HLS histology 1 : Bone marrow and hematopoiesis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Definition of bone marrow
specialized vascular connective tissue rich in cells that are responsible for formation of blood cells.
Sites of hematopoiesis <fill the numbers>
- at very early embryo ...<1>...
- Newborn ...<2>...
- at childhood bones , axial skeleton have ...<3>... marrow and appendicular skeleton have ...<4>... marrow
- adults bones , the axial skeleton have ...<5>... marrow and appendicular skeleton have ...<6>... marrow
<1> Yolk sac
<2> liver , Spleen
<3> Red marrow <active>
<4> Red marrow
<5> Red marrow
<6> Yellow marrow
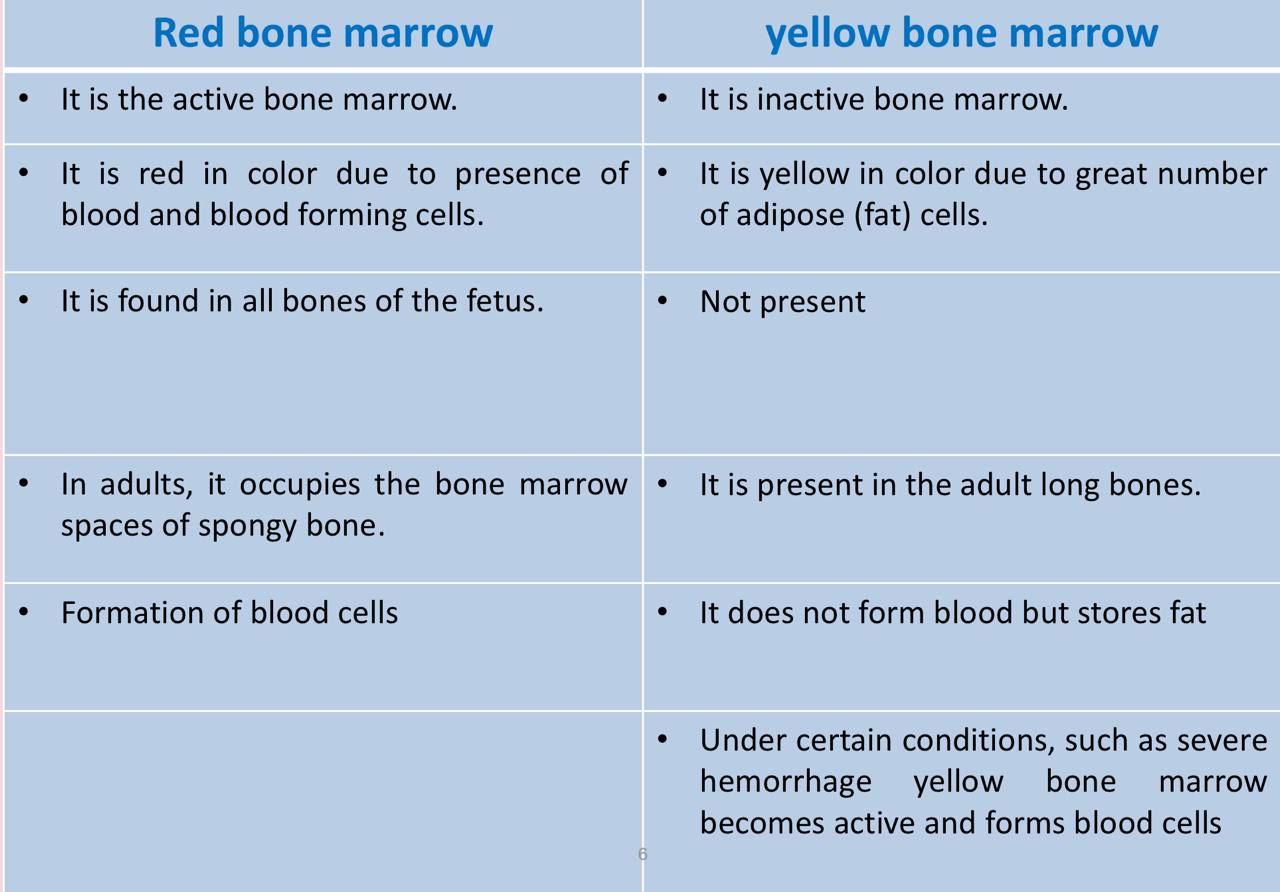
The bone marrow have 2 Types , Red and yellow bone marrow , compare between them according to:
1- which type is the active one
2- Reasons of red and yellow color
3- which type is present in Fetus bones
4- where both types present in adult bones
5- which type can form blood cells
The network of the red bone marrow stroma is formed from….
Reticular fibers + reticular cells.
<T/F>
The matrix of the red bone marrow stroma have collagen Type 1 and collagen type 5
False
collagen type 1 and collagen type 3
<T/F>
Sinusoidal capillaries is a wide, very thin walled lined with a single layer of fenestrated endothelial cells with discontinuous basement membrane through which trans endothelial migration of newly formed blood cells occurred.
True
the function of hematopoietic cords of red bone marrow is?
