falling objects
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
in the vertical or y-direction,
objects move under the influence of gravitational force
without another force (such as air friction), falling objects
all objects fall with the same acceleration near the surface of the planet
g - acceleration of all objects falling towards Earth’’s surface
9.8 m/s
what affects the value of g
air friction (upward) will reduce g (downward)
the mass of a falling object does NOT affect the value of g
unless noted, we will not consider air friction/air drag
innertia
the tendency of mass to remain at rest or constant motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force
heavier objects require greater inertia because they require more force to accelerate
heavier objects are more sluggish, and resist acceleration
mass is innertia. more mass = more innertia
velocity of falling object
start with v=0 at t=0, pick up 9.9 m/s of speed each second after that, until it hits the ground
all objects with no external forces have the same v(t) graph
velocity increases downward. the slope is acceleration, which is negative (downwards)
acceleration = 9.8 m/s/s at every point on the graph
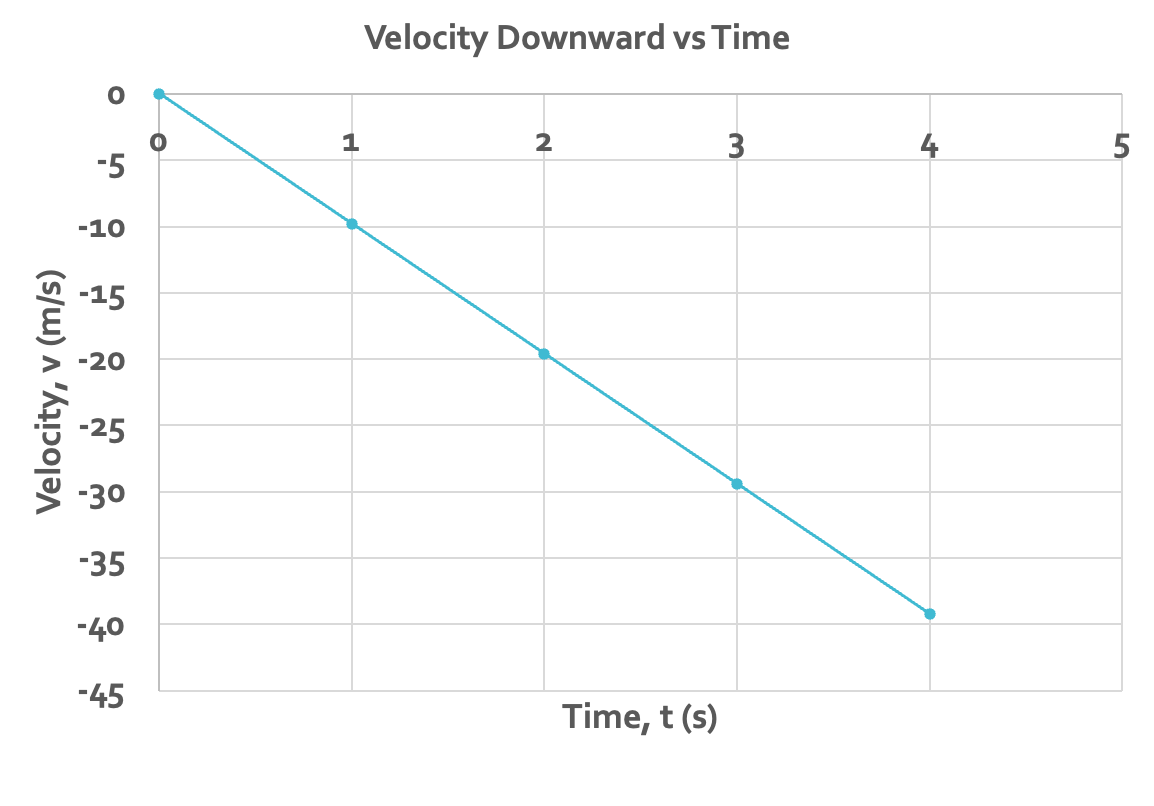
displacement on v(t) graph
area under graph (between line and x-axis)
displacement downward at 3 seconds is 45 m
when is the answer negative
if you make downward (g) negative, the change in y will be negative
why is a falling object accelerating
because it is picking up speed as it falls downward
initial velocity of a dropped object
zero
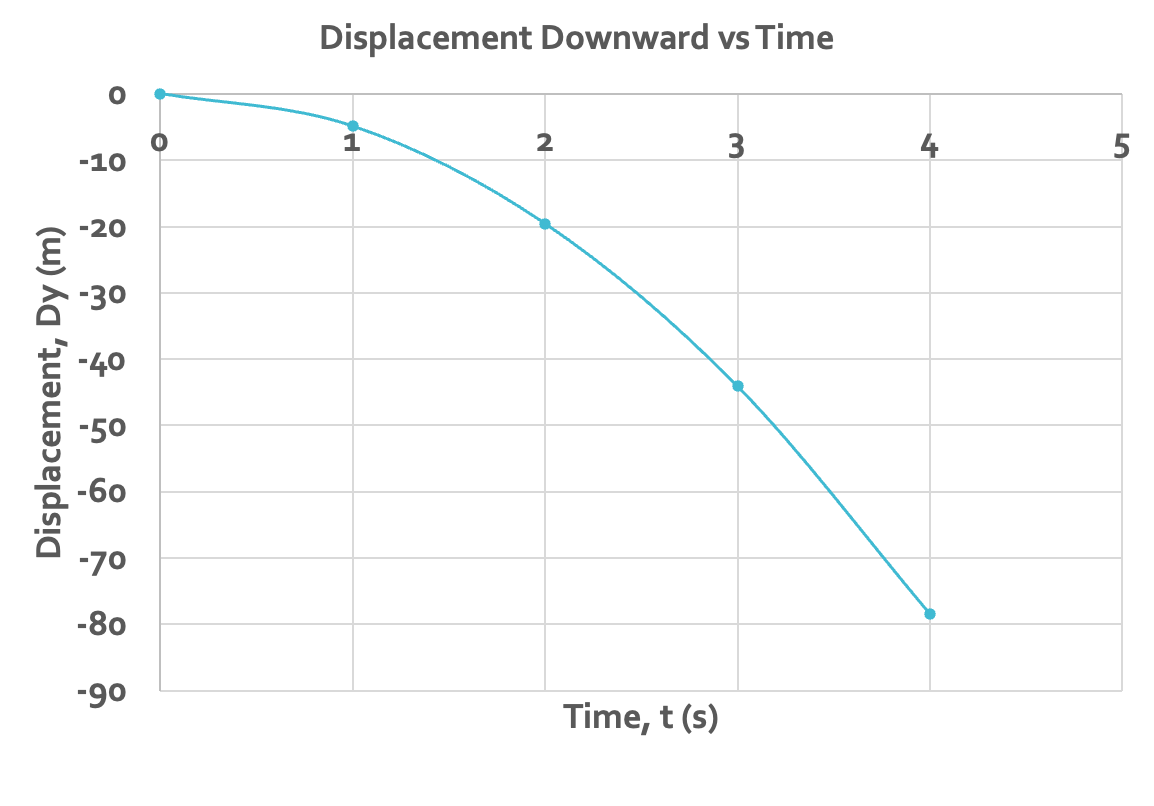
displacement downward vs. time graph of a falling object
the slope is negative and decreasing, so the velocity is negative and increasing in the negative direction
each second, the ΔY gets bigger
the grapg is a curve because the object is accelerating
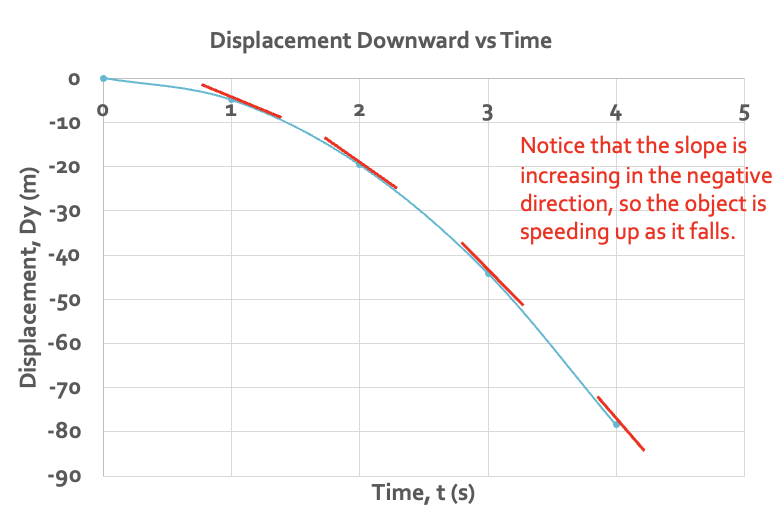
