ECM & Cell Adhesion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what are the 4 types of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
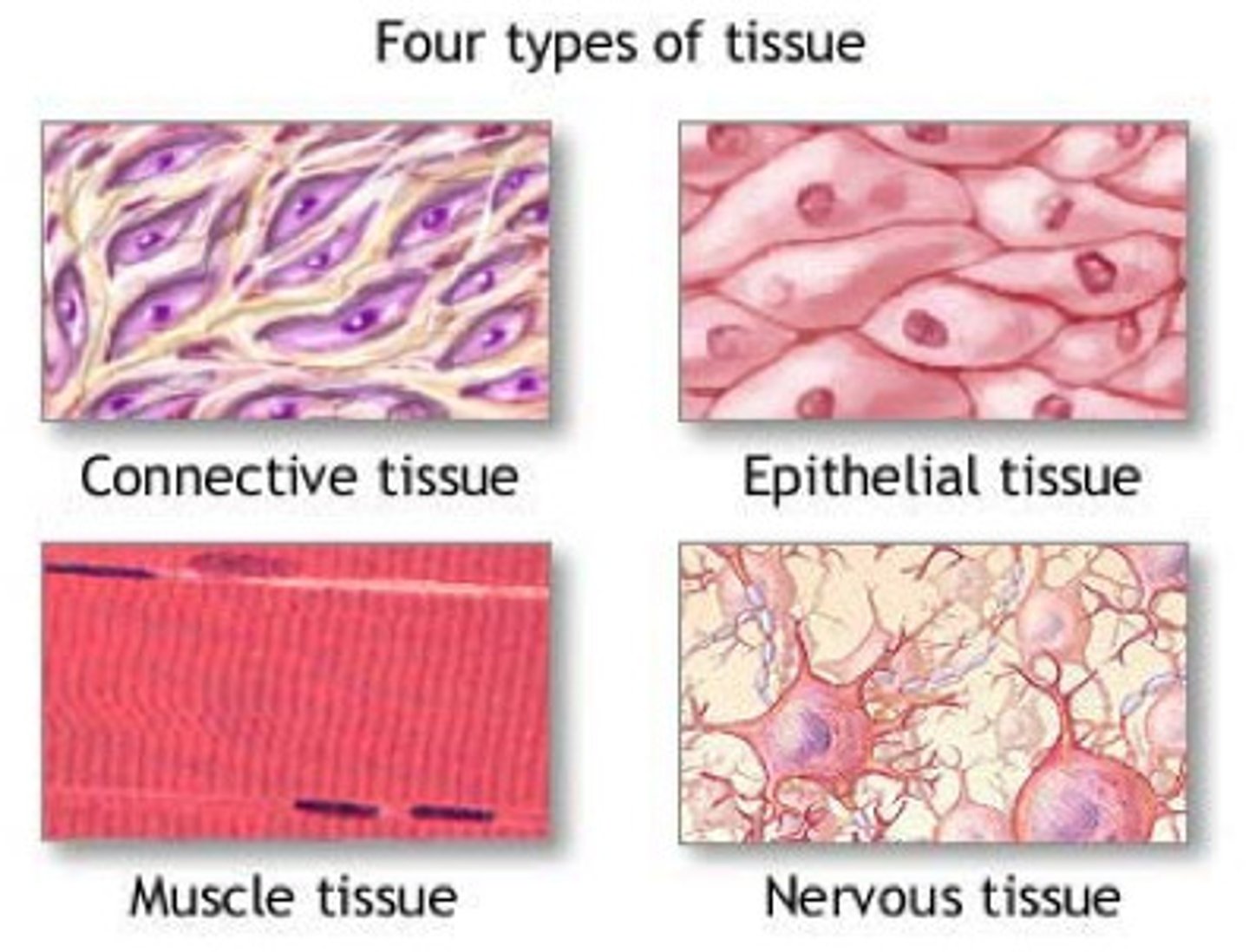
what are the functions of epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue?
- epithelial: covers the entire body surface; first-line defense; protection, secretion, absorption, and filtrations
- muscle: motion and contraction
- nervous: conducts impulses to control muscles, mental activity, and bodily functions
what is the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
a large network of proteins and other molecules that surround, support, and give structure to cells and tissues in the body
- contains proteins, polysaccharides, and minerals
- provides a scaffold for cell attachments and transmits chemical messengers; helps hold tissues together and supports the plasma membrane
T/F: ECMs vary from tissue to tissue
TRUE
what is connective tissue? what are its functions?
principally ECM with fewer cells per volume; ECM contains an abundant matrix of macromolecules
- widely distributed throughout the body
- provides strength, protection, and elasticity
- ex: blood, bone, cartilage, fat, ligaments, lymph, and tendons
what are the 3 major categories of EC molecules that make up the ECM?
- glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)/proteoglycans
- fibrous proteins (collagen, elastin; found in CT, skin, and blood vessel walls)
- adhesive proteins (fibronectin, laminin, integrins)
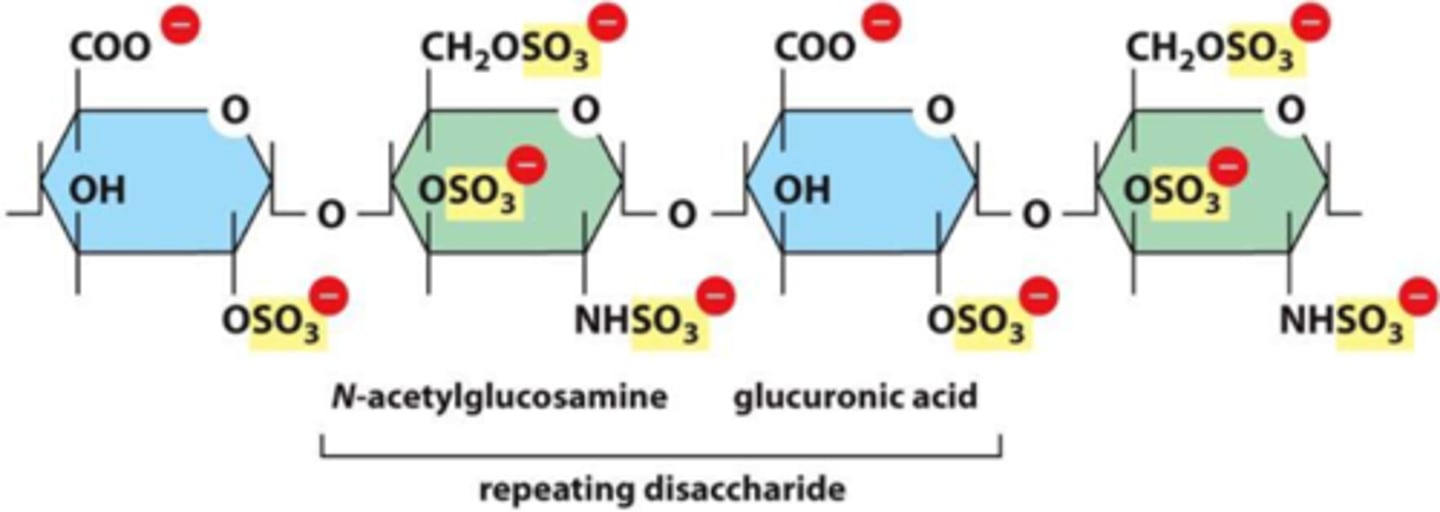
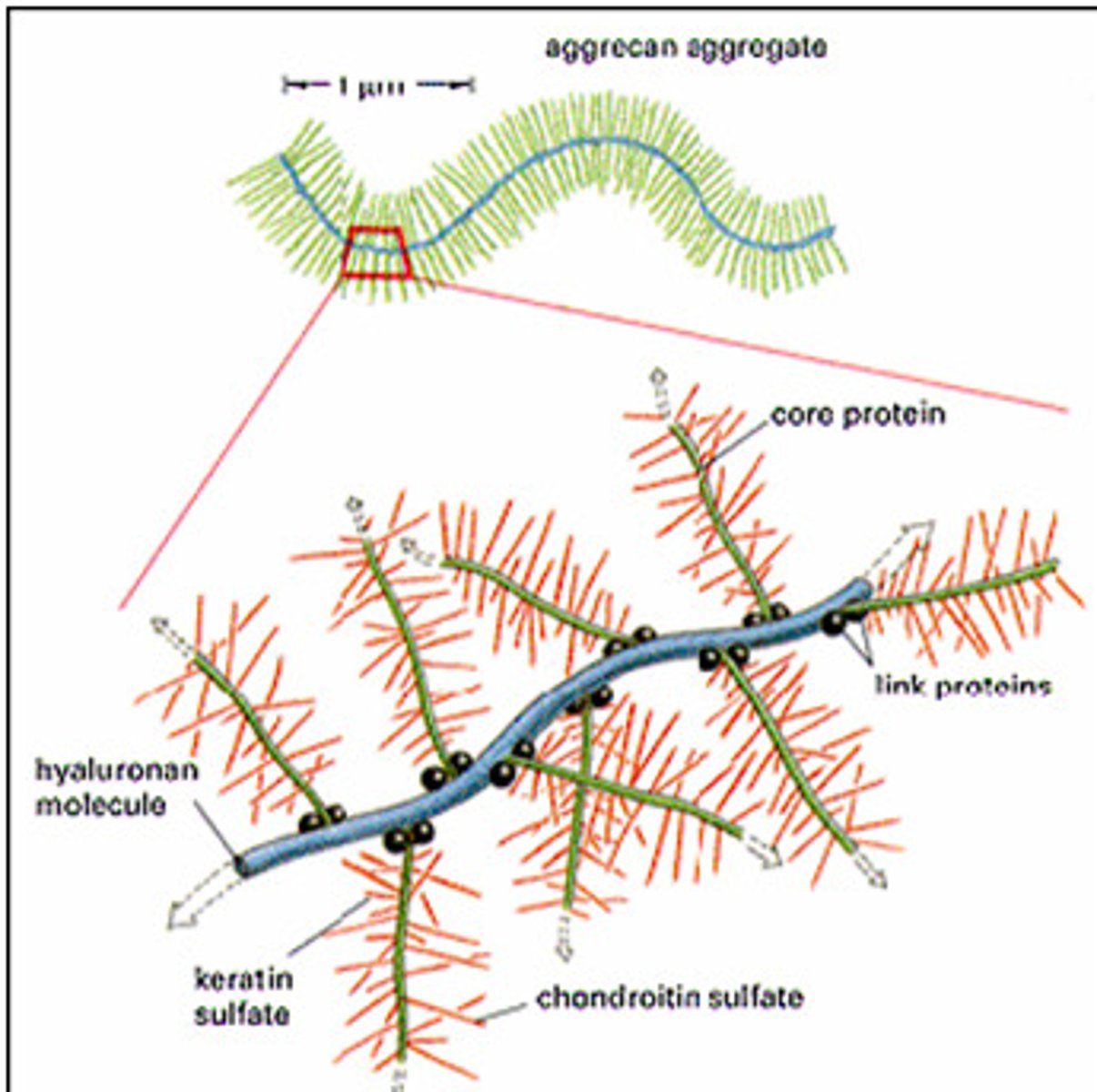
what are GAGs? proteoglycans?
