Injury & Mental Disorders
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Name some data sources for burden of injury in NZ
national surveys
ACC claims database
ZNHIS
Agency databases
Research publications and projects
In injury epidemiology why is the denominator used important?
using the whole population can lead to inaccuracies in interpreting injury data. its important that the denominator represents people who have been exposed to the same risk but didn’t have the outcome (e.g. drivers in a specific area, hours spent driving, etc)
Is exposure to risk of injury always constant
no it can be transient and intermittent
What is an intermittent and transient exposure?
transient exposure happen for brief periods of time
intermittent exposures are not continuous
Explain the epidemiological triad in the context of injuries
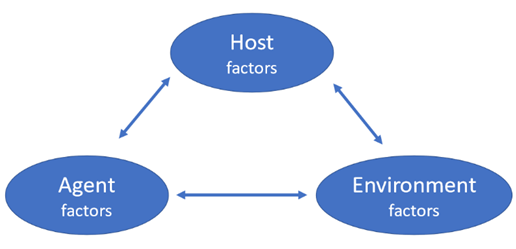
host: who was affected by the injury and what happened to them
agent: what caused the injury - the energy/force
environmental: where the injury occurred
Give a simple definition of injury
physical or physiological harm caused by interaction of the body with energy that exceeds physical or physiological tolerances
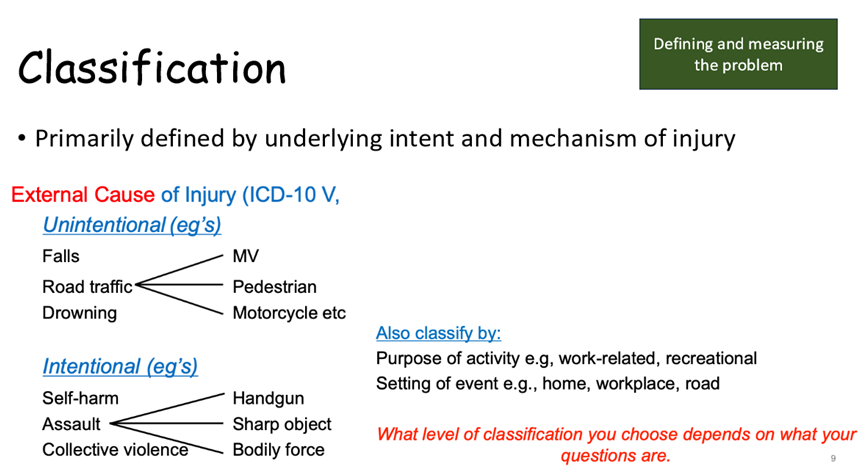
How are injury classified
External causes of injury are classified by
intentional
non-intentional
(Sometimes the purpose of the activity)
What are the 2 types of injuries that are the leading causes of injury related health loss in NZ?
self inflicted
transport injuries
What is the most common injury for older demographics?
falls
What are the four injuries that have the highest DALYs?
self inflicted
transport
falls
interpersonal
which two risk factors contribute about ¼ each to all injury related health loss?
alcohol
mental illness
_____ experience ____ the rate of injury related health loss compared to _____
Māori; twice; non-Māori
Health loss from ____ is 4 times higher in ____
assault; Māori
over half of all injuries occur in those under ____ years
35
injuries are the ___ most important cause of health loss in children and young people and ___ in all age groups
3rd; 5th
Which external causes of injury have the highest mortality rates?
