ambiguity - ex. Google's Culture
U) Uniqueness - ex. Mona Lisa
P) Path Dependence - ex. historical conditions that happened (Microsoft and the cpu mouse)
S) Socially Complex - ex. company doesn't directly control "brand name...goodwill"
Tangible Resources (ch 4 textbook)
Resources that can be readily seen, touched, and quantified
Intangible Resources (ch 4 textbook)
Resources that are difficult to see, to touch, or to quantify. ex. Skill level of employees, firms reputation, culture, etc.
Capabilities (ch 4 textbook)
What the organization can do based on the resources it possesses.
Dynamic Capability (ch 4 textbook)
A unique ability to create new capabilities by continually updating a firm's array of capabilities to keep pace with external changes in environment
Distinctive Competence (ch 4 textbook)
A set of activities that an organization performs especially well. ex. Apple's unique ability to devise game-changing products/Exceptionally persuasive defense lawyer for a firm
Marketing Mix = 4 P's Marketing (ch 4 textbook)
Product - what is sells to consumer
Price - should be a "good match" with value perceived
Place - physical purchase point or distribution channel
Promotion - communications to market the product
Intellectual Property Types (ch 4 textbook)
Patents - 18 years of protection of imitation ex. pharma
Trademarks - ex. phrases, pictures, names
Copyrights - ex. books, movies, songs
Trade Secrets - formula unknown to competitors
Value Chain (ch 4 textbook)
*Know the picture too (PowerPoint)
Primary Activities
Support Activities
(These all make the end product VALUABLE to consumer along the way)
Primary Activity
An action directly involved in the creation and distribution of goods/services ex. Inbound logistics, sales, operations, etc. (FRONT OFFICE)
Secondary Activities
An action NOT directly involved in the creation and distribution of goods/services ex. firm infrastructure, resource mgmt, accounting (BACK OFFICE)
What do the best Value Chain's focus on? (Ch 4 Textbook)
Focus on adding the most VALUE, does NOT fixate on TIME
2 Business Level Strategies?
1) Low Cost Leadership
2) Differentiation
3 Sources of Differentiation (PLR)
P) Product itself - ex. features, timing, complexity
L) Linkage between firms ex. product mix, alliances, distribution channels
R) Relationship between firm and customer ex. marketing, reputation, customization
3 Sources of Low Cost Leadership (SLI)
S) Economies of Scale
L) Economies of Learning ex. older firm has more efficiency advantages
I) Input Costs ex. lowest input costs win, Walmart
Pros of Low Cost Leader (Ch 5 Textbook)
1) High Profits if High market Share
2) Can withstand price wars b/c of LOWEST COST not LOWEST PRICE
Cons of Low Cost Leader (Ch 5 Textbook)
1) Perception of lower value
2) Large volumes are a must (slim margins )
Pros of Differentiation (Ch 5 Textbook)
1) Buyer Loyalty
2) Strong Margins
Cons of Differentiation (Ch 5 Textbook)
1) Cyclical Business
2) Imitations may steal customers ex. knock off's (watches...etc.)
Best Cost Strategy (Ch 5 Textbook)
An (additional) business level strategy followed by firms that charge relatively low prices AND offer substantial differentiation
Ex. Chipotle/Southwest Airlines
"Stuck in the middle" (Ch 5 Textbook)
Textbook example: Arby's Restaurant
*Wendy's sold Arby's in 2011 to a PE Fund...they thought the firm would perform poorly because it doesn't really lean one way or another (Low Cost/Different)