Chapter 2: Cell Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:12 AM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
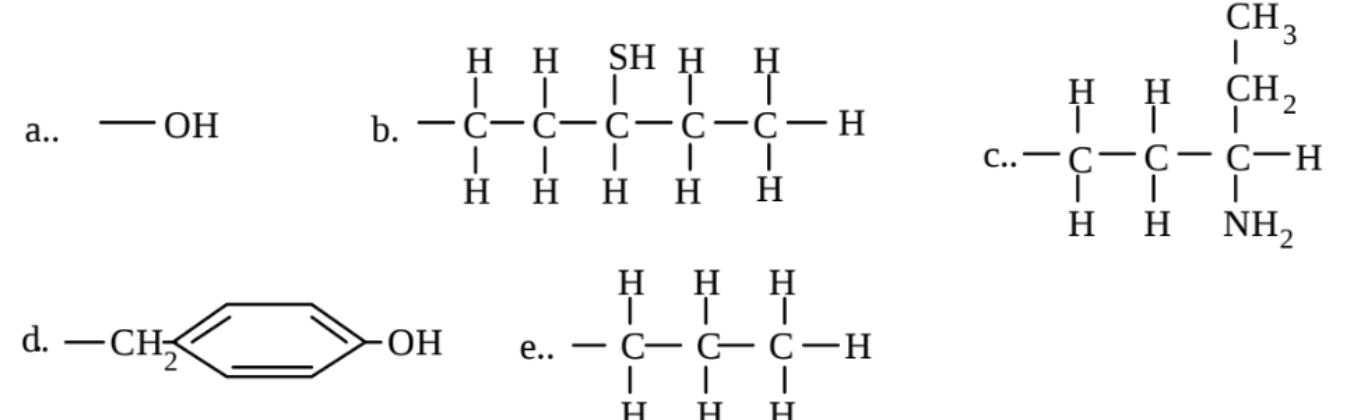
Which of the groups below is capable of only hydrophobic interactions?
\
\
C-C-C
2
New cards
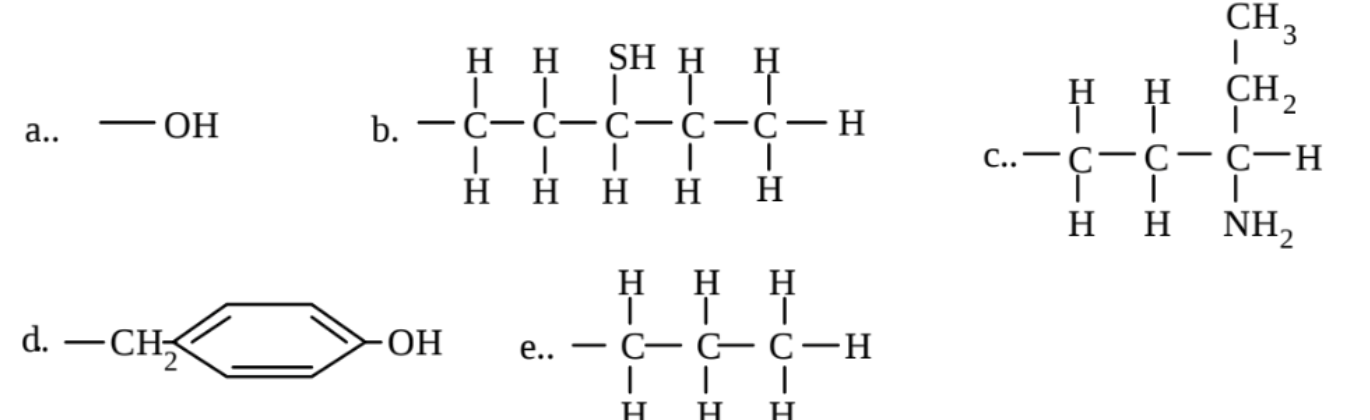
Which of the following groups is capable of only hydrophilic interactions?
O=C-OH
3
New cards
Which of the following is a NOT a property of water?
Its a highly asymmetric molecule.