- GAGs (mucopolysaccharides): repeating disaccharide chains; one of the sugars is an N-acetylated amino sugar
- proteoglycans: aggregates of glycosaminoglycans attached to proteins; monomers consist of a core protein with chains of GAGs extending out from it; monomers then bind to a protein
what is the most common GAG? list other examples
chondroitin sulfate is most common
- others include hyaluronic acid, keratin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, heparin, and heparan sulfate
- both chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate are cartilage proteoglycans
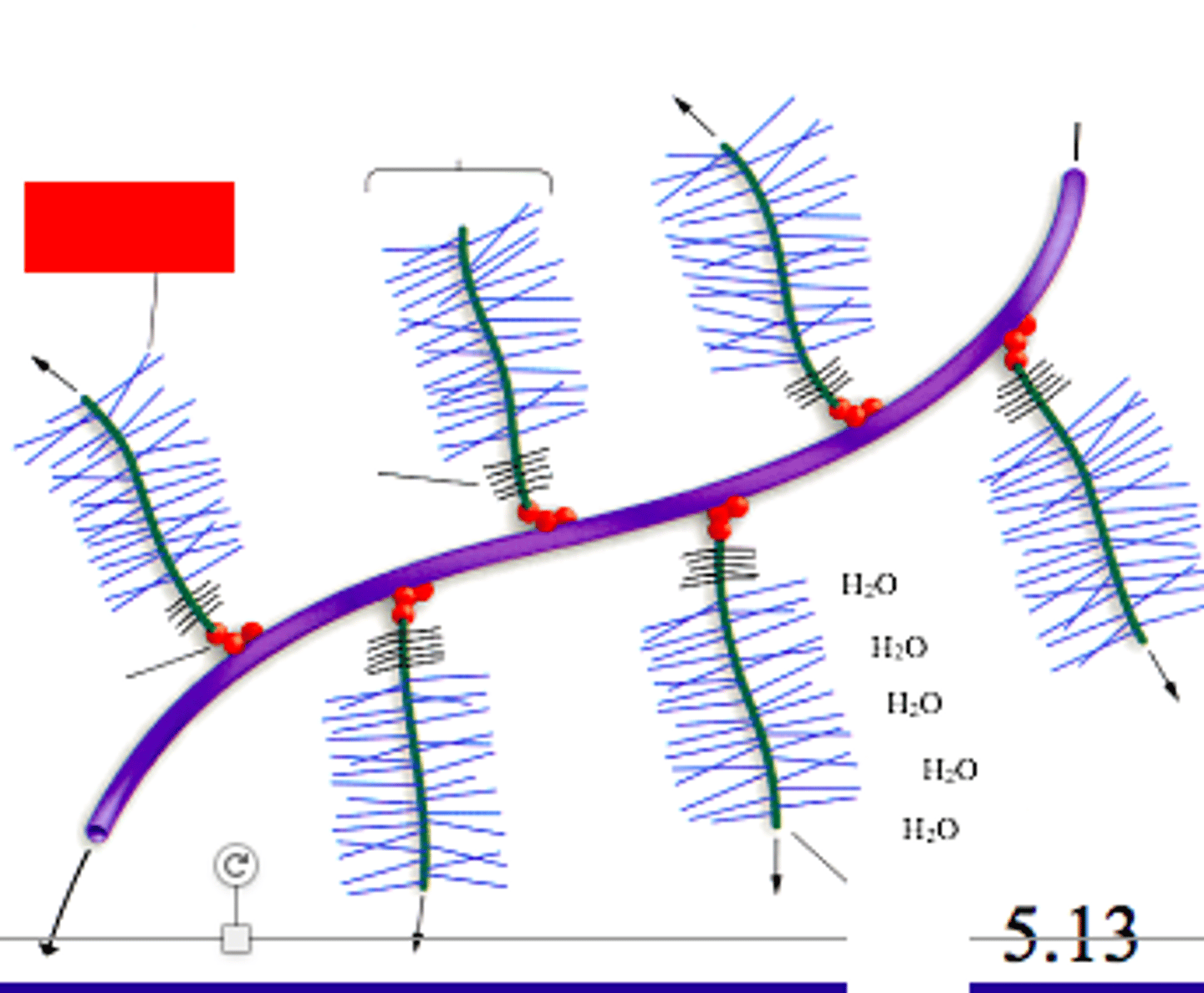
in proteoglycan aggregates, what molecule is the primary backbone to which the monomers attach?
hyaluronic acid
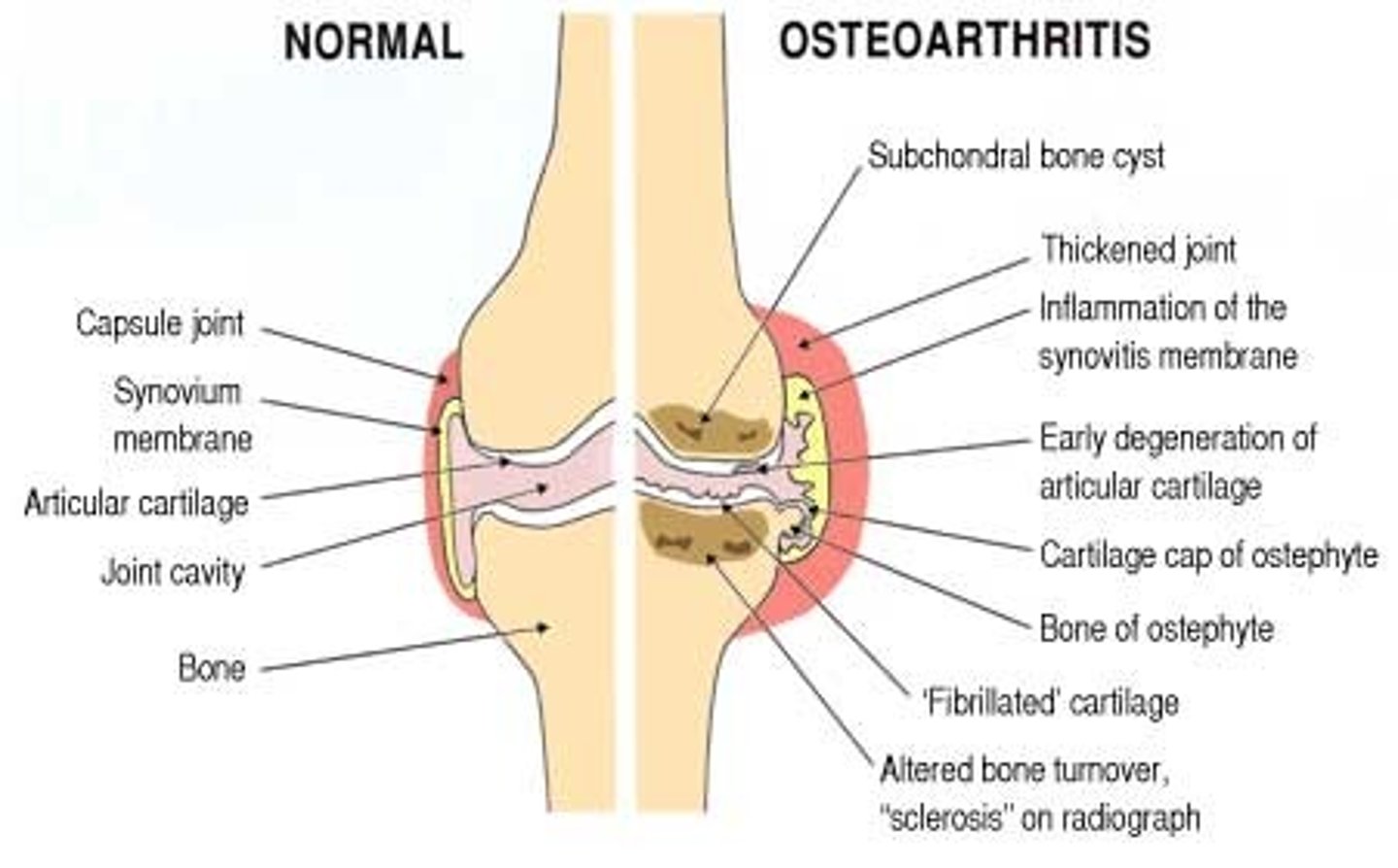
what is osteoarthritis, and what OTC dietary supplements can help ease consequential discomfort/pain?
