IB Biology HL- Nucleic acids
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Nucleic acids
large molecules contained in the nucleus of cells
2 types of nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
DNA
the genetic material of all living organisms
Viruses use _______ as their genetic material, but they are not considered ___________.
RNA; living
Role of Nucleic acids
Storage and transfer of genetic information to make proteins
Nucleic Acid components(CHOPN)
C- Carbon
H- Hydrogen
O- Oxygen
P- Phosphorous
N- Nitrogen
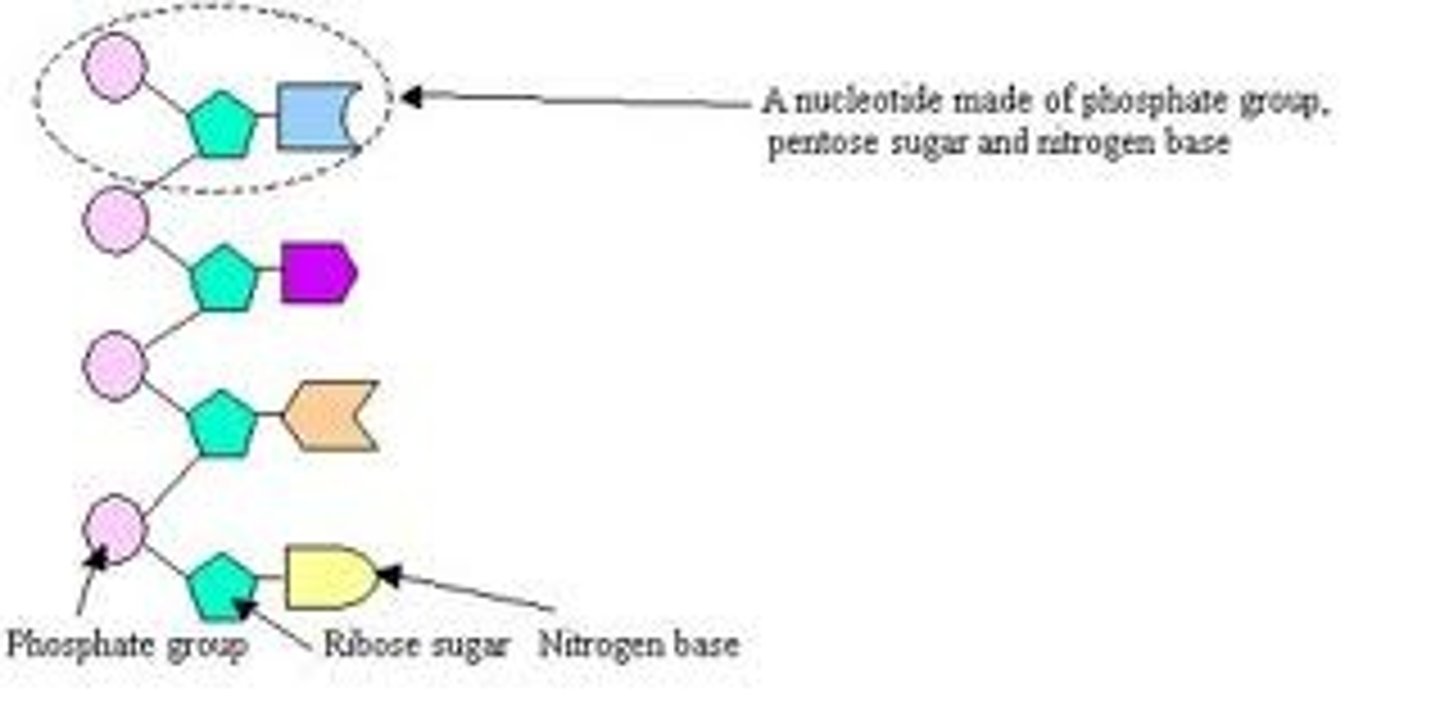
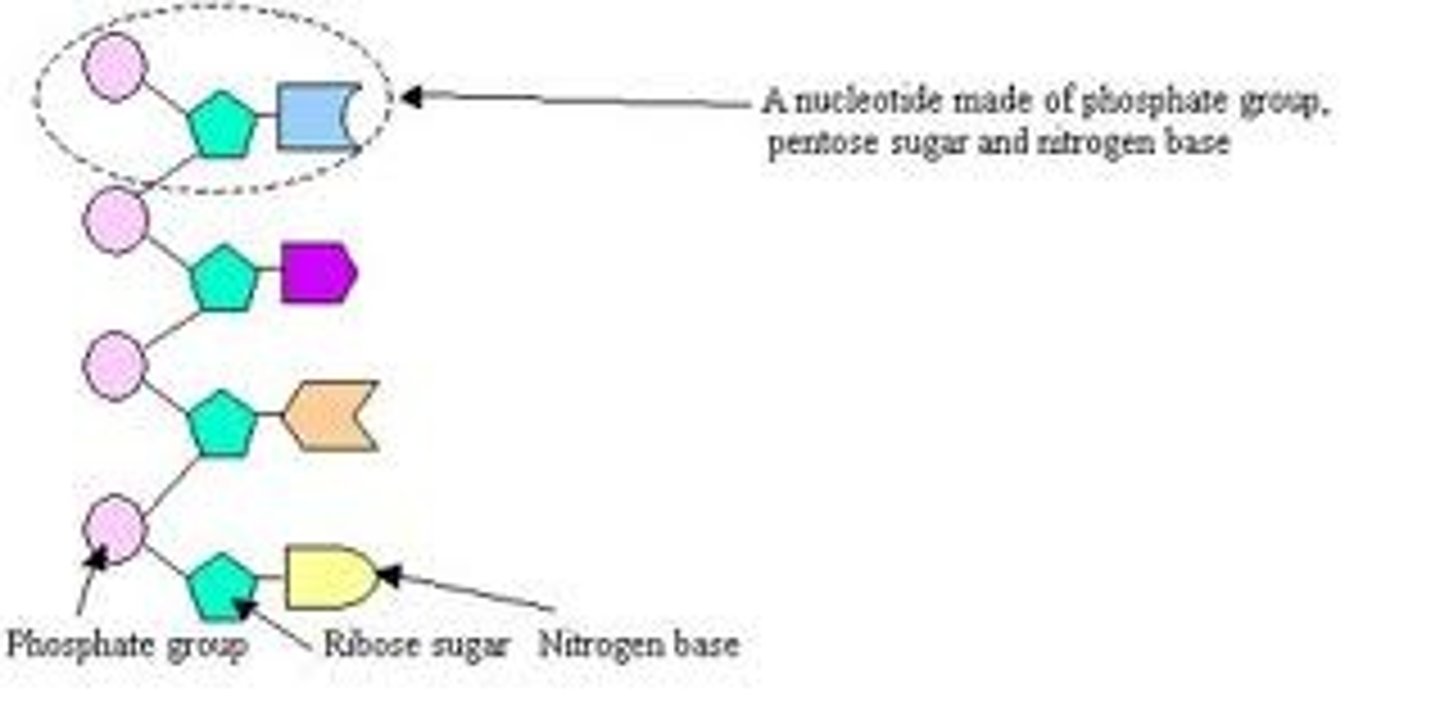
Component of nucleotides
Phosphate group(circle) - Pentose sugar(pentagon)- Nitrogenous base(rectangle)
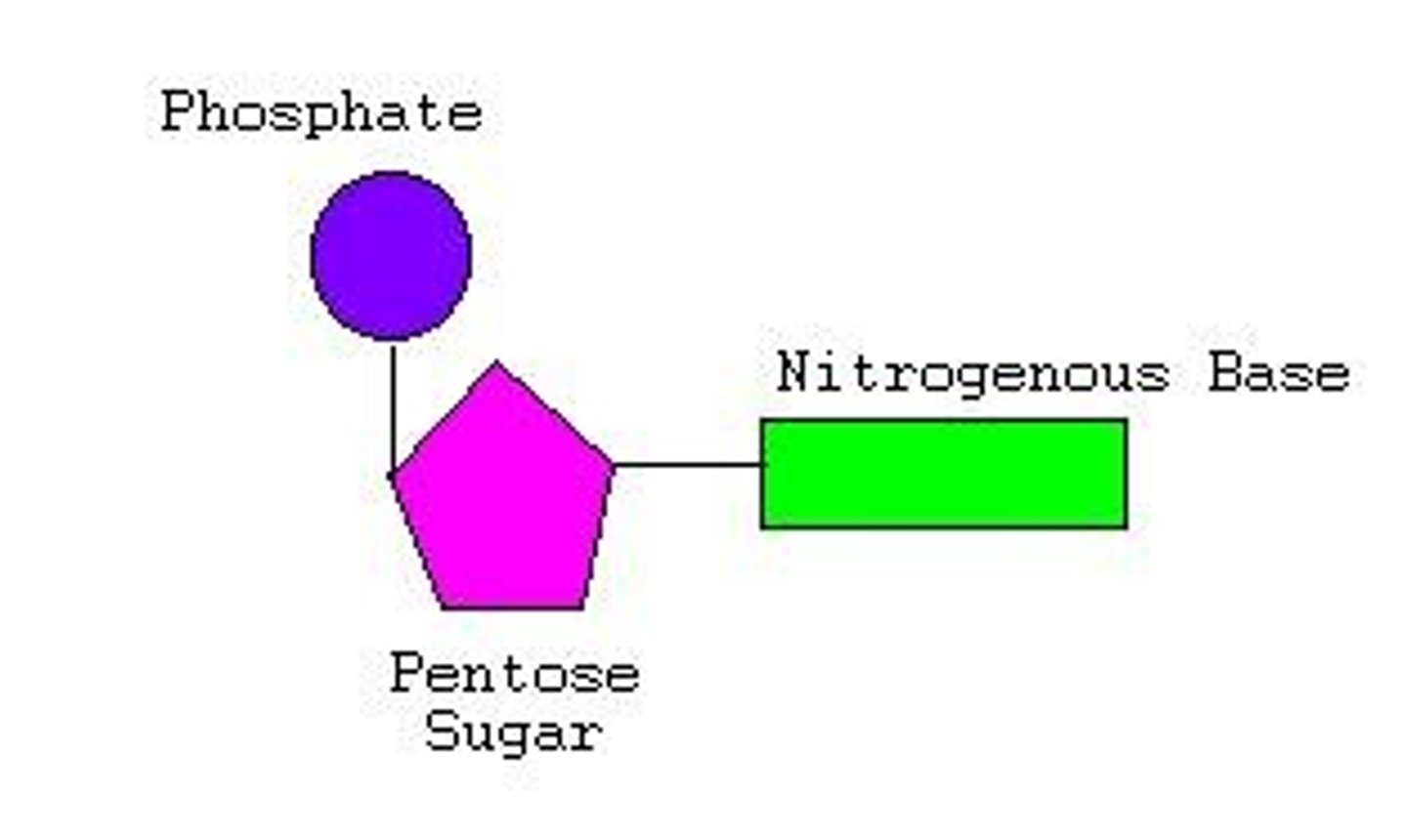
Nucleotides
Monomers of nucleic acids, form the basis of DNA and RNA
