Mircobiology final exam
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Newborns exposed to the Gram-positive bacterium ________ during vaginal birth are at risk of developing neonatal meningitis.
Streptococcus agalactiae
West Nile virus is transmitted by ________
Mosquitos
Which of the following is the most common outcome of Cryptococcus neoformans infection?
subclinical respiratory infection
________ plague is easier to treat than the other two forms.
Bubonic plague
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome is treated using ________ care.
Supportive care
Which artery carries deoxygenated blood?
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Which of the following is a type of primary lymphoid tissue?
Bone marrow is a type of primary lymphoid tissue.
A person is brought to the emergency room with constant high fever, extensive edema, low blood pressure, and petechiae. From which of the following may the person be suffering?
septicemia
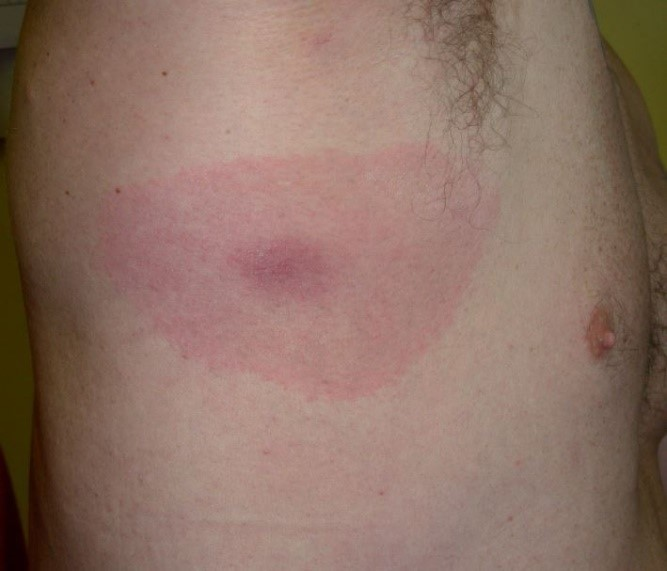
The appearance of this rash is characteristic of infections with which of the following?
Borrelia burgdorferi - Lyme disease
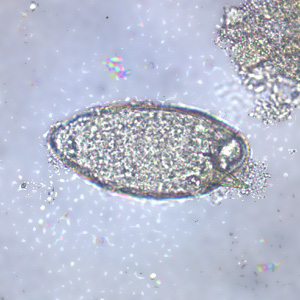
Identify the eukaryote shown here:
Schistosoma sp.
What disease/infection is caused by G. lamblia?
Giardiasis, a diarrheal illness caused by the Giardia lamblia parasite.
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is also known as ________.
Trench mouth
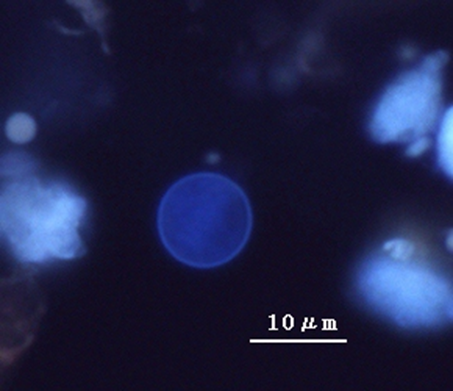
The patient came to the emergency room stating that he has explosive & watery diarrhea, vomiting, cramps, fever, & loss of appetite. Furthermore, when asked if he had traveled anywhere in the past week he explained how he had come back from Mexico about 8 days ago. He stated that he was fine when he landed but after the seventh day back he started noticing the symptoms. Height 5’8 weight 180 BP 120/90 pulse 120 temp 38 °C (100.4 °F). A stool O&P examination was used for diagnosis, there were oocytes that had a distinctive blue halo when using the ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy. What is the most likely disease/infection and etiology? What is one common antimicrobial medication used to treat it? Is a vaccine available? If so, what is it? Note: be as specific as possible; do NOT abbreviate (spell out the genus), and spelling counts!
Disease: Cryptosporidiosis
Etiology: Cryptosporidium parvum.
Antimicrobial: Nitazoxanide.
Vaccine: No.
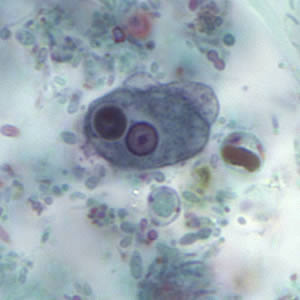
Identify the eukaryote shown here:
Entamoeba histolytica
The movement of Ancylostoma braziliense through the skin causes the condition known as cutaneous larva migrans. Which of the following is a distinctive symptom of this condition?
Their tracks are visible and cause itching.
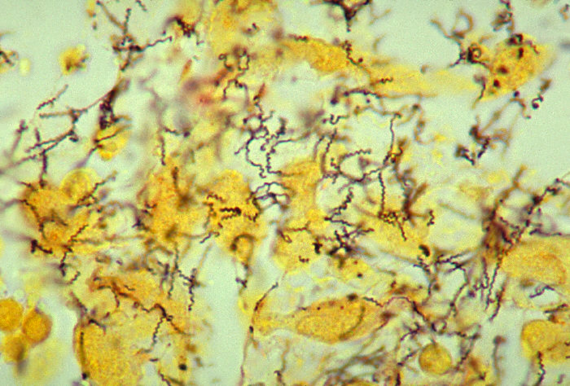
Amanda attends a party at her university and has unprotected sex. She feels tenderness near her inguinal lymph nodes (region: groin) about 10 days later. She does not worry because she does not feel pain in this region and she cannot indicate alternate symptoms. The aforementioned tenderness soon passes. However, Amanda notices tenderness in her inguinal lymph nodes once again about 14 days later. Amanda wakes up the next morning to intense abdominal pain and heavy vaginal bleeding. She was rushed to the ER, where a stain of the exudate revealed the pathogen (see stain below). What is the most likely disease/infection and etiology? What is one common antimicrobial medication used to treat it? Is a vaccine available? If so, what is it? Note: be as specific as possible; do NOT abbreviate (spell out the genus), and spelling counts!