4
New cards
Which of the following tripeptides would be most likely to be soluble in an organic (hydrophobic)
solvent like benzene?
a) N - phenylalanine - alanine - glycine – C
b) N - leucine - alanine - lysine - C
c) N - proline - phenylalanine - leucine - C
d) N - arginine - lysine - proline - C
e) N - glutamate - aspartate - glycine – C
solvent like benzene?
a) N - phenylalanine - alanine - glycine – C
b) N - leucine - alanine - lysine - C
c) N - proline - phenylalanine - leucine - C
d) N - arginine - lysine - proline - C
e) N - glutamate - aspartate - glycine – C
N - proline - phenylalanine - leucine - C
5
New cards
What kind of bond results from an unequal sharing of electrons?
a) ionic bond
b) polar covalent bond
c) H bond
d) nonpolar covalent bond
a) ionic bond
b) polar covalent bond
c) H bond
d) nonpolar covalent bond
polar covalent bond
6
New cards
Under which circumstances would electrons be most likely to be shared equally?
a) when they are equidistant from nuclei
b) when they are equidistant from each other
c) when atoms of the same element are sharing them
d) when the atoms sharing them are different
a) when they are equidistant from nuclei
b) when they are equidistant from each other
c) when atoms of the same element are sharing them
d) when the atoms sharing them are different
when atoms of the same element are sharing them
7
New cards
The most electronegative atoms typically present in biological molecules are ____ and ____.
a) O, C
b) O, P
c) O, N
d) C, N
e) C, Na
a) O, C
b) O, P
c) O, N
d) C, N
e) C, Na
O, N
8
New cards
The most stable atoms and thus those that are typically nonreactive are the atoms that have
a) equal numbers of electrons and protons
b) equal numbers of electrons and neutrons
c) full inner shells
d) full outer shells
e) all covalent bonds
a) equal numbers of electrons and protons
b) equal numbers of electrons and neutrons
c) full inner shells
d) full outer shells
e) all covalent bonds
full outer shells
9
New cards
Why are free ionic bonds of little importance and relatively unlikely to form in living organisms?
1)Cells are composed mostly of water, which interferes with ionic bonds between free ions.
2)Cells are largely hydrophobic.
3)They are crystals.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 1 and 2
e) 2 and 3
1)Cells are composed mostly of water, which interferes with ionic bonds between free ions.
2)Cells are largely hydrophobic.
3)They are crystals.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 1 and 2
e) 2 and 3
1
10
New cards
In a living organism, where are ionic bonds most likely to be found?
a) in the cytoplasm
b) between DNA strands
c) deep in a protein's core where water is excluded
d) on the surface of a protein
e) on the surface of a lipid
a) in the cytoplasm
b) between DNA strands
c) deep in a protein's core where water is excluded
d) on the surface of a protein
e) on the surface of a lipid
deep in a protein's core where water is excluded
11
New cards
Which interaction is most important in enhancing the solubility of macromolecules in water?
a) hydrophobic interactions
b) nonpolar covalent bonds
c) H bonds
d) van der Waals forces
e) Both hydrophobic interactions and nonpolar covalent bonds
a) hydrophobic interactions
b) nonpolar covalent bonds
c) H bonds
d) van der Waals forces
e) Both hydrophobic interactions and nonpolar covalent bonds
H bonds
12
New cards
Where are hydrophobic interactions most likely to occur?
a) on the surface of a water-soluble protein
b) the core of a water-soluble protein
c) in contact with water molecules
d) between two charged molecules
e) between two ions
a) on the surface of a water-soluble protein
b) the core of a water-soluble protein
c) in contact with water molecules
d) between two charged molecules
e) between two ions
the core of a water-soluble protein
13
New cards
What kind of noncovalent interaction is typified by interactions between two molecules that are so
close together that they can experience weak attractive forces bonding them together?
a) H bonds
b) ionic bonds
c) hydrophobic interactions
d) polar covalent bonds
e) van der Waals forces
close together that they can experience weak attractive forces bonding them together?
a) H bonds
b) ionic bonds
c) hydrophobic interactions
d) polar covalent bonds
e) van der Waals forces
van der Waals forces
14
New cards
A molecule that is capable of releasing or donating a hydrogen ion is termed a(n) _______.