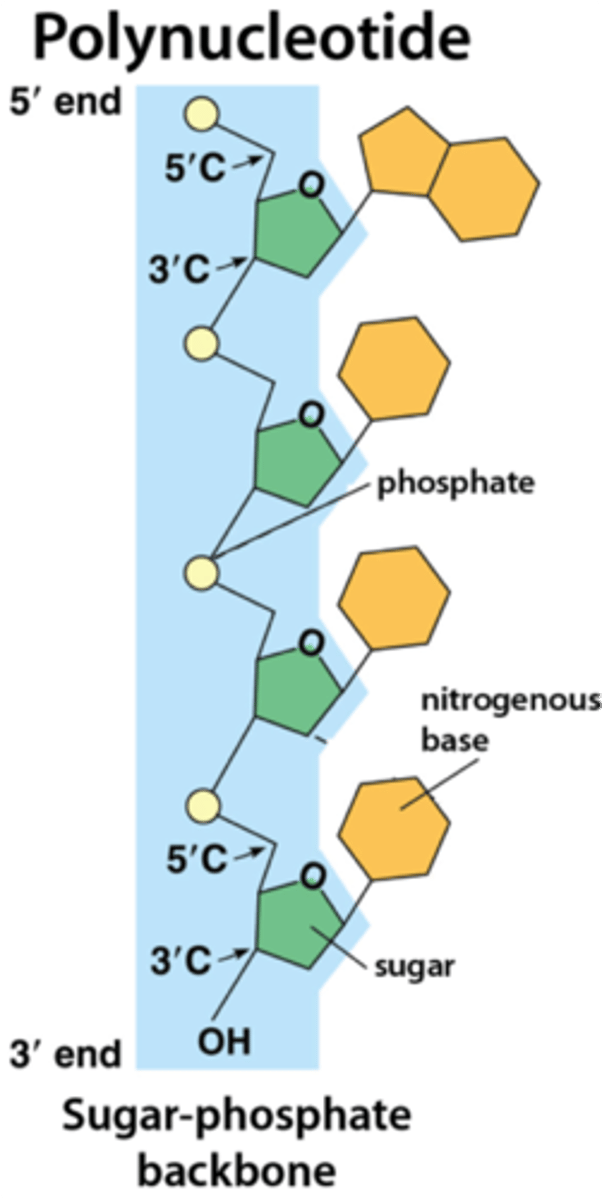
Sugar-phosphate bonding as back bone
Makes a continuous chain of covalently bonded atoms in each strand of nucleotide, forms a strong "backbone"
Nitrogenous bases
A- Adenine
T- Thymine
C- Cytosine
G- Guanine
RNA
A long polynucleotide strand formed by condensation of nucleotide monomers
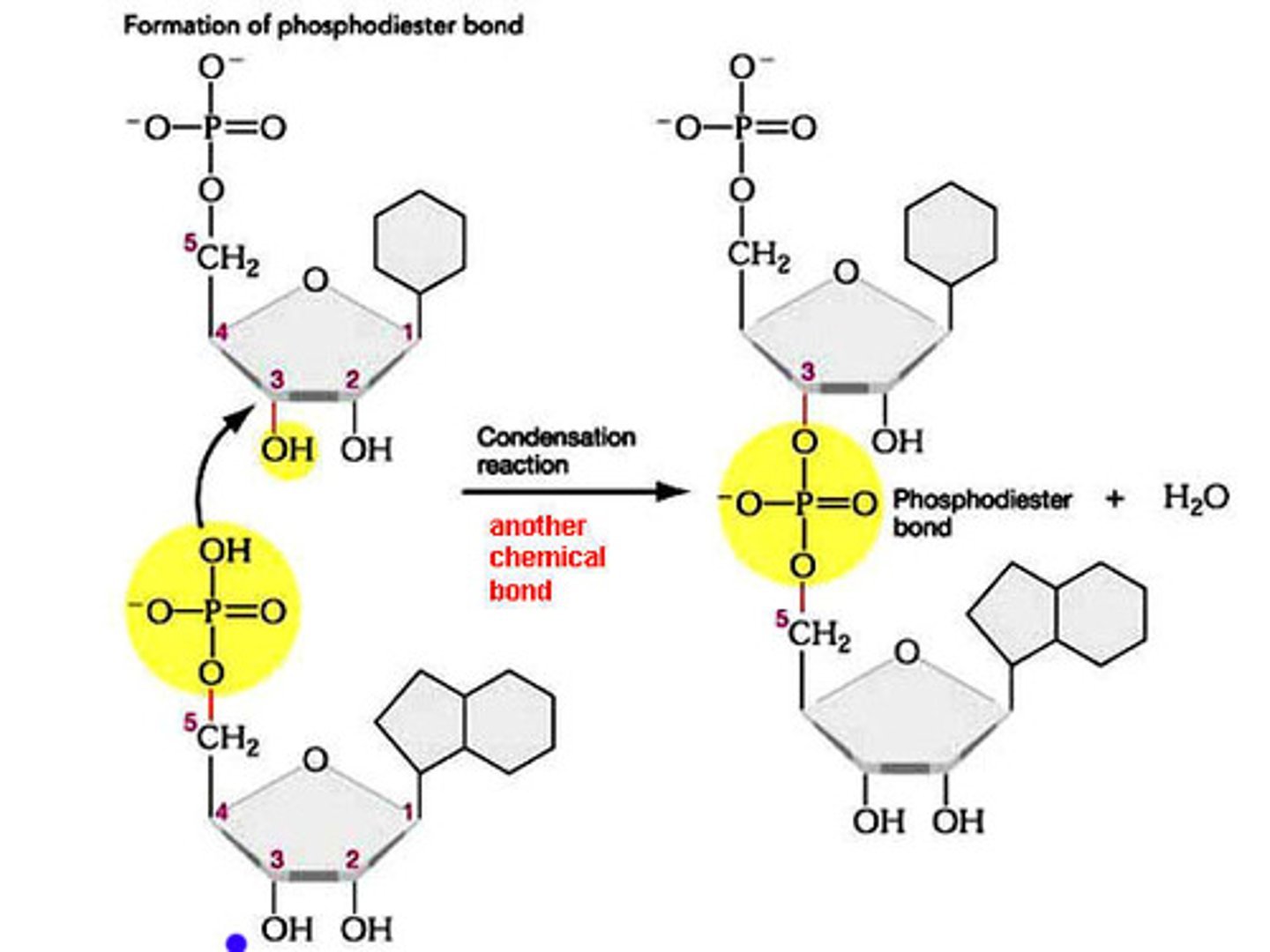
Condensation reaction in RNA
Forms a Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester bond
Linkage of the 5' phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3' hydroxyl (OH) group of the adjacent nucleotide's pentose sugar molecule
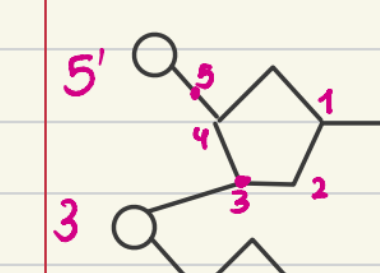
5' to 3' linkage in replication and transcription
The only direction that polymerase can synthesize DNA/RNA
it does so by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a DNA strand.
