Antimicrobial Resistance
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
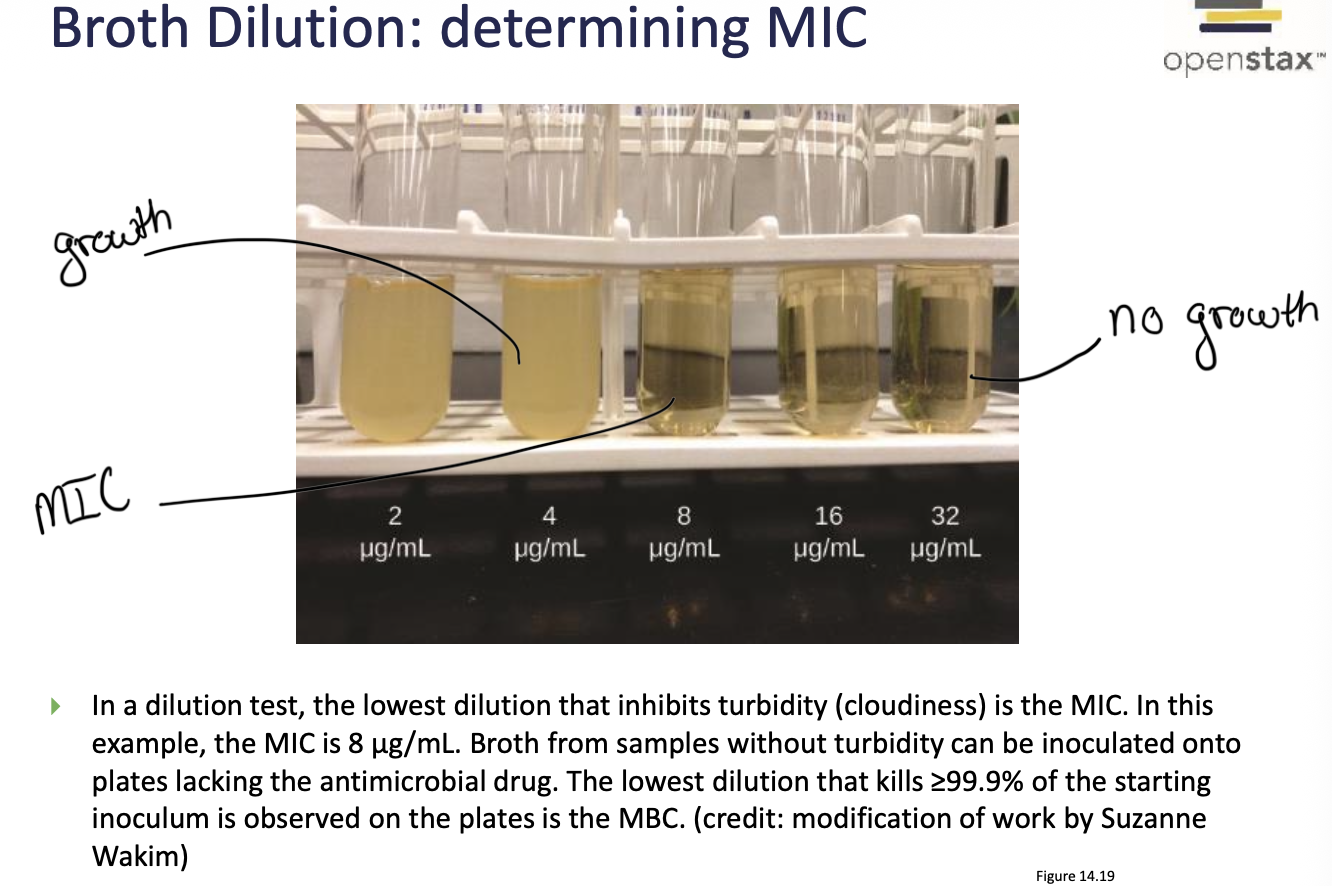
What is MIC (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration)
The lowest concentration of a antibiotic that inhibits visible growth
What does the Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Test
measures the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It’s a qualitative test where the zone of inhibition around each antibiotic disk indicates whether the bacterium is susceptible, intermediate, or resistant to that antibiotic.
Broth dilutions
These test specific concentrations of drugs allowing for the determination of MIC
What is an e-test
combines diffusion and dilution. It provides the MIC on a strip
Soon after a new drug is introduced why do we see resistance in bacteria?
This is because of natural selection. The bacteria that have resistance survive and reproduce. This could not be prevented; however, it has been accelerated due to the overuse of medications.
What two factors cause Antimicrobial resistance
Intrinsic factors - such as cell wall composition, which are naturally occurring resistance based on biological structures.
Acquired - caused by mutations and horizontal gene transfer, these convert it from sensitive to resistant
Drug-tolerant bacteria (persisters)
They lack the mechanisms for antibiotic resistance. They are generally unaffected by the presence of antibiotics.
Ex:
Biofilms - antibiotics cannot effectively penetrate
Growing too slowly to be inhibited
What are some examples of microbes that have intrinsic resistance? How is this performed
Mycoplasma pneumoniae - lacks a cell wall (resistant to drugs that target cell walls)
Clostridium difficile - forms endospores
Gram negative bacteria - Outer membrane is impermeable to many compounds, resistant to daptomycin and vancomycin
What are the steps in horizontal gene transfer?