a) base
b) hydrion
c) acid
d) anachronism
e) pain
a) base
b) hydrion
c) acid
d) anachronism
e) pain
acid
15
New cards
A release of hydrogen ions to a solution would most likely ____________.
a) raise pH
b) lower pH
c) buffer pH
d) change salinity
e) keep pH steady
a) raise pH
b) lower pH
c) buffer pH
d) change salinity
e) keep pH steady
lower pH
16
New cards
Why is silicon not suitable for making covalent bonds stable and strong enough to form the basis of
living organisms, even though it is just below carbon on the periodic table?
a) Silicon is too large for its nucleus to attract the valence electrons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together sufficiently.
b) Silicon is too small for its nucleus to attract the valence electrons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together sufficiently.
c) Silicon is too large for its nucleus to attract the protons of neighboring atoms enough to hold molecules
together.
d) Silicon is too small for its nucleus to attract the protons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together.
living organisms, even though it is just below carbon on the periodic table?
a) Silicon is too large for its nucleus to attract the valence electrons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together sufficiently.
b) Silicon is too small for its nucleus to attract the valence electrons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together sufficiently.
c) Silicon is too large for its nucleus to attract the protons of neighboring atoms enough to hold molecules
together.
d) Silicon is too small for its nucleus to attract the protons of neighboring atoms enough to hold
molecules together.
Silicon is too large for its nucleus to attract the valence electrons of neighboring atoms enough to hold molecules together sufficiently.
17
New cards
The low-molecular-weight building blocks of polymers are called _______.
a) minipolymers
b) monoblocks
c) monomers
d) portions
e) octamers
a) minipolymers
b) monoblocks
c) monomers
d) portions
e) octamers
monomers
18
New cards
What bond is responsible for the branch points in glycogen and amylopectin?
a) alpha (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
b) beta (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
c) alpha (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
d) beta (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
e) 3'-5' phosphodiester linkages
a) alpha (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
b) beta (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
c) alpha (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
d) beta (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
e) 3'-5' phosphodiester linkages
alpha (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
19
New cards
Which polysaccharide bond cannot be broken by mammalian enzymes that normally digest polysaccharides?
a) alpha (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
b) beta (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
c) alpha (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
d) beta (1—>6) glycosidic linkages e) phosphate ester linkages
a) alpha (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
b) beta (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
c) alpha (1—>6) glycosidic linkages
d) beta (1—>6) glycosidic linkages e) phosphate ester linkages
beta (1—>4) glycosidic linkages
20
New cards
Why do sugars tend to be highly water soluble?
a) because they have only a few hydroxyl groups
b) because of their large numbers of hydroxyl groups
c) because of their large numbers of sulfhydryl groups
d) because of their large numbers of methyl groups
e) because of their small molecular weights
a) because they have only a few hydroxyl groups
b) because of their large numbers of hydroxyl groups
c) because of their large numbers of sulfhydryl groups
d) because of their large numbers of methyl groups
e) because of their small molecular weights
because of their large numbers of hydroxyl groups
21
New cards
Which of the following is not a macromolecule formed by polymerization?
a) proteins
b) lipids
c) polynucleotides
d) polysaccharides
e) DNA
a) proteins
b) lipids
c) polynucleotides
d) polysaccharides
e) DNA
lipids
22
New cards
What is the maximum number of 100 amino acid long polypeptides that could be made?
a) 10020
b) 2,000
c) 20100
d) 20101
e) 20
a) 10020
b) 2,000
c) 20100
d) 20101
e) 20
20100
23
New cards
How do amino acids like hydroxylysine and thyroxine, which are not among the 20 amino acids that
are inserted into proteins, get into proteins?
a) They are inserted directly.
b) They are the result of the alteration of R groups of the 20 amino acids after their incorporation into the
polypeptide.
c) They are the result of the alteration of R groups of the 20 amino acids before their incorporation into
the polypeptide.
d) There are more than the 20 amino acids that are said to be inserted into proteins.
e) Their atoms are altered by insertion into the polypeptide.
are inserted into proteins, get into proteins?
a) They are inserted directly.
b) They are the result of the alteration of R groups of the 20 amino acids after their incorporation into the
polypeptide.
c) They are the result of the alteration of R groups of the 20 amino acids before their incorporation into
the polypeptide.
d) There are more than the 20 amino acids that are said to be inserted into proteins.
e) Their atoms are altered by insertion into the polypeptide.