road injuries
self harm
falls
Mortality by poisoning is higher in __________
low and middle income countries
____ are more at risk of death from injuries and violence
men
In which age group are road injuries the highest cause of mortality
15-29 years
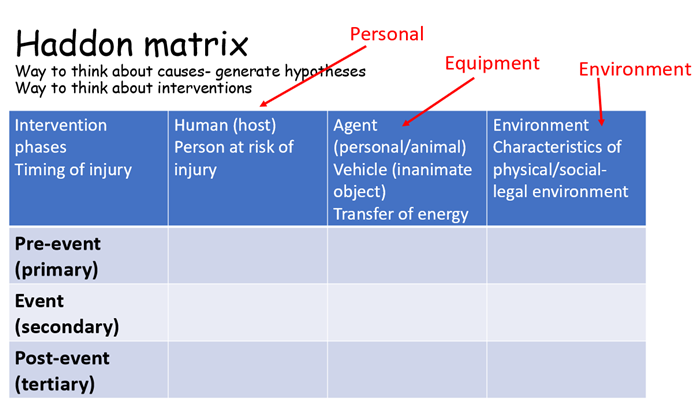
What are the dimensions of the Haddon’s matrix - the rows
pre event (primary)
event (secondary)
post event (tertiary)
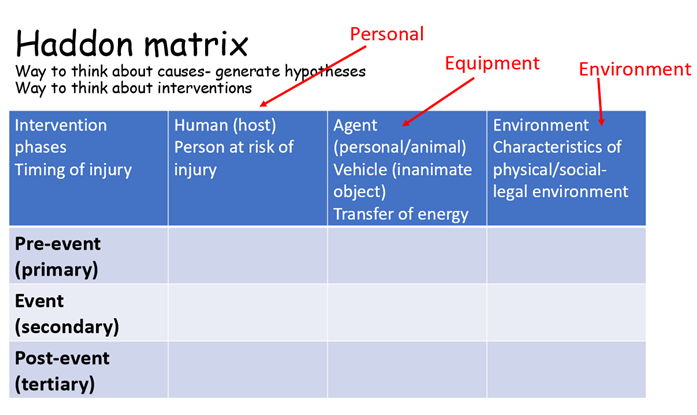
What are the dimensions of the Haddon’s matrix - columns
host (human) - person at risk of injury
agent (vehicle)
proximal environment (physical)
distal environment (social-legal)
What are strengths and limitations of descriptive studies for answering research questions about injury control?
strengths: can identify the descriptive epidemiology and burden of injury
describes the problem and the context in which it occurs
Limitations: describes factors associated with injury but not whether they are causal
What are strengths and limitations of cohort studies for answering research questions about injury control?
Strengths:
can examine multiple exposures and multiple outcomes
temporal relationship
can use existing datasets with high risk populations
Limitations:
most injuries are rare outcomes therefore need large samples
loss to follow up - common in young people as they are more mobile
expensive and long follow up
Difficult to measure transient exposures
What are strengths and limitations of case control studies for answering research questions about injury control?
strengths
info on transient risk factors
no risk of loss to follow up
good for measuring rare events
controls come from the same source population as the cases
limitations
recall bias
misclassification of exposed and non-exposed
no incidence rates just relative risk which is estimated by OR
confounding
What are strengths and limitations of RCTs studies for answering research questions about injury control?
Strengths
good for testing interventions
no confounding
Limitations
cannot randomise people to potentially harmful exposures or interventions - need equipoise
What are strengths and limitations of Ecological studies for answering research questions about injury control?
strengths
useful in injury prevention policy evaluation
acknowledges the contribution of the physical and social environment in injury
differences between groups
Limitation
ecological fallacy
clues to cause but no causal association
provides limited information on injury
What is an example of an intermittent exposure
driving
what are the downstream determinants of injury?
the factors relating to the individual and individual lifestyle factors
what are the upstream determinants of injury?
the causal factors outside the individual
most injuries are ____ and therefore ____
predictable; preventable
Provide two examples of intentional injuries
family violence
self inflicted harm
What is the prevalence of any ACEs for men and women?
