Electronic Circuits - CMOS - Tier 3
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is the benefit of a low-voltage cascode mirror?
Reduces minimum headroom voltage needed.
Allows operation at lower supply voltages compared to standard cascode.
Achieved by biasing intermediate node closer to source.
What is the effect of noise in CMOS circuits?
Dominant noise sources:
Thermal noise: from channel resistance.
Flicker noise (1/f noise): from traps at oxide-semiconductor interface.
PMOS generally has lower flicker noise than NMOS.
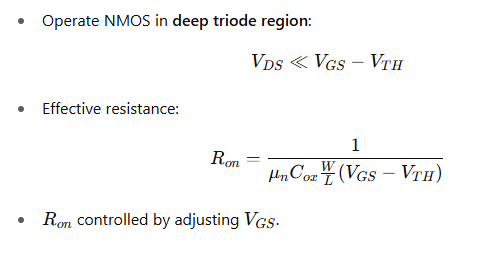
How do you use an NMOS as a tunable resistor?
What are the design trade-offs of using long-channel devices?
Pros:
Higher output resistance ror_oro.
Lower short-channel effects (e.g., better saturation behavior).
Lower drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL).
Cons:
Larger capacitance → reduced speed.
Increased area → higher parasitics.
What is the role of diode-connected loads in high-frequency designs?
Acts as a high-resistance load with minimal area.
Helps maintain small signal gain.
Increases input capacitance slightly due to gate-drain capacitance.
How does CMOS compare with bipolar in gain-bandwidth performance?
Bipolar:
Higher intrinsic g_m per bias current.
Better gain-bandwidth (higher f_T).
CMOS:
Lower power.
Easier integration of digital and analog blocks.
Lower g_m but still sufficient at scaled nodes.