Developing blood cells
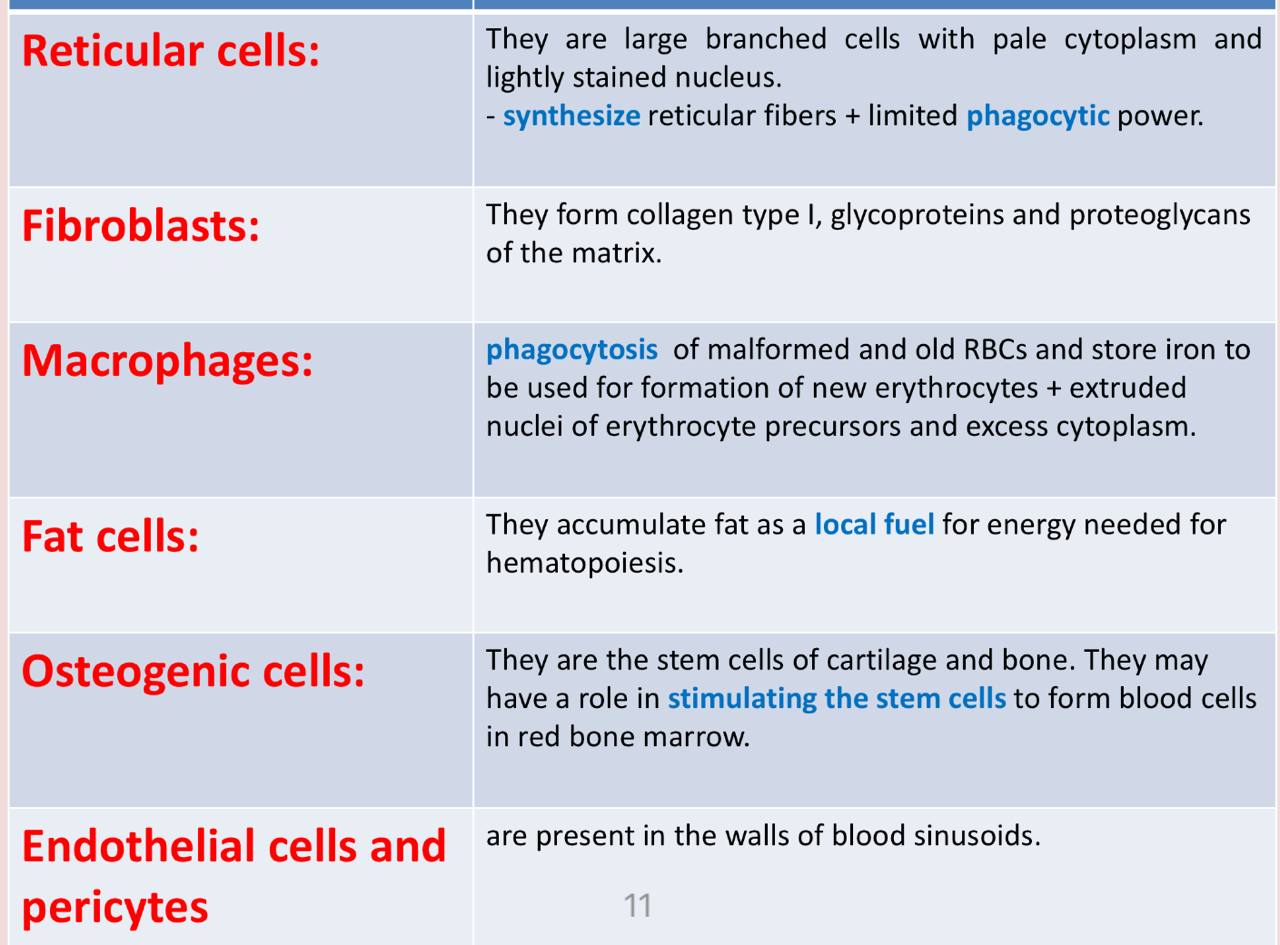
Function of fat cells at the bone marrow
They accumulate fat as a local fuel for energy needed for hematopoiesis.
Function of fibroblasts at the bone marrow
They form collagen type I, glycoproteins and proteoglycans of the matrix
Function of reticular cells at the bone marrow <2 functions>
1-Synthesize reticular fibers
2-limited phagocytic power
N.B : they are active cells so they are large branched cells with pale cytoplasm and lightly stained nucleus
Function of macrophages at the bone marrow <2 functions>
1-phagocytosis of malformed and old RBCs and store iron to be used for formation of new erythrocytes +
2-extruded nuclei of erythrocyte precursors and excess cytoplasm.
Function of osteogenic cells at the bone marrow
Stimulating the stem cells to form blood cells in red bone marrow.
N.B : They are the stem cells of cartilage and bone
to memorize
<T/F>
Pluripotential stem cells Produce all types of blood cells and its 0.1% of bone marrow cells.
True
<T/F> about multipotential stem cells
1- Lymphoid will be developed into lymphocytes.
2- Myeloid will be developed into myeloid cells <erythrocytes, granulocytes, monocytes & megakaryocytes>
True
…… Form colonies of blood cells.
Progenitor cells <CFU>
<T/F>
Both Precursor cells and Progenitor cells have the ability to self renewing
False
the Precursor cells cant
<T/F>
Both Precursor cells and Progenitor cells have high mitotic activity
True
N.B : They are common in bone marrow and lymphoid organs.
<T/F>
Precursor cells are unipotential cells and Progenitor cells unipotential or bipotential stem cells.
True
<T/F>
mature cells have no mitotic activity
True
N.B: They are common in bone marrow and hematopoietic organs
……cells used in cell therapy due to their ability to quickly expand in culture conditions while retaining their multilineage potential
Mesenchymal stem cells or marrow stromal cells
N.B : they are multipotent stem cells
<T/F>
Only mature blood cells contain the membrane proteins, such as aquaporin and glycophorin, that are required to attach to and pass the blood vessel endothelium can cross bone marrow barrier
True