ACEs are more prevalent in women (62%) compared to men (54%)
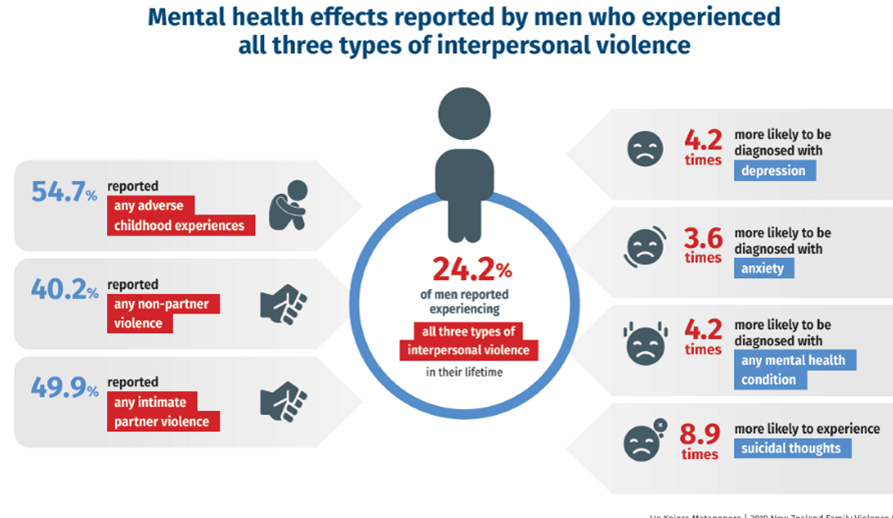
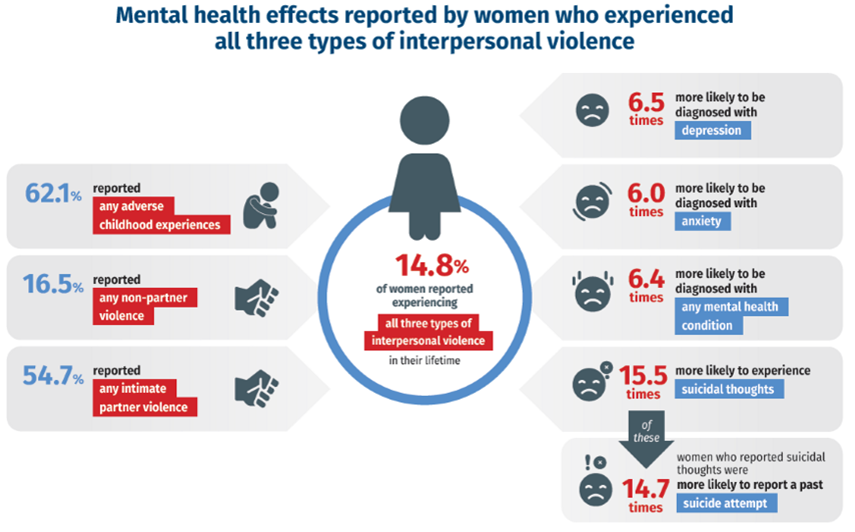
Who experiences more non-partner violence?
men
Who experiences more intimate partner violence?