chronic joint disease characterized by the degradation of joint cartilage; signs/Sx include pain, stiffness, and swelling
- can take OTC glucosamine and chondroitin dietary supplements to help reduce pain and swelling → glycosaminoglycans are used as joint lubrication in the body (supports cartilage and tendons)
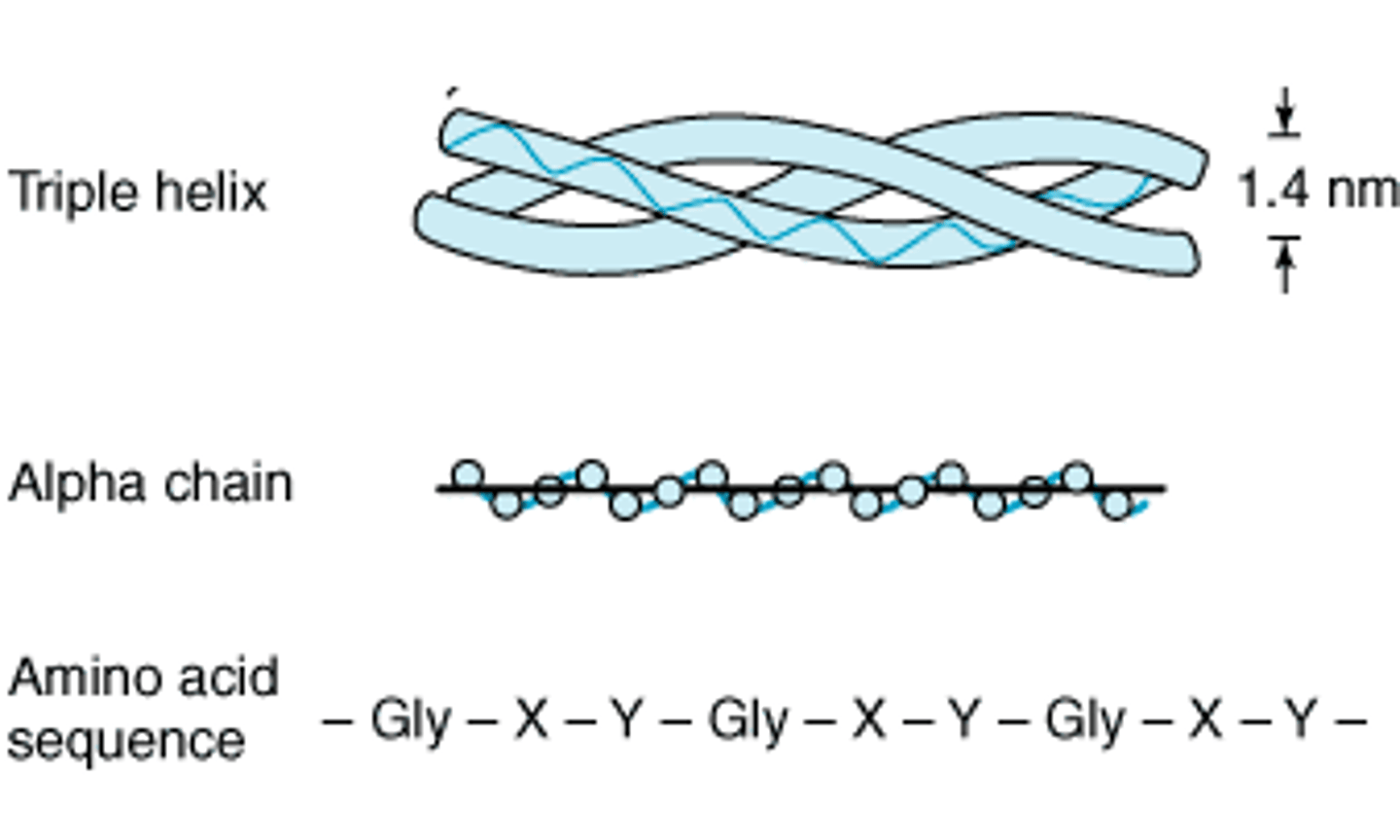
what is the main type of protein in bone, tendon, and skin?
collagen (fibrous)
describe the structure of collagen
composed of 3 helical polypeptide α chains; triple helix
- rich in proline, lysine, and glycine → found in repeating patterns of X-Y-Gly, where X is proline and Y is a modified form of either proline (hydroxyproline) or lysine (hydroxylysine)
how is collagen synthesized?
hydroxylation reactions that require molecular O, Fe2+, and vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
- the hydroxyl group of the hydroxylysine residues of collagen may be enzymatically glycosylated
- most commonly, glucose and galactose are sequentially attached to the polypeptide chain prior to triple-helix formation
there are several types of collagen found in the body, but 90% of the body's collagen belongs to types...?
I, II, III, and IV
- I: fibril-forming; skin, bone, tendon, blood vessels, cornea
- II: fibril-forming; cartilage, intervertebral disk, vitreous body
- III: fibril-forming; blood vessels, skin, muscle
- IV: network-forming; basement membrane
how is collagen affected as the body ages?
as we age, we produce more collagenase, which degrades collagen; as age increases, collagen decreases
- collagen fibers become rigid and wrinkles form
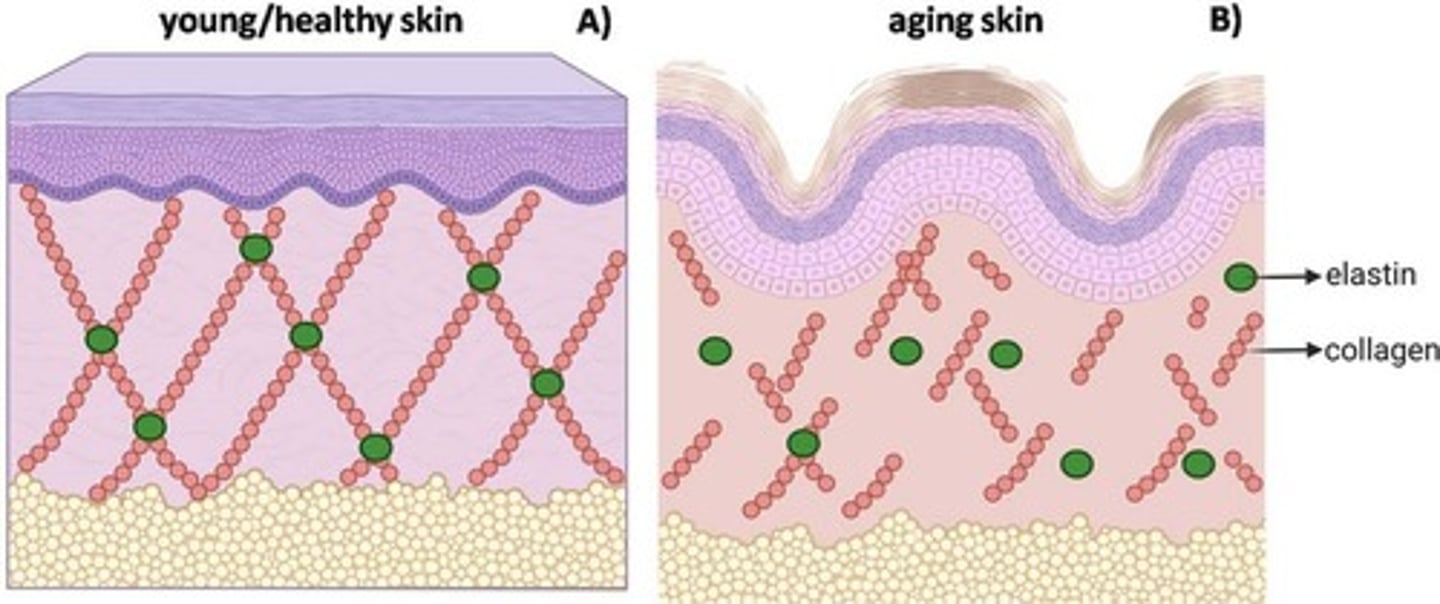
what are 2 primary ingredients of antiaging products? how do they help prevent skin aging?