They are the result of the alteration of R groups of the 20 amino acids after their incorporation into the polypeptide.
24
New cards
Some of the functions of proteins include: \n Option A: regulation. \n Option B: antibodies. \n Option C: growth factors. \n Option D: all of the choices are correct.
all of the choices are correct
25
New cards
Which amino acid is most likely to be found in the core of a protein?
a) methionine
b) asparagine
c) serine
d) threonine
e) glutamic acid
a) methionine
b) asparagine
c) serine
d) threonine
e) glutamic acid
methionine
26
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a structural polysaccharide?
Option A: chitin \n Option B: cellulose \n Option C: glycogen \n Option D: glycosaminoglycan
Option A: chitin \n Option B: cellulose \n Option C: glycogen \n Option D: glycosaminoglycan
glycogen
27
New cards
___________ help(s) unfolded or misfolded proteins achieve their proper three-dimensional conformation.
\n Option A: Ribosomes \n Option B: Endoplasmic reticulum \n Option C: Ribonuclease \n Option D: Molecular chaperones
\n Option A: Ribosomes \n Option B: Endoplasmic reticulum \n Option C: Ribonuclease \n Option D: Molecular chaperones
Molecular Chaperones
28
New cards
The term "conformation" refers to:
Option A: the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms of a molecule. \n Option B: the spatial organization of atoms in a molecule. \n Option C: the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. \n Option D: both the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms of a molecule and the spatial organization of atoms in a molecule.
Option A: the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms of a molecule. \n Option B: the spatial organization of atoms in a molecule. \n Option C: the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. \n Option D: both the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms of a molecule and the spatial organization of atoms in a molecule.
both the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms of a molecule and the spatial organization of atoms in a molecule.
29
New cards
Water is sometimes called the 21st amino acid because of its importance in defining protein structure. The basis for this is the so-called hydrophobic effect. Which of the following BEST describes the hydrophobic effect?
\
Option A: Polar regions of the protein are repelled by water, driving them to the interior of the protein. \n Option B: Non-polar regions of the protein are repelled by water, driving them to the interior of the molecule. \n Option C: Water and the protein arrange themselves so that the nonpolar surface in contact with water is maximized. \n Option D: All of the choices are correct.
\
Option A: Polar regions of the protein are repelled by water, driving them to the interior of the protein. \n Option B: Non-polar regions of the protein are repelled by water, driving them to the interior of the molecule. \n Option C: Water and the protein arrange themselves so that the nonpolar surface in contact with water is maximized. \n Option D: All of the choices are correct.
Non-polar regions of the protein are repelled by water, driving them to the interior of the molecule.
30
New cards
What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure?
a) beta-pleated sheet
b) double helix
c) alpha-helix
d) supercoiling
a) beta-pleated sheet
b) double helix
c) alpha-helix
d) supercoiling
alpha-helix
31
New cards
The B -pleated sheet is characterized by orientation of ______ the molecular axis.
a) H bonds parallel to
b) H bonds perpendicular to
c) ionic bonds parallel to
d) ionic bonds perpendicular to
e) peptide bonds perpendicular to
a) H bonds parallel to
b) H bonds perpendicular to
c) ionic bonds parallel to
d) ionic bonds perpendicular to
e) peptide bonds perpendicular to
H bonds perpendicular to
32
New cards
Proteins are often composed of two or more distinct modules that fold up independently of one
another. They often represent parts of a protein that function in a semi-independent manner. These
modules are called ______.
a) protein motifs
b) functionals
c) domains
d) dominoes
another. They often represent parts of a protein that function in a semi-independent manner. These
modules are called ______.
a) protein motifs
b) functionals
c) domains
d) dominoes
domains
33
New cards
Amino acids are to proteins as __________ are to carbohydrates.
