Plant Systematics Exam whatever this one is
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Family Fabaceae flower characteristics
5 connate sepals, 5 petals (distinct or connate). <10 to many stamens (free or connate). 1 carpel, HYPOGYNOUS
What is a pulvinus and what family is it found in?
Enlarged section at the base of a plant leaf/leaflet. Uses turgor to move leaves. Fabaceae
What does monadelphous mean and what family is it found in?
Flower has 10 connate stamen. Fabaceae
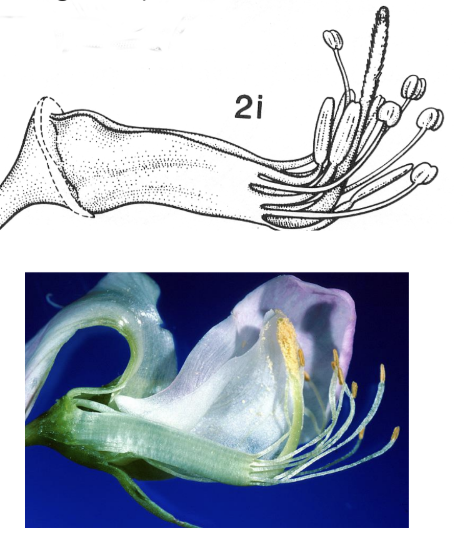
What does diadelphous mean and what family is it found in?
Flower has 9 connate stamen with one extra on the loose. Fabaceae
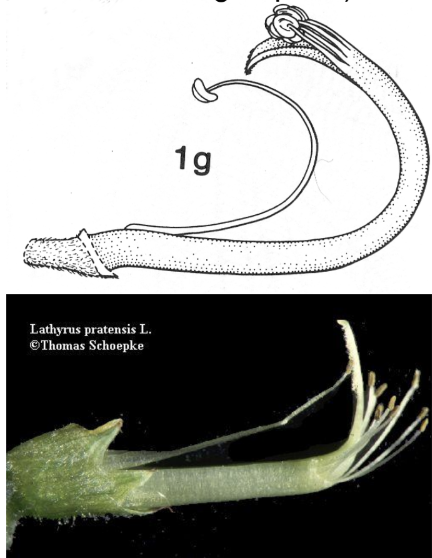
Fabaceae placentation and fruit type
Marginal placentation, legume or loment
What characteristic does Fabaceae have that we have not seen before?
Symbiosis with rhizobia, nitrogen fixing bacteria
What family has a symbiotic relationship with ants?
Fabaceae, develop nectaries that produce nectar and beltian bodies
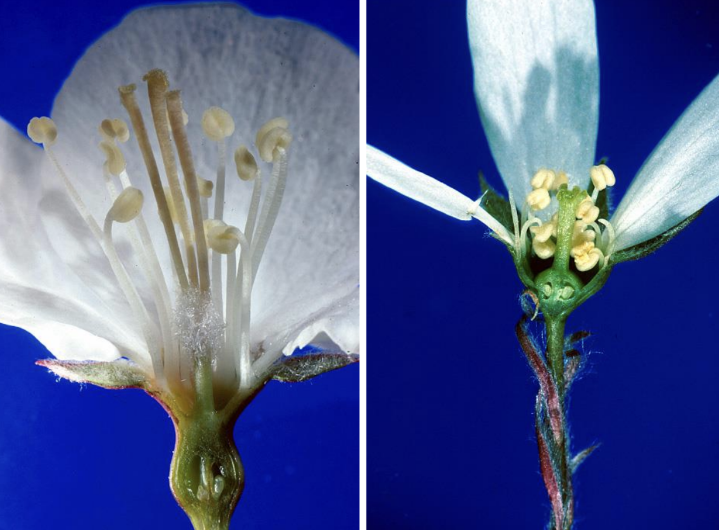
Family Rosaceae flower characteristics
Solitary or inflorescence, 5 connate sepals, 5 free petals. Many stamens. 1-many carpels (4 flower types) Perigynous to epigynous, usually with hypanthium
Flower type 1 of Rosaceae
Many FREE carpels, but may arise from elongated receptacle. Perigynous with hypanthium
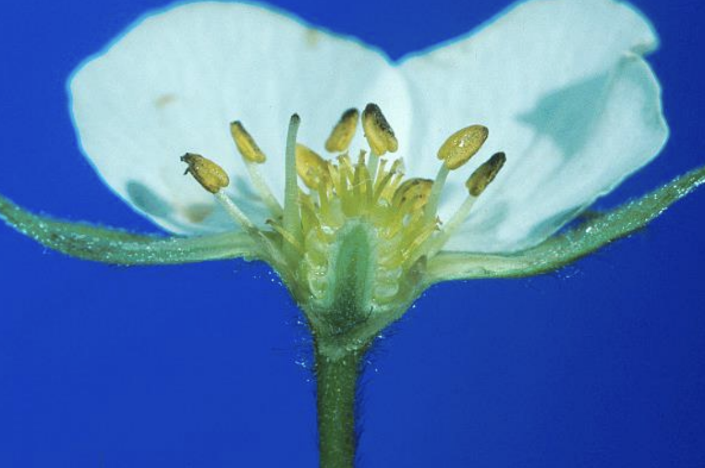