women (54.7%) (men (49.9))
List 3 health consequences that are associated with the experience of intimate partner violence
pain and discomfort
increases risk of being diagnosed with mental disorders like depression and anxiety
increases risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and CVD
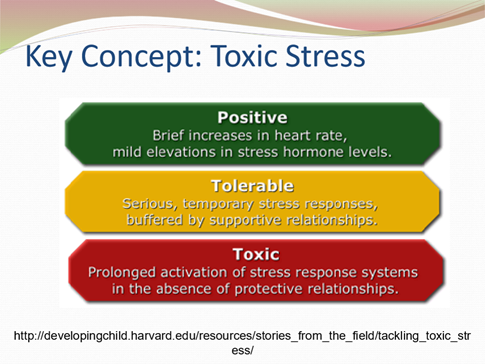
What’s the difference between positive/good, tolerable and toxic stress
good stress is good for motivating a person, there are mild elevations of stress hormone levels and a slight increase in heart rate
tolerable stress is caused by a stressful event which results in a prolonged experience of stress but is buffered by supportive relationships
toxic stress occurs as a result of prolonged activation of the stress response system without protective relationships to help
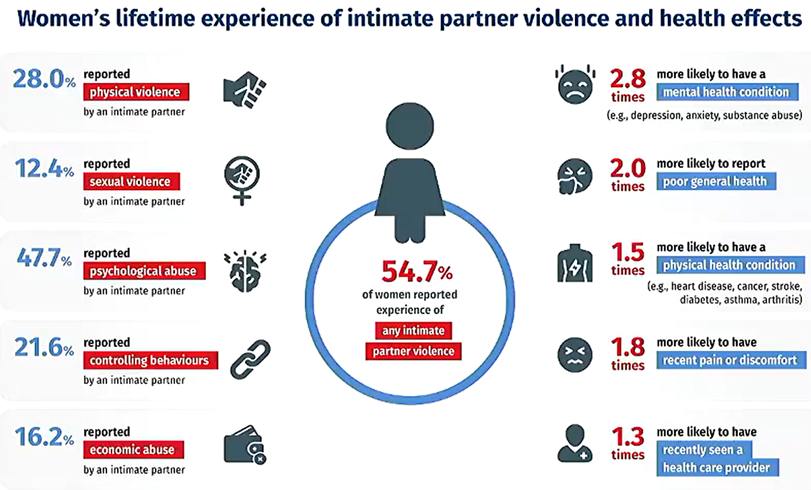
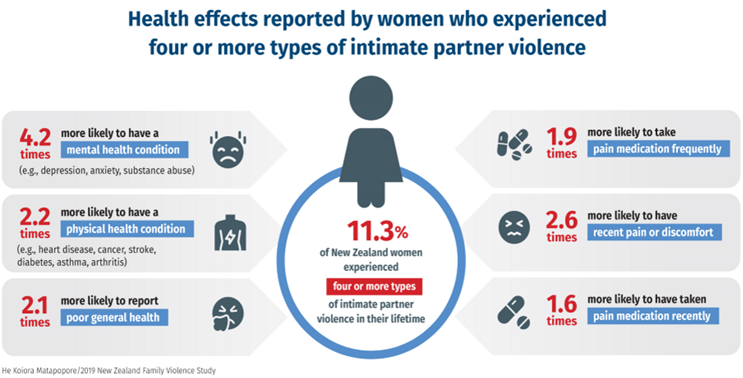
Describe the magnitude of intimate partner violence in NZ
There is a high prevalence of IPV in both men and women
women experience (62%) more IPV than men(49%)
54% of women reported experiencing any form of IPV while 11% of women reported experiencing 4 or more types of IPV
What is the relationship between IPV and health
There is a dose response effect - the more IPV events experienced, the poorer the health outcomes.
Describe the magnitude of child abuse in NZ
18% of adults reported experiencing physical abuse
18% of adults reported experiencing sexual abuse
29% of adult reported experiencing emotional abuse
women experienced more ACEs than men
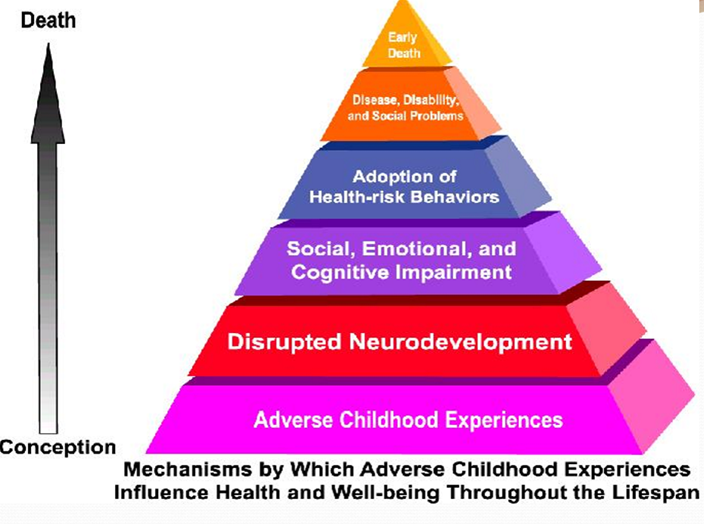
what are some of the mechanisms which contribute to the long-term health consequences of family violence
developmental/physiological
emotional
behavioral
What is promotion and what is an example of how it is used in Family Violence?
