Biology EOC
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
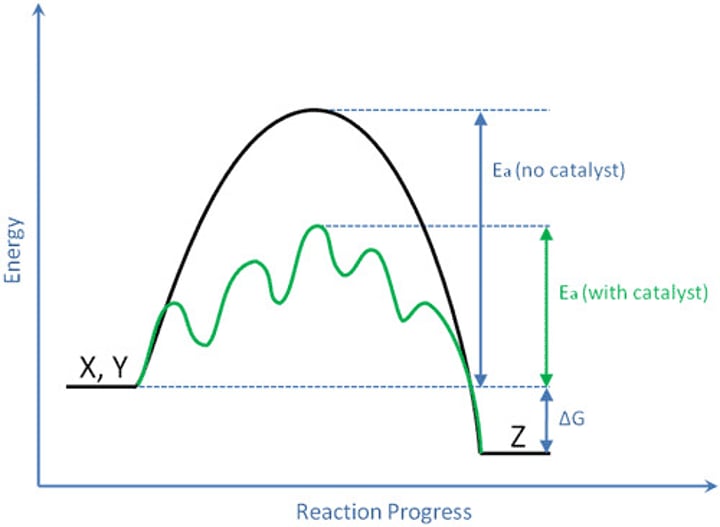
Activation Energy
amount of energy needed to start a reaction
Amino Acid
Bounded by peptide bonds; monomer of a protein
Carbohydrate
(monosaccharides) main source of energy for the cell; 1 gram = 4 calories
Catalyst
used in enzymes to lower the activation energy and speed up the reaction
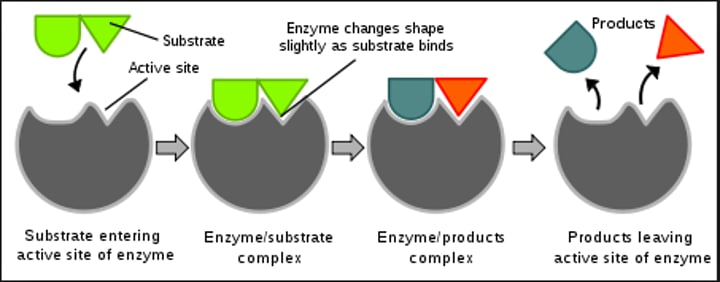
Enzyme
Protein and Catalyst; have an active site and a substrate
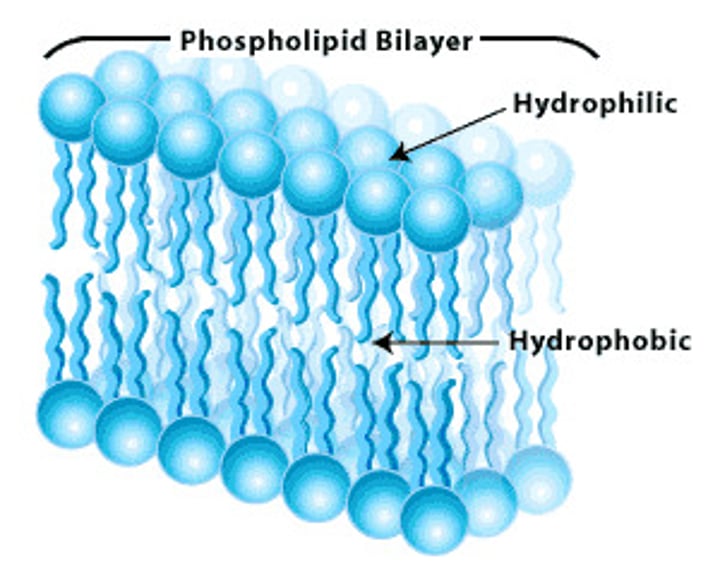
Lipid
(1 glycerol = 3 fatty acids) used for long term energy storage, make up the phospholipid bilayer; 1 gram = 9 calories
Monosaccharide
simple sugars, monomer for carbs (glucose and sucrose)
Nucleic Acids
Made of nucleotides, function is to store genetic information which can be seen in DNA and RNA
Organic Molecule
bounded molecules made of carbon
Protein
(amino acids) referred to as the building blocks
Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells; Cells come from other cells; Cells are the basic structure and function of an organism
Differentiation
How cells (stem cells) get their jobs
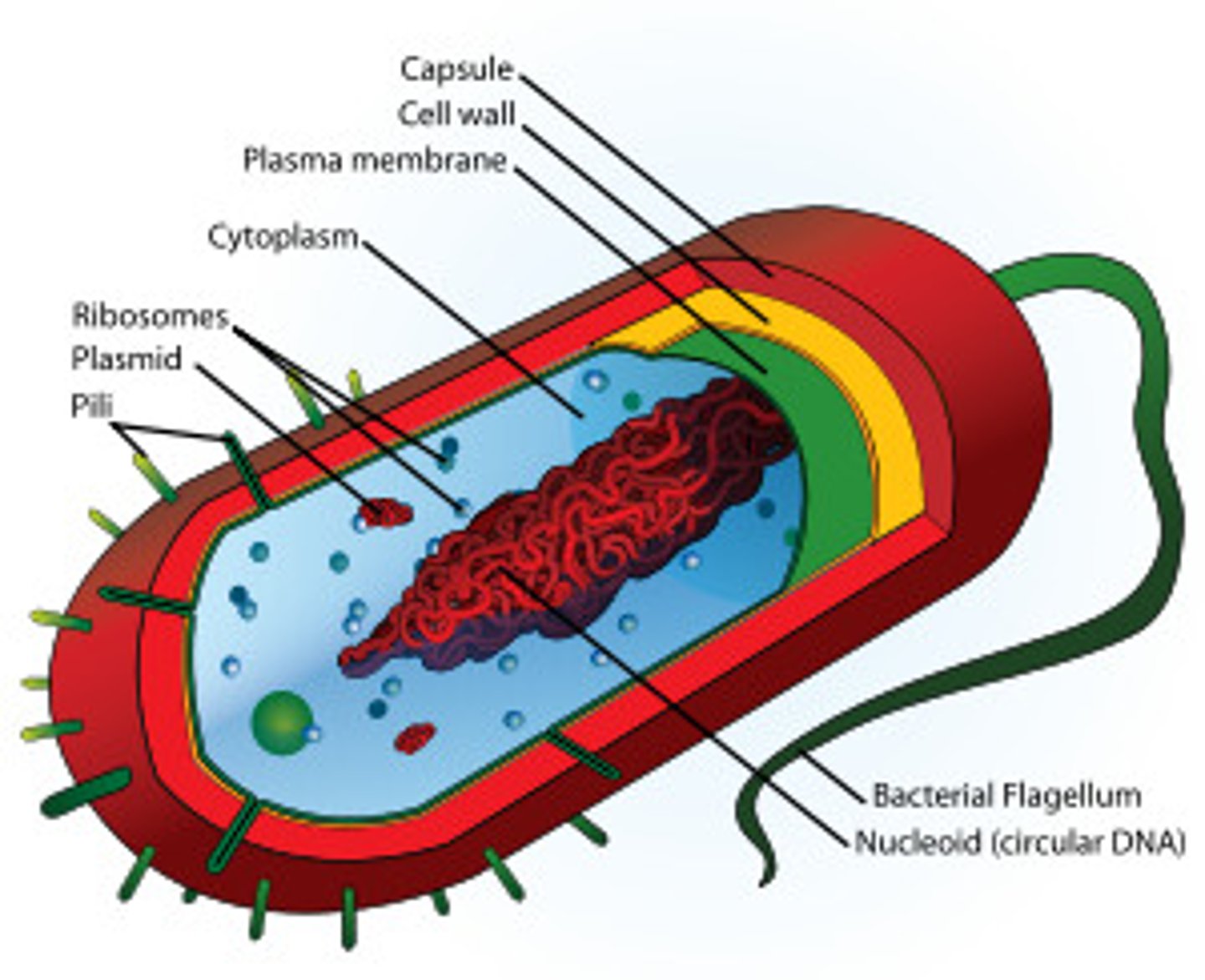
Eukaryote
Cells that have a nucleus, large, complex (Ex. Plants and Animals)

Multicellular Organisms
Organisms composed of many cells (Ex. tissue, humans, etc.)

Organelles
Small structures that perform various functions for the cell (reside within the cytoplasm)
Prokaryote
Cells with no nucleus, small, simple (Ex. Bacteria)
Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells
Unicellular Organism
Organisms composed of only one cell (Ex. Bacteria)