Disease: syphilis
Etiology: Treponema
pallidum.
Antimicrobial: penicillin G.
Vaccine: No.
Soft chancres are a symptom of ________, an infection of the reproductive tract.
Chancroid
Bacterial vaginosis is associated with a(n) ________ in vaginal pH.
increase
Identify the bacterial disease with the following distinguishing characteristics: causes severe coughing that can last for months; especially dangerous for infants; can be effectively prevented through vaccination
Pertussis - whopping cough
Neonatal conjunctivitis is commonly treated with which of the following?
erythromycin
Which term describes tingling or numbness in peripheral nerves?
Which of the following infections is transmitted by ticks?
ehrlichiosis
What disease is most associated with Clostridium perfringens?
gas gangrene
Which form of Schistosoma penetrates the skin?
cercariae.
Which of the following diseases is caused by a spirochete?
relapsing fever.
Which of the following is a disease that is often transmitted by undercooked, contaminated poultry?
Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis.
The bacterium ________ adheres to and grows on teeth, contributing to dental plaque formation.
Streptococcus mutans
Which cause of viral gastroenteritis can be prevented by vaccination?
Rotavirus
Which is true about the treatment for ETEC?
It is usually self-limiting, although medications such as fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, TMP/SMZ, and rifamixin can be used.
Colitis
Inflammation of the colon
Enteritis
Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa
gastritis
Inflammation of the stomach
Gastroenteritis
Inflammation of both the stomach and intestinal mucosa
gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
Salpingitis is inflammation of the _____
fallopian tubes
________ may be chronic or acute and can develop after S. pyogenes infection.
Glomerulonephritis
Which microbe causes streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat)?
s. pyogenes
Aspergillosis
Rare in healthy individuals; may cause upper or lower respiratory tract symptoms, such as headaches, fever, congestion, cough, shortness of breath, black oral lesions.
Blastomycosis
Causes aches, fever, chills, cough, and chest pain in immunocompromised individuals; causes crusted lesions that may lead to scarring when disseminated
coccidioidomycosis (valley fever)
Causes lesions to develop on the face that may spread and cause meningitis.
histoplasmosis
may cause lung lesions resembling Ghon complexes, weakness and chest pain
Murmycosis
causes respiratory symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath; pneumonia and pulmonary or cerebral hemorrhages may occur
True or False: Herpes simplex virus 1 only causes lesions on and around the mouth.
False
For what purpose would a health-care professional use a Wood’s lamp for a suspected case of ringworm?
To visualize the fungus
True or False: The normal microbiota of skin tends to inhibit transient-microbe colonization by producing antimicrobial substances and outcompeting other microbes that land on the surface of the skin.
True
Which of these assays has the following application: serotyping bacteria?
Indirect hemagglutination
A positive result of the _____ results in agglutination of RBCs.
direct coombs test
Which type of antibody is preferable for western blot tests and why?
polyclonal antibodies, because they can bind to multiple epitopes, generally produce a stronger signal, and are less expensive
In the lab, you receive a blood sample from a patient with an order to quantify the amount of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the serum. Which test should you perform?
an indirect ELISA
Which type of immunity would be acquired from being ill and recovering from an infection?
Natural active
Which is the best term to describe the process that occurs when an immune cell releases cytokines to nearby cells to trigger a response?
Paracrine
Which of the following statements about LPS is false?
LPS is an endogenous pyrogen
The phenomenon of ________ facilitates the binding of phagocyte pseudopodia to pathogens.
opsonization
A mosquito bites a person who subsequently develops a fever and abdominal rash. What type of transmission would this be?
biological vector transmission
Which of the following applies to hyaluronidase?
It acts as a spreading factor.
In the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test, the _______ of the zone of inhibition is measured and used for interpretation.
Diameter
_____ is a process that kills nonspore-forming pathogenic pathogens.
Pasteurization
aerotolerant anaerobes
An organism that grows equally well with or without oxygen
Facultative anaerobe
An organism that can grow without oxygen but that grows best with oxygen
Microaerophile
An organism that requires a low concentration of oxygen (less than the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere)
obligate aerobe
An organism that requires oxygen to survive
obligate anaerobe
An organism that requires a oxygen free environment
The excision of the viral genome from the host chromosome is known as which of the following?
Induction
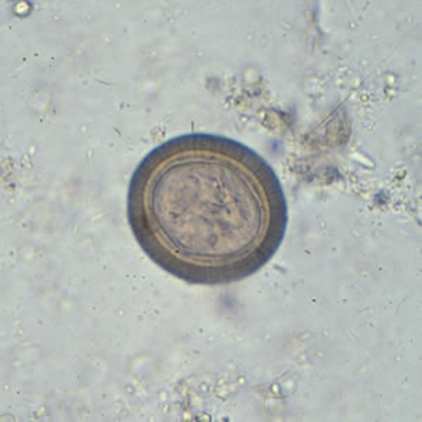
You see the following in a stool sample from a patient that has recently eaten undercooked pork and is experiencing abdominal pain. Which of the following is the most likely causative agent of your patient’s illness?
Taenia spp.
____ is an organized layer located outside of the cell wall and usually composed of polysaccharides or proteins.
Capsule