Structure of single nucleotides
5' to 3' linkage role
Ensures the accuracy of the order of DNA/RNA/amino acids to form protein
5' to 3' linkage in translation
Ribosomes read the mRNA and synthesize the polypeptide chain in a 5' to 3' direction
Structure of RNA polymers
DNA structure
- Double helix
- Two antiparallel strands of nucleotides
- Linked by hydrogen bond between complementary base pair
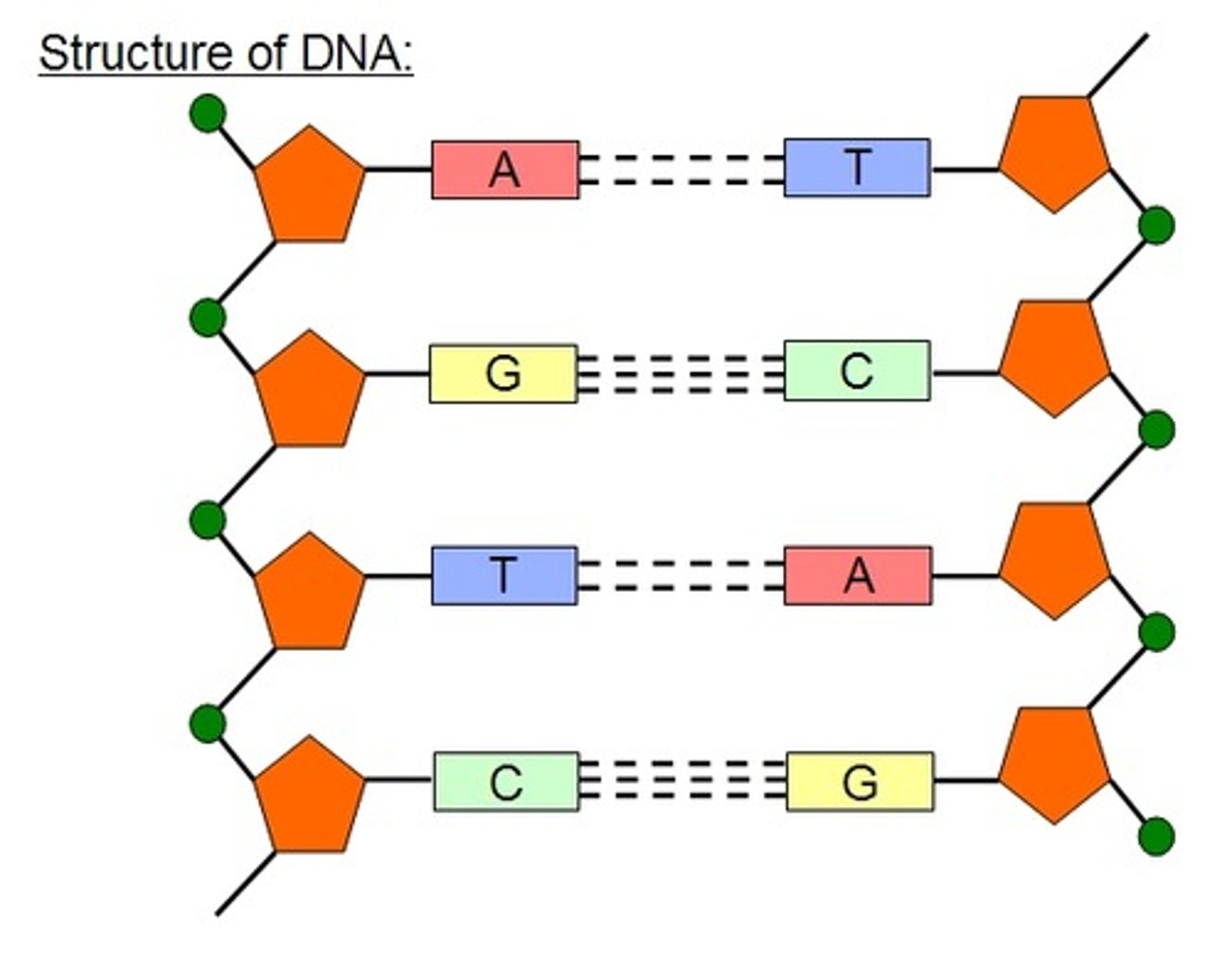
Complementary base pairing
A-T(DNA)/U(RNA), C-G
A and G
Purine
U, T and C
Pyrimidine
Purine Pyrimidine bonding
- same lengths for AT and CG➡️same three-dimensional structure➡️maintain the stable, twisted structure of DNA double helix
Differences between DNA and RNA
1. Strands: RNA 1, DNA 2
2. Bases: RNA U, DNA T
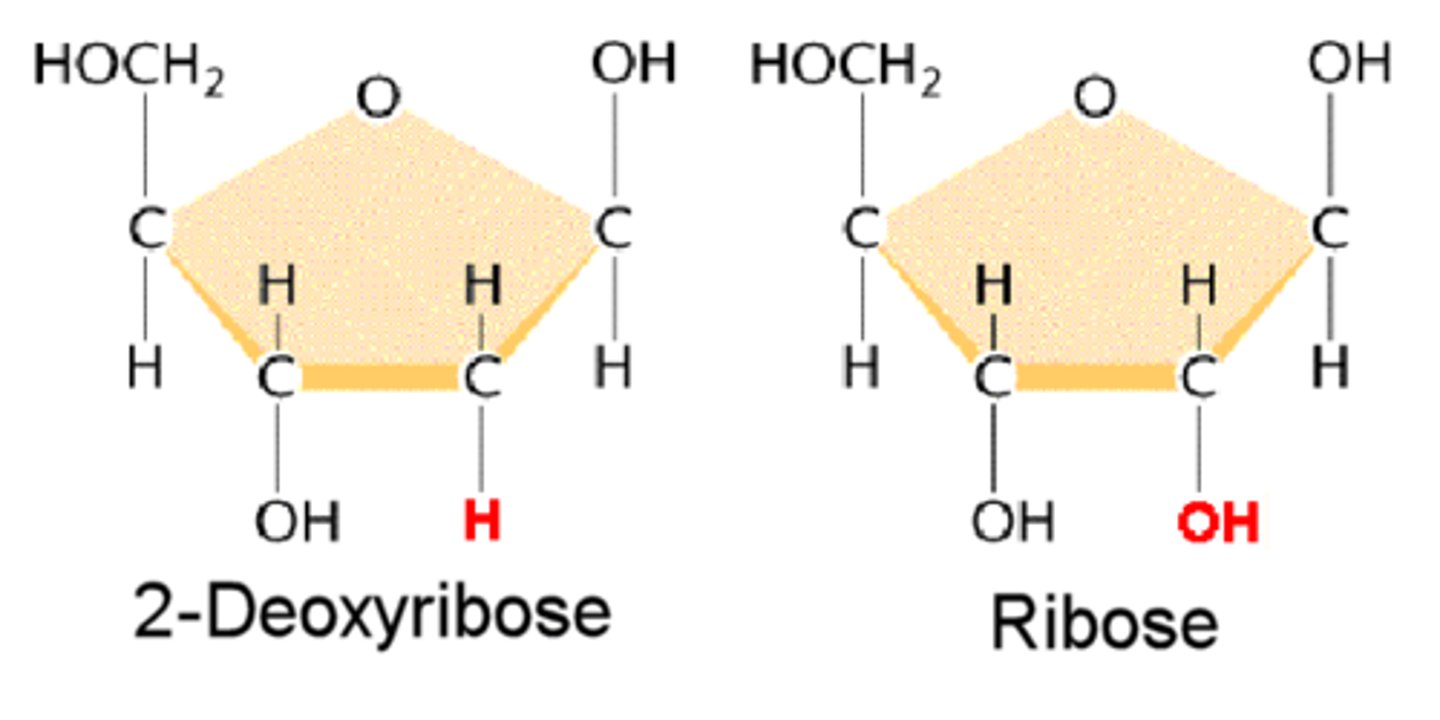