promotion is about encouraging healthy relationships and norms. These can be though social marketing and campaigns
an example of this is the its not OK campaign for family violence
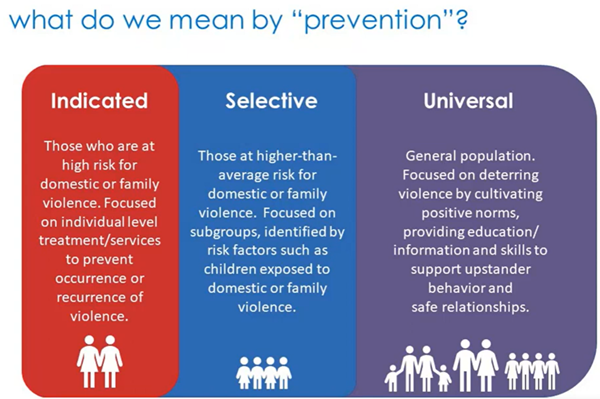
What are the three types of prevention methods and what are they for?
indicative - individuals at high risk
selective - subgroups at high risk
universal - the general population
Parenting programmes, programmes for adolescents who may be at high risk are examples of which prevention method?
indicative
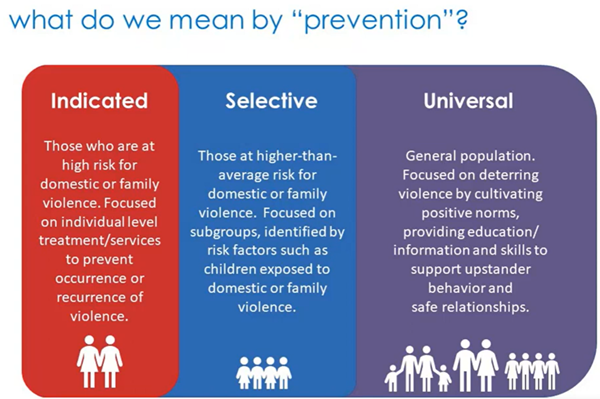
healthy teen dating educational campaigns are examples of which prevention method?
selective
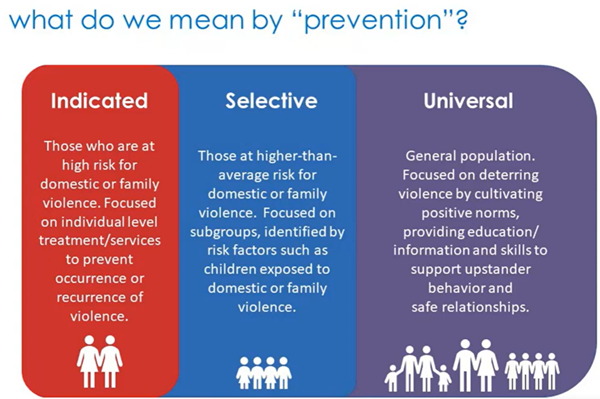
child protection services, police involvement, treatment are examples of what?
response (to an event of violence. response refers to how the person is being supported)
strengthening anti-violence social norms, promoting gender equality and reducing poverty is an example of which type of prevention?
universal
Where can you access information on evidence based strategies to address violence?
vine
CDC
Te Puna Aonui
____ are the _____ leading cause of unintentional injury deaths worldwide and the most common way to injure yourself in _________
falls; second; New Zealand
Describe fall mortality by HDI
higher in low and middle income countries
Falls are often severe in older adults. one in __ people over 65 injures themselves in a fall. This rises to one in _ people once you reach —
3; 2; 80
From which age do falls become the leading cause of injury deaths?