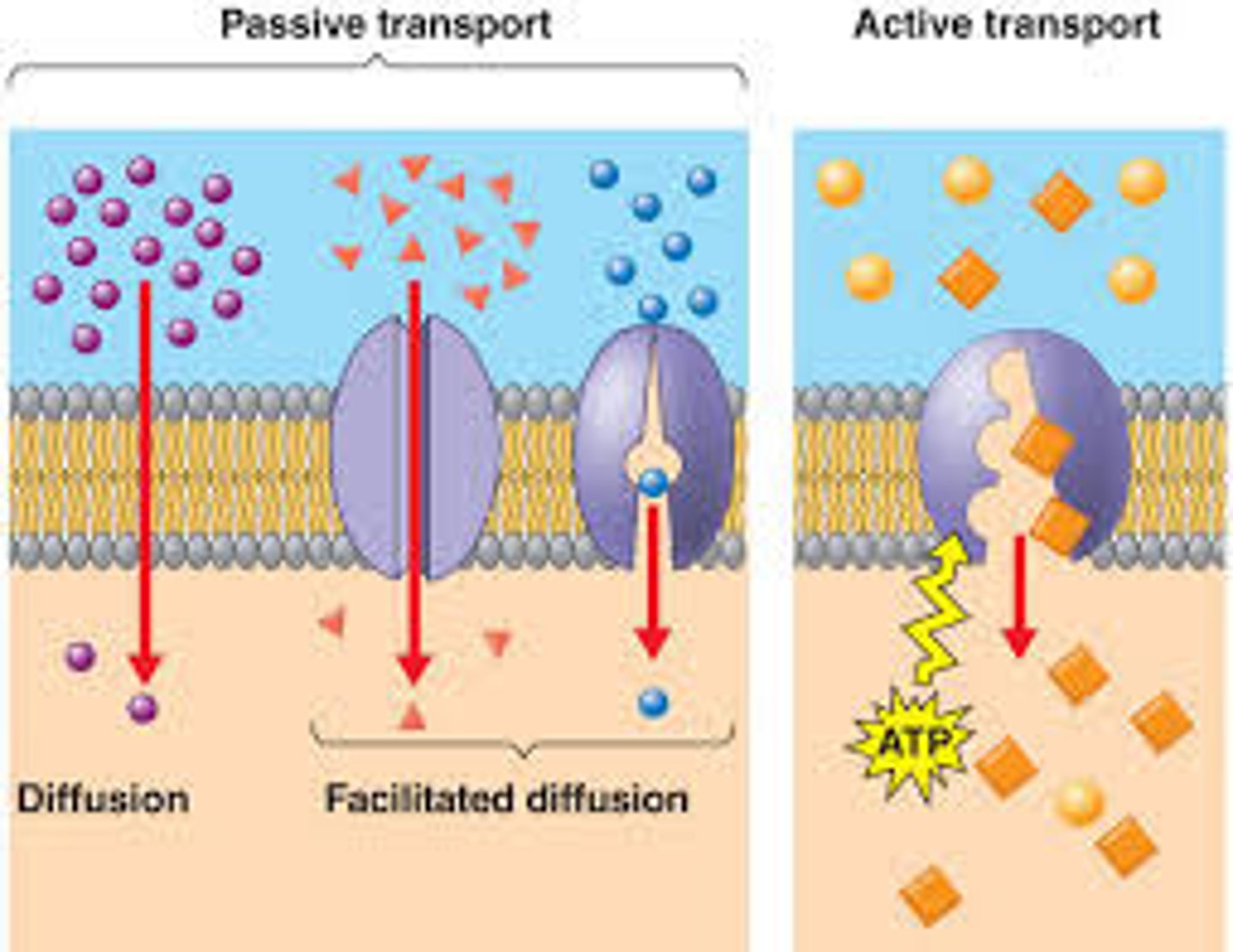
Passive Transport
No energy required; transport of small and medium materials across the plasma membrane (Osmosis, Diffusion, and Facilitated Diffusion)
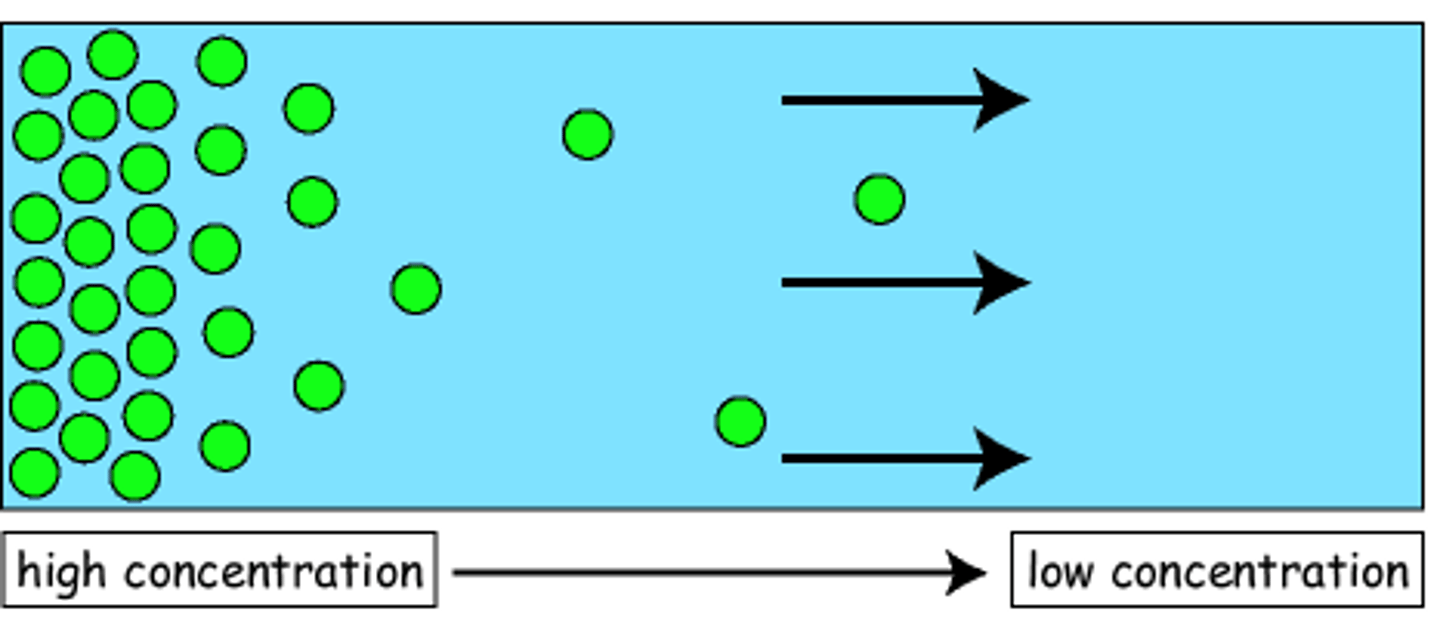
Diffusion
No energy required; transports molecules from high to low concentrations in order to even them out (for small materials)
Osmosis
No energy required; transports WATER from high to low concentrations in order to even them out

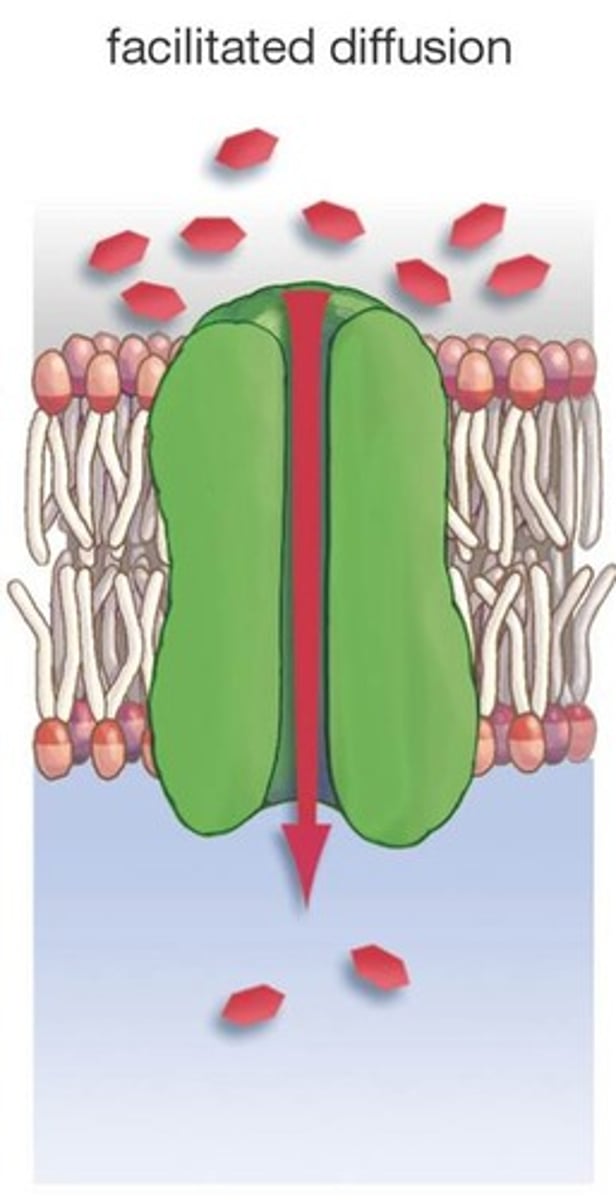
Facilitated Diffusion
"Semi-active" uses transport proteins to help move material across the plasma membrane, but still doesn't require energy
Homeostasis
Internal condition is balanced
Active Transport
Requires energy (ATP) for large molecules. Gets molecules across the cell through pumps and vesicles (endocytosis and exocytosis)
Pumps
Molecules are "pumped" by a transport protein to get across the membrane, requiring energy
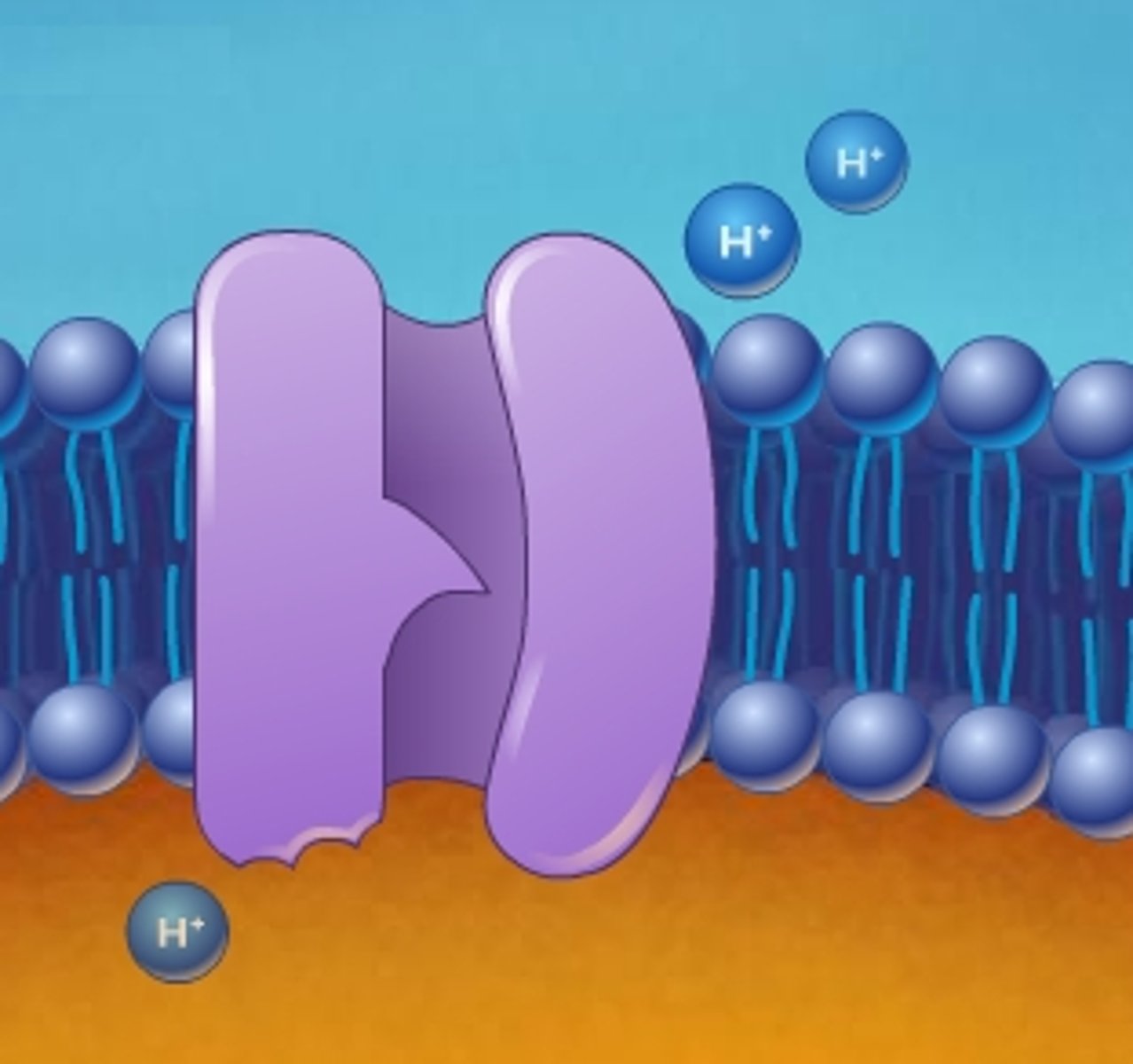
Vesicles
Used when molecules are too large to pass through the membrane, even with the help of a transport protein
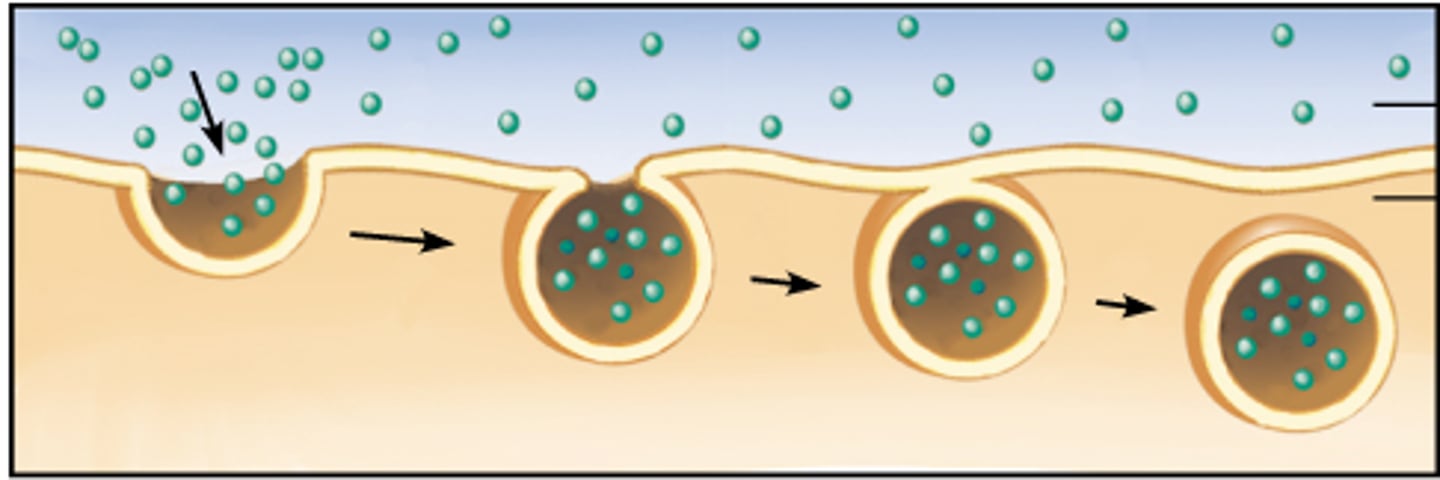
Endocytosis
Large molecules going INTO the cell
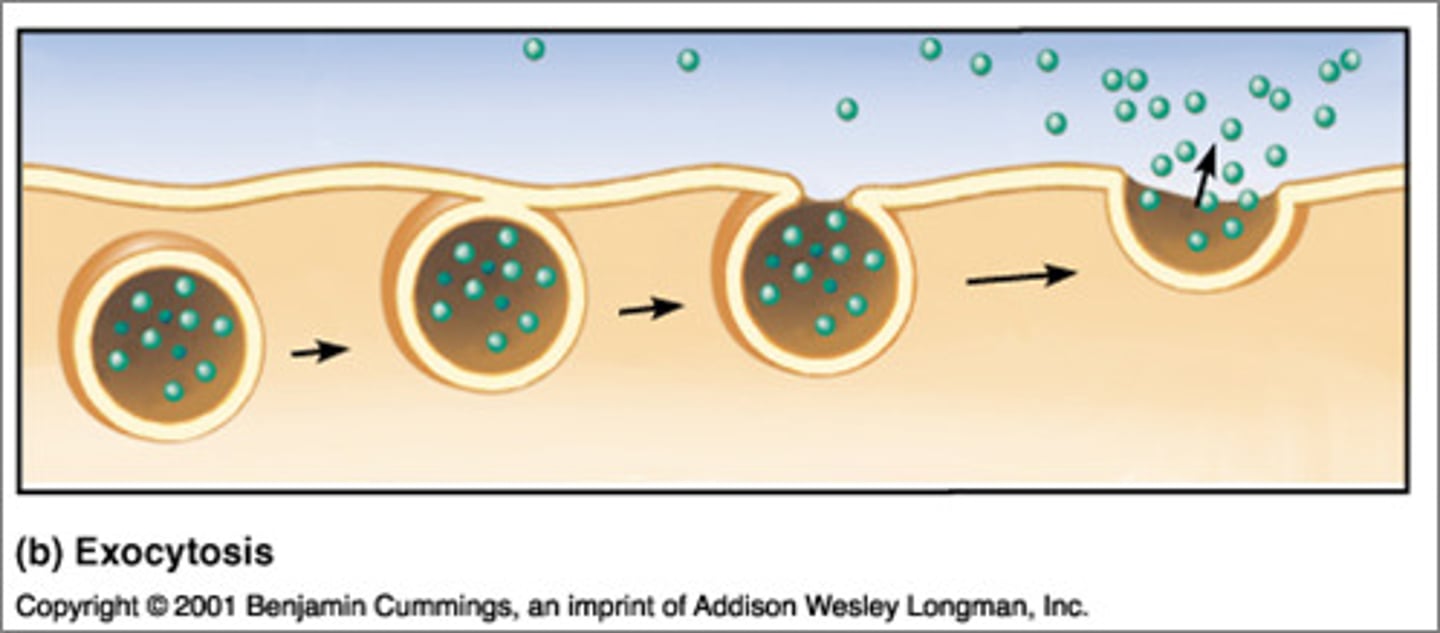
Exocytosis
Large molecules going OUT of the cell
Concentration Gradient
Drives diffusion; moves from left to right
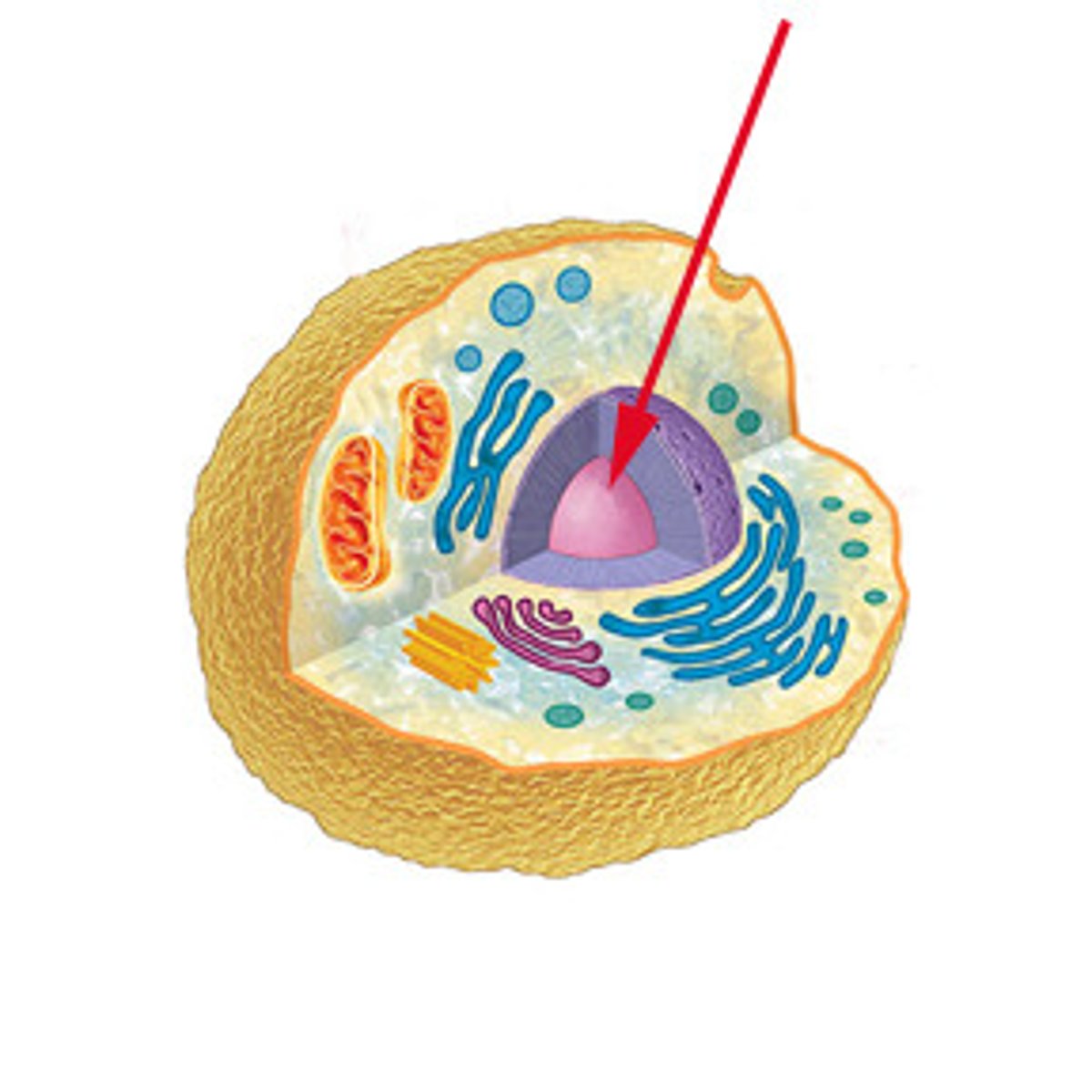
Nucleus
Only in eukaryotic cells, holds DNA
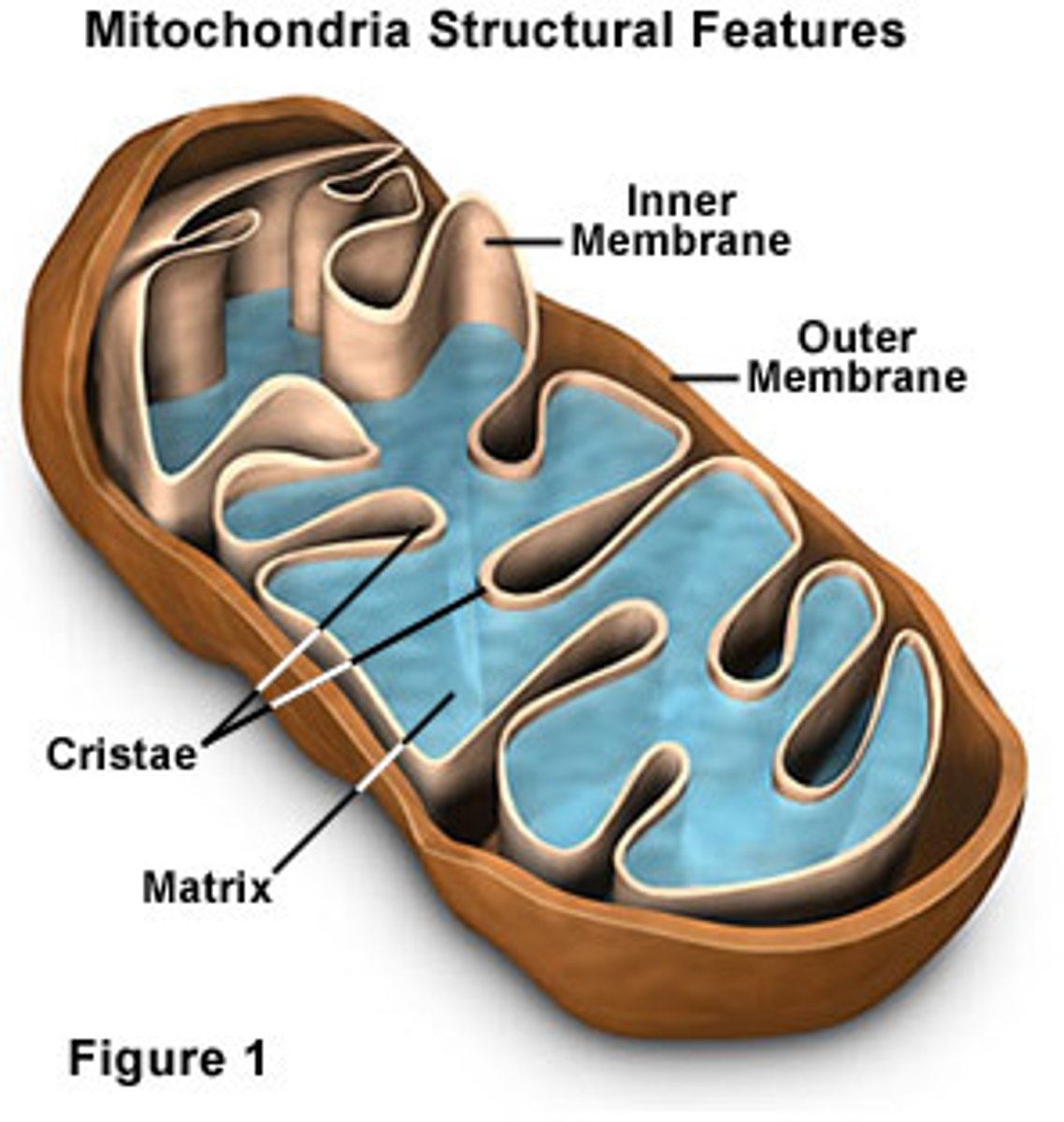
Mitochondria
Makes ATP, (Power house of the cell); Where Cellular Respiration occurs
Chloroplast
Makes glucose for the plant; Where Photosynthesis occurs

Lysosomes
Breaks down waste, food, etc.