- antioxidants: inhibit free radicals and slow the damage to collagen
- retinoic acid: stimulate the production of new collagen fibers in the skin
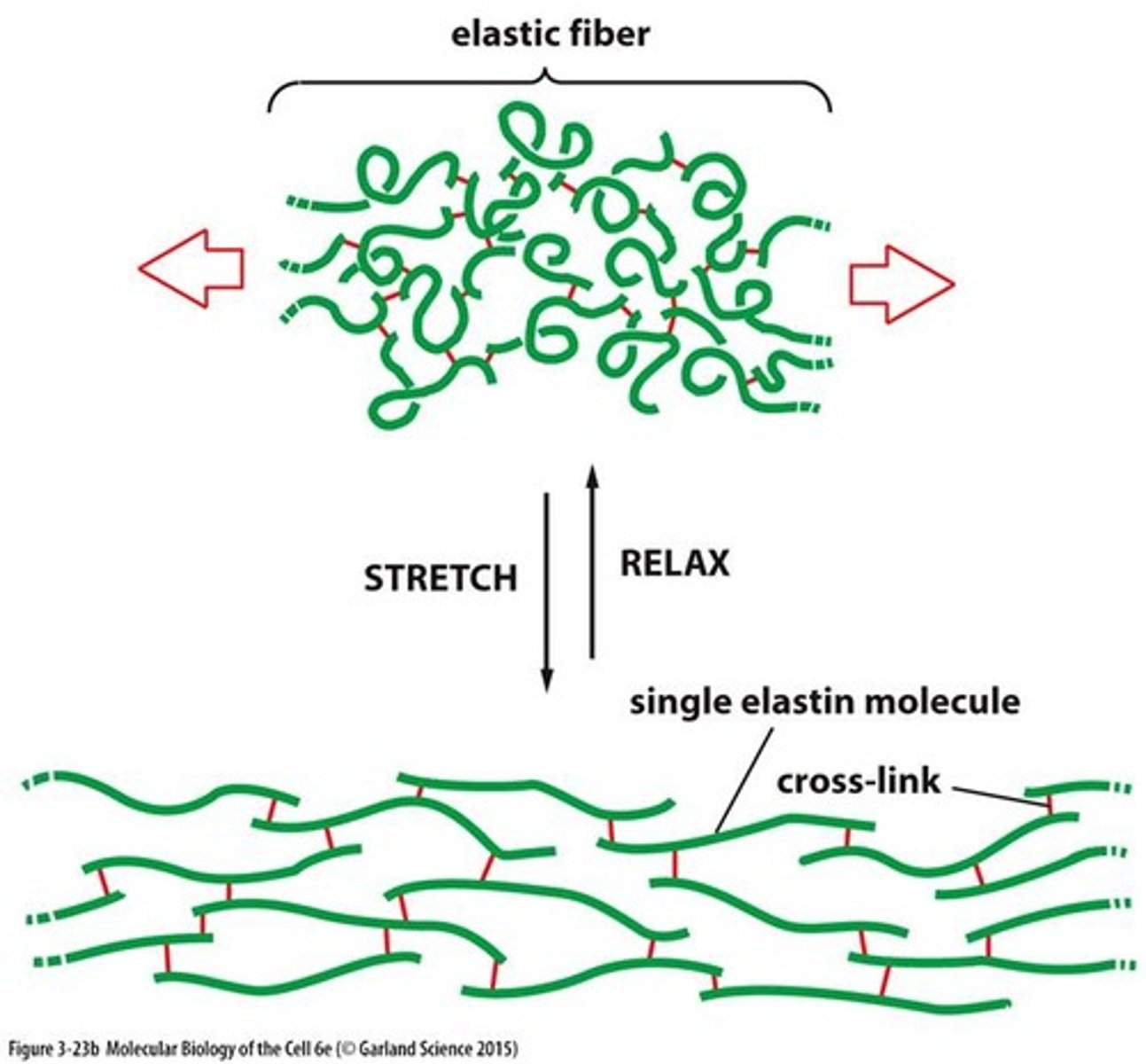
what is elastin? describe its structure
connective tissue protein with elastic properties
- rich in glycine, alanine, proline, and lysine; also contains hydroxylproline
- desmosine cross-link structure
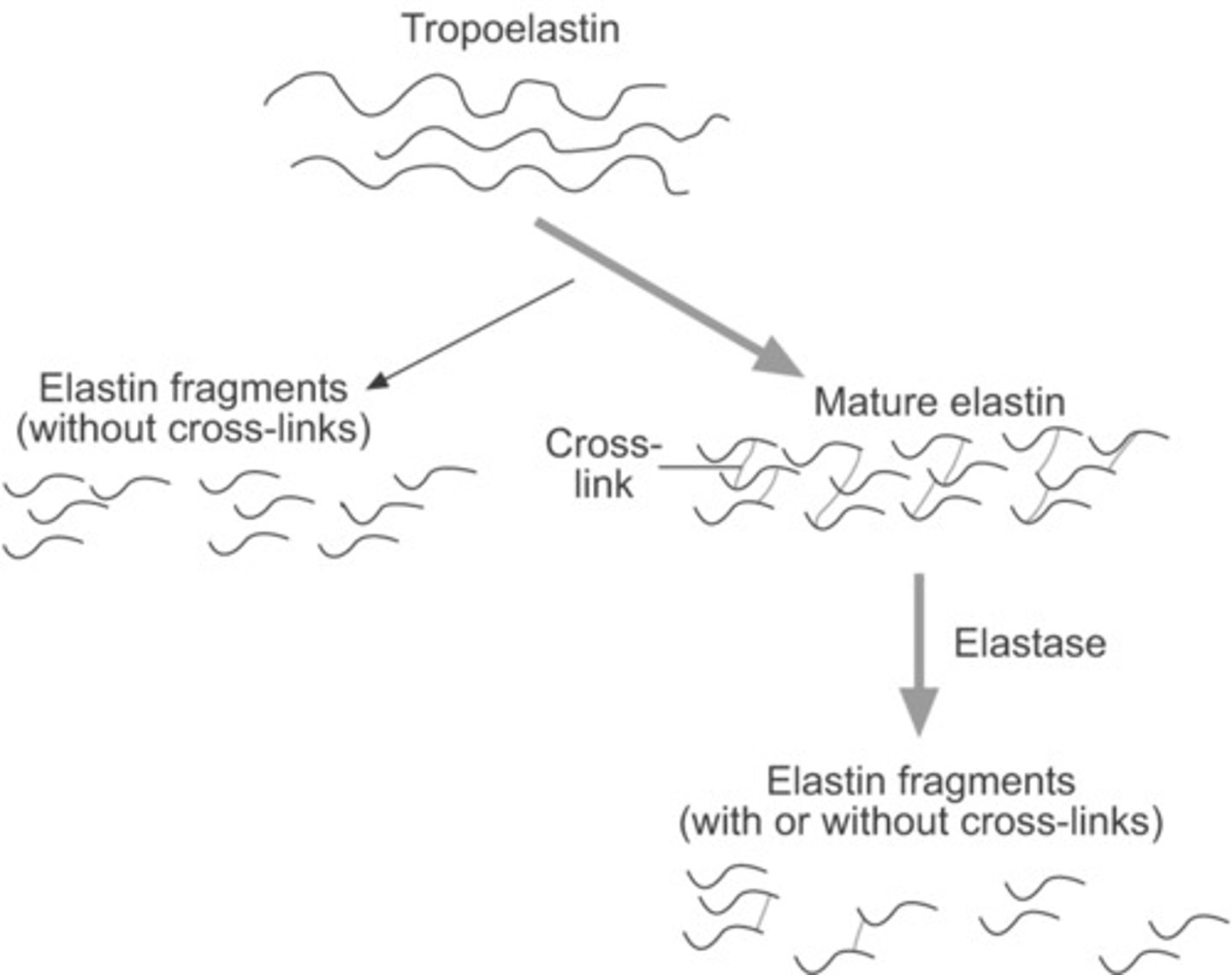
what is tropoelastin? how are some residues modified to alter its activity?
precursor of elastin
- some lysyl residue side chains are modified to form allysine, allowing tropoelastin to interact with glycoprotein microfibrils (like fibrillin)
what causes scurvy?