75
describe the magnitude of the health burden from falls in older adults in the future.
as our population continues to age, the burden of falls in older adults will likely increase and continue to be a large health burden.
what are some environmental (home and residential areas) interventions?

Which groups have the highest alcohol consumption?
18 - 24 year olds
Māori
what determines patterns of drinking
speed and volume
How do patterns of drinking influence injury risk?
Drinking volume and speed determines how intoxicated becomes and depending on the context and situation they are in, their risk of injury could increase
What is classified as binge drinking for men and women?
6 or more standard drinks for men
4 or more standard drinks for women
What major types of injuries does alcohol contribute
car crashes
interpersonal violence (at home and with strangers)
self harm
boating
Describe the contribution of alcohol to car crashes and boating
A high proportion of serious injury car crashes are attributed to car crashes
as the fatality/seriousness of the car crash goes up, the probability that alcohol was a contributing factor also increases
risk of boating fatality increases significantly with BAC (blood alcohol concentration)
List some interventions for reduction of alcohol related injury for which there is evidence of effectiveness
taxing and pricing
drink driving countermeasures and enforcement
restrictions on alcohol promotion and advertisement
limiting physical availability
outlets
times in which they can sell alcohol
distance of outlets from certain institutions
What are some interventions for reduction of alcohol related injury for which there is no evidence of effectiveness
lowering the drinking age
educational and persuasive approaches including warning labels (no sustained effect on drinking)
What are the prospects for control of alcohol related injury in different contexts?
road injuries
random breath testing
improving safety of cars
airbags
Drowning
teaching people to swim
Define ‘mental disorder’
a behavioural or psychological syndrome associates with clinically significant distress or disability (functional impairment)
A mental disorder must cause ______
clinically significant distress and disability
What is a challenge about mental health diagnosis?
there is no biological marker or test that can conclusively diagnose people. this is a point of a lot of criticisms
Mental disorders are defined by clusters of mostly ____ ____ symptoms some of which may not be _____ to ____
self reported; obvious; observers
What are the most common disorders?
anxiety disorders as a group but depression as an individual disorder
You must have ___ out of ___ symptoms to be diagnosed with major depressive disorder
5/9
One of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is a ______ (sadness or emptiness) every day, most of the day, for at least _____
depressed mood; 2 weeks
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is ______ in activities you used to enjoy. What is another term for this?
reduced interest; anhedonia
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is having ____ disturbances
sleep → fatigue (another criteria)
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is _______ retardation or ____
psychomotor; agitation
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is weight _____
change
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is _______ concentrating, holding a conversation, and ________
difficulty; making decisions
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is feeling ________ or excessive ____
worthless; guilt
one of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder is ______ thoughts or intentions
suicidal
Abnormally elevated mood or irritability is a symptom of which disorder?
Bipolar/ mania
Decreased need for sleep and an inflated self esteem are symptoms of which disorder?
bipolar/mania
excessive involvement in pleasurable but risky activities is associated with which disorder?
bipolar/mania
Why is hospital/health service data insufficient in measuring mental health epidemiology?
only tells you about the most severe cases and people who has sought help - this leaves out a lot of people
Why is it difficult to conduct mental health surveys
there is a lot of stigma around mental health conditions which makes it difficult to get people to answer questions about it
people might not know which mental disorder they have
what are the challenges of using cross sectional surveys for mental disorder prevelence?
need a very large sample especially for rate disorders
requires long interviews
requires a high response rate to reduce bias
what are the challenges of using prospective surveys for mental disorder prevalence?
usually smaller samples and restricted age ranges (limits generalisability)
What are the benefits of using prospective surveys for mental disorder prevalence?
good for measuring risk factors
What are the 3 methods/studies used to measure disorder prevalence?
cross sectional surveys
prospective surveys
mental disorder assessment
What was the sample for the NZ mental health survey?
non institutionalized general adults (16+)