Option A: fatty acids \n Option B: nucleic acids \n Option C: monosaccharides \n Option D: nucleotides
Option A: fatty acids \n Option B: nucleic acids \n Option C: monosaccharides \n Option D: nucleotides
monosaccharides
34
New cards
Scientists can produce novel proteins by modifying existing proteins using:
Option A: modular construction. \n Option B: affinity-related targeting. \n Option C: site-directed mutagenesis. \n Option D: the yeast two-hybrid system.
Option A: modular construction. \n Option B: affinity-related targeting. \n Option C: site-directed mutagenesis. \n Option D: the yeast two-hybrid system.
site-directed-mutagenesis
35
New cards
Which of the following structures of proteins is composed of two or more polypeptide chains? \n Option A: Primary \n Option B: Secondary \n Option C: Tertiary \n Option D: Quaternary
Quaternary
36
New cards
What level of structure in proteins is held together by intermolecular R group interactions?
a) primary structure
b) secondary structure
c) tertiary structure
d) quaternary structure
a) primary structure
b) secondary structure
c) tertiary structure
d) quaternary structure
quaternary structure
37
New cards
Water has extraordinary properties to support life such as the capacity to:
Option A: form hydrogen bonds with up to four other water molecules. \n Option B: evaporate easily at relatively low temperatures. \n Option C: dissolve a very limited number of substances. \n Option D: prevent forming interactions with many other chemicals.
Option A: form hydrogen bonds with up to four other water molecules. \n Option B: evaporate easily at relatively low temperatures. \n Option C: dissolve a very limited number of substances. \n Option D: prevent forming interactions with many other chemicals.
form hydrogen bonds with up to four other water molecules.
38
New cards
Tertiary structure in DNA is also known as ________. \n A) primary structure \n B) supercoiling \n C) double helix \n D) -helix
supercoiling
39
New cards
You treat a partially purified preparation of protein with a reagent that breaks bonds between sulfur atoms. Which level(s) of protein structure are likely to be affected the most?
tertiary
40
New cards
You are working with an enzyme altase that you denature in the presence of urea. If altase were denatured no further by the addition of mercaptoethanol, what would that suggest to you about the enzyme?
it doesnt have disulfide bonds
41
New cards
What level of structure in DNA would be disrupted by a reagent that breaks apart hydrogen bonds?
Secondary structure
42
New cards
What is now thought to have been the genetic material in the first living organisms on Earth? \n A) RNA \n B) DNA \n C) protein \n D) polypeptides
RNA
43
New cards
Which of the following is a nucleotide?
a) phosphate + ribose
b) adenine + deoxyribose
c) sugar + nitrogenous base
d) adenine + ribose + phosphate
a) phosphate + ribose
b) adenine + deoxyribose
c) sugar + nitrogenous base
d) adenine + ribose + phosphate
adenine + ribose + phosphate
44
New cards
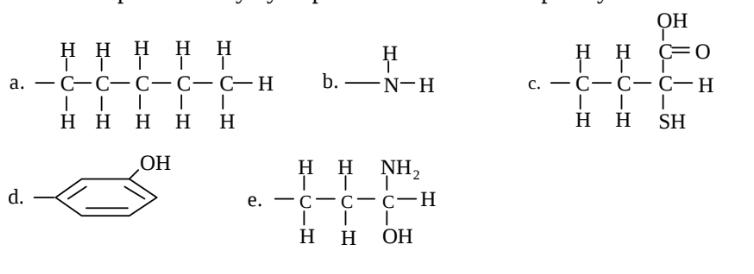
Which of the groups below is capable of only hydrophobic interactions? Explain your answer.
Which is capable of only hydrophilic interactions? Explain your answer.
\
Which is capable of only hydrophilic interactions? Explain your answer.
\
A is capable of only hydrophobic interactions. It contains no ionizable or hydrophilic groups. B
is capable of only hydrophilic interactions, since it has no component with a long carbon chain or a
carbon-containing ring and no nonpolar covalent linkages. It is also capable of ionization.
is capable of only hydrophilic interactions, since it has no component with a long carbon chain or a
carbon-containing ring and no nonpolar covalent linkages. It is also capable of ionization.