deficiency of vitamin C
- hydroxylation of prolyl and lysyl residues cannot occur
- defective pro-α chains that cannot form a stable triple helix
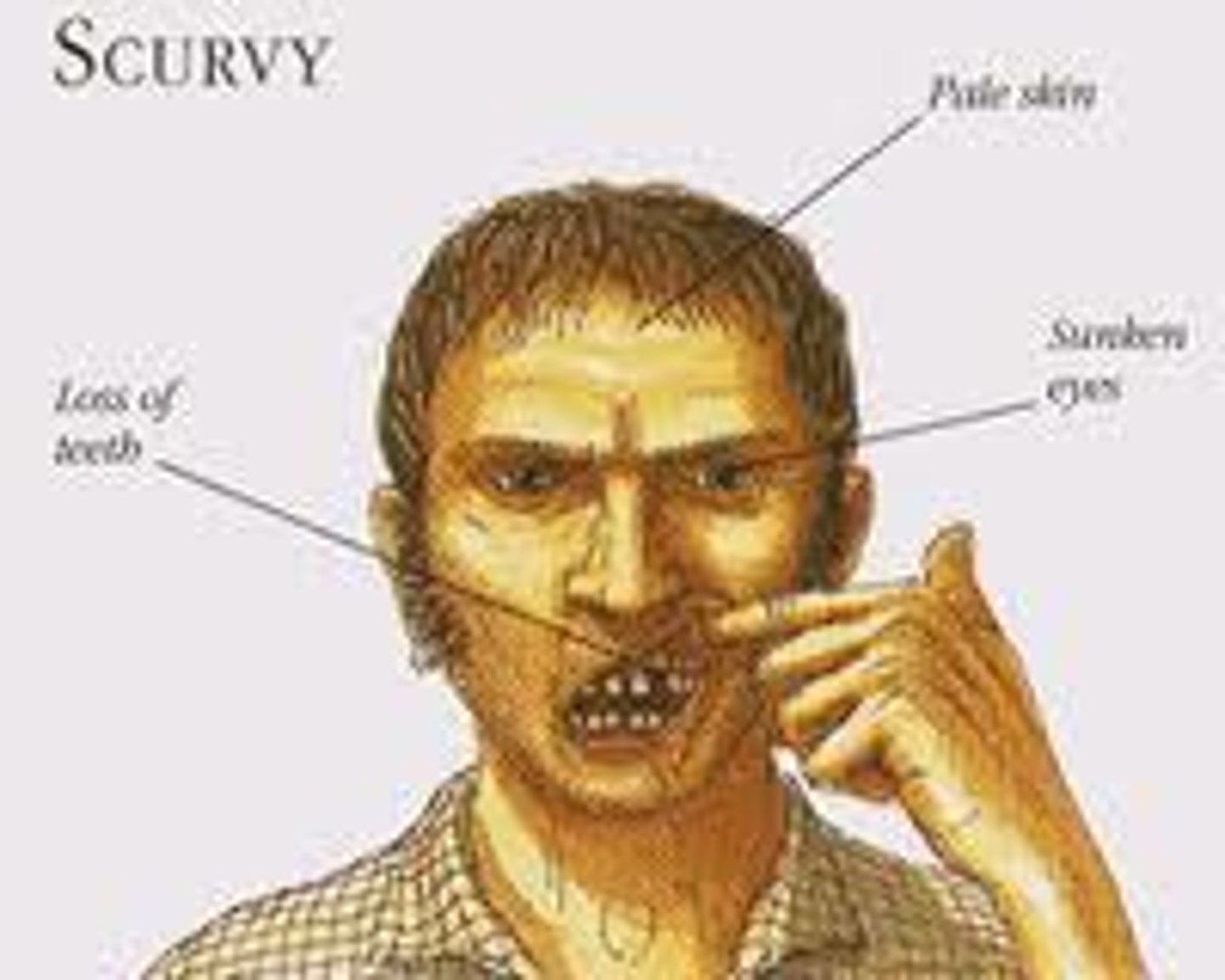
what are the physical consequences of a lack of collagen in the body?
reduced strength and stability of tissues
- blood vessels become fragile
- bruising
- slowed wound healing
- gingival hemorrhage and tooth loss
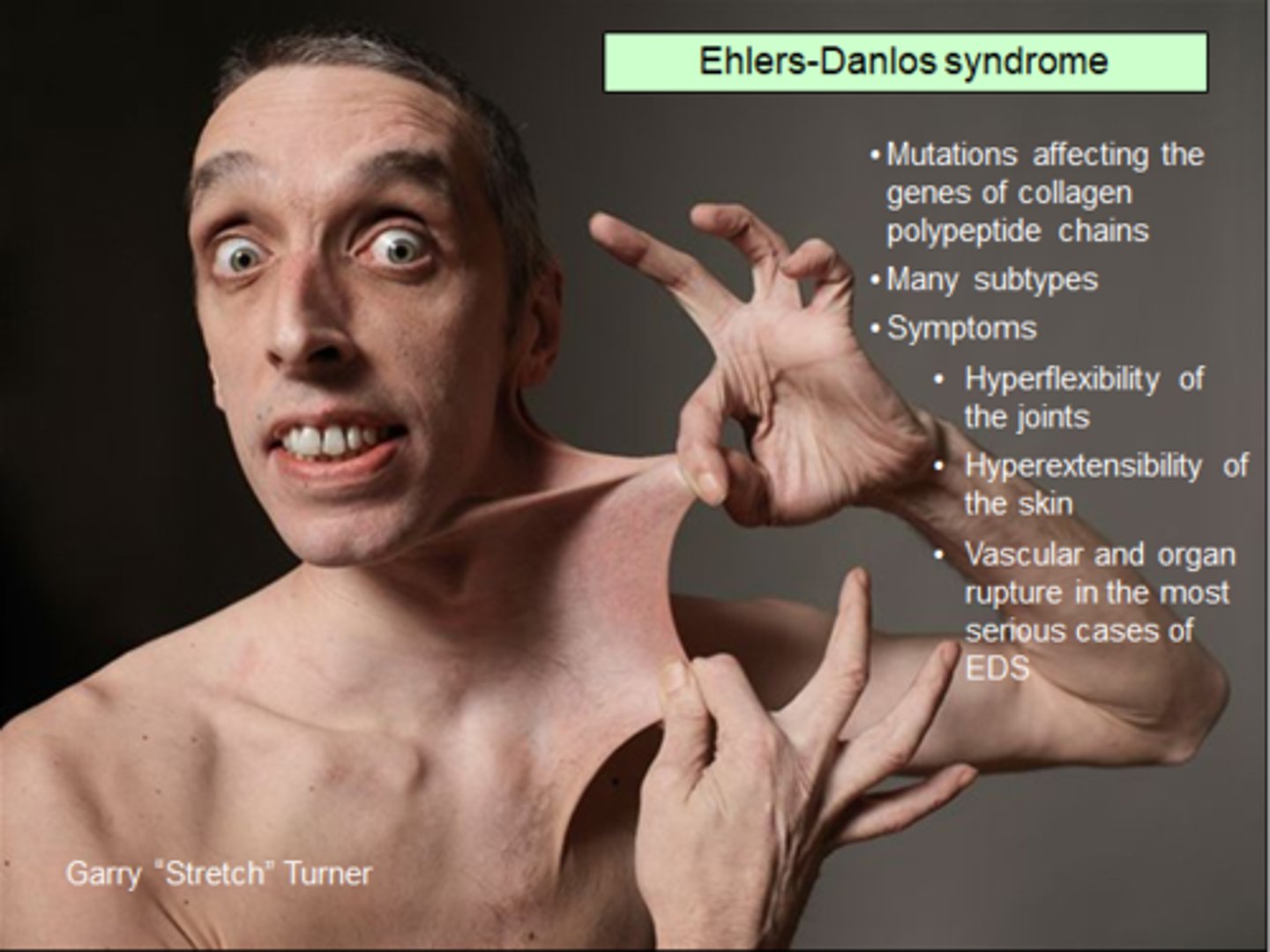
what is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
connective tissue disorder caused by defects in the structure, production, or processing of fibrillar collagen
- skin is not properly bound to bone!