Conjugation (plasmid exchange)
Transformation (DNA uptake)
Transduction (bacteriophage transfer)
What are humans doing to contribute to the spread of resistance?
We are overusing and misusing antibiotics. Also, incomplete treatment (when the patient does not finish their dose) and agricultural use in animal feed
What are mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
Enzymatic drug inactivation
altered target sites
minimize drug concentration in cell
Growth patterns
What are the enzymatic inactivation processes
Enzymatic inactivation refers to when bacteria produce enzymes that chemically destroy or modify antibiotics, rendering them ineffective.
Examples:
Bacteria can produce B-lactamase enzymes that breakdown the b-lactam ring, once the ring is broken the antibiotic can no longer bind
Acetylation of drugs - such as the enzyme Chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT)
What is a B-lactamase inhibitor
a drug that can treat bacteria that produced b-lactmases
How does altering a target promote resistance
If the target is altered then that drug will no longer interact with its target and the drug has no effect
Ex:
B-lactam drugs targeting transpeptidase (crosslinks PG strands)
Vancomycin binds the terminal aa of pentapeptide
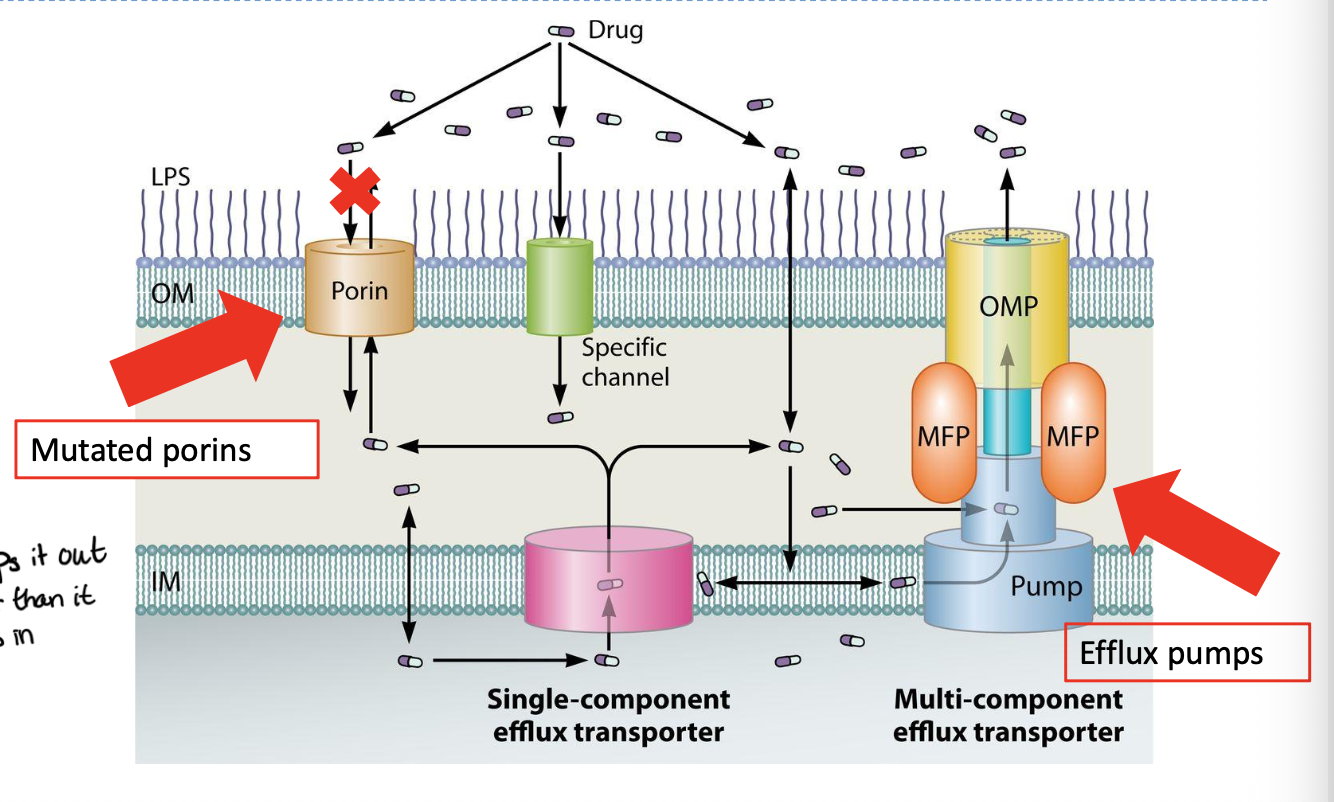
How is drug concentration in the cell minimized
mutations can alter the tranproter/porins which are structures that can limit drug entry
Pumping drugs through efflux pumps whic tend to remove diverse classes of drugs and contribute to multidrug resistance
What are the different ways that biofilms promote resistance
Slows diffusion of drug thru biofilm due to extracellular matrix
Diverse microenvrionments
Persister cells that exist in a dormant state and do not divide
What are ways we can combate resistance?
Antimicrobial stewardship - use narrow-spectrum agent when possible, and avoid unnecessary prescriptions
Combination therapy
Infection prevention - vaccination, hygiene, isolation
Bacteriophage therapy