AP PSYCH Unit 0
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
hindsight bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it-
"I knew it all along"
validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to do
theory
well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations; using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
operational definition
A statement of the exact procedures or measurements used to define research variables
replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
case study
a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
survey
a descriptive technique for obtaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group
population
the whole group that you want to study and describe
random sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Convenience sample
choosing individuals who are readily available for study
sampling bias
flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
naturalistic observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
correlation
A measure of the relationship between two variables (does not show causation)
correlation coefficient
A statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1)
scatterplot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables.
illusory correlation
The perception of a relationship where none exists
experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more variables to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process
random assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
double-blind study
An experiment in which neither the participant nor the researcher knows whether the participant has received the treatment or the placebo
placebo effect
Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which is assumed to be an active agent.
experimental group
A subject or group of subjects in an experiment that is exposed to the factor or condition being tested.
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
independent variable
the experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied
confounding variable
A factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment.
dependent varibale
the outcome factor the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variables --what you are measuring
mode
Measure of central tendency that uses most frequently occurring score.
mean
Average
median
A measure of center in a set of numerical data.
range
Distance between highest and lowest scores in a set of data.
standard deviation
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score.
normal curve
the symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes.
statistical significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
Quantitative measures
Data that is in numbers
Qualitative measures
Data not recorded in numerical form (example, open ended answers from an interview)
meta-analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
informed consent
A written agreement to participate in a study made by an adult who has been informed of all the risks that participation may entail.