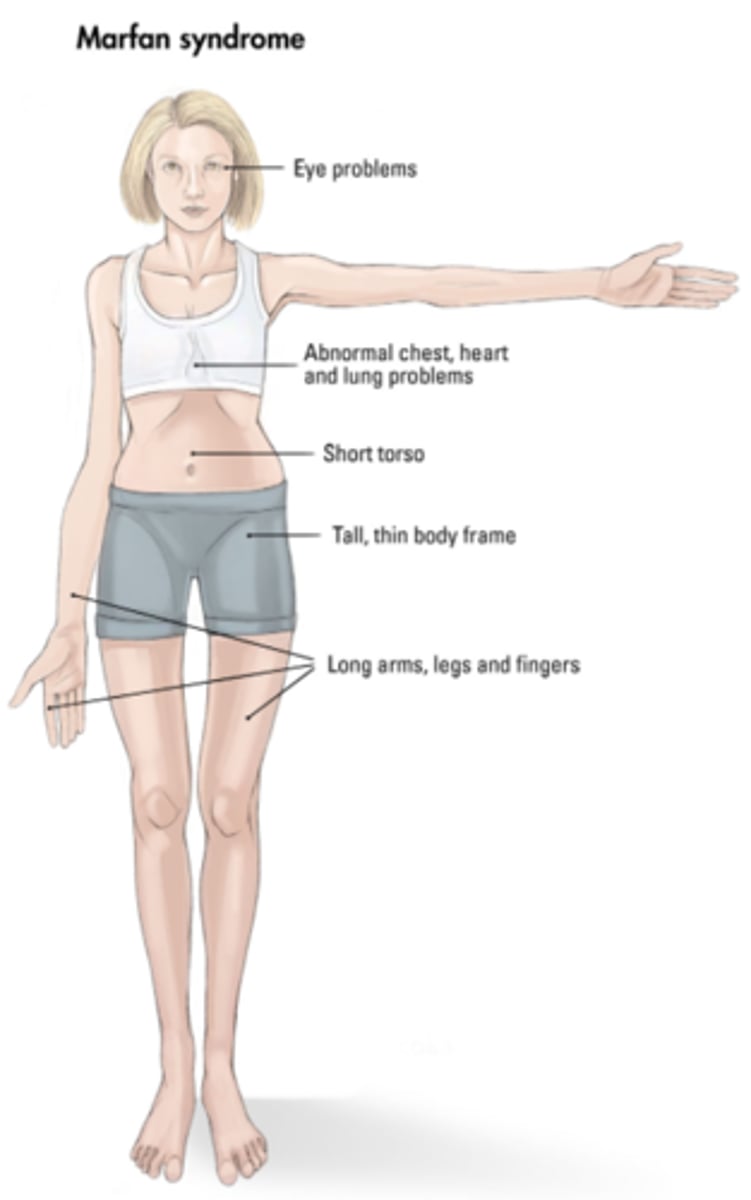
what is Marfan syndrome? what causes it, and how might a patient with this condition look?
connective tissue disorder caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes fibrillin-1, which is essential for elastin maintenance
- affects the aorta, ligaments, and eyes
- patients tend to have a tall stature, scoliosis, abnormal joint mobility, and hyper-extensibility of hands, feet, elbows, and knees
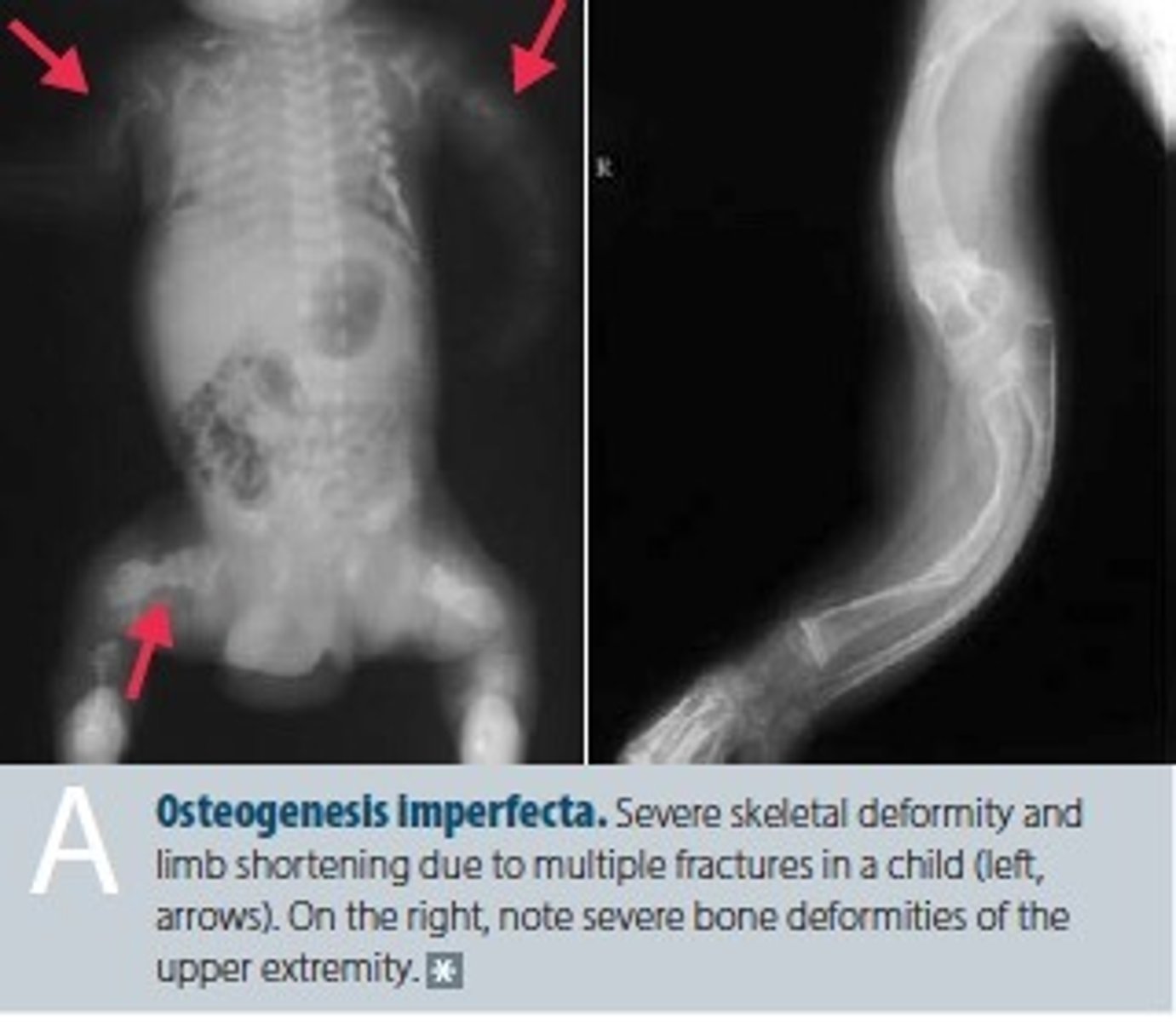
what is osteogenesis imperfecta?
an inherited collagen disorder; aka "brittle bone disease"
- caused by mutations in a collagen gene, resulting in abnormal type I collagen and subsequent weak bones
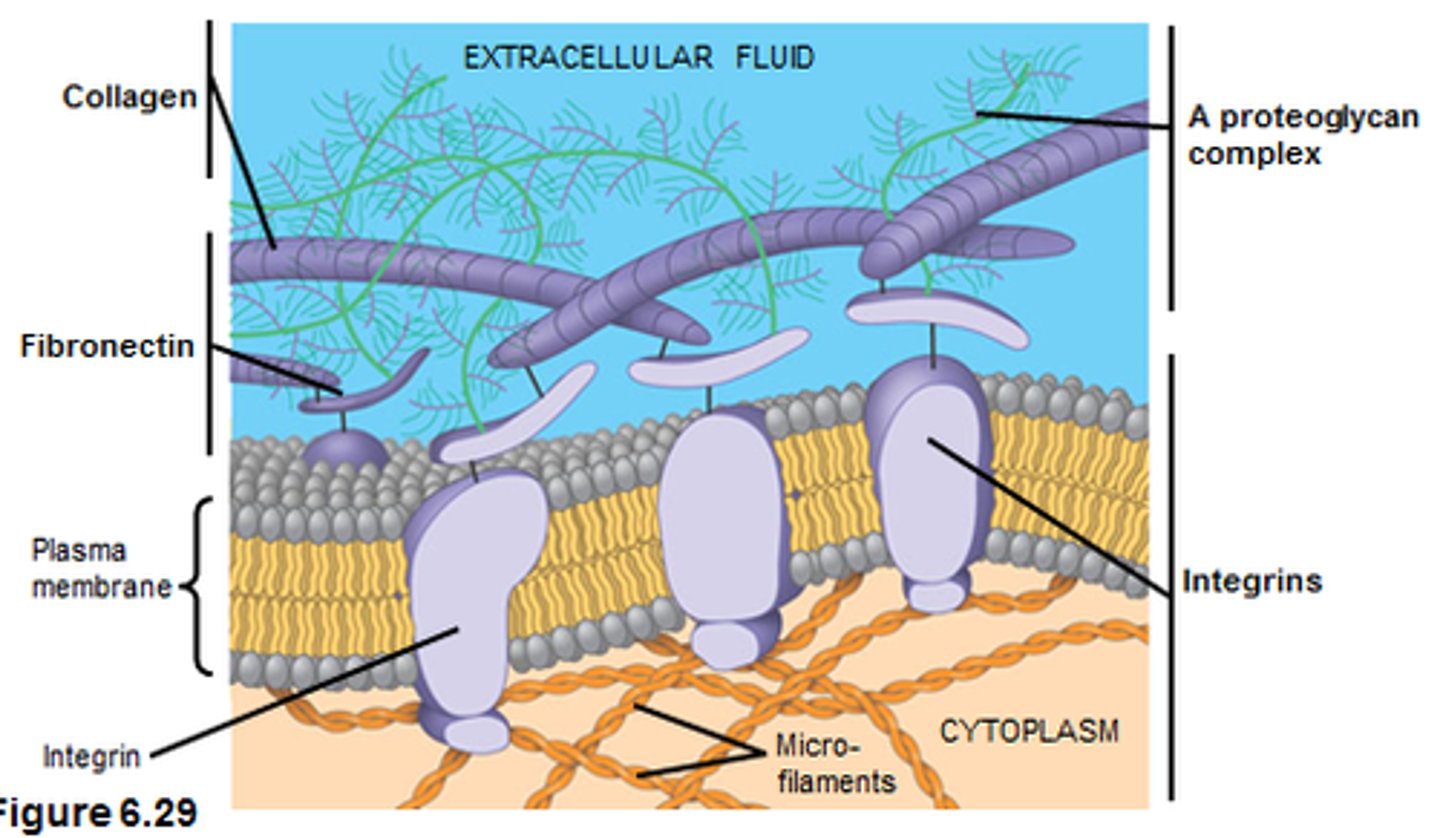
how do cells adhere to each other and to the ECM? what are the primary glycoproteins involved?
via cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
- cells secrete fibronectin (connective tissue) and laminin (epithelial tissue) into the ECM
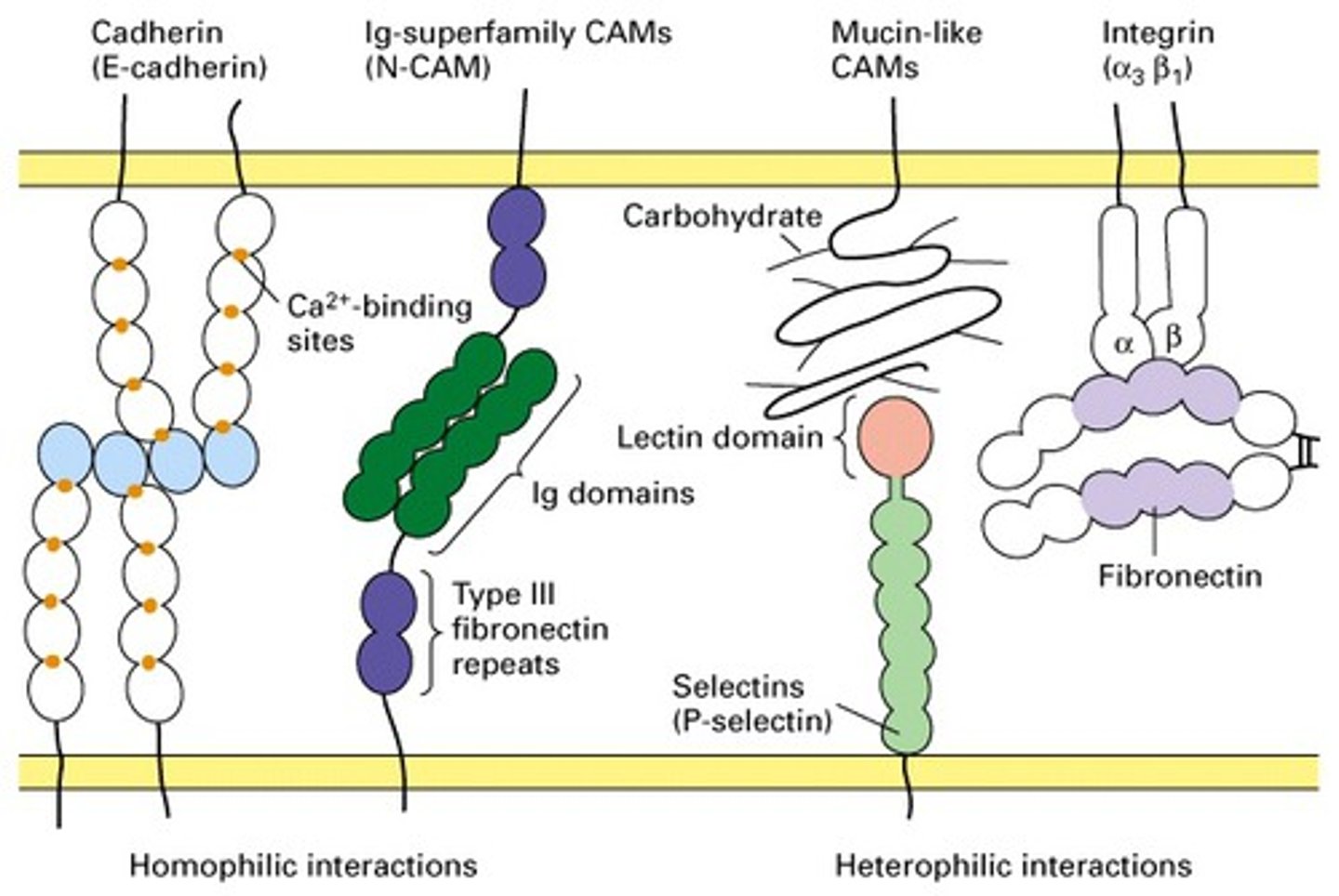
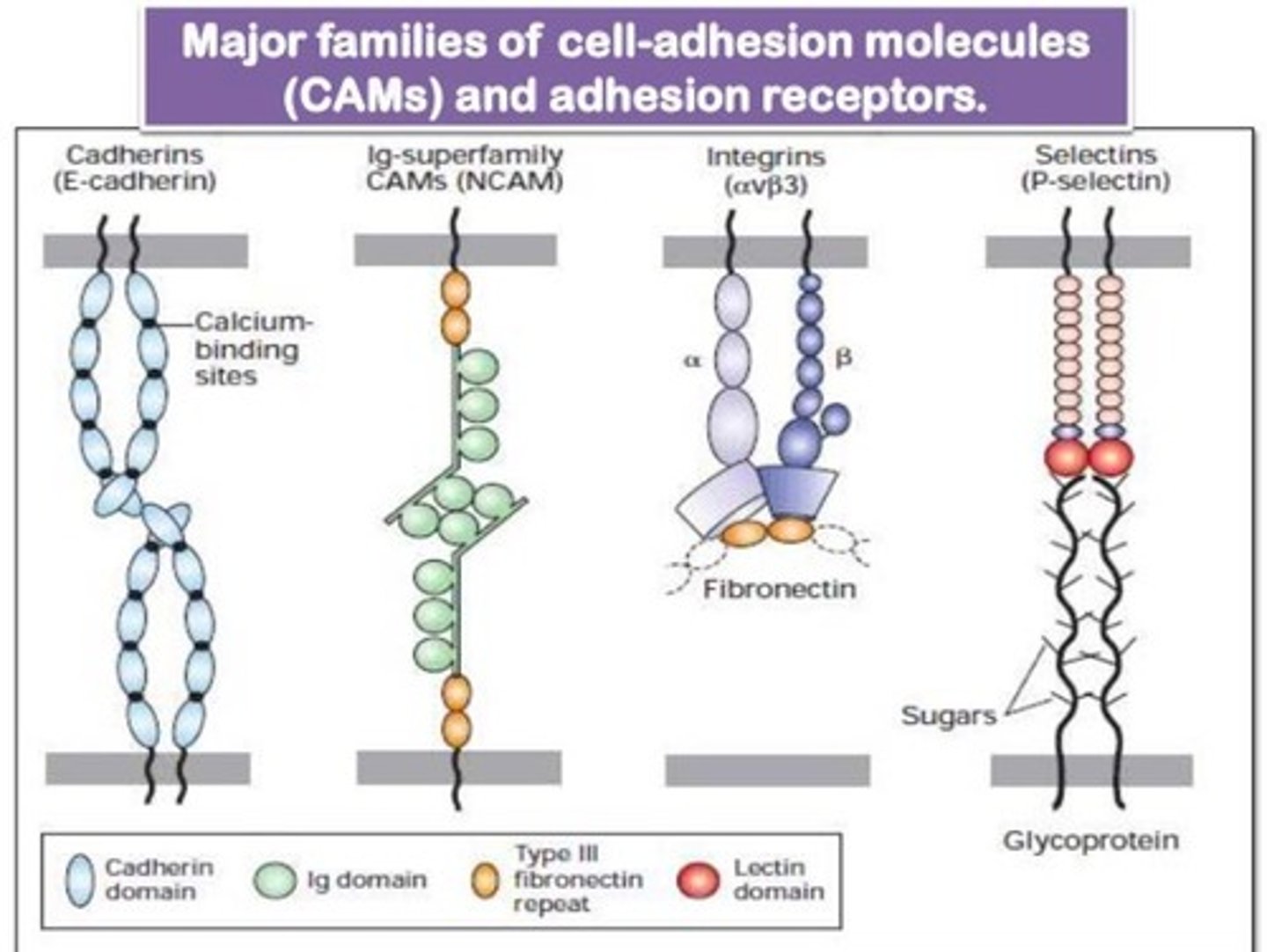
describe the 4 families of CAMs
- cadherins: hold cells together to maintain tissue integrity
- selectins: supports WBC migration to sites of inflammation
- Ig superfamily: facilitate adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells lining blood vessels during injury/stress
- integrins: α and β chains; anchor the cell to the ECM and relay signals from the ECM to the cell
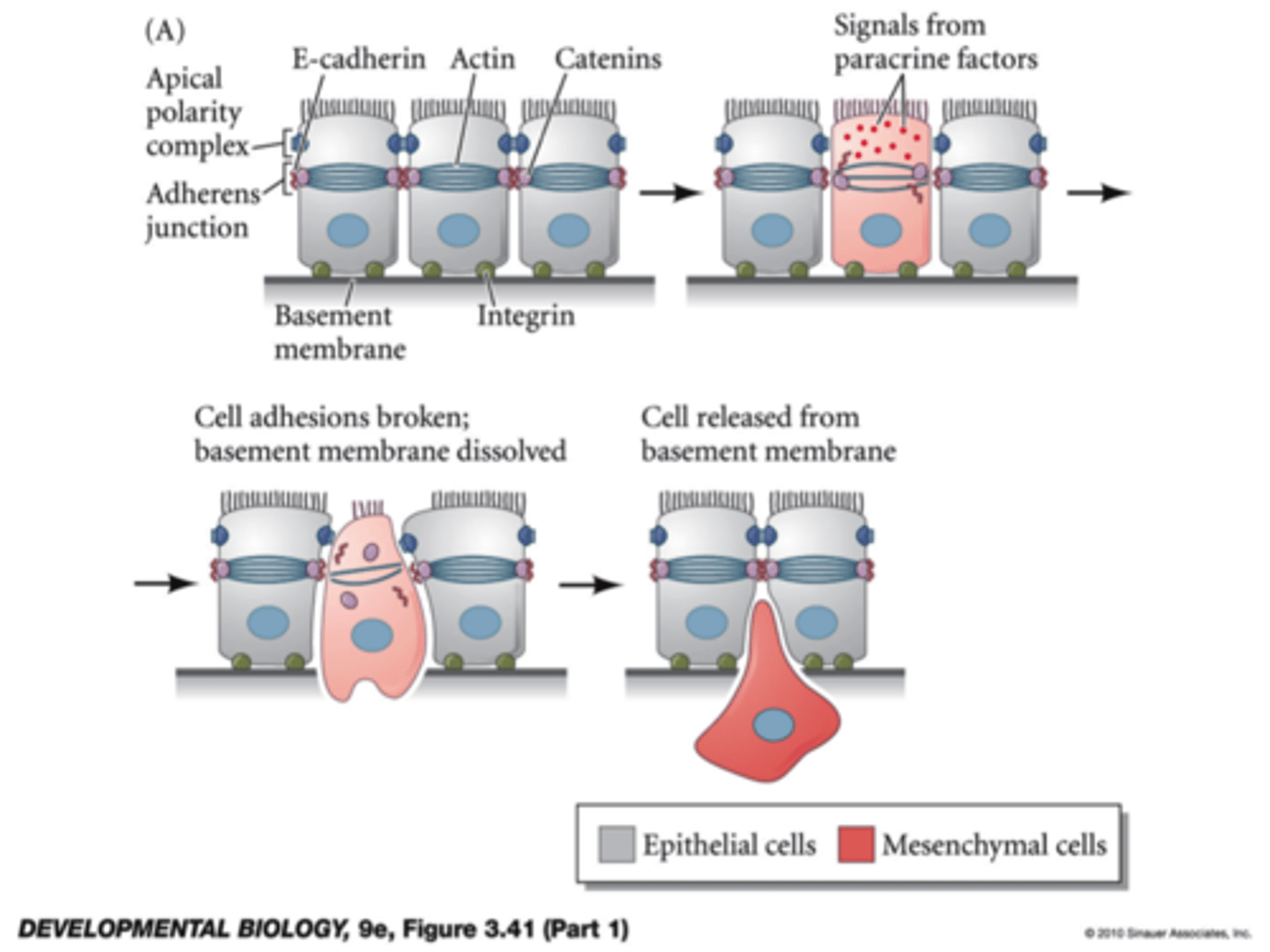
what is epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)?
process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell-cell adhesion ability, and gain migratory and invasive properties