3. Pentose sugar: RNA ribose, DNA deoxyribose
Difference between ribose and deoxyribose
ribose has a 2'-OH group and deoxyribose has a 2'-H
Role of complementary base pairing
- accurate DNA replication, Transcription, Translation
Complementary base pairing is based on _____________________________.
Hydrogen bonding
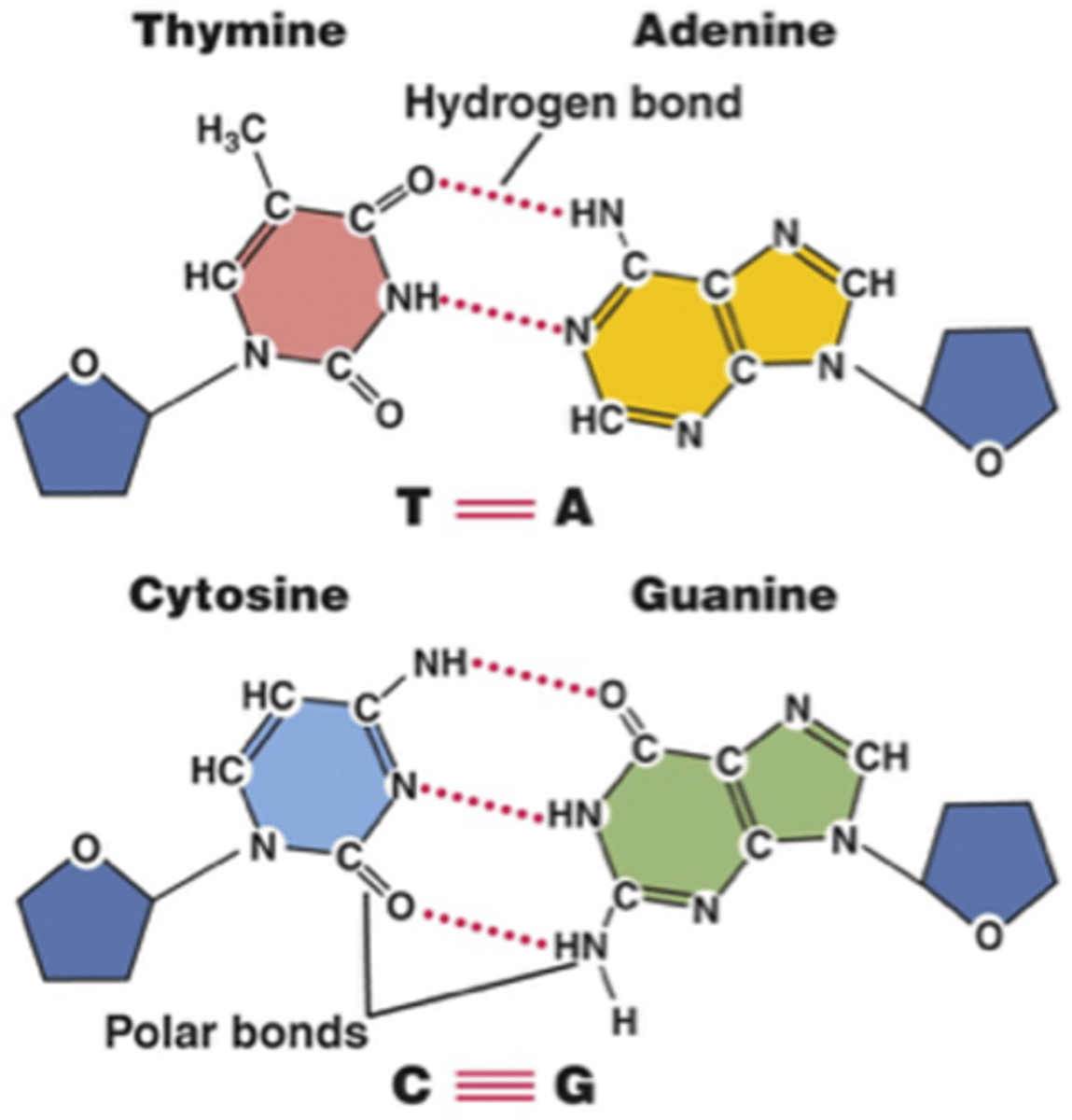
Any vertical sequence of nitrogenous bases is possible
Phosphodiester bond will form any way as long as phosphate group and pentose sugar present
DNA can be any length
increasing the number of possibilities of base sequences, enormous capacity in a limited amount of space
Possibilities of potential base sequences with n bases
4^n
Structure of a nucleosome
Core DNA wrapped around histone octamer
Held together an additional H1 histone protein attached to the linker DNA