What is a hypanthium and what family do we see it in?
Bowl like shape/structure of the flower seen in Rosaceae
Flower type 2 of Rosaceae
2-5 FREE carpels. Perigynous with hypanthium

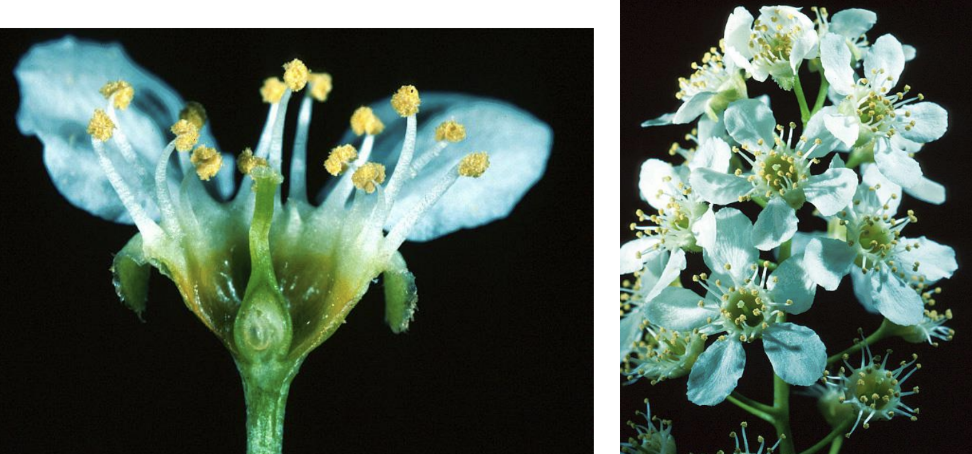
Flower type 3 of Rosaceae
1 carpel. Perigynous with hypanthium