instantaneous velocity of displacement downward vs time graph
the slope at each point
the slope increases in the negative direction - the object speeds up as it fals
object being thrown up
the acceleration vector is downward the ENTIRE TIME (way up & down)
object being thrown up (on way up)
speed decreases
because the velocity vector is upward, and the acceleration vector is downward
objects speed will decreaseuntil it reaches zero, then it will trun around and fall downward
vertical speed of ubject at max height of throw
zero
object being thrown up (on the way up)
speed increases downward
because the velocity vector is downward, and the acceleration vector is also downward
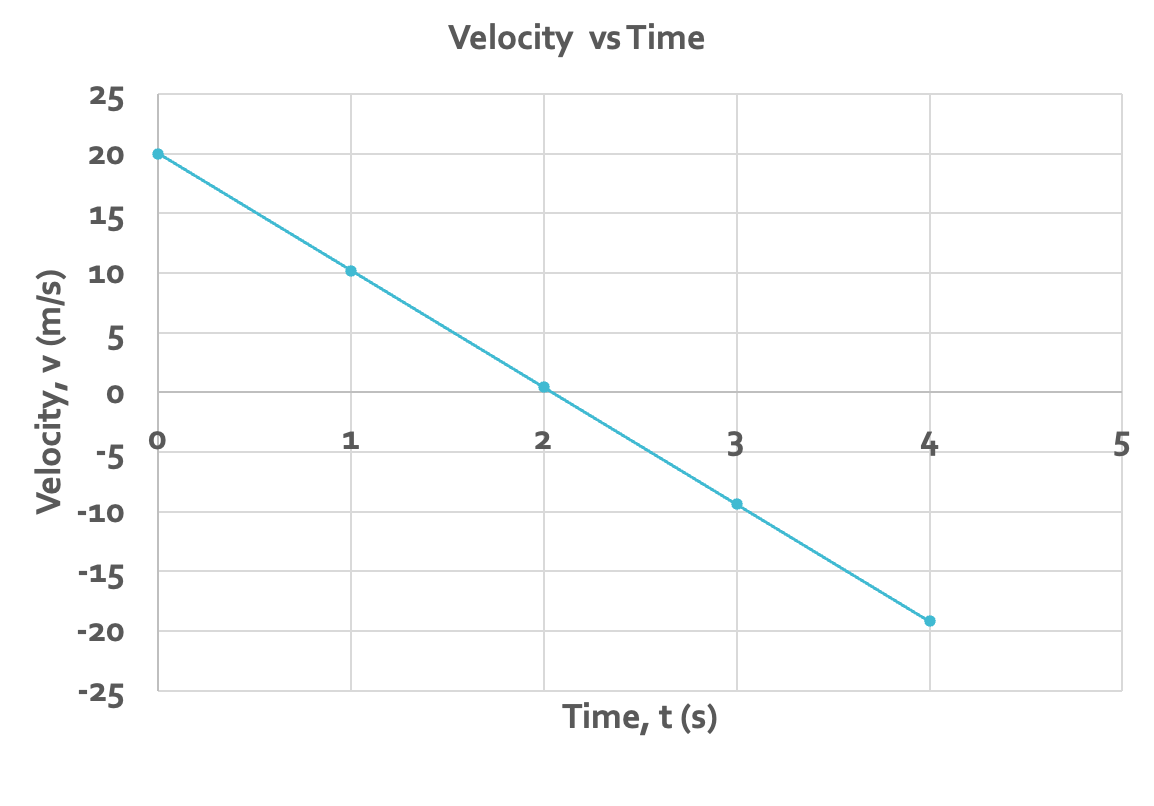
v(t) graph of an object thrown upward
constant velocity; crosses zero
the slope is the same the entire time (so acceleration is -9.8m/s/s the ENTIRE TIME)
postition-time graph of ball being thrown
NOT the path of the ball, just the height of throw for ecah second.