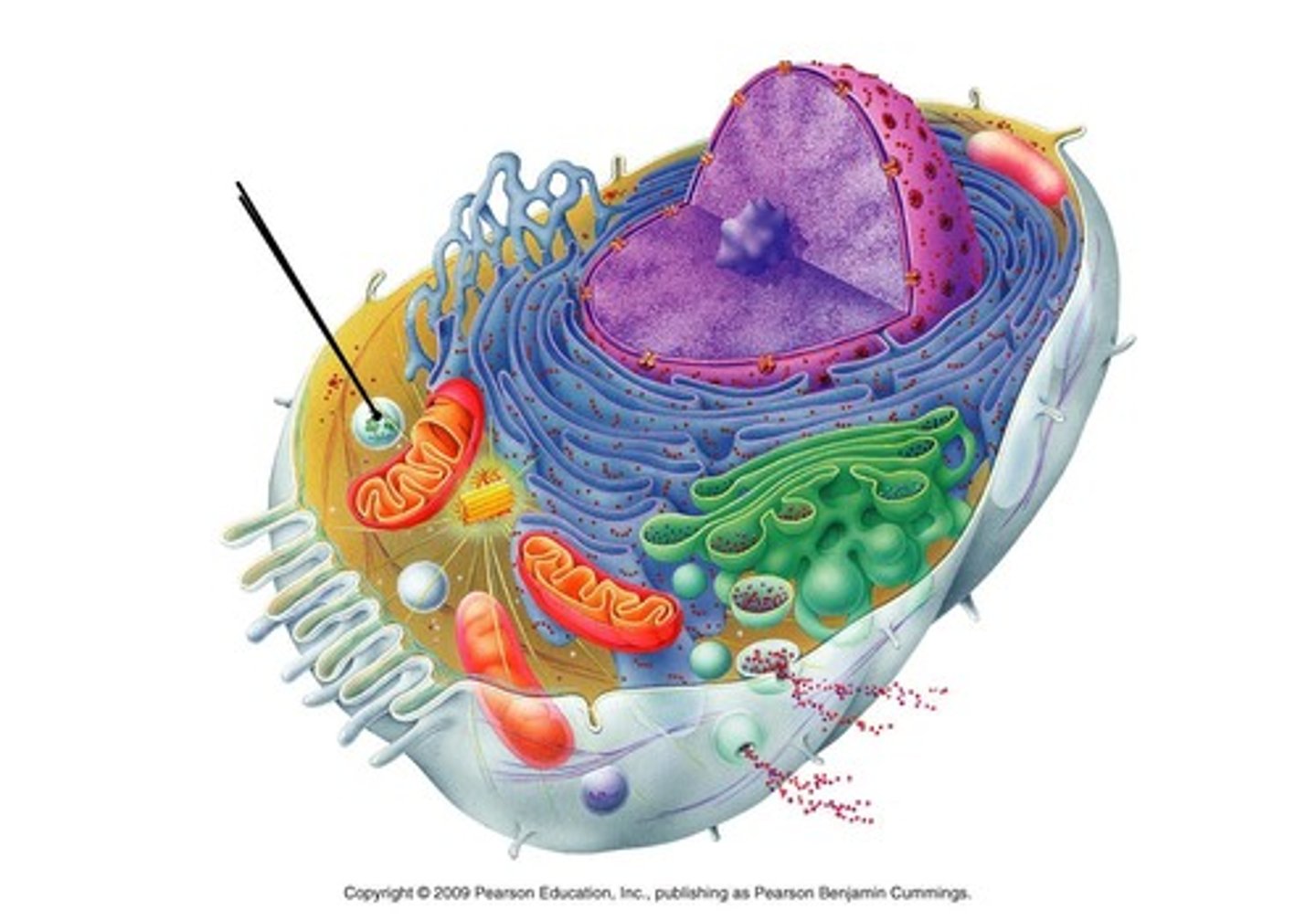
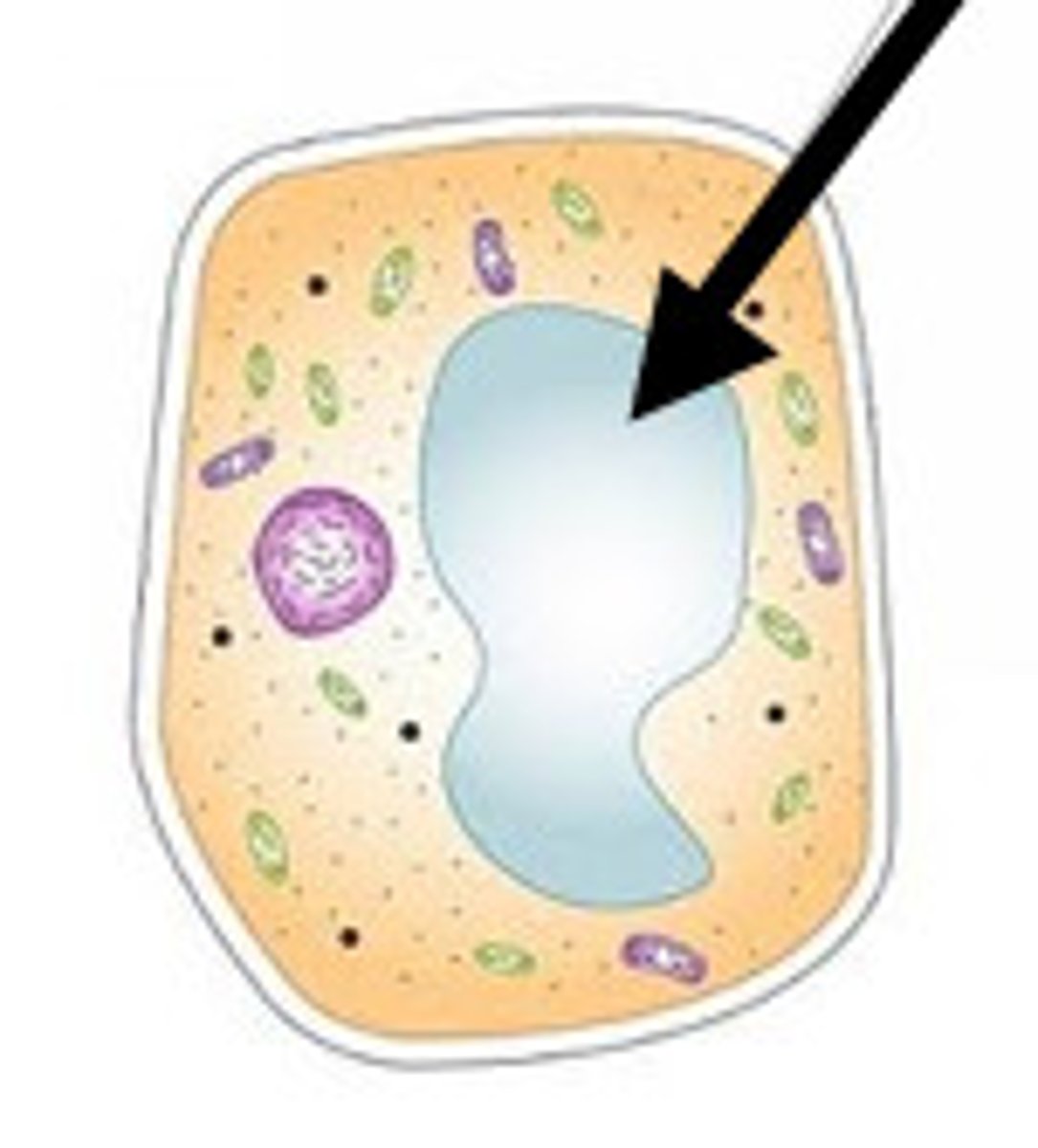
Vacuole
Where molecules, waste, etc. is stored; Bigger in Plant Cells
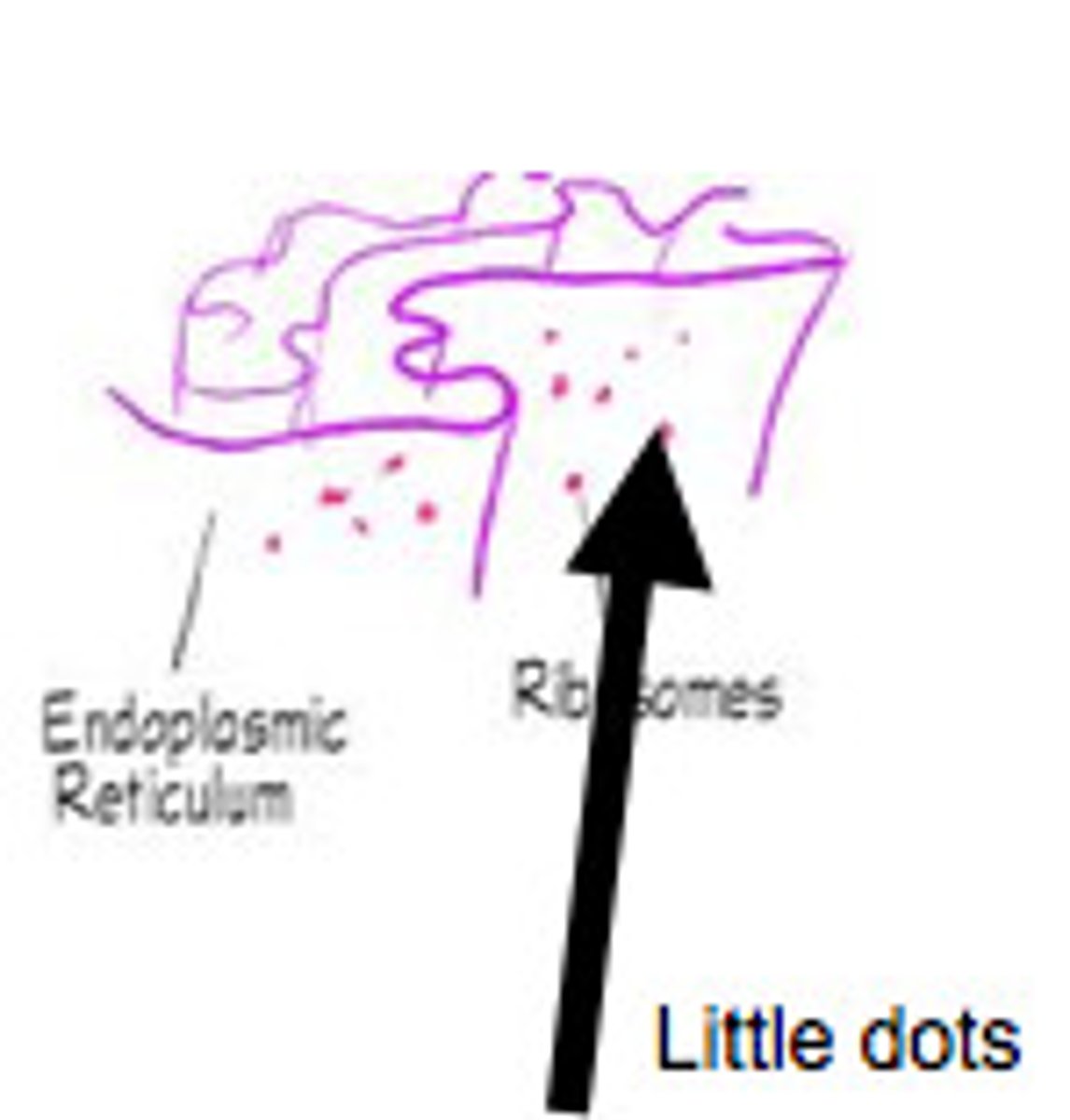
Ribosomes
Makes protein; Where translation in protein synthesis occurs
Rough ER
Transports Proteins; Has Ribosomes
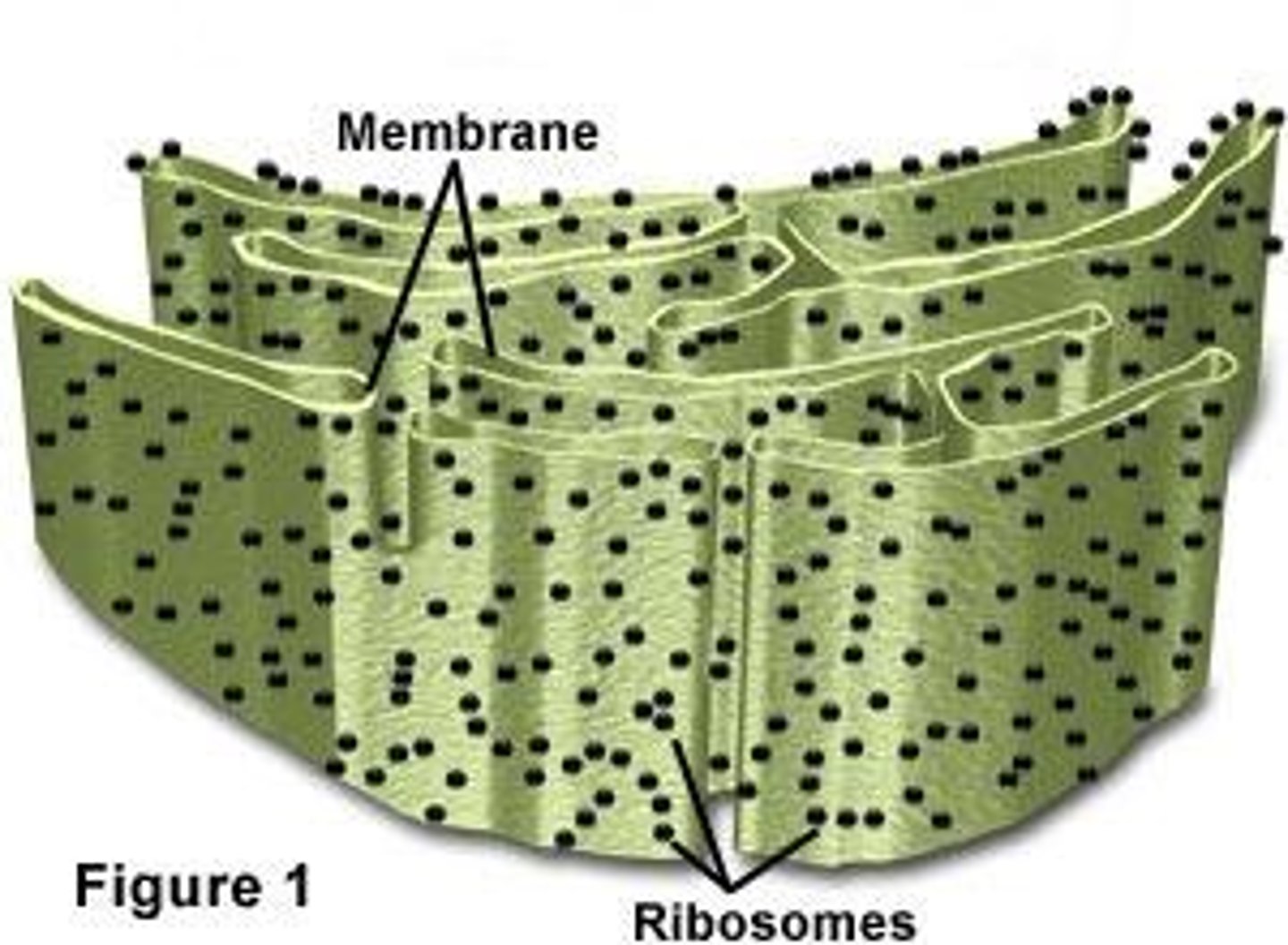
Smooth ER
Transports Proteins; Does not have Ribosomes
Golgi Apparatus
UPS of the cell; Sorts and packages molecules

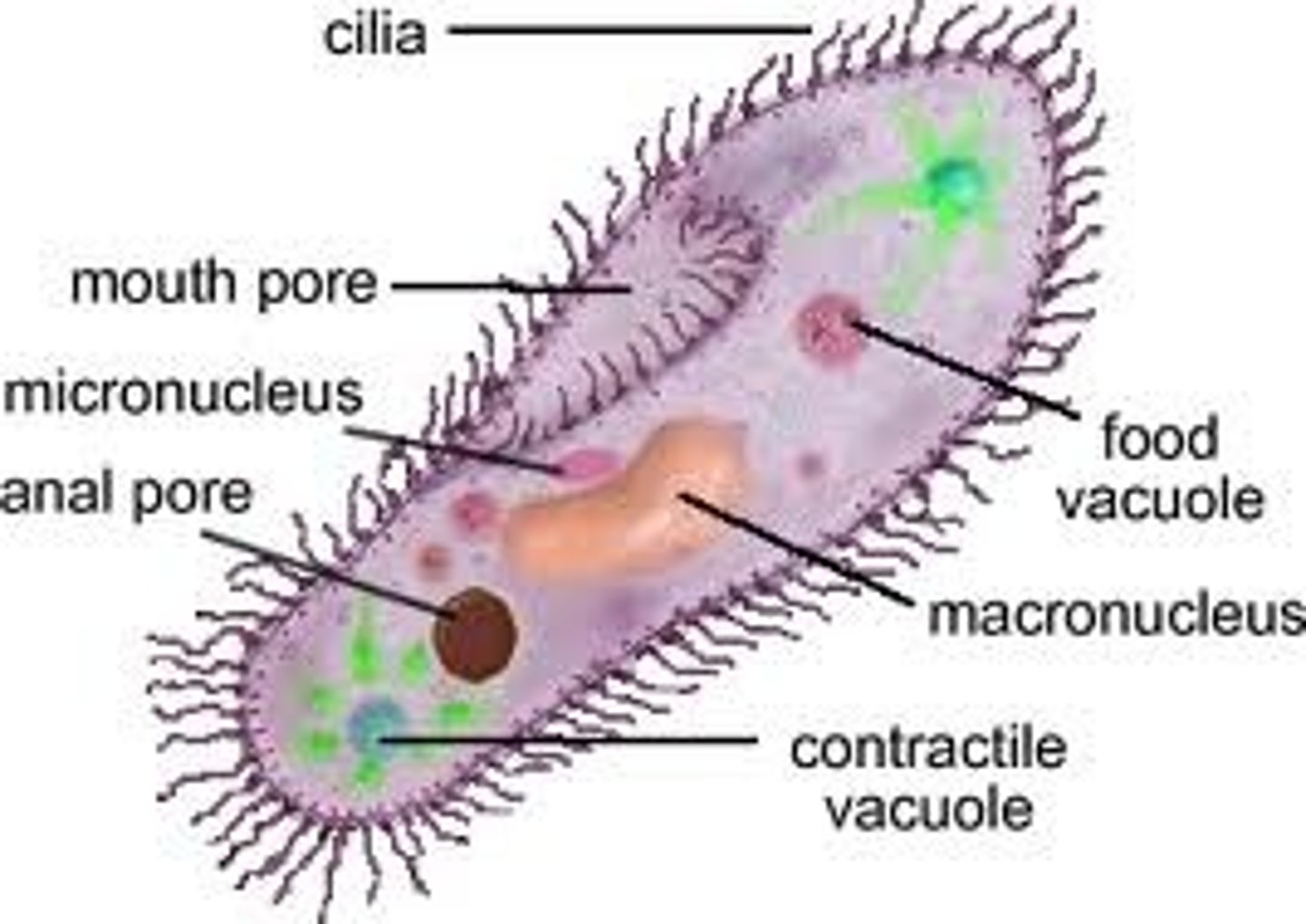
Cilia
Movement for Eukaryotes
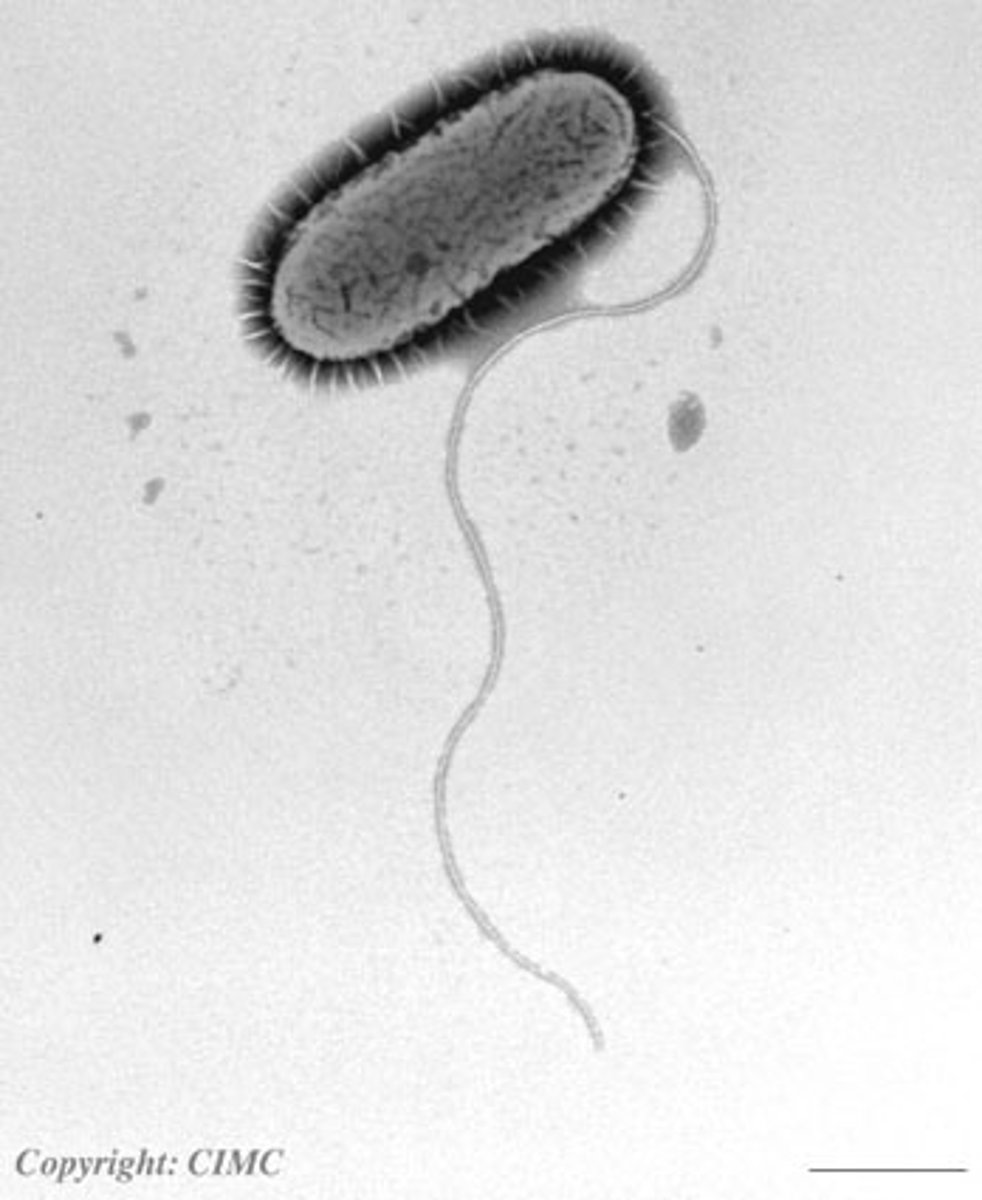
Flagella
Movement for Prokaryotes
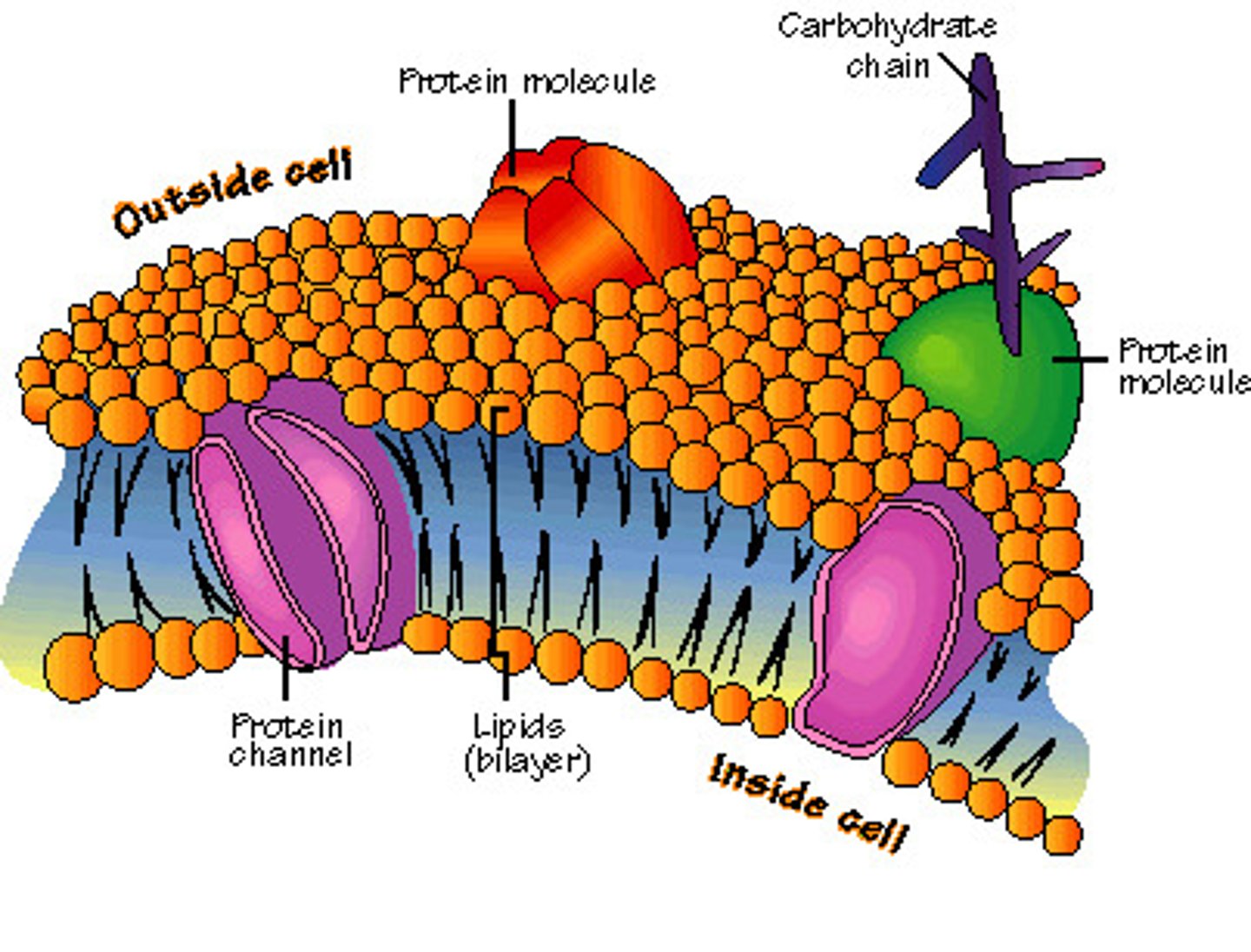
Cell Membrane
Semi-permeable, therefore maintains homeostasis
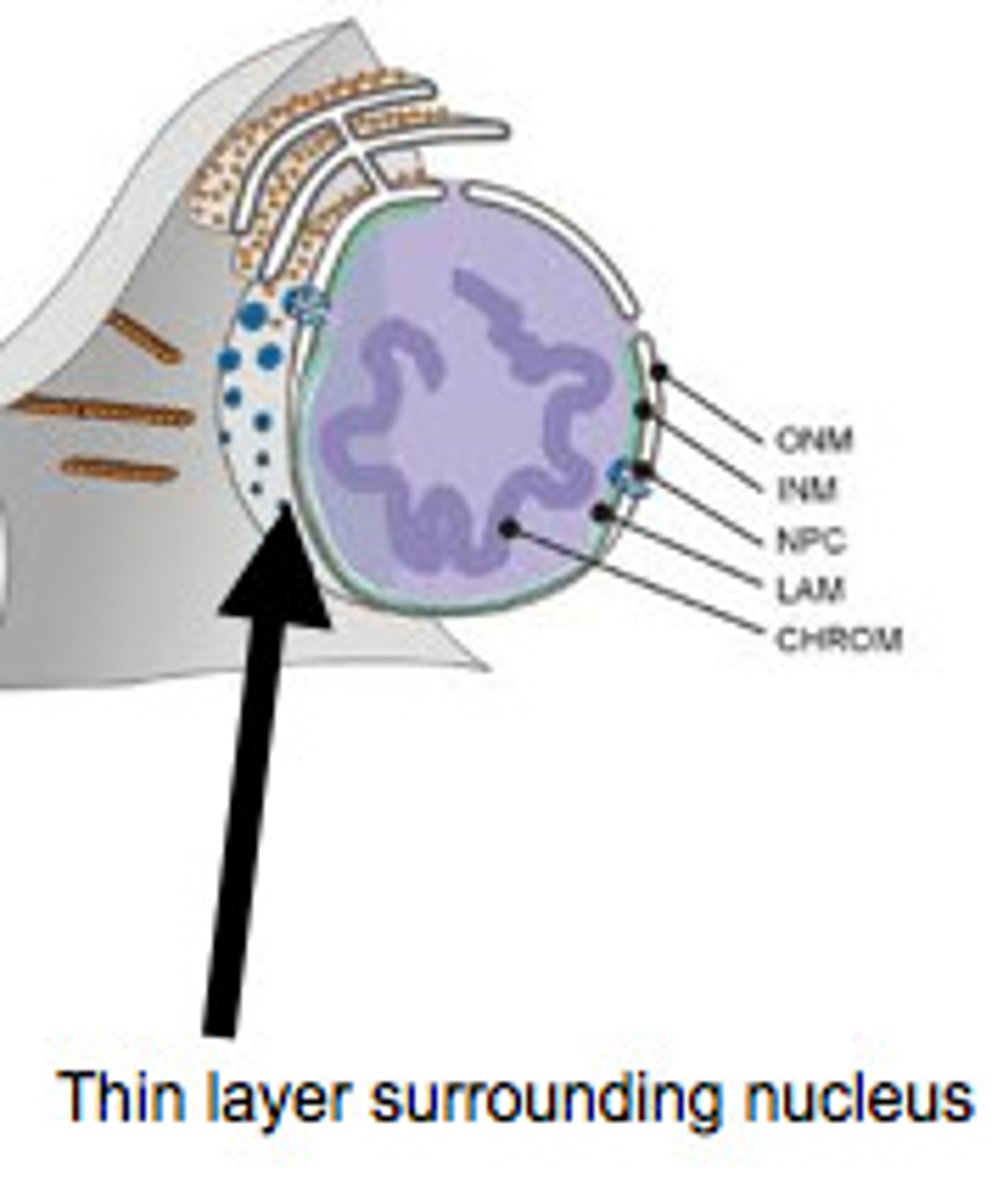
Nuclear Envelope
Controls what goes in/out of the nucleus
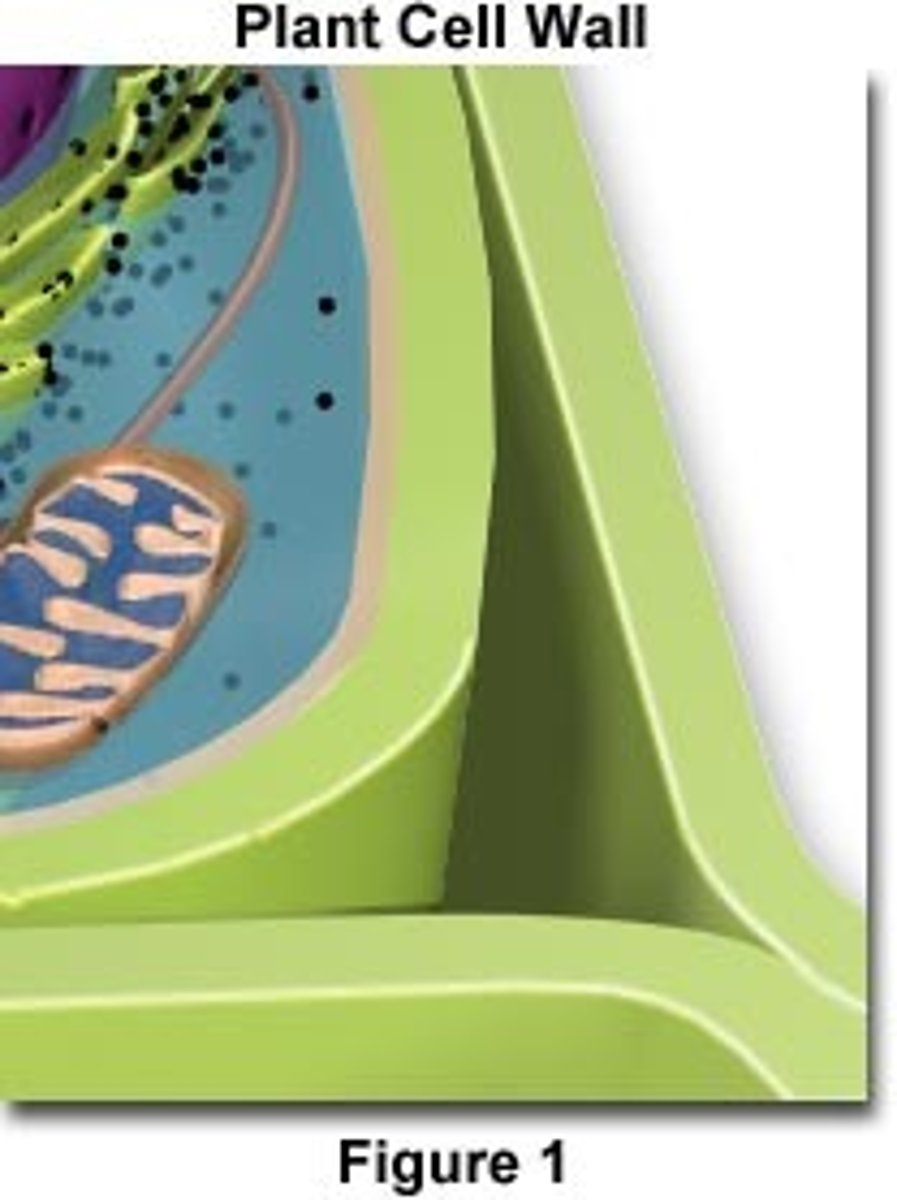
Cell Wall
Only in Plant Cells; supports and provides protection
Cytoplasm
dissolves nutrients, allowing diffusion to occur; holds all the organelles
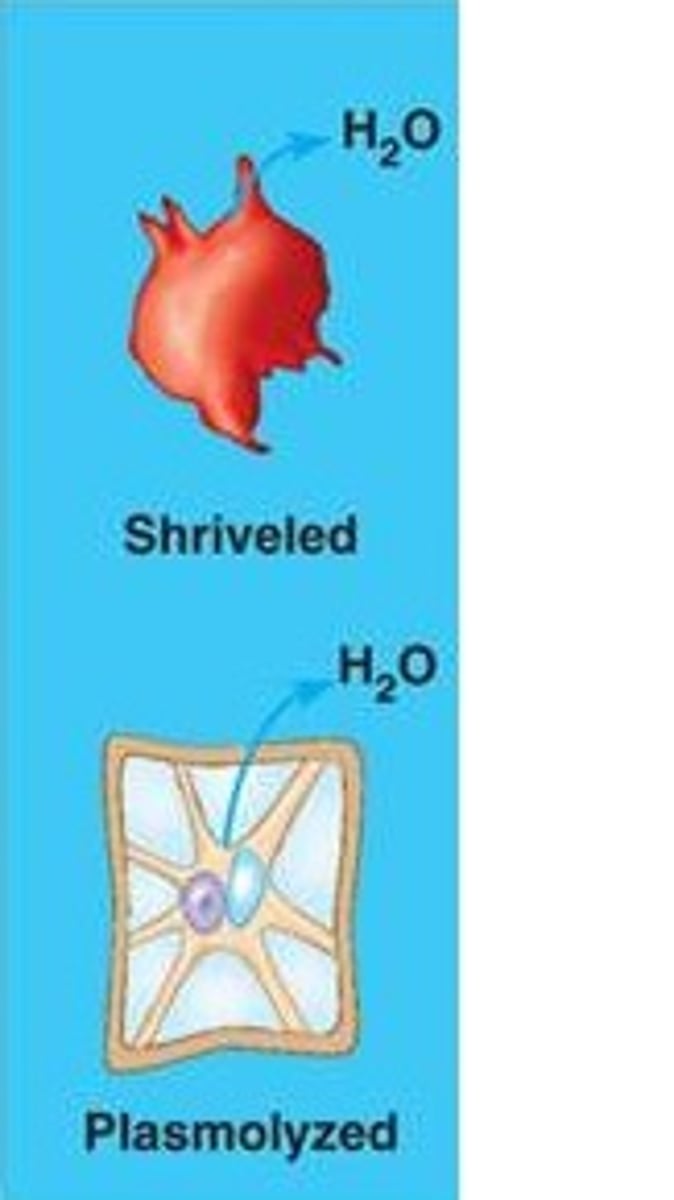
Hypotonic
Water only entering the cell, resulting in it being Lysed/Burst
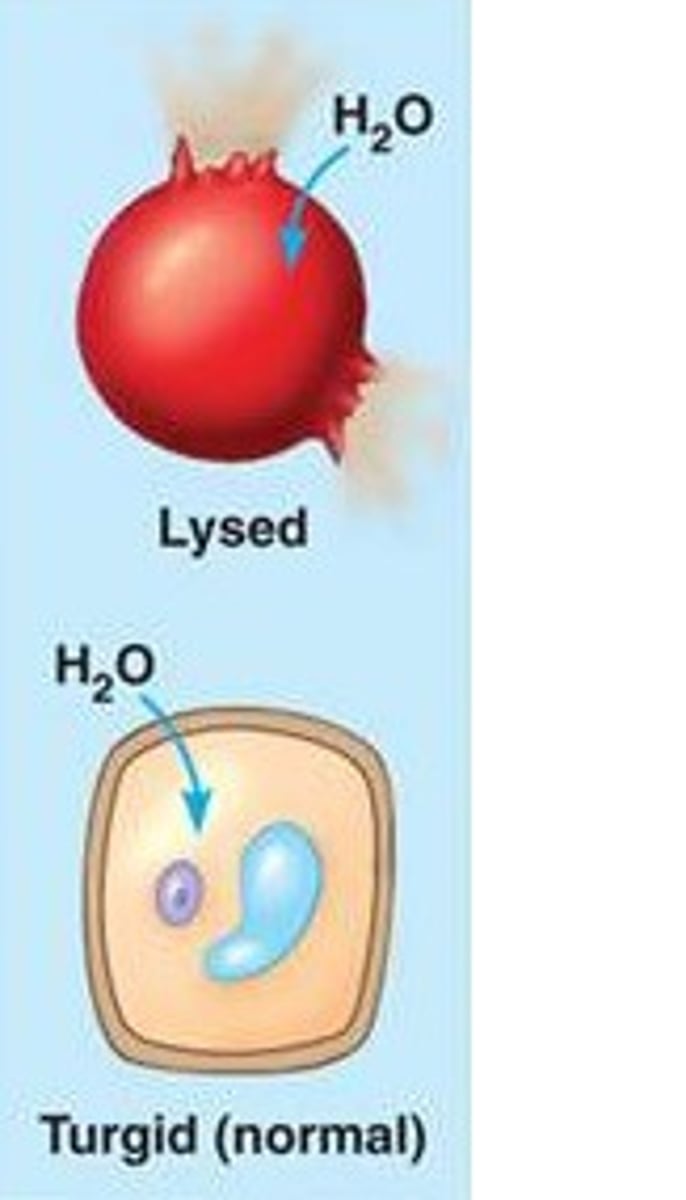