45
New cards
The chloride ion has an extra electron relative to the number of protons in its nucleus. Thus, chloride:
Option A: has a negative charge. \n Option B: has lost an electron. \n Option C: can bind a cation. \n Option D: has a negative charge and can bind a cation.
Option A: has a negative charge. \n Option B: has lost an electron. \n Option C: can bind a cation. \n Option D: has a negative charge and can bind a cation.
has a negative charge and can bind a cation.
46
New cards
Which of the following statements about RNA is TRUE?
It can have catalytic activity.
47
New cards
The properties of carbon allow it to form _____ backbones.
branched
48
New cards
Amino acids:
Option A: can form peptide bonds. \n Option B: are composed of a central carbon surrounded by an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom and a variable side chain. \n Option C: can have side chains that are polar, nonpolar, or with unique properties. \n Option D: all of these statements are true.
Option A: can form peptide bonds. \n Option B: are composed of a central carbon surrounded by an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom and a variable side chain. \n Option C: can have side chains that are polar, nonpolar, or with unique properties. \n Option D: all of these statements are true.
all of these statements are true
49
New cards
Fats that remain solid at room temperature are MOST likely to be:
saturated.
50
New cards
Which of the following statements about phospholipids is TRUE?
\n Option A: Each one has three fatty acid chains. \n Option B: The glycerol backbone is bonded to a small nonpolar group. \n Option C: Their biological function remains unknown. \n Option D: Each one has two fatty acid chains and the glycerol backbone is bonded to a small polar group.
\n Option A: Each one has three fatty acid chains. \n Option B: The glycerol backbone is bonded to a small nonpolar group. \n Option C: Their biological function remains unknown. \n Option D: Each one has two fatty acid chains and the glycerol backbone is bonded to a small polar group.
Each one has two fatty acid chains and the glycerol backbone is bonded to a small polar group.
51
New cards
A proteome is:
Option A: an inventory of all of the proteins in a tissue, cell, or cellular organelle. \n Option B: all of the mRNA in a cell. \n Option C: the cell's rDNA. \n Option D: another name for a genome.
Option A: an inventory of all of the proteins in a tissue, cell, or cellular organelle. \n Option B: all of the mRNA in a cell. \n Option C: the cell's rDNA. \n Option D: another name for a genome.
The entire inventory of proteins in a particular organism, cell type, or organelle.
52
New cards
The infectious agent for Creutzfeld-Jakob disease is a ________.
\n Option A: virus \n Option B: bacterium \n Option C: protein \n Option D: fungus
\n Option A: virus \n Option B: bacterium \n Option C: protein \n Option D: fungus
protein
53
New cards
All of the following are parts of a nucleotide EXCEPT: \n Option A: a five-carbon sugar. \n Option B: a six-carbon sugar. \n Option C: a phosphate group. \n Option D: a nitrogenous base.
a six-carbon sugar.
54
New cards
What is the consequence of placing a proline side chain within an alpha helix?
Option A: Proline stabilizes the folded alpha helical structure, causing it to kink. \n Option B: Proline isomerizes to the trans form and the alpha helix is undisturbed. \n Option C: Proline disrupts the structure of an alpha helix, causing it to kink. \n Option D: All of the choices are correct.
Option A: Proline stabilizes the folded alpha helical structure, causing it to kink. \n Option B: Proline isomerizes to the trans form and the alpha helix is undisturbed. \n Option C: Proline disrupts the structure of an alpha helix, causing it to kink. \n Option D: All of the choices are correct.
Proline disrupts the structure of an alpha helix, causing it to kink.
55
New cards
The primary structure of a polypeptide is:
Option A: the DNA sequence that encodes the protein. \n Option B: the specific linear sequence of amino acids that constitutes the polypeptide chain. \n Option C: the nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan tRNA. \n Option D: the three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Option A: the DNA sequence that encodes the protein. \n Option B: the specific linear sequence of amino acids that constitutes the polypeptide chain. \n Option C: the nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan tRNA. \n Option D: the three-dimensional structure of the protein.
the specific linear sequence of amino acids that constitutes a chain.
56
New cards
Tertiary structure can be determined using:
Option A: X-ray crystallography. \n Option B: nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. \n Option C: both X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. \n Option D: thin layer chromatography.
