Biology Test 3
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Identify different body sizes that are effects of natural selection
Predator- Big
Prey- Small
Food limitation- Small
Female fecundity- large
Temperature- Large
Temperature in ectotherms- Small
4 types of organic molecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Properties of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides- Simple sugars and glucose
Disaccharides- 2 monomers fused together through dehydration synthesis
Polysaccharides- Multiple Monosaccharides EX Starch
Examples of carbohydrates
Glycogen + Glucose+ Maltose, Starch
Lipids
Largely non polar, hydrophobic
Examples of Lipids
waxes, oils, fats, steroids, phospholipids
Protiens
Composed of long chains of amino acids
Examples Of proteins
Ex Enzymes and Amino acids
Nucleic Acid
Composed of long chains of nucleotides.
Examples of Nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Relationship between monomers and polymers
Monomers are the building blocks of polymers.
Monomers are small molecules, mostly organic, that can join with other similar molecules to form polymers.
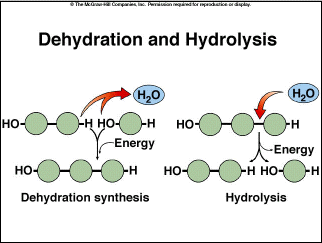
Hydrolysis
Addition of water to break polymer bond
Dehydration synthesis
Release of water, forming bond between monomer, releasing water
Why are cells limited to a small size?
Surface area to volume ratio-
Cell size is limited due to the inability of very large cells to provide nutrients and water and remove wastes in an efficient manner.
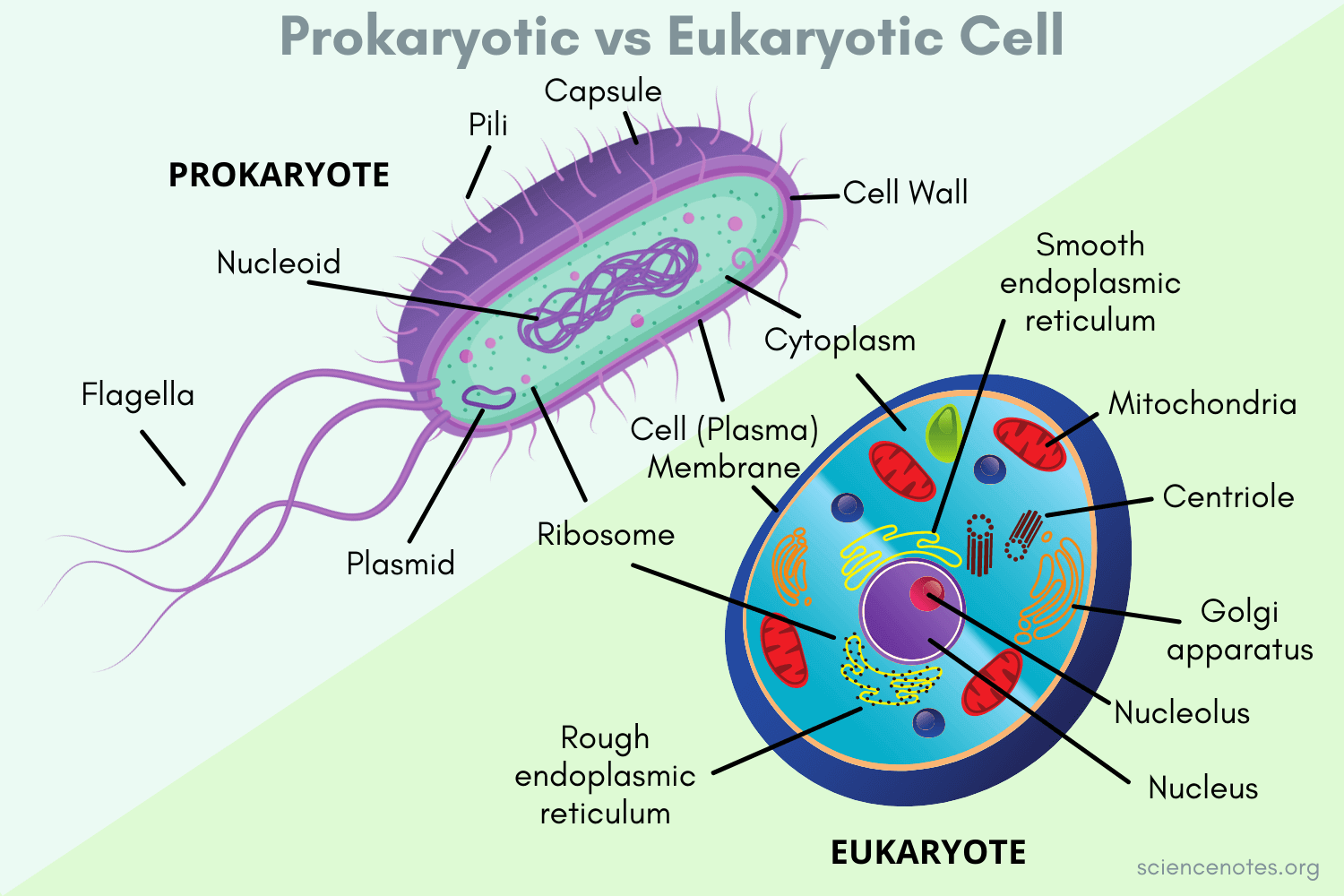
Prokaryote
No membrane bound organelles
Have nucleic structures/ no nucleus
contains DNA
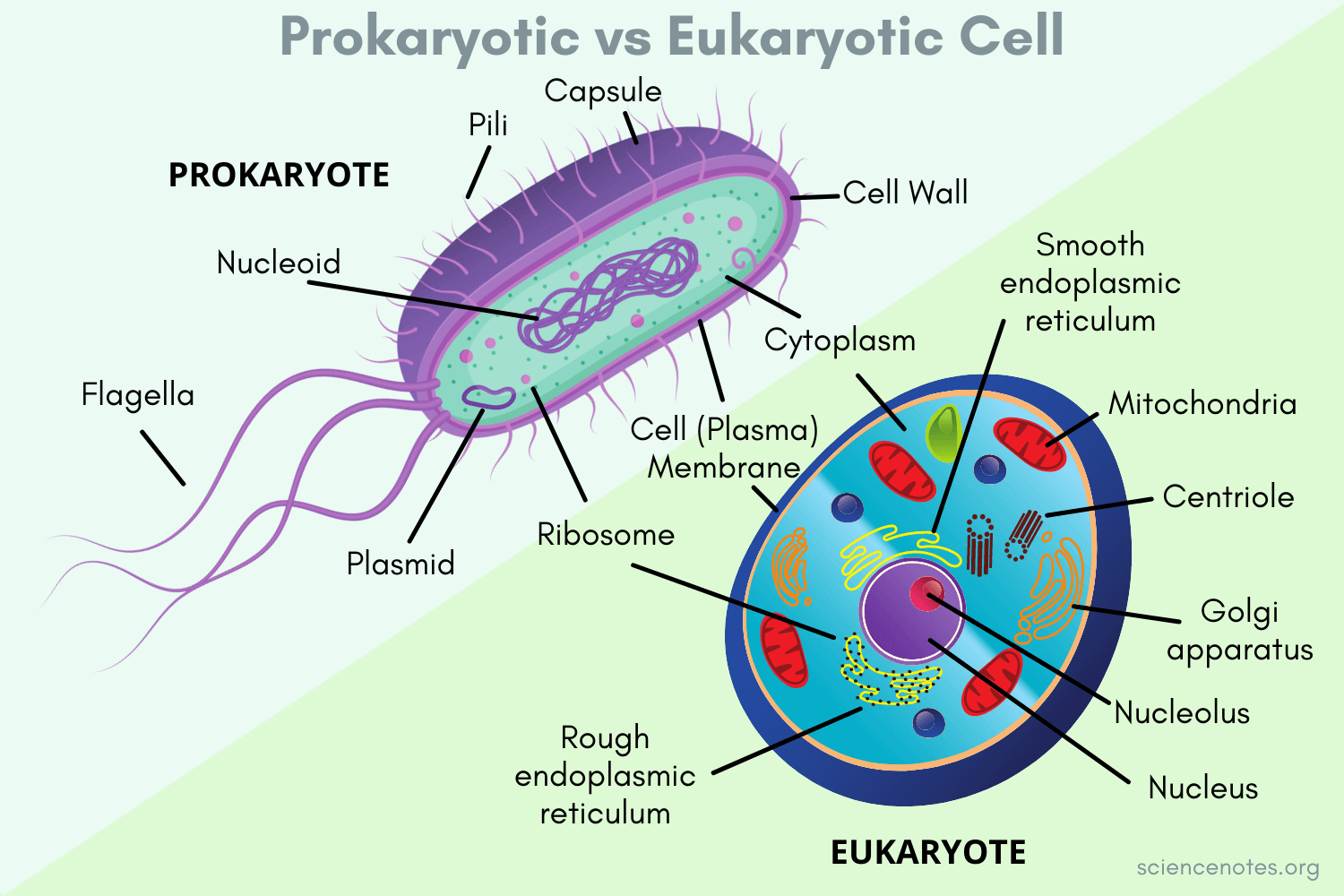
Eukaryotic cells
Contain membrane bound organelles
Contains nucleus
Plant + Animal + Protest cells
Plant cells
Cell wall made of cellulose
large central vacuole
Chloroplasts
Animal cells
Lack Cell walls
Centrosomes
Lysosomes
Cell wall
Made of cellulose
Forms shape of cell
only in plant cell
for protection
Chloroplast
in only plant cells
contains green pigment Chlorophyl
where photosynthesis takes place.
Plasma Membrane
separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment
Golgi Apparatus
packages proteins and sends them off to vesicles
Ribosomes
Involved in protein synthesis
translates RNA into amino acids to form protiens
nucleus
Contains chromosomes
houses genetic information
flagellum
hair like projection used for locomotion in cell
Cytoskeleton
holds organelles in place
Maintains structural integrity of cell
Endoplasmic reticulum
Transport system
lysosome
break down excess and worn out cell parts
vesicle
transport materials within plasma membrane
Vacuole
store nutrients and water on which a cell can rely for its survival
Function of cellular respiration
Produce ATP, used for metabolic self processes
Inputs of cellular respiration
Oxygen and glucose
Outputs of cellular respiration
ATP
Bi Product of cellular respiration
Co2 and H20
Main steps of cellular respiration
Glycolysis
Citrid acid cycle
electron transport chain
Glycolysis
Breakdown of sugar
Pyruvate processing
pyruvate is broken down making NADH and FADH2
Electron transport chain
electrons are supplied by NADH and FADH2
Redox reaction electrons get passed molecule by molecule down chain, move it to lower energy state
Used to pump energy across membrane
produces proton that stores energy
O2 is the final acceptor of electrons forming water, H+ ions reenter mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase
34 ATP produced
Role of protiens in electron transport chain
electrons energy is being used by each protein to pump proteins into inter-membrane space
Role of O2 in cellular respiration
final electron receptor
ATP synthase cannot function without it leading to cell death
Role of proton gradient and ATP synthase
Like charges repeal and when the “Door” opens they all rush through pushing ATP synthase windmill
Trace flow of energy through steps of cellular respiration
Glycolysis, pyruvate, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain
How does fermentation differ from cellular respiration
No electron transport chain
Just perform glycolysis and makes 2 ATP
Outputs of fermentation
Alchohol
lactic acid
Observation of reddish light coming from chlorophyll
When the bright white light hits the chlorophyll, the energy in the photons from the light is absorbed and 'excites' electrons in the chlorophyll to a higher energy state. However, the electron then quickly drops back down to ground state, releasing the energy as light, usually of a longer wavelength, otherwise known as fluorescence.
why does chlorophyll in leaf behave differently then isolated chlorophyll
Energy from leaf chlorophyll is being used
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis similar
Both produce ATP
Both produce some form of energy
both use electron transport chain
How are cellular respiration and Photosynthesis different
Inputs and outputs
where it takes place
citric acid cycle vs calvin cycle
Inner relation between cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Output of photosynthesis is the input of cellular respiration
They need each other to function
Trace flow of energy as they would occur in plant cell
Sunlight, glucose, ATP
explain general mechanism of how enzymes function
Sustrate enters activation site
substates react with each other
bonded substates leave enzyme, enzyme is ready to be used again
What determines specificity of enzymes for reactions they catalyze
Shape of enzyme activation site
recall mechanism of ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and PI
Hydrogen atoms turn rutor pushing ADP and PI together
Recall general function that gradient serves in cell
Do biological work
Energy storage
produce most of cells ATP
How do gradients function in cell using example of ATP synthase
Like charges repel pushing ADP and PI together
examples of how gradients in cells are used to work
Diffusion
ATP synthase