top of motion is 2 ish seconds
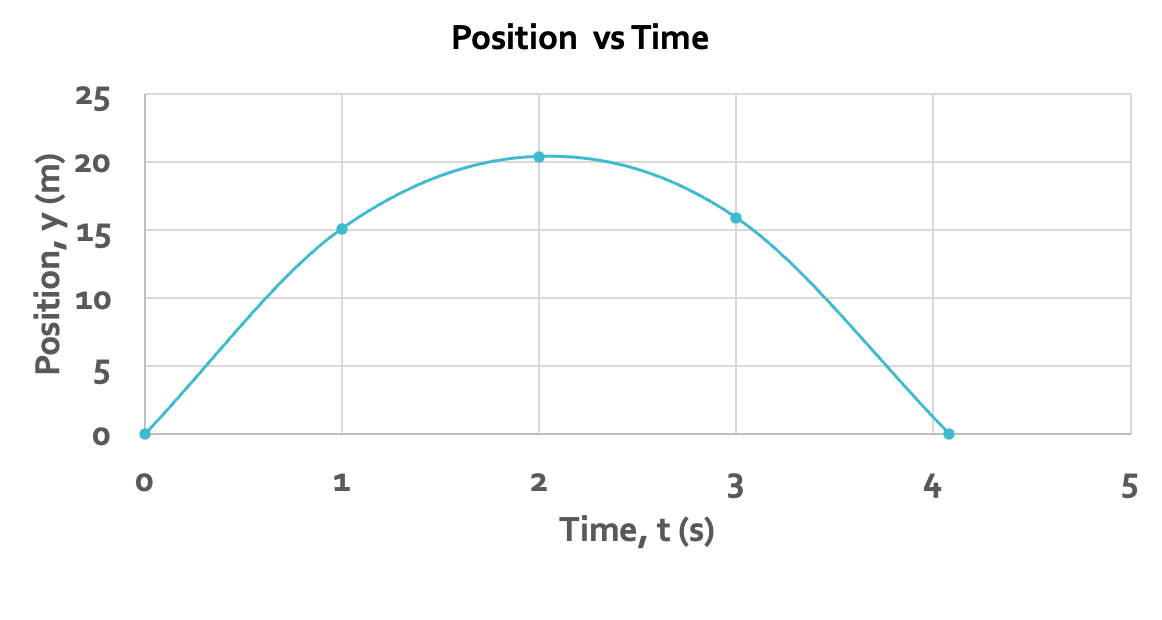
if you throw a ball straight upward, when is its velocity zero?
at the peak of its motion; its max height
if you drop a ball, when is its velocity zero
at the moment it is dropped
the INITIAL velocity
also after it has hit the ground and come to a stop
if you throw a ball or drop a ball, when is acceleration the greatest
the acceleration s a constant -9.8 m/s/s if there is no air drag; no max acceleration, it is always the same
if you drop a bowling ball and basketball at the same time, which one will hit the grown first
in the absence of air friction, all obects will hit at the same time.