debriefing
A verbal description of the true nature and purpose of a study
sample
A part of the population you are studying.
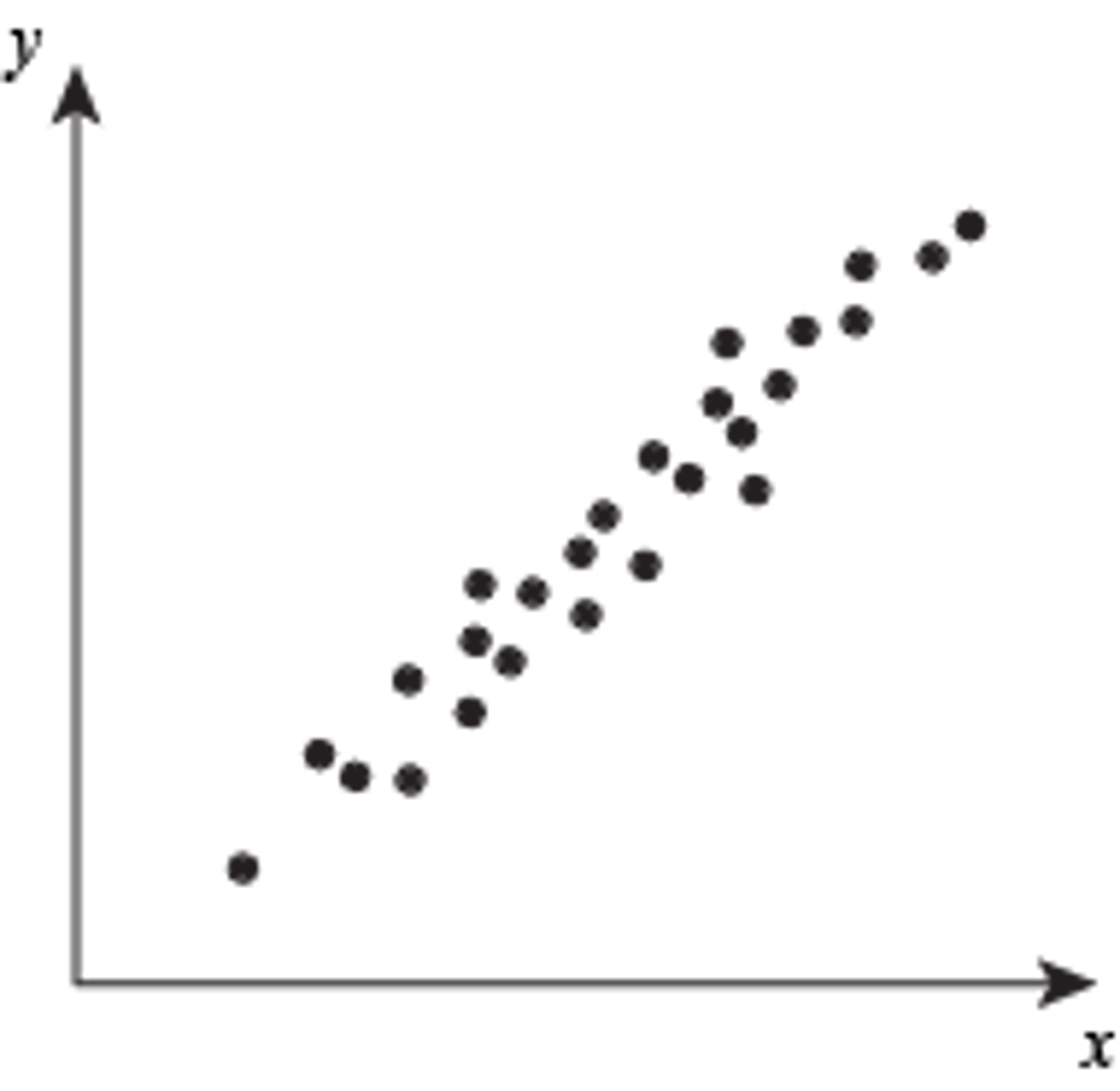
positive correlation
two variable rise and fall together, such as height and weight
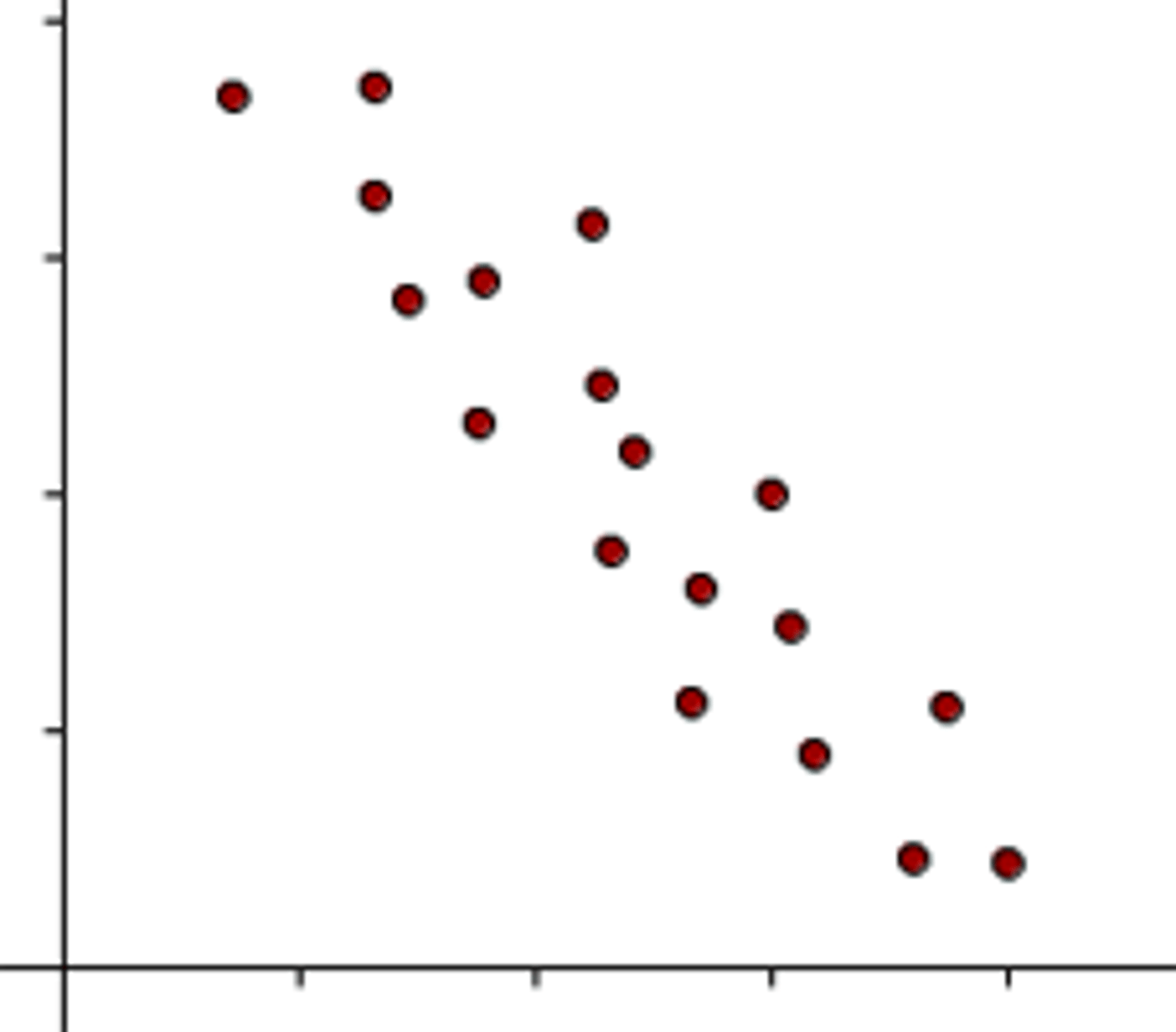
negative correlation
variables are related inversely, one goes up and the other goes down, such as inner speech and psychological distress
descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups, including measures of central tendency and variation
measures of central tendency
refers to how the data measures the center of a set of data
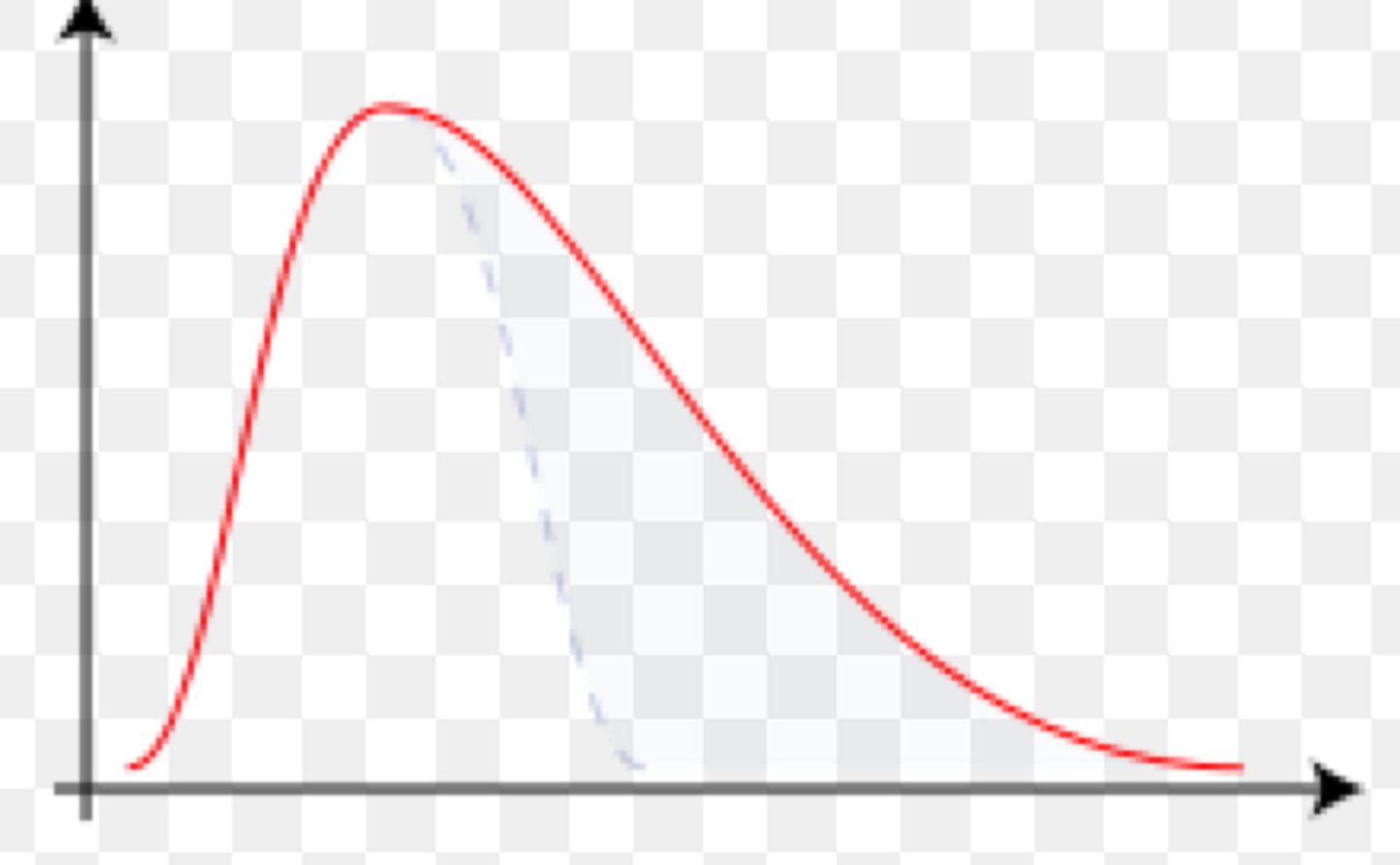
positive skew
high outlier
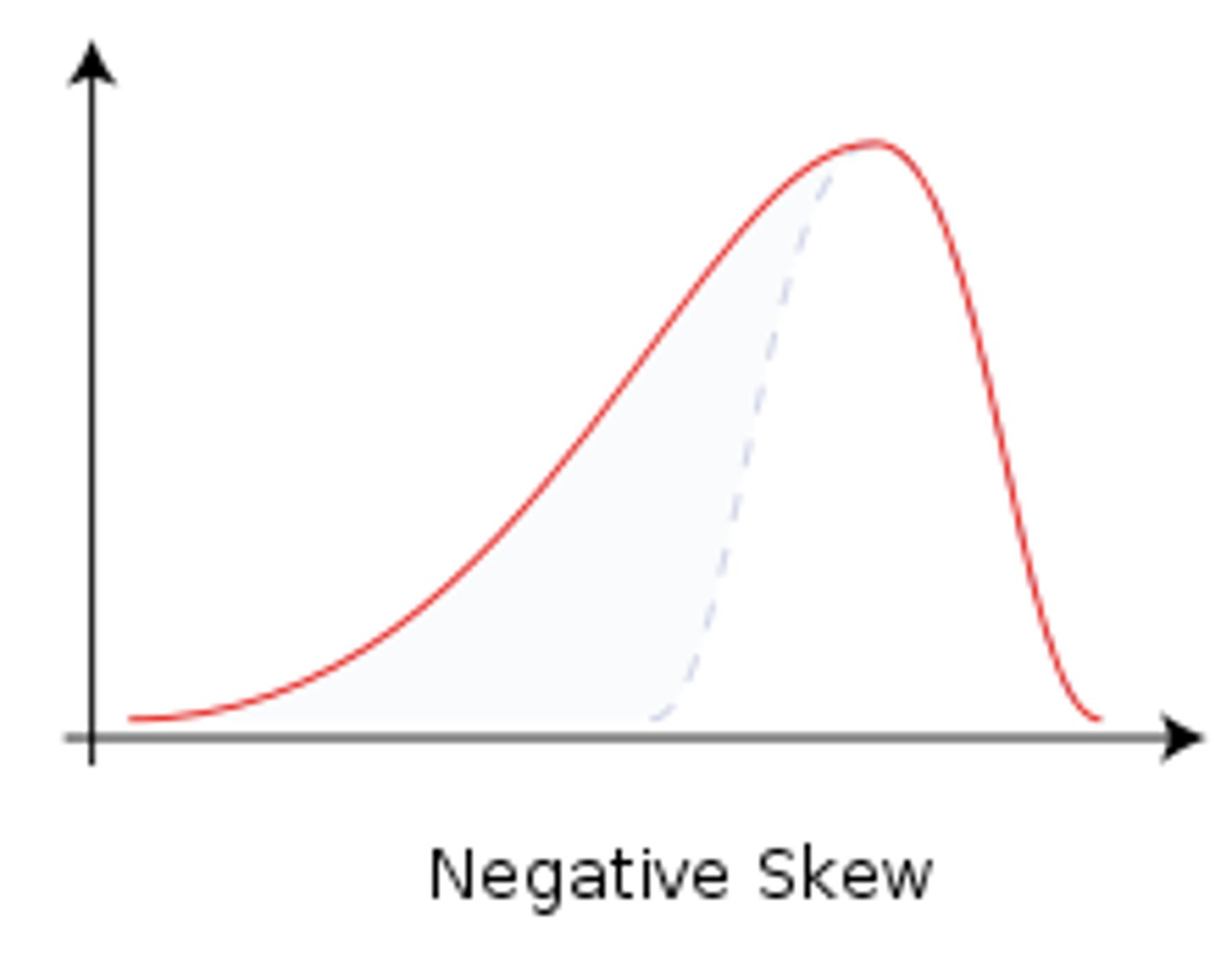
negative skew
low outlier
inferential statistics
numerical data that allows one to generalize (T-tests, chi square, ANOVAS)
statistically significant
how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance (p-value)
effect sizes
A large effect size means that a research finding has practical significance, while a small effect size indicates limited practical applications.
ethics in research
informed consent
protection from harm/discomfort
maintain confidentiality
debriefing
peer review
A process by which the procedures and results of an experiment are evaluated by other scientists who are in the same field or who are conducting similar research.
Overconfidence
Tendency to overestimate our ability to make correct predictions
generalizablity
extent to which we can claim that our findings inform us about a group larger than we studied.
regression toward the mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores/results to fall back (regress) toward their average.
experimenter bias
a phenomenon that occurs when a researcher's expectations or preferences about the outcome of a study influence the results obtained
Likert Scale
a way of formatting a survey questionnaire of attitudes, so that the respondent can choose an answer along a continuum; includes a set of possible answers with labeled anchors on each extreme. (Ex. strongly agree to strongly disagree)
percentile rank
the percentage of scores below a specific score in a distribution of scores
Cognitive psychology
the scientific study of mental processes, including perception, thought, memory, and reasoning.
Biological psychology
a branch of psychology that looks at mental health through a more medical lens, exploring the effect of neurological, chemical, and genetic causes and effects.
Socio-cultural psychology
how behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures and countries
Humanistic psychology
A clinical viewpoint emphasizing human ability, growth, potential, and free will.
psychodynamic psychology
a branch of psychology that studies how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior.
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different age cohorts or subgroups are studied in the same way, and then compared with one another