Isotonic
Same amount of water entering the cell as existing, resulting in an equilibrium, normal Cell

Hypertonic
Water only exiting the cell, resulting in it being shriveled
Photosynthesis
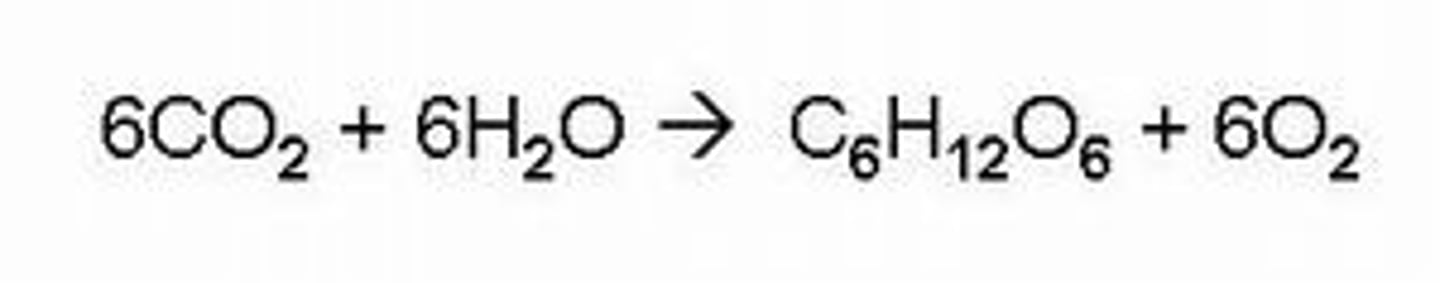
Cellular Respiration
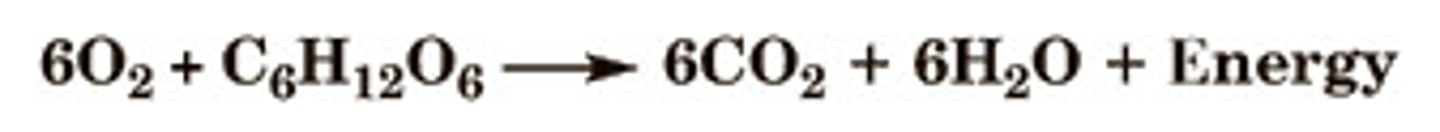
Anaerobic Respiration
Doesn't require oxygen; includes Lactic Acid Fermentation and Alcohol Fermentation of Cellular Respiration
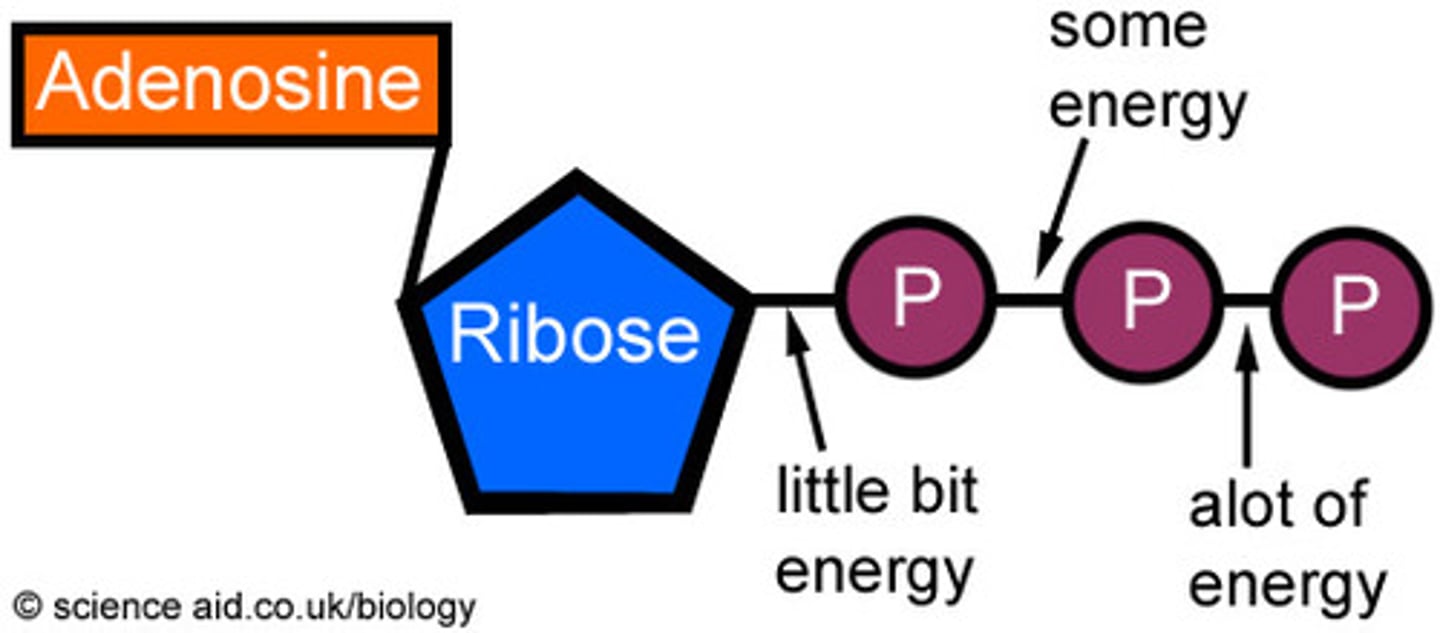
ATP
Main source of energy for the cell; made in the Mitochondria. When used in the cell it turns into ADP and returns to the Mitochondria to be converted back
Aerobic Respiration
Stage of Cellular Respiration that requires Energy; includes the Krebs Cycle and ETC
Lactic Acid Fermentation
In Anaerobic Respiration- pyruvates break down creating energy (found in muscles)
Alcohol Fermentation
In Anaerobic Respiration- occurs mostly in yeast, pyruvates break down forming alcohol, CO2, and releasing energy
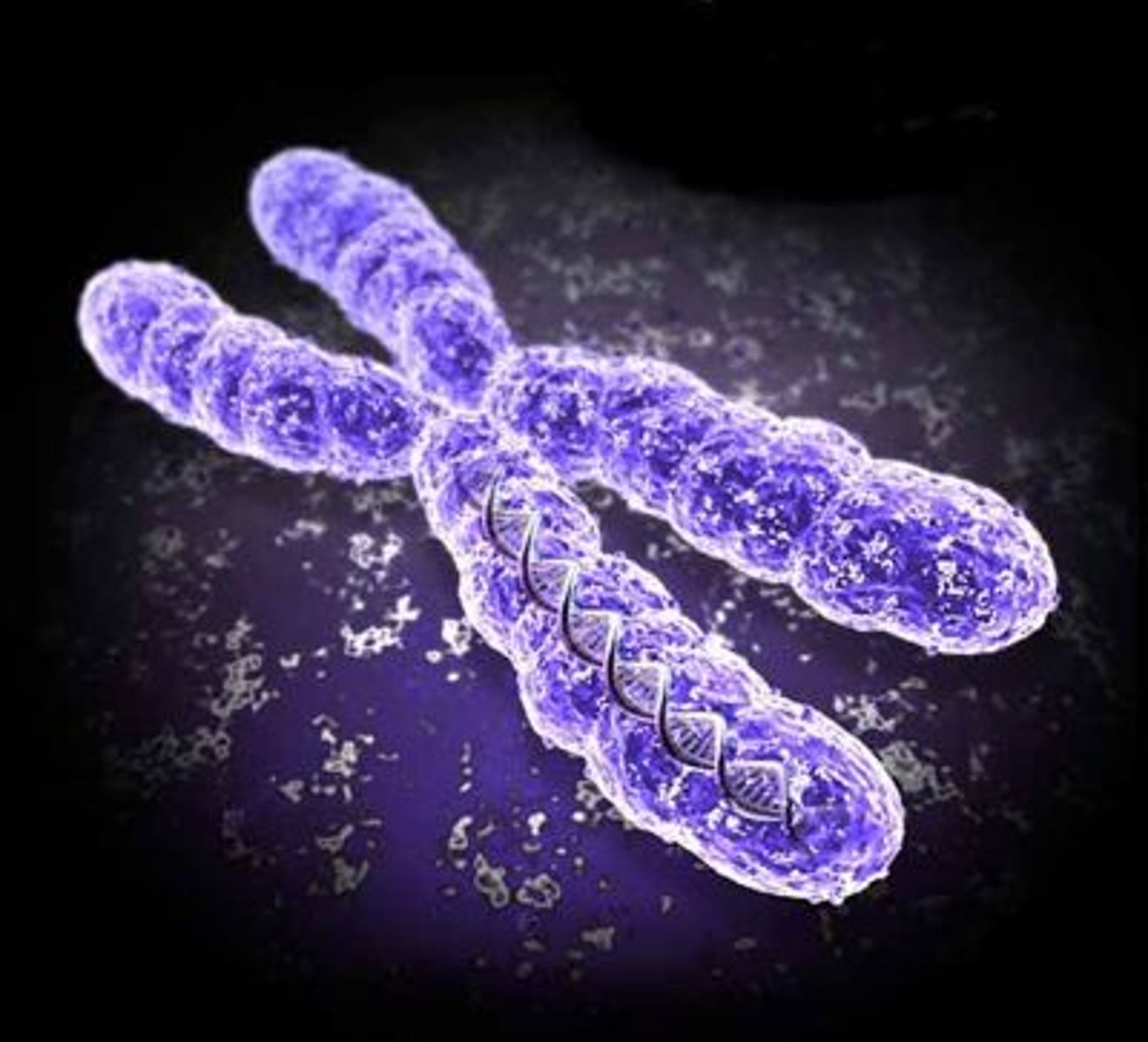
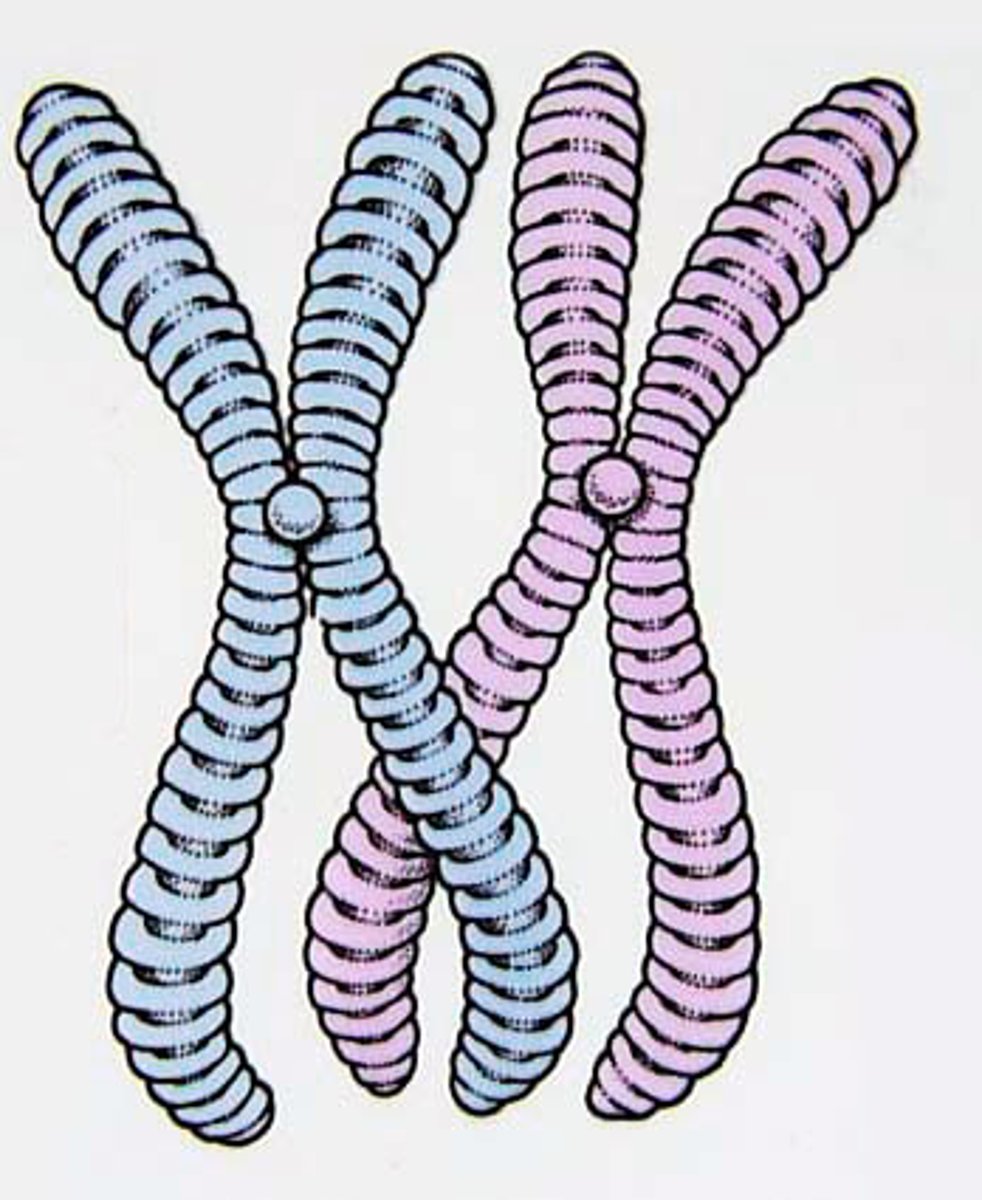
Chromosome
long thread of DNA containing genetic information
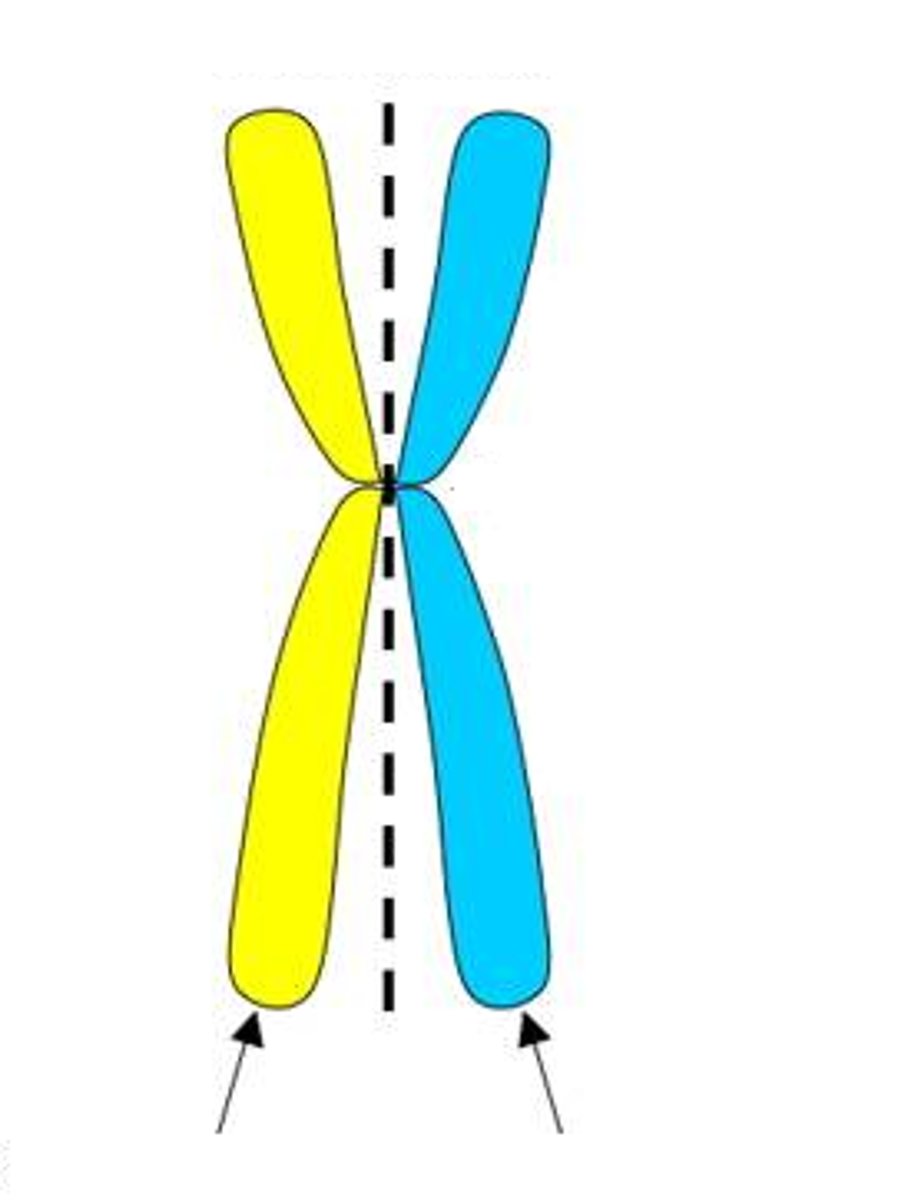
Sister Chromatid
One of 2 strands of a chromosome that becomes visible during mitosis
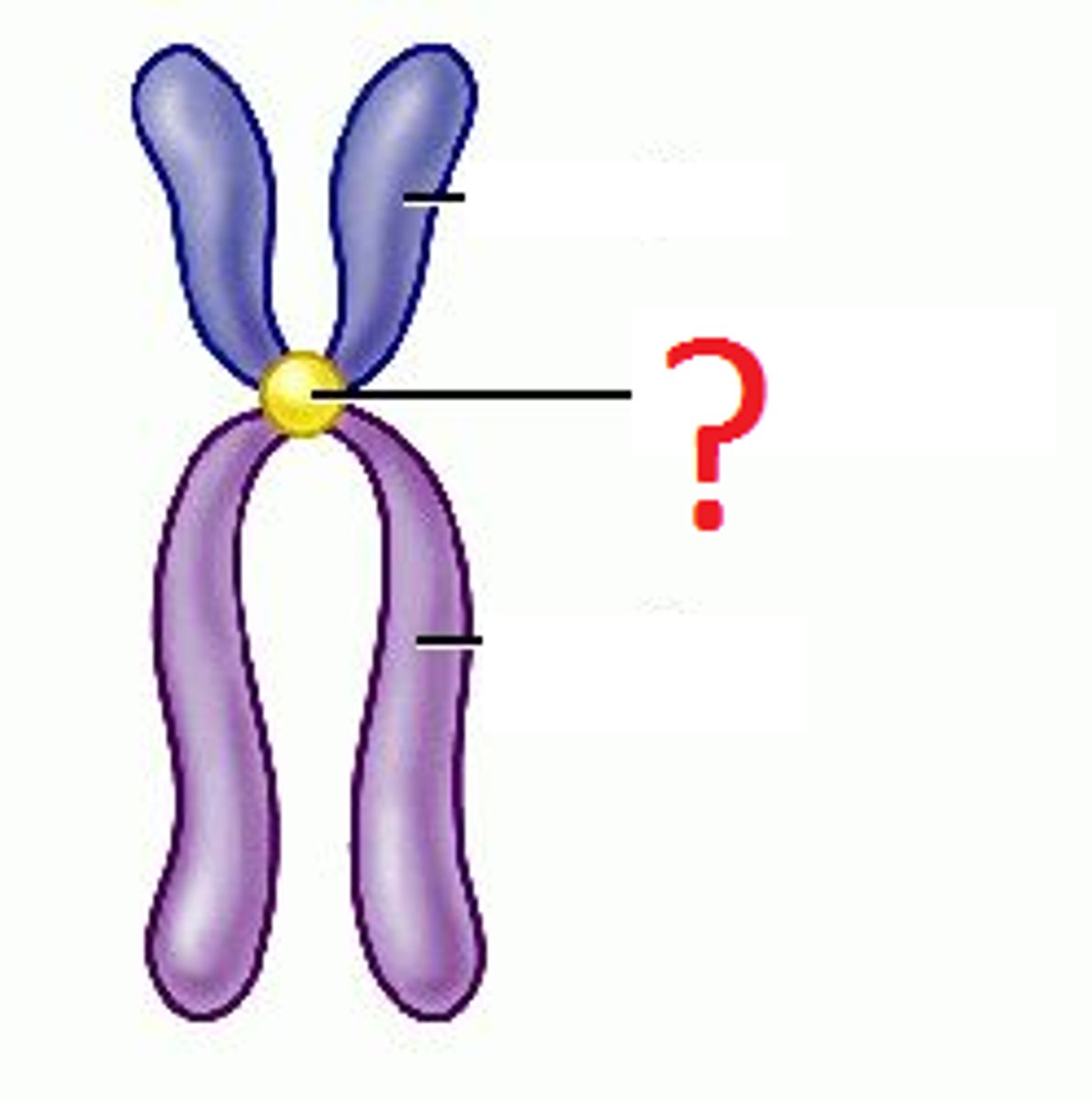
Centromere
region of chromosomes that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis
Centriole
(fishing pole) cell organelle that produces spindle fibers
Spindle Fibers
Fibers that extend across a dividing eukaryotic cell and assists in the separation of chromosomes
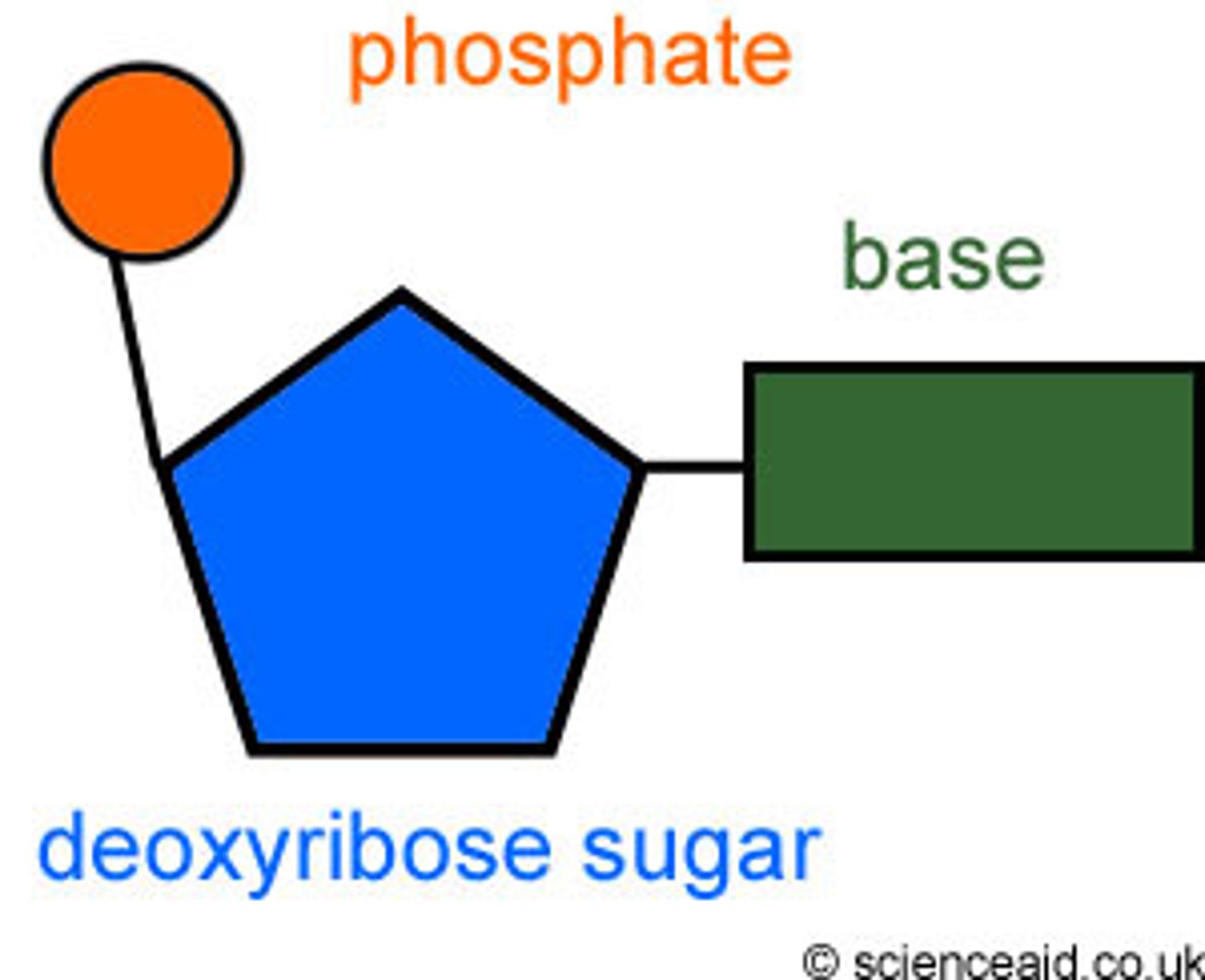
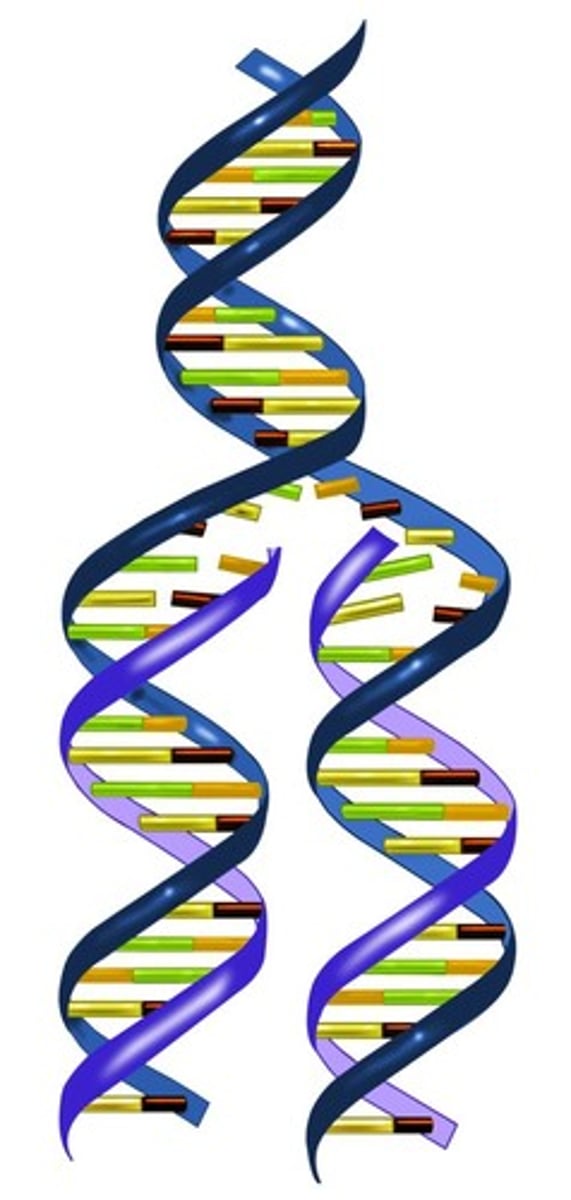
DNA
Makes up chromosomes and copies itself during cell division, provides a blueprint for protein synthesis by specific arrangement of nitrogenous bases; Deoxyribose, Double Helix

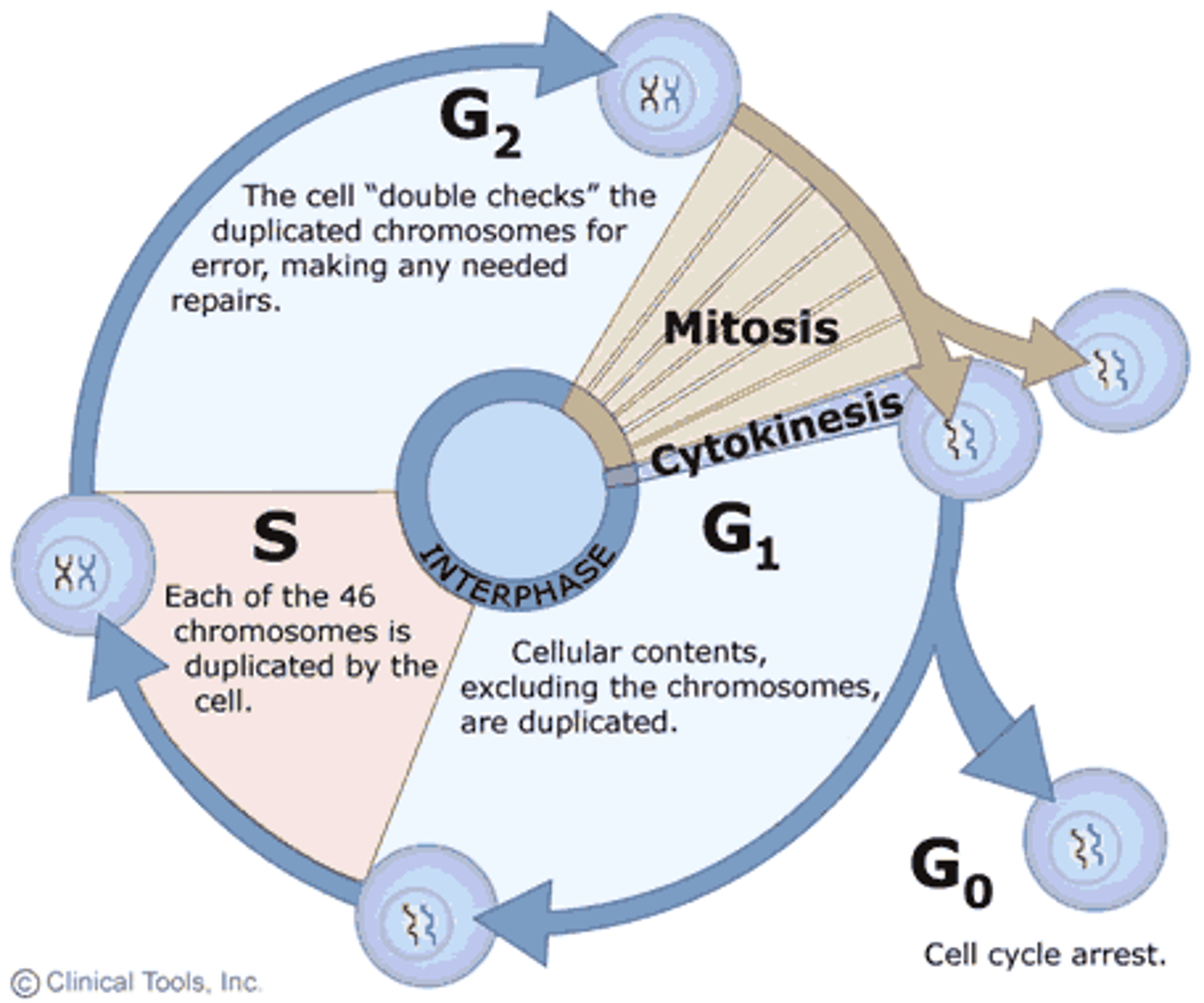
Cell Cycle
Repeated pattern of growth and division that occurs in eukaryotes
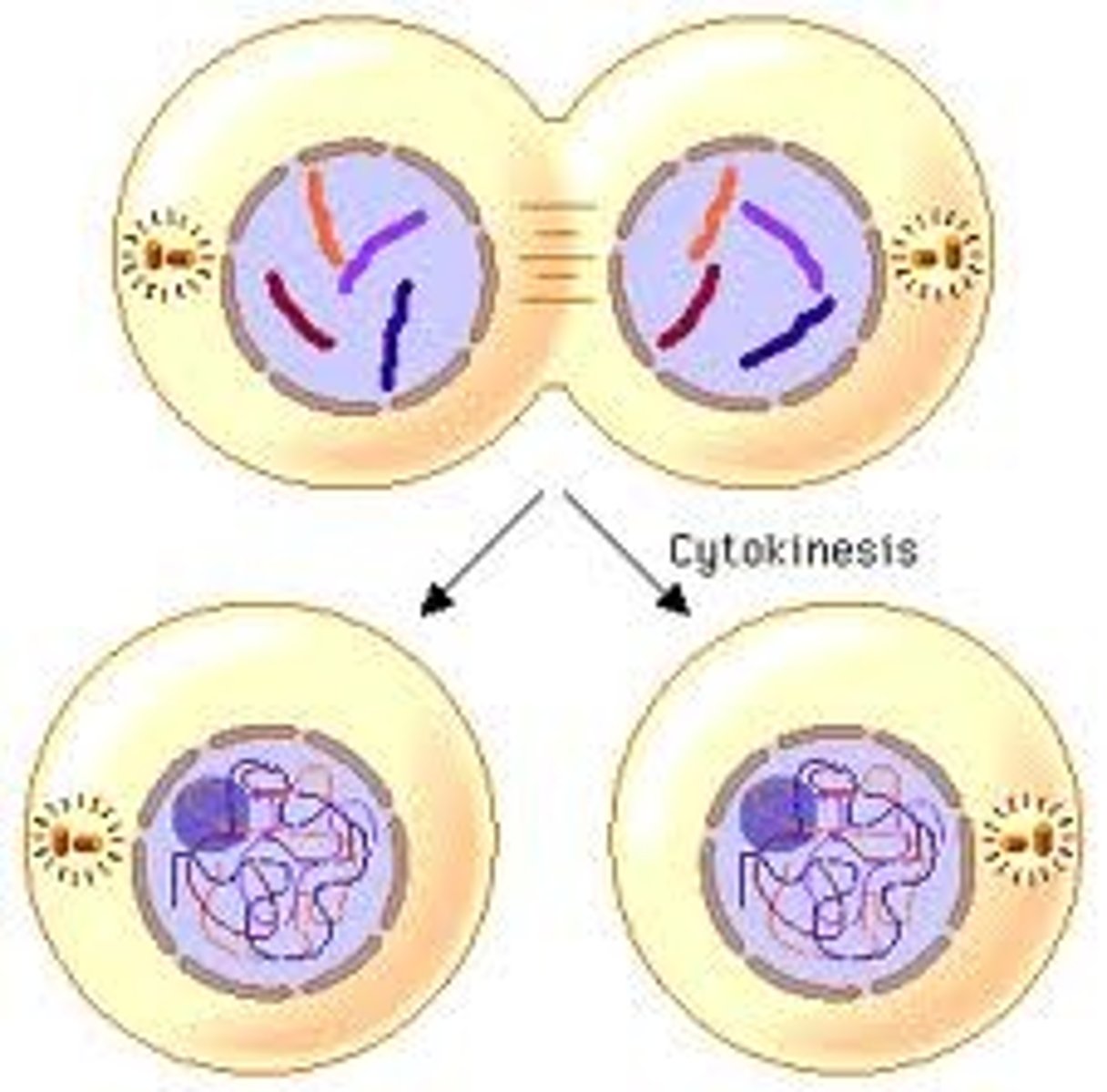
Daughter Cells
Created at the end of mitosis, each has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell and will be identical to each other
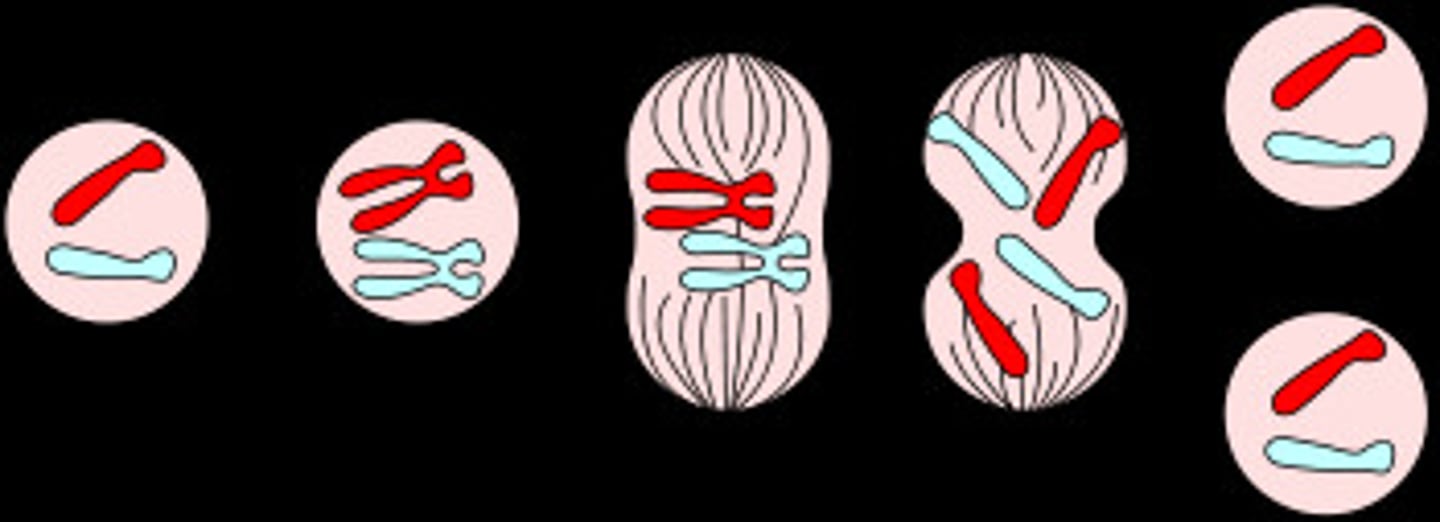
Mitosis
Somatic Cells undergo this in order to repair and regrow, creating two identical diploid daughter cells
Interphase
G1: growth
S: (synthesis) replicate DNA
G2: growth
Prophase
Preparing, Cell membrane begins to break down and spindle fibers form

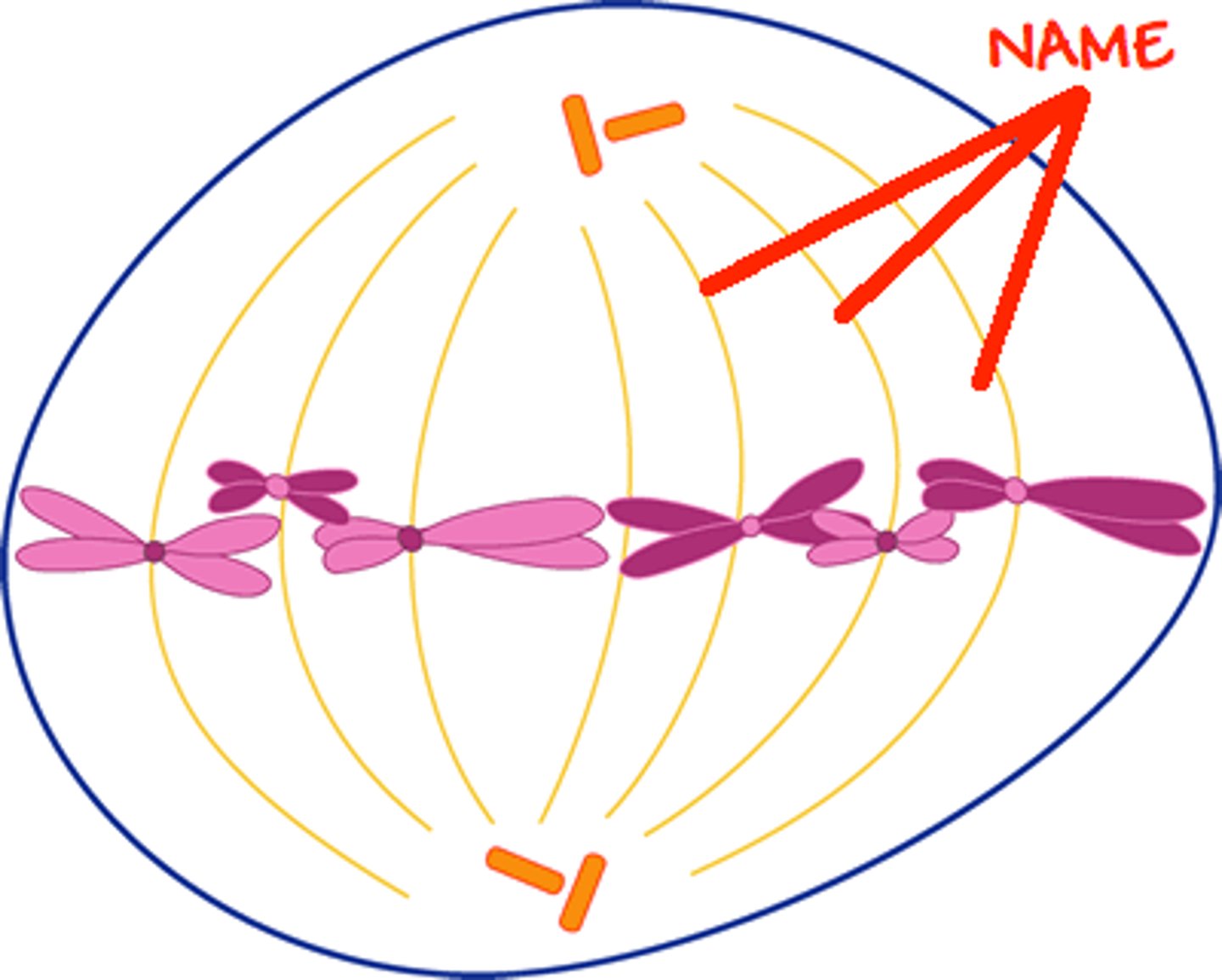
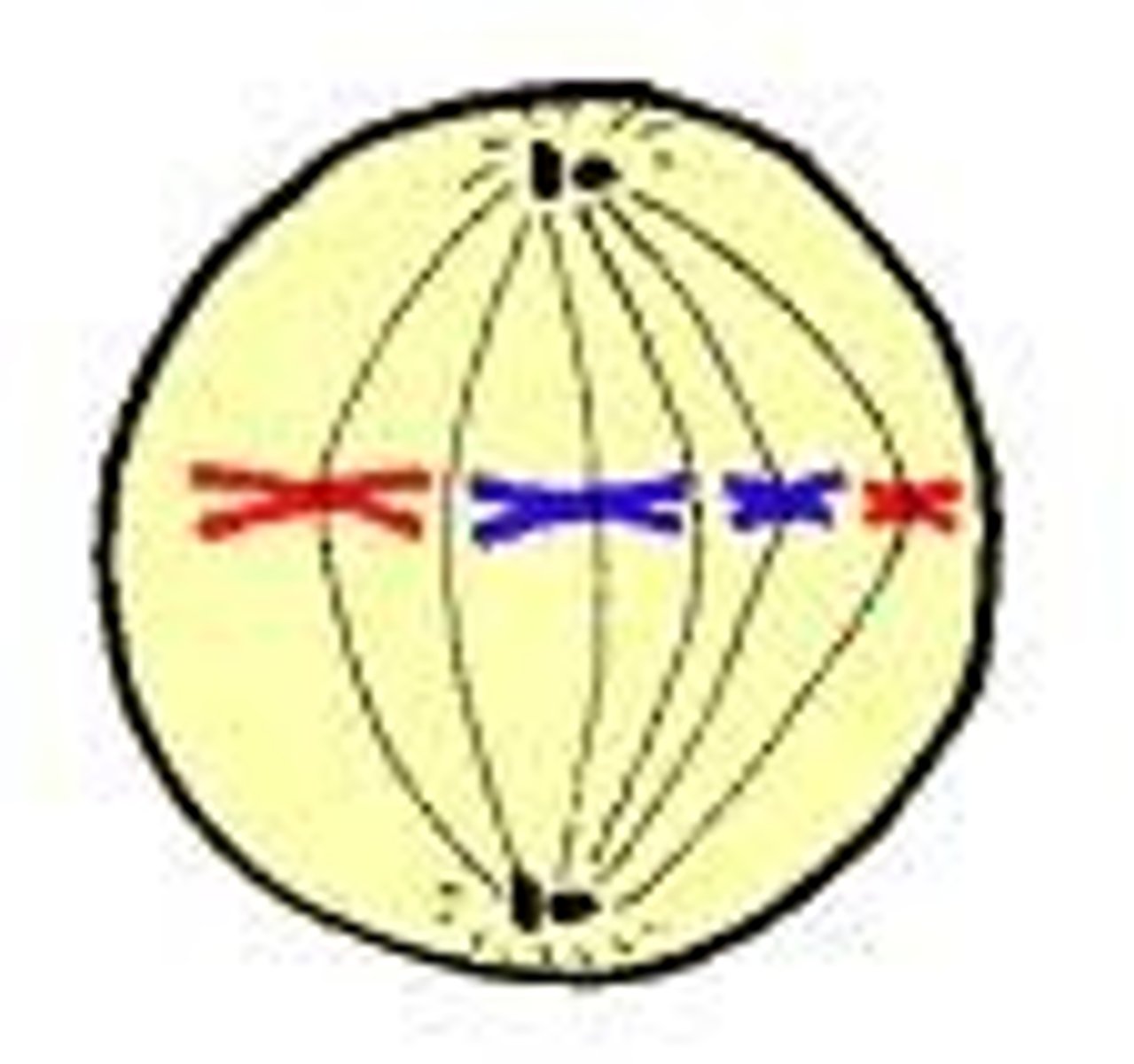
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle and spindle fibers attach to the centromere
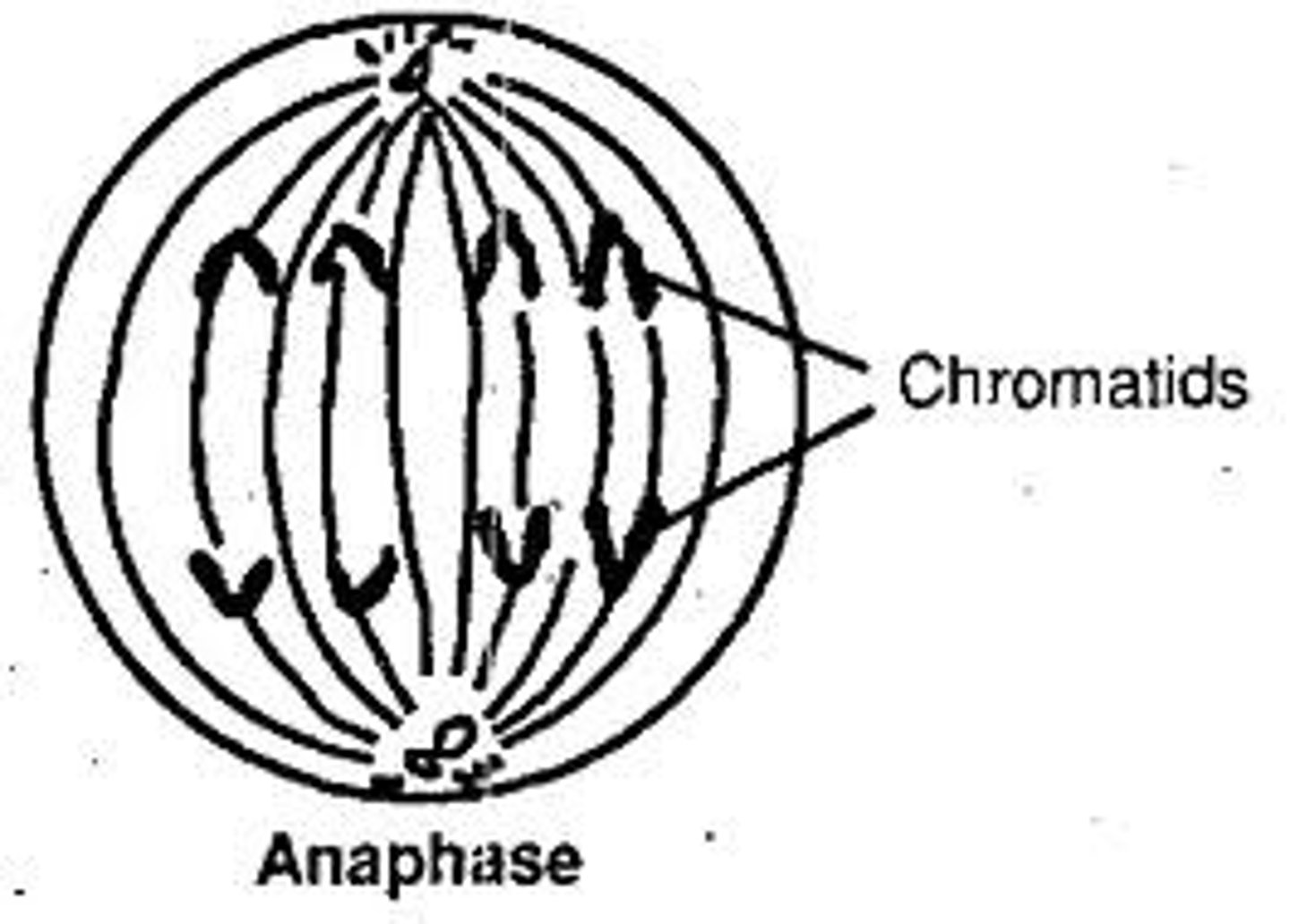
Anaphase
Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart, pulling them away from the center of the cell
Telophase
Cells membrane forms, spindle fibers retract, and chromosomes uncoil as the cell starts to become two
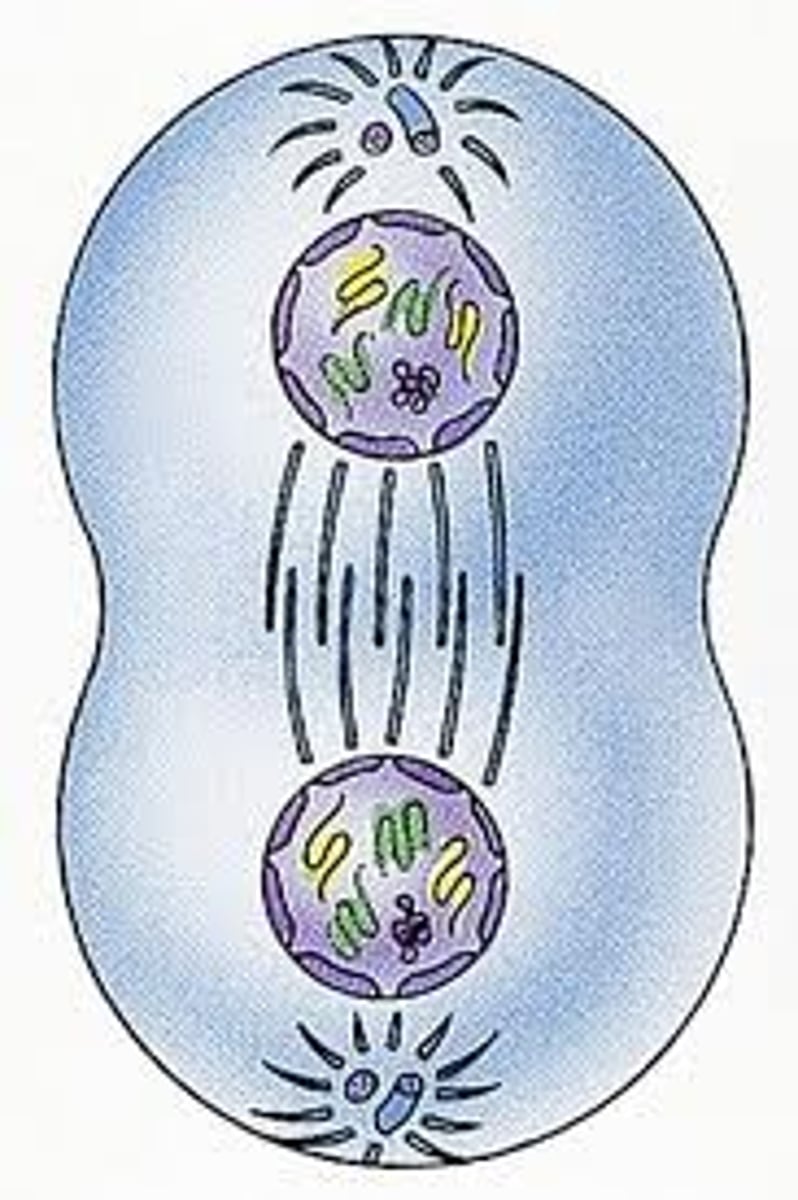
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm into two individual cells
Cancer
Uncontrolled Cell Growth (tumor)
Gamete
Sexual reproductive cell (egg and sperm)
Somatic
Body cell (liver, skin, etc.)
Haploid
(1n) one set of chromosomes (egg and sperm)
Diploid
(2n) two sets of chromosomes from each parent
Homologous Pair
Cluster of four chromosomes, two from male and two from female, can exchange genetic information through crossing over
Zygote
offspring (baby) where the egg and sperm meet
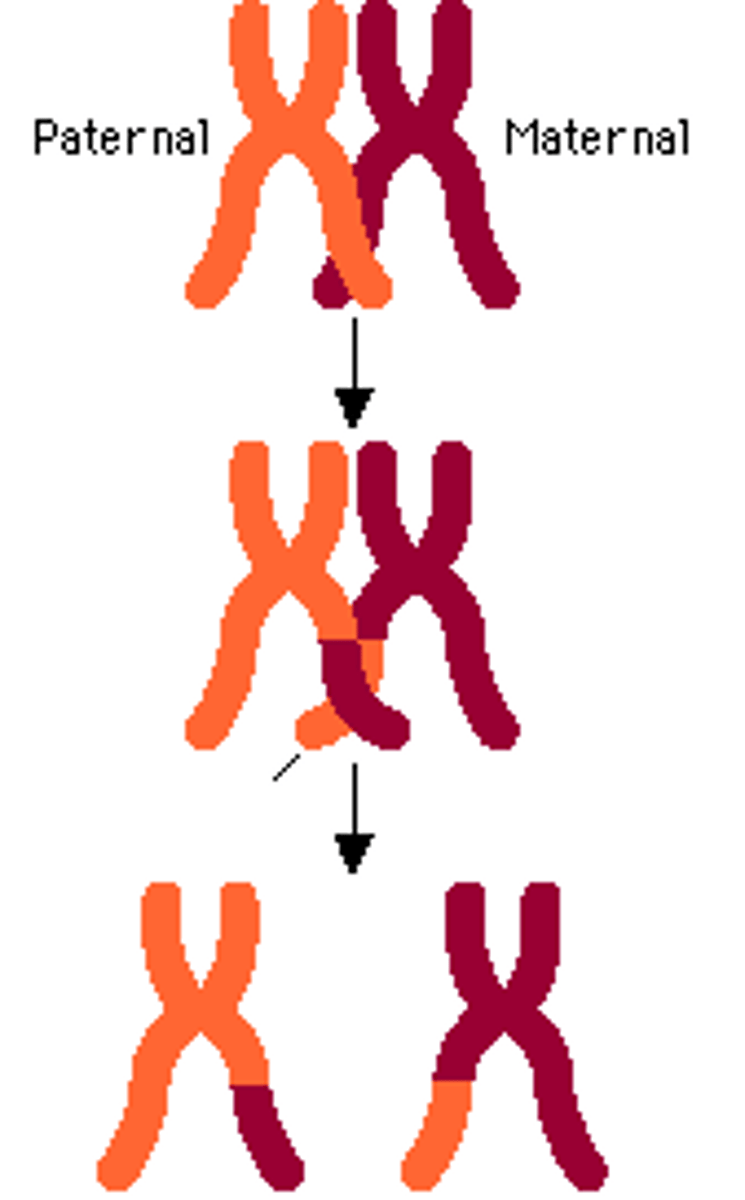
Crossing Over
Allows for genetic diversity where the genetic information from male and female swap; occurs during Prophase I
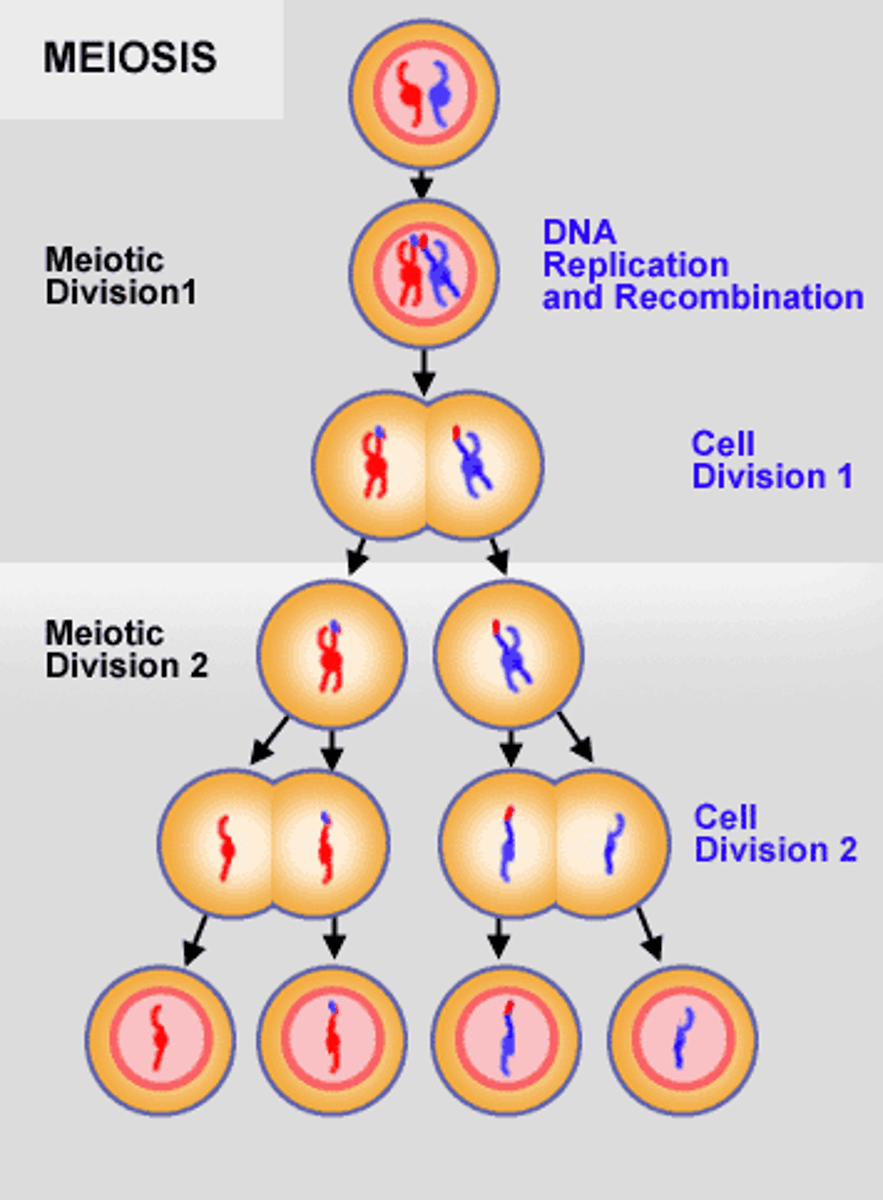
Meiosis
Start with one diploid cell and end with four unique haploid cells
Alleles
different forms of a gene (Ex. 'A')
Dominant
Trait is always expressed if present
Recessive
Trait is only seen if dominant allele isn't present
Homozygous
When an organism has two alike alleles for a trait (Ex. AA or aa)
Heterozygous
When an organism has two different alleles for a trait (Ex. Aa)
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism, revealing the types of alleles he/she has inherited (Ex. AA)
Phenotype
Physical appearance/characteristic of an organism (Ex. Blue eyes)
Monohybrid Cross
examines the inheritance of one trait
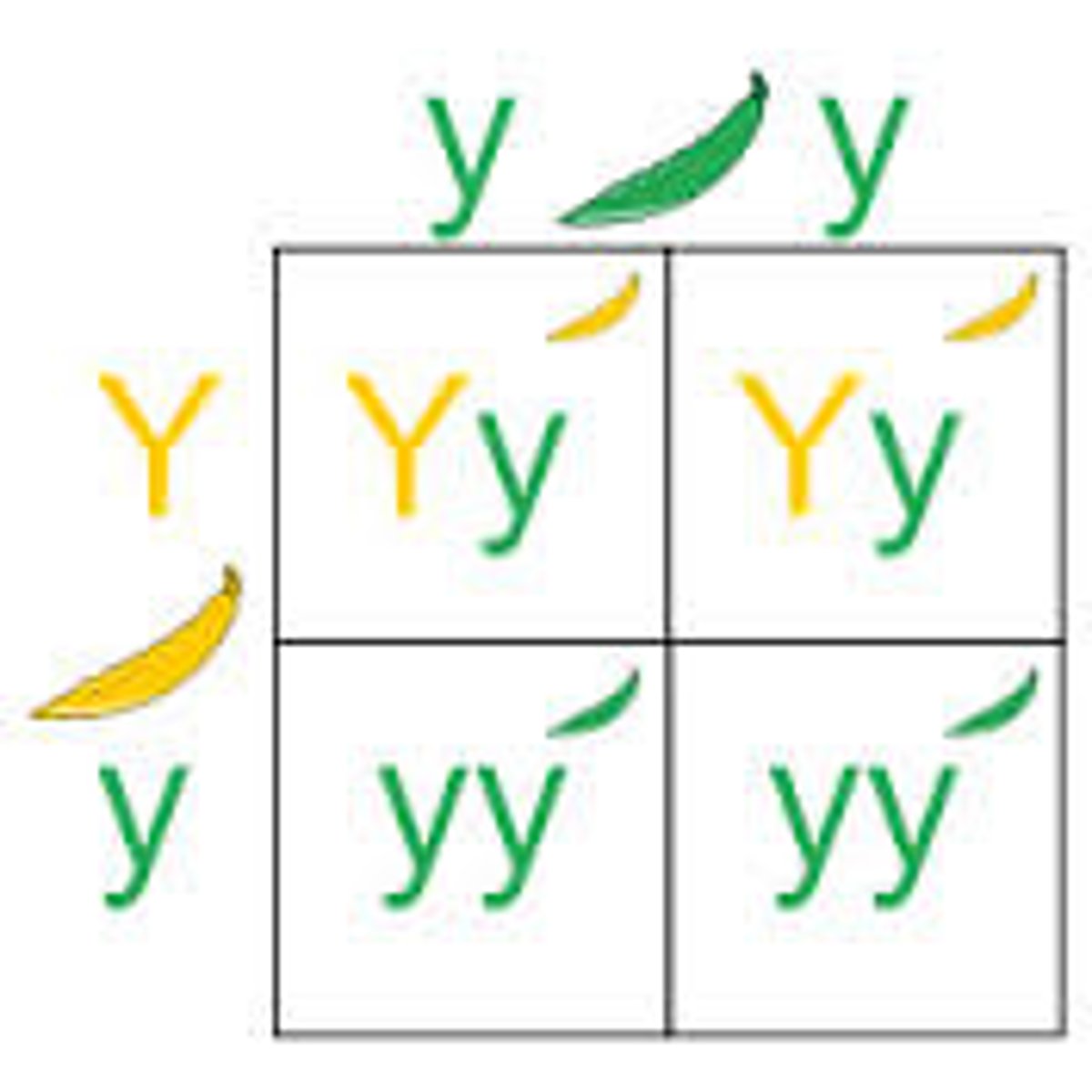
F1 Generation
the first generation's offspring
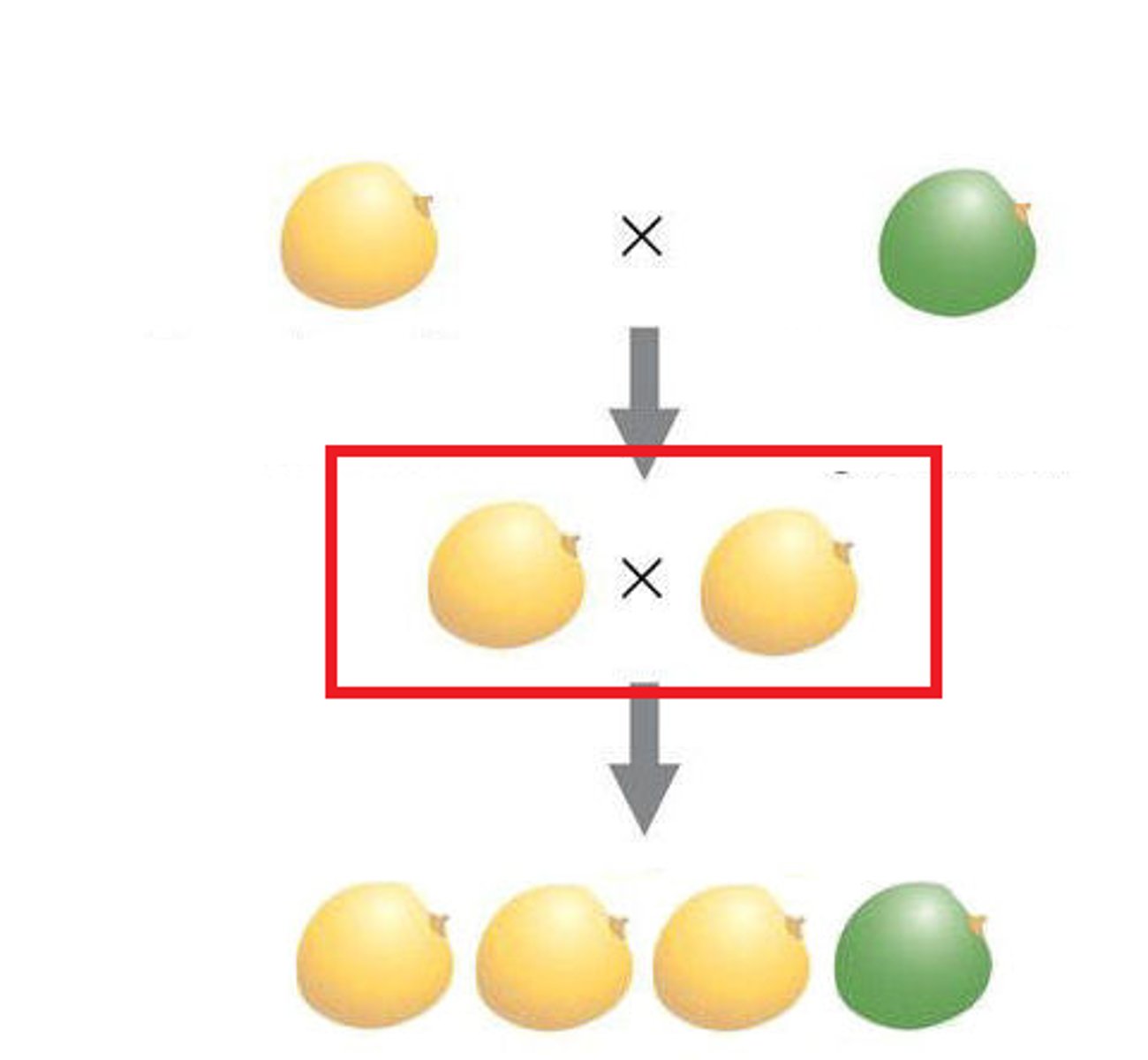
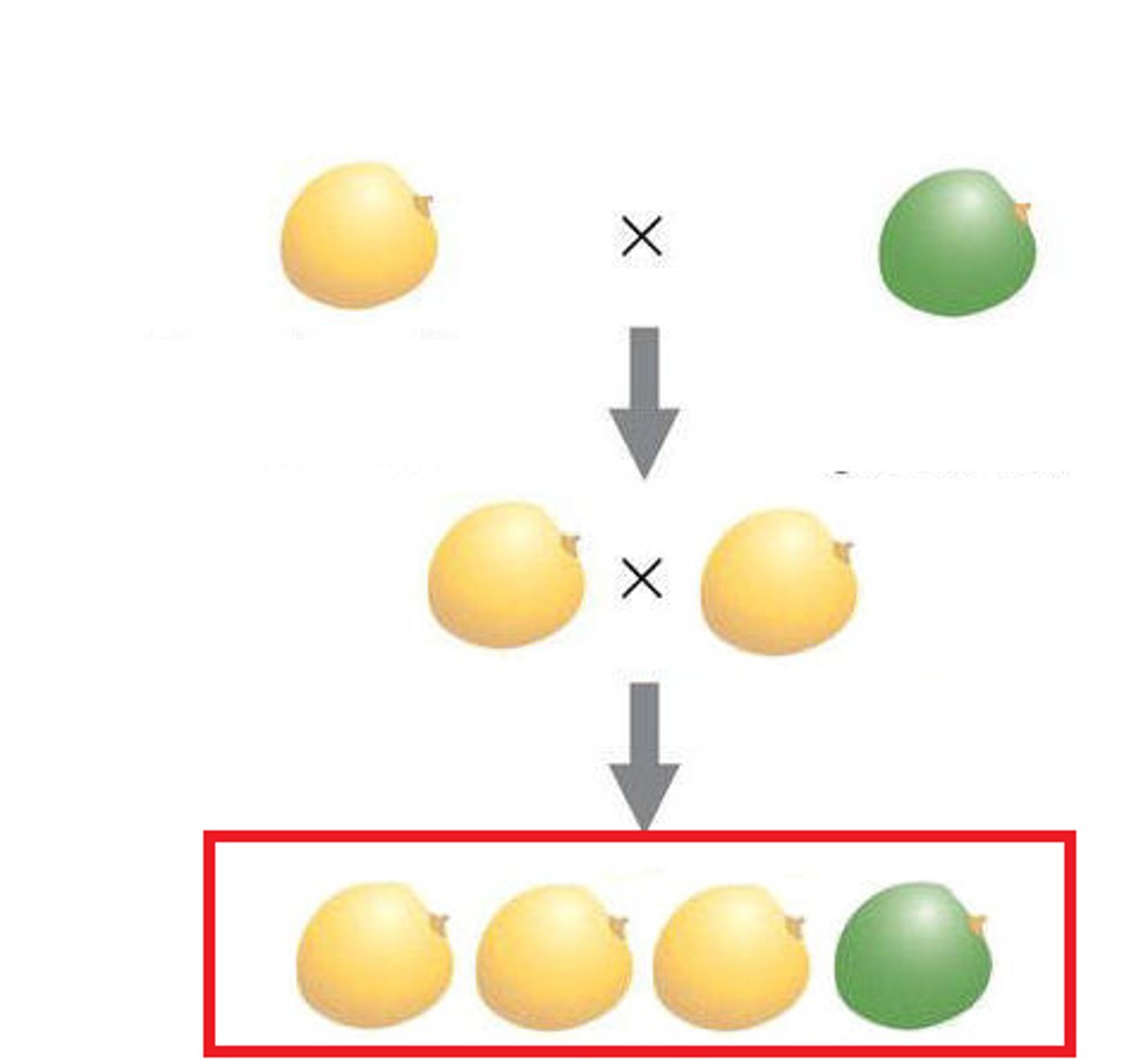
F2 Generation
the second generation's offspring
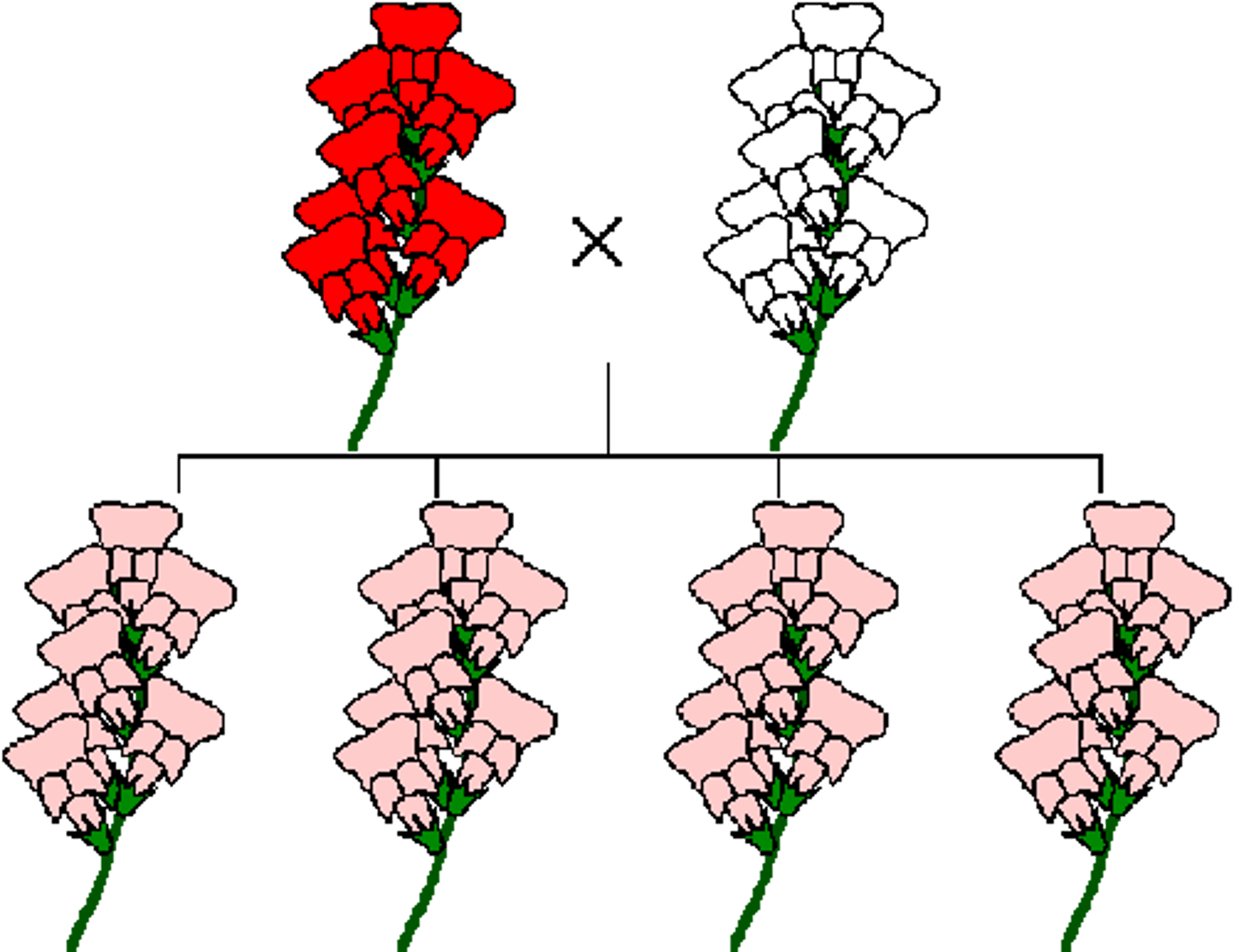
Incomplete Dominance
Offspring is a mixture of the parent's characteristics through multiple generations