Option A: X-ray crystallography. \n Option B: nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. \n Option C: both X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. \n Option D: thin layer chromatography.
Both X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
57
New cards
The normal blood pH is about 7.4. What is the concentration of the hydrogen ion?
\[H+\] = 10^−7.4 ≈ 0.0000040 = 4.0 × 10−8 M.
58
New cards
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily? \n a) large and hydrophobic \n b) small and hydrophobic \n c) large polar \n d) small and ionic
small and hydrophobic
59
New cards
Which of the following are least likely to diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane? \n
a) large hydrophobic molecules
b) small hydrophobic molecules
c) carbon dioxide
d) small ions
a) large hydrophobic molecules
b) small hydrophobic molecules
c) carbon dioxide
d) small ions
small ions
60
New cards
Which of the following statements describes a characteristic feature of a carrier protein in a plasma membrane?
a) It exhibits specificity for a particular type of molecule.
b) It requires the expenditure of cellular energy to function.
c) It works against diffusion.
d) It has no hydrophobic regions.
a) It exhibits specificity for a particular type of molecule.
b) It requires the expenditure of cellular energy to function.
c) It works against diffusion.
d) It has no hydrophobic regions.
It exhibits specificity for a particular type of molecule.
61
New cards
Which of the following would likely diffuse through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly? \n a) sucrose \n b) an amino acid \n c) O2 \n d) Na+
O2
62
New cards
Which of the following molecules dramatically increases the rate of diffusion of water across cell membranes? \n
a) the sodium-potassium pump
b) aquaporins
c) gated ion channels
d) ATP
a) the sodium-potassium pump
b) aquaporins
c) gated ion channels
d) ATP
aquaporins
63
New cards
Which of the following statements about diffusion is true? \n a) It is very rapid over long distances. \n b) It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell. \n c) It is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
d) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
d) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
64
New cards
Which of the following processes includes all of the others? \n a) osmosis \n b) facilitated diffusion \n c) passive transport \n d) transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient
passive transport
65
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes osmosis? \n a) Osmosis only takes place in red blood cells. \n b) Osmosis is an energy-demanding or "active" process. c) In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration. \n d) In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration.
In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration.
66
New cards
Which molecule will diffuse most quickly across a lipid bilayer membrane? \n a) H2O \n b) O2 \n c) H2PO4- \n d) glucose \n e) Na+
O2
67
New cards
A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in ________. \n a) lysosomes \n b) Golgi vesicles \n c) vacuoles \n d) secretory vesicles
lysosomes
68
New cards
The force driving simple diffusion is ________, while the energy source for active transport is ________. \n
a) a concentration gradient; ADP
b) a concentration gradient; ATP hydrolysis
c) transmembrane pumps; an electrochemical gradient
d) phosphorylated carrier proteins; ATP
a) a concentration gradient; ADP
b) a concentration gradient; ATP hydrolysis
c) transmembrane pumps; an electrochemical gradient
d) phosphorylated carrier proteins; ATP
a concentration gradient; ATP hydrolysis
69
New cards
White blood cells engulf bacteria using ________. \n a) phagocytosis \n b) pinocytosis \n c) osmosis \n d) receptor-mediated exocytosis
phagocytosis
70
New cards
Which of the following membrane activities requires energy from ATP hydrolysis? \n a) facilitated diffusion of chloride ions across the membrane through a chloride channel \n b) movement of Na+ ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid \n c) movement of glucose molecules into a bacterial cell from a medium containing a higher concentration of glucose than inside the cell \n d) movement of carbon dioxide out of a paramecium
movement of Na+ ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid
71
New cards
A sodium-potassium pump ________. \n a) moves three potassium ions out of a cell and two sodium ions into a cell while producing ATP for each cycle \n b) moves three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis \n c) moves three potassium ions out of a cell and two sodium ions into a cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis \n d) move three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell and generates an ATP in each cycle
moves three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis
72
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions for typical plant and animal cells? The animal cell is in ________.
a) a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
b) an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution
c) a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
d) an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
a) a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
b) an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution
c) a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
d) an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution