Mitochondrial Disorders - BioChem Genetics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Mitochondria
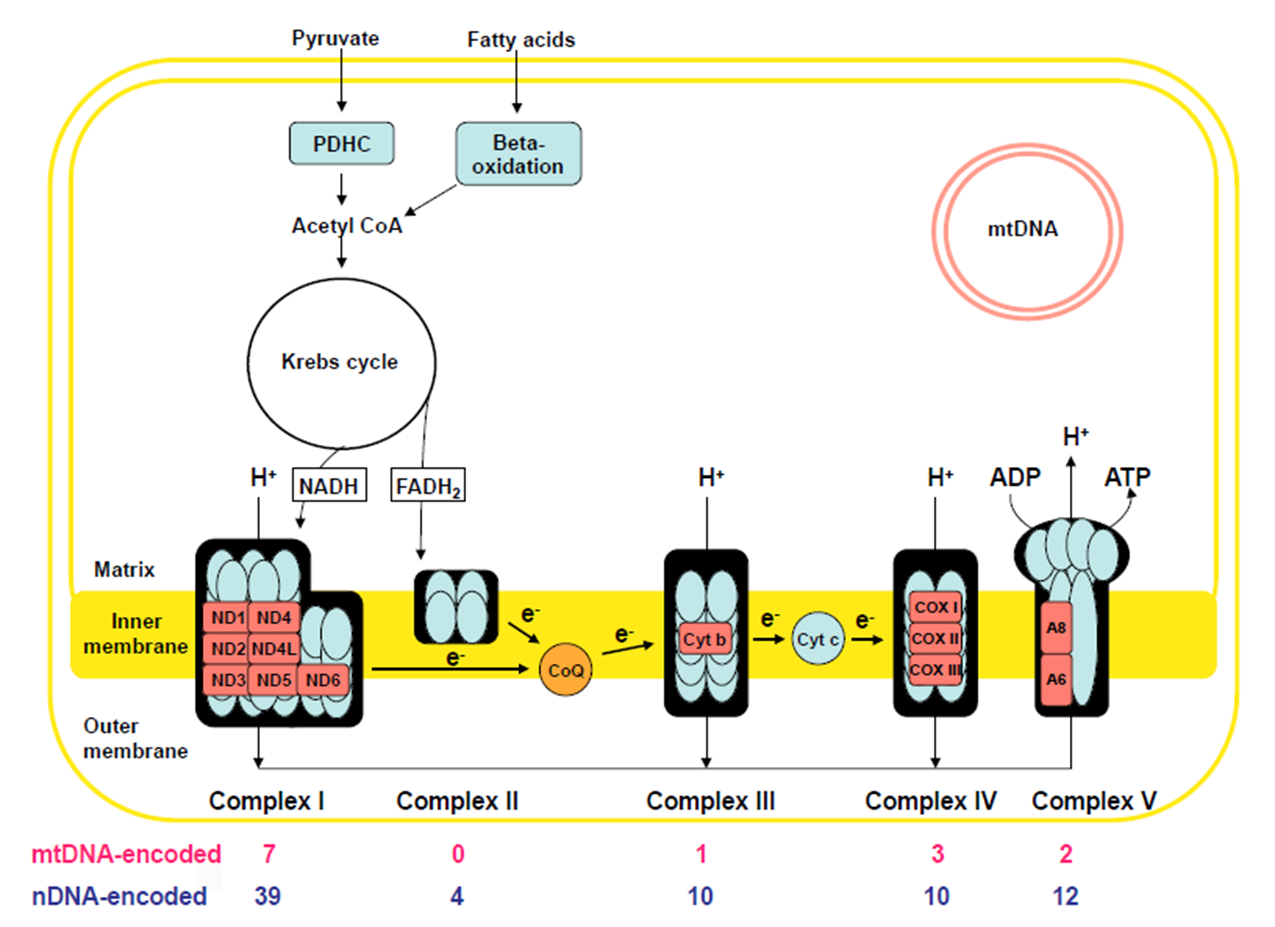
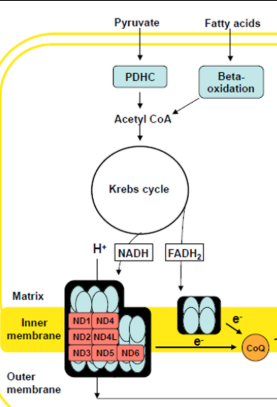
Site of oxidation phosphorylation: via the electron transport chain embedded in the inner mito membrane
Produce ATP
The other biochemical processes occur in the Mito:
Pyruvate oxidation
Krebs Cycle
Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The electron transport chain
Inner membrane has 5 distinct protein complexes embedded: some encoded by nuclear DNA, some encoded by Mito DNA
Use NADH + FADH coming form Krebs cycle break down of Actyl-CoA
Fatty Acids (generated via F.A. B-Oxidation)
Pyruvate (generated via glycolysis)
Electron transport down the chain of complexes: creates gradient by pumping IN H+ ions
Complex V uses gradient to Generate ATP as H+ ions move OUT
Mitochondrial Disorders
Oxidative Phosphorylation/Electron Transport chain dysfunction
Two varieties:
Secondary Mitochondrial dysfunction: Non-genetic conditions
Hypoxemia (inadequate Oxygen for Oxidative Phosphorylation)
Medication: valproic acid, HIV meds
Toxins: cyanide, rotenone
Primary Mitochondrial Disease
mitochondrial DNA itself or nuclear DNA mutations
Mitochondrial Genome
The Mitochondrial Chromosome: encodes 37 genes
only 3% of Mito. proteins are encoded by mito DNA
97% are encoded by nuclear DNA and imported into mitochondria
Complex 1
46 total proteins
MtDNA encoded: 7
nuDNA: 39
Leigh Syndrome
Leukodystrophy
Complex 2
4 proteins: ALL nuDNA ENCDOED
Leigh Syndrome
Paraganglioma
Pheochromocytoma
Complex 3
11 proteins
MtDNA: 1
nuDNA: 10
Leigh syndrome
GRACILE syndrome
Complex 4
mtDNa: 3
nuDNA: 10
Leigh Syndrome
Hepatopathy
Cardioencephalomyopathy
Leukodystrophy/tubulopathy
Complex V
mtDNA: 2
nuDNA: 14
Maternal Inheritance
mtDNA mutations can only be inherited through the mother
all mito provided by the ovum
no mito contriubted by the sperm
Heteroplasmy
Mito genomes can differ between mitochondria in a given cell and % of mutant mtDNA can vary in an individual from cell-to-cell and tissue-to-tissue
Each cell has up to 1000 mitochondria, each with their own copy of the mito genome
mtDNA mutation rate is 10-20x nuclear DNA mutation rate
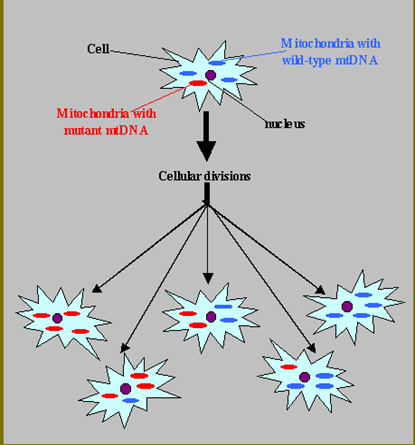
Threshold Effect.
energy requirements vary between tissues
mtDNA mutation burden varies tissue to tissue (heteroplasmy)
Tissue specific % mutant mtDNA threshold for disease
Phenotypic variability results
Example: Brain and Muscle have a lower threshold than Skin and Kidney
Mitochondrial Disorders: Presentation
Can present in almost any way and vary from person to person, but 3 general categories
“Classic” Mitochondrial diseases: reproducible, multi-organ pattern
Unexplained multi-organ dysfunction:
Hearing loss short stature
Diabetes + hypertrophic cardio myopathy
ophthalmoplegia +ptosis
Unexplained single organ syndrome: just hearing loss, epilepsy, GI
Often elevated Lactic acid in Blood or CNA and Mitochondrial proliferation in muscle
Myopathy, Encephalopathy,, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS)
Age of Onset: before 40yo (average 5-15)
Clinical
Stroke like episodes + Epilepsy, Dementia
Muscle weakness (myopathy), Cardiomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis
Hearing-Loss, Retinopathy, Diabetes
CT/MRI: Infarcts→ but not seen in vasuclar regions: infarct occurs due to region engery insufficney from Mitocondrial
Etiology: heterogeneous mtDNA mutations (Often mt-t RNA) → VERY dependent on Heteroplasmy with individual
Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged Red Fibers (MERRF)
Adolescent onset
Clinical manifestations
Epilepsy (myoclonic)
Muscle weakness (myopathy), Lactic acidosis, Ataxia
Encephalopathy, Hearing Loss
EMG
EEG:
Muscle Biopsy: (if done on affected muscle) will show ‘ragged red fibers’ caused by mitochondria proliferation
Etiology: Single mtDNA-tRNA mutation 80 to 90%
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
Age of onset 20-24 yo
Clinical:
Acute or sub-acute bilateral central vision loss→ Rapid progression to blindness (usually confined to optic nerve)
Rarely: heart block, dystonia, MS-like symptoms
Fundoscopy: early tortuous retinal arteries, followed by optic atrophy
Etiology: 95% mtDNA “ND” (electron transport subunit) gene mutations MATERNAL INHERITANCE
****4:1 M:F ration → X-linked modifier genes that make females less affected****
Ophthalmoplegia, Ptosis and Myopath
Chronic Progressive Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO)
External ophthalmoplegia, bilateral ptosis, mild myopathy
Onset after 20yo (slowly progressive)
Kerns-Sayre Syndrome (KSS)
Retinitis Pigmentosa, Cardiac conduction defects, ataxia, CSF protein >100
Also: myopathy, dysphagia, Sensory hearing loss, dementia, diabetes
Etiology:
Mainly mtDNA deletions→ can be smaller or larger chunks of mtDNA (smaller =CPEO, larger=KSS)
Majority are SPONTEOUS
Subacute Necrotizing Encephalopathy (Leigh Syndrome)
6-12 months - 3-5 years (25% have later onset or slower forms)
Clinical: (often abrupt decompensations/regression with infection/fever)
Developmental stagnation and regression
Seizures, Ataxia, Hypotonia, spasticity
ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, optic atrophy
Diagnostic Testing
Elevated CSF blood, MRspect: LacticAcid peaks, MR Basal.G lucciences
Deficiencies in Complex I (20%), IV(20%), PDH/PC (10%)
Leigh Etiology
Genetic Heterogeneity
10-30% mitochondrial DNA mutations → maternal inheritance
90-70% nuclear DNA mutations → Classic Mendelian
HETEROPLASMY AFFECT: If a lower # of mito. in a cell have these mutations = Later onset Neuropathy, Ataxia, Retinitis Pigmentosa (NARP)
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDHC) Deficiency: Clinical + Testing
Failure to convert Pyruvate to Actyl-CoA (via PDH)
Lactic Acid levels elevated (PDHC most common cause of Lactic Acidosis)
Clinical Features: Progressive intermittent neurologic deterioration
hypotonia, seizures, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, dystonia
Presents similar to mitochondrial dysfunction
Suggestive Abnormal Tests
Plasma: increased Lactic Acid + Pyruvate, but normal Pyr : L.A ratio
***MITOCONDIRLA DISORDERS: increased L.A but norm pyruvate***
Cerebral Spinal Fluid: increased Lactic Acid
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDHC) Deficiency: Metabolism +Etiology
Failure to convert Pyruvate to Actyl-CoA (via PDH)
Lactic Acid levels elevated (PDHC most common cause of Lactic Acidosis)
Etiology: PDHC is a multisubunit complex
Catalytic components: E1, E2, E3
Regulatory component: PDH Phosphatase
Confirmation:
PDHC enzyme activity assay
Sequencing of
E1 → PDHA1 : MOST COMMON , X-Linked (males only)
E2 → DLAT, Recessive
Mitodoncrial Diease: Work Up
Serum levels: increased anion gap + metabolic acidosis
Lactic Acid: Pyruvate ratios (>30 Mito. Dis ; <10 PDHC Def.)
Imaging: brain MRI, Spectroscopy ( LA peaks over brain regions( BasalGang)
Basal Ganglia hypodensities: generalized atrphy
Hypoplastic corpus callosum if fetal lactic acidosis
Muscle Biopsy
Genetic Testing
Mitochondrial Disease: Muscle Biopsy
Allows for:
Detecting ragged red fibers (mito. proliferation)
Abnormal mitochondria proliferation
Detecting enzyme activity of the chain-genes
Mutational analysis of mitoDNA
Pitfalls:
need 1 gram of flesh (large amount)
biopsy of moderately affected muscle
may not distinguish exact genetic mechanisms
Genetic Testing
mtDNA:
Leigh Syndrome
LHON
MERRF (blood/muscle)
MELAS (blood/muscle)
NARP (blood/muscle)
KSS/CPEO (muscle)
nDNA (all in blood)
Leigh syndrome
MNGIE
Mohr-Tranebjaerg
Friedreich’s Ataxia
AR spastic paraparesis
AD PEO
Mitochondrial Disorders: Treatments
Less evidence for specific treatments that actually improve outcomes
Trials with Vitamins that optimize Electron Transport chain function:
Carnitine
Biotin
thiamine
Riboflavin
High Fat/ Low Carb diet: low carb→ less glycolysis→ less LA
Avoid Mito toxic meds
Reduce LA, control acidosis (dialysis/vent)