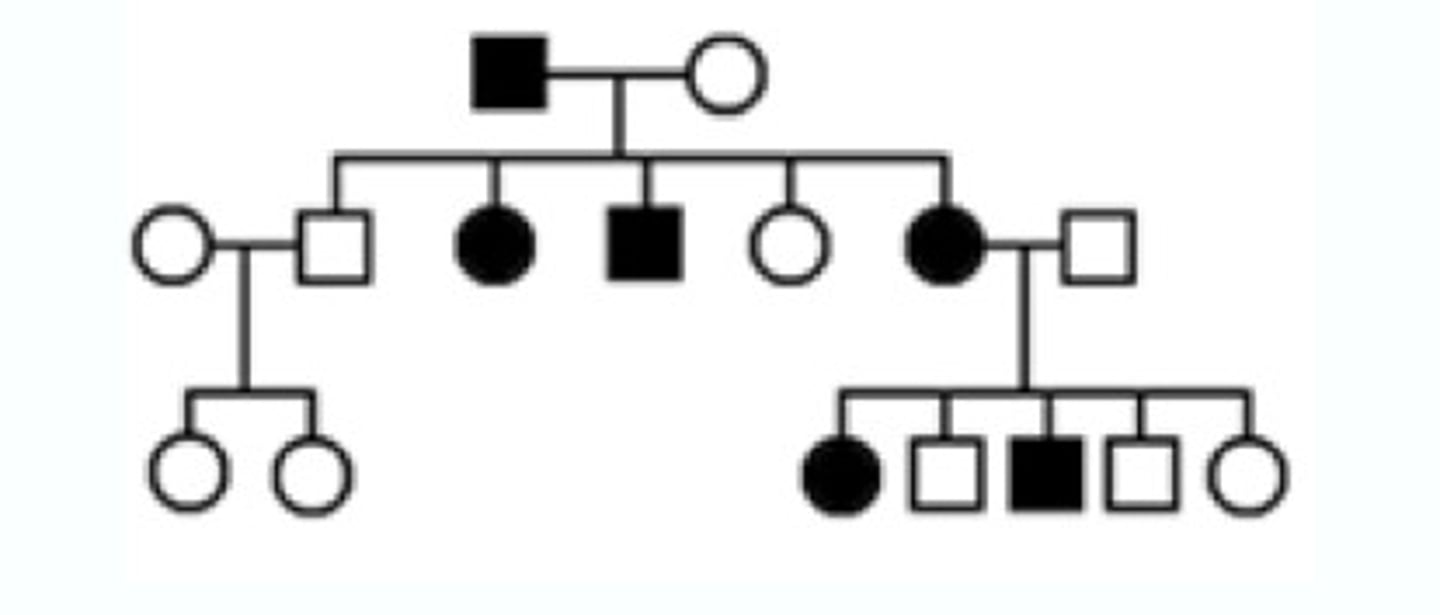
Pedigree
A chart made to show inheritance patterns within a family
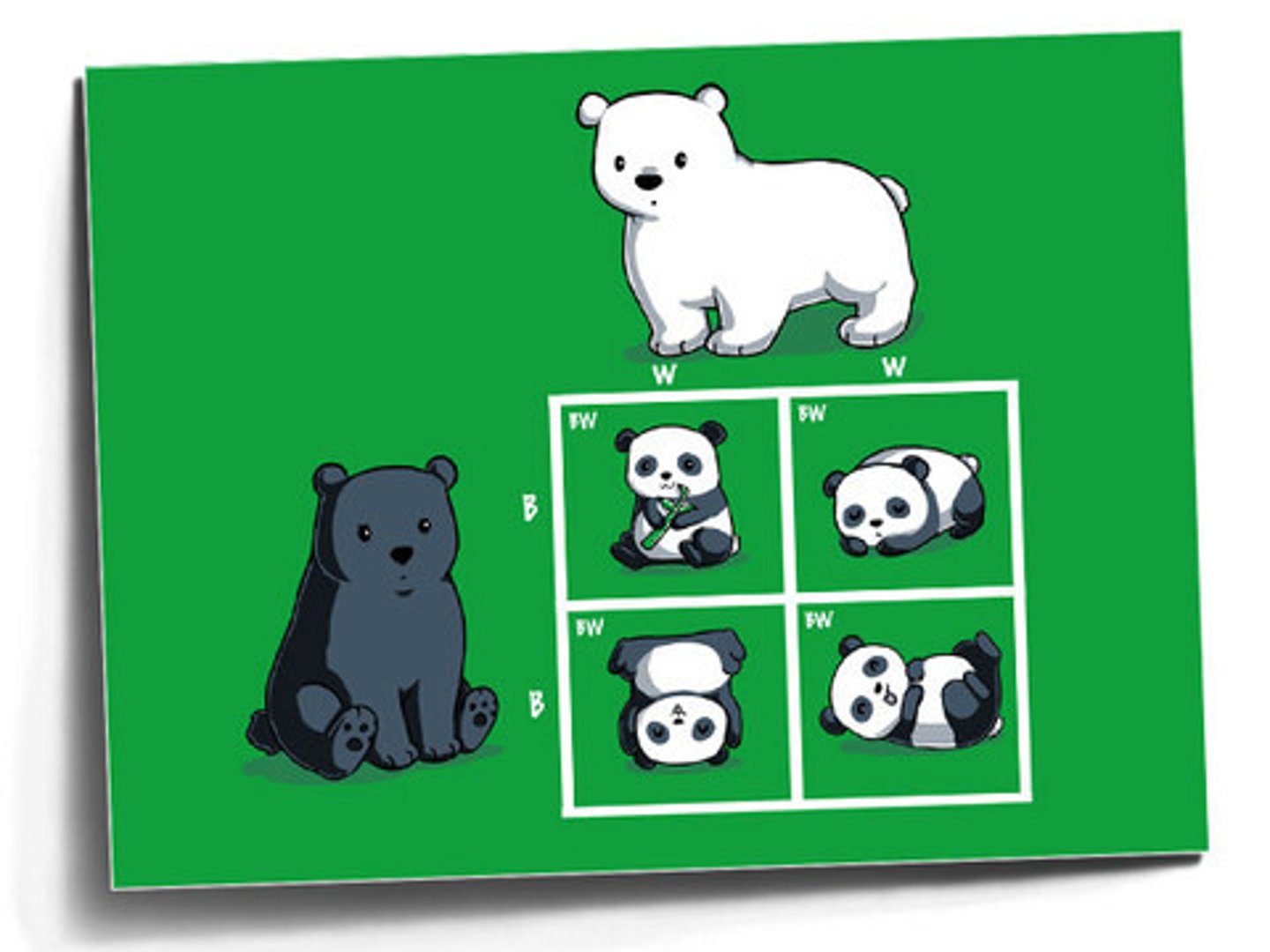
Codominance
offspring contains BOTH parent's characteristics distinctly
Polygenic Trait
Trait controlled by two or more genes (Ex. Skin color and Eye Color)
Multiple Alleles
Exists for a particular trait even through only two alleles are inherited (Ex. Blood Type)
Sex-Linked Trait
Involves genes on either the X or the Y chromosome; Passed most normally through the Y chromosome (Ex. Color blindness, Hemophilia)
Trait
Characteristic that can be passed from one parent to offspring
Heredity
Passing of traits from parent to offspring
Genetics
Study of Heredity, each somatic cell is a diploid where chromosomes are inherited from offspring's parent
Mendel
Father of Genetics; responsible of the Law of Inheritance

Nitrogenous Base
Part of a nucleotide, consists of Thymine (only DNA), Uracil (only RNA), Adenine Guanine, and Cytosine
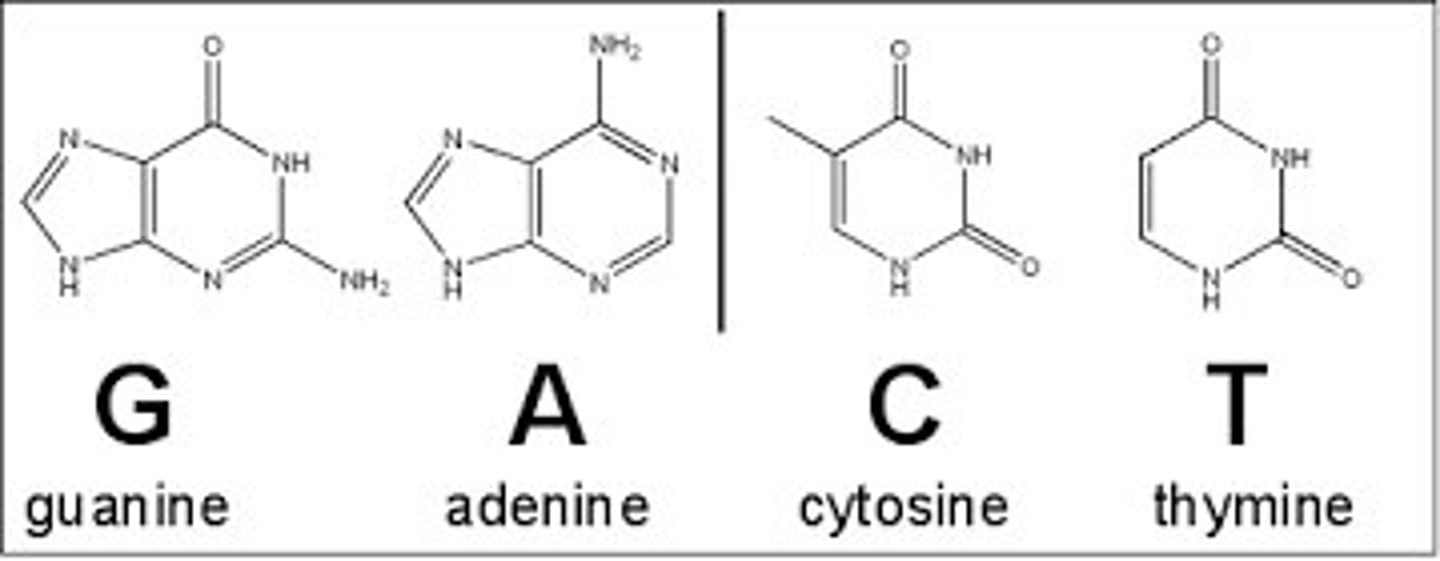
Nucleotide
small subunits composed of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group