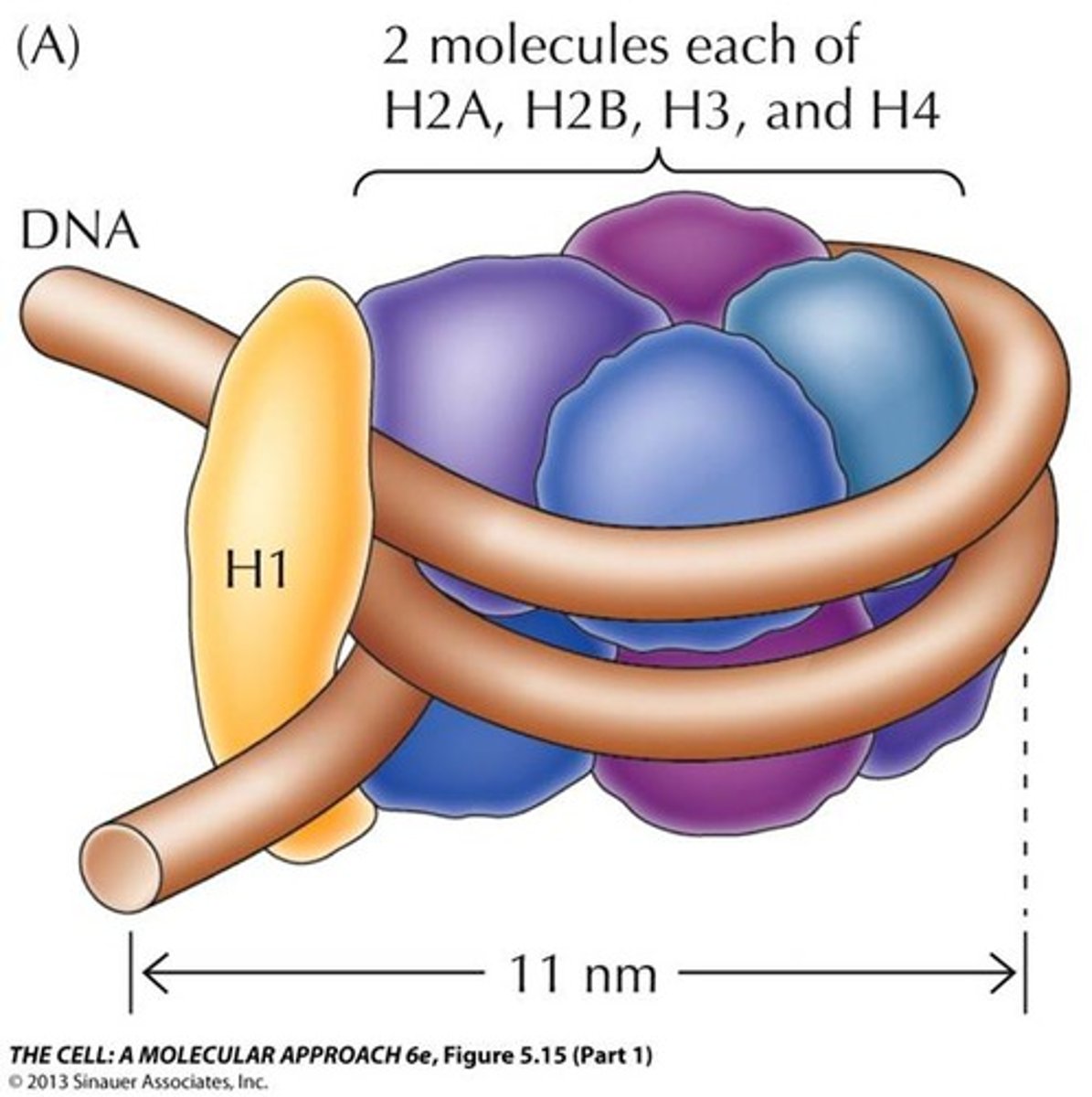
Nucleosomes allow DNA to ____________.
Supercoil
Hershey-Chase experiment conclusion
DNA is the genetic material, instead of protein
Hershey-Chase experiment design
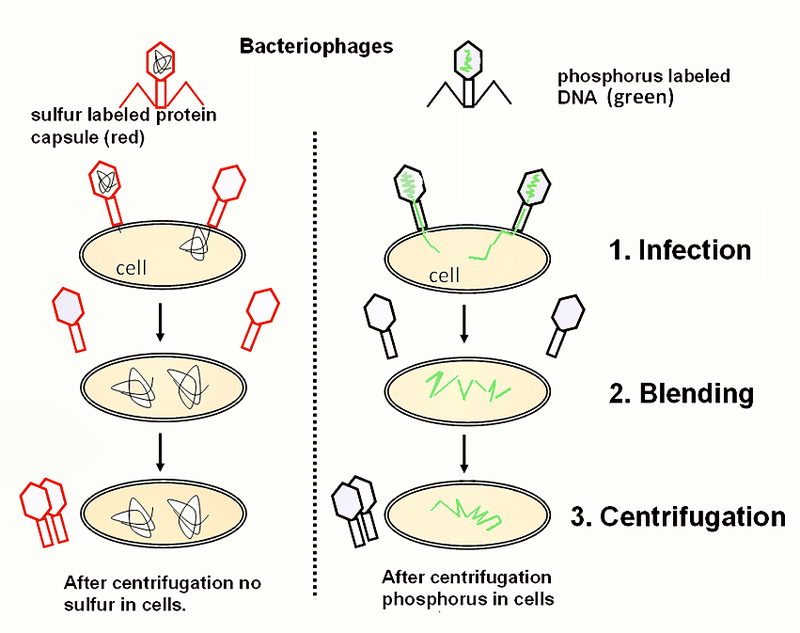
Used bacteriohages(virus) that infect bacterial cell by injecting genetic information for bacterial ribosomes to build new phages causing burst of the cell, thus further infect other bacterial cells
1. Add phages to grow in E.Coli radioactive medium (S35 phage coat labelled, P32 phage DNA labelled)
2. Put radioactive T2 phages with bacteria for infection and the injection of genetic material
3. Centrifugation to separate "ghost" phage(protein) from bacterial cell
Hershey-Chase experiment result
Radioactivity in supernatant for S35(phage coat), Radioactivity in pellet for P32(bacteria), supporting the conclusion that protein is not not the genetic material ,DNA is
Hershey-Chase experiment NOS: technological developments
Radioisotopes were made available to scientists as research tools, their experiment became possible.
Chargaff's data conclusion
- The amounts of the nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, and G) were not found in equal quantities.
- Instead amount of A = amount of T, amount of C = amount of G
Chargaff's data design
DNA was extracted from the given species, hydrolyzed to break apart the nucleotides, and then analyzed chemically.
Chargaff's data NOS: certainty of falsification
Chargaff's data falsified the tetranucleotide hypothesis that there was a repeating sequence of the four bases in DNA.