- occurs in embryogenesis and cancer progression
how do CAMs affect metastasis?
tumor spread occurs when a cell loses its E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion capabilities
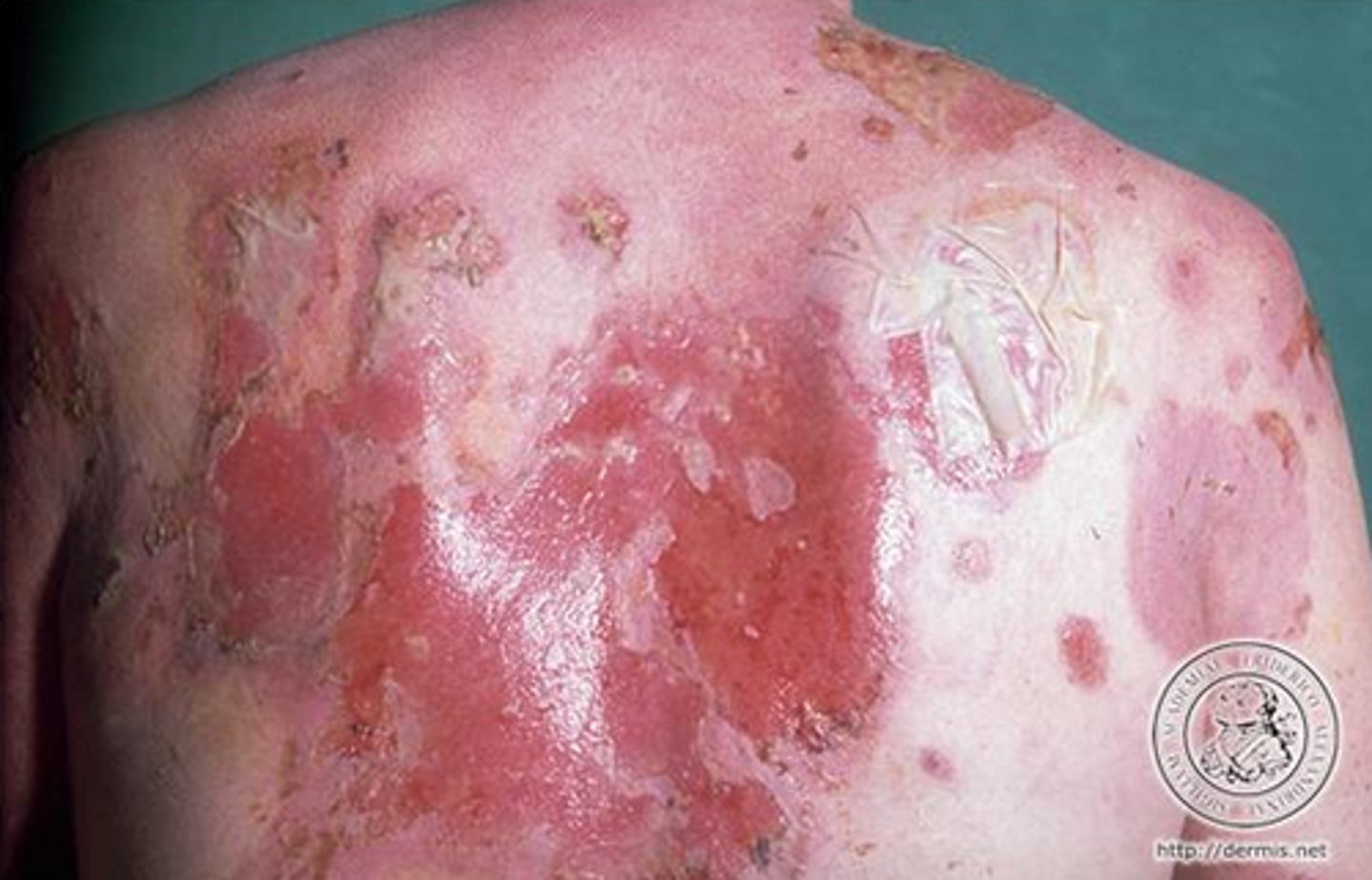
what is pemphigus?
an autoimmune condition characterized by the disruption of cadherin-mediated cell adhesions
- autoantibodies bind to proteins of a cadherin subfamily
- causes extreme blistering
what CAM is related to the development of asthma? what other conditions may be affected by CAM defects?
increased ICAM-1 expression is observed in the respiratory tract of patients with asthma
- in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, bone cells may have an increased expression of adhesion molecules
- CAMs may also assist in viral infection