Flower type 4 of Rosaceae
2-5 connate carpels. Epigynous

Rosaceae placentation and fruit type
When carpels are free- basal, apical or parietal (marginal). aggregate fruit of drupelets, achenes, or follicles
When carpels are connate- axile. drupe or pome
Families in Order Fagales
Fagaceae, Betulaceae, Juglandaceae
Family Fagaceae flower characteristics
Small unisexual flowers.
Staminate- catkins. Very reduced perianth. 4-many distinct stamens
Carpellate- solitary or in a cluster. Very reduced perianth. 3 connate carpels. Epigynous
Family Fagaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation, nut with an involucre
What is an involucre and what family do we see it in?
Cap on an acorn or spiky shell on a chestnut. Fagaceae
What is the difference between red/black oaks and white oaks?
Red/black- have bristle tips on the lobes/teeth of leaves. Acorns mature at the end of 2nd season and root in the spring.
White- leaves without a bristle tip. Acorns mature at the end of the 1st year and root in the fall
Family Betulaceae flower characteristics
Small flowers in catkins (both sexes), unisexual flowers. Many cymules in a single catkin.
Staminate flower- very reduced perianth with 1-4 distinct stamens
Carpellate flower- very reduced perianth with 2 connate carpels. Epigynous
What is a cymule and what family do we see it in?
Found in a catkin, 2-3 flowers clumped together
Betulaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation, 1 seeded nutlet or samara with bracts (winged bracts or hard cone like structure)
Juglandaceae flower characteristics
Unisexual flowers (monoecious).
Staminate- catkins with 3-many distinct stamens
Carpellate- flowers in clusters. 2 connate carpels. Epigynous
Juglandaceae placentation and fruit type
Similar to axile placentation. Drupe like nut with a husk
Family Brassicaceae flower characteristics
Inflorescence. Mostly radial symmetry with bisexual flowers. 4 distinct petals usually forming a cross. 4 distinct sepals. Usually 6 stamens (some tetradynamous). 2 connate carpels. Hypogynous
What does tetradynamous mean and what family is it found in?
6 stamens, 4 tall and 2 short. Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae placentation and fruit types
Parietal placentation. Berry or capsule (silique or silicle)
What is the difference between silique or silicle and what family are they found in?
Silique- long and skinny
Silicle- rounded or heart shaped
Brassicaceae
What is the difference between holoparasitism and hemiparasitism?
Holoparasite- does not photosynthesize
Hemiparasite- does some photosynthesis
What is a haustorium?
Specialized absorption structure derived from root tissue, used by parasitic plants to gather nutrients from host.
Family Viscaceae flower characteristics
Inflorescence. Small, unisexual (monoecious or dioecious) with radial symmetry. 3-4 tepals (distinct or connate). 3-4 stamens opposite the tepals. 3-4 connate carpels. Epigynous
Viscaceae placentation and fruit type
Basal placentation. Single seeded berry, often sticky
What characteristics are seen in Order Caryophyllales?
Betalains- red/violets and yellow/oranges
CAM photosynthesis
Family Caryophyllaceae flower characteristics
Swollen nodes. Single flowers or inflorescence. 5 sepals and petals. 4-10 stamens (free, connate, or adnate). 2-5 connate carpels. Hypogynous
Caryophyllaceae placentation and fruit type
Free central placentation. Capsule
Family Cactaceae flower characteristics
Betalains provide color for flowers. Solitary and bisexual with radial symmemtry. Many tepals. Many free stamens. 3-many connate carpels. Epigynous
Cactaceae placentation and fruit type
Parietal placentation. Berry- often with spines or glochids
Various mechanisms of capturing animal prey
Snap traps (venus fly trap), pitfall traps (pitcher plants), flypaper (drosera) suction bladders
Family Droseraceae flower characteristics
Small flowers in an inflorescence. 5 sepals (connate), petals (distinct), and stamens (mostly distinct). 3 connate carpels. Hypogynous
Droseraceae placentation and fruit type
Basal or parietal placentation. Capsule
Family Ericaceae flower characteristics
Inflorescence or single flower, bisexual. 2 flower types (radial and bell shaped, bilateral and open) 4-5 sepals and petals, connate. 8-10 stamen (free, adnate to petals, connate). 2-10 connate carpels. Hypogynous
What is special about Family Ericaceae?
Ericoid mycorrhizae, some species non-photosynthetic (mycoheterotrophic)
Ericaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation. Capsule, berry, or drupe.
Family Sarraceniaceae flower characteristics
Large and showy flowers solitary on stem. Bisexual with radial symmetry. 5 sepals, 5 petals, many stamen. 3 or 5 fused carpels. Hypogynous. Style is umbrella shaped with stigmas at the tips
Sarraceniaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation. Capsule
Family Solanaceae flower characteristics
Inflorescence or single flower. Bisexual and radially symmetrical. 5 connate sepals. 5 petals, connate to form a bowl or funnel. 5 stamens adnate to petals. 2-5 connate carpels. Hypogynous
What type of pollination is found in Solanaceae?
Buzz pollination from bumblebees and solitary bees
Solanaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation, berry or capsule
Family Convolvulaceae flower characteristics
Solitary or inflorescence. Bisexual with radial symmetry. 5 sepals, usually free. 5 petals, often connate with folds. 5 stamens adnate to petals. 2 connate carpels. Style often deeply embedded in ovary (gynobasic). Hypogynous.
Convolvulaceae placentation and fruit type
Axile placentation. Capsule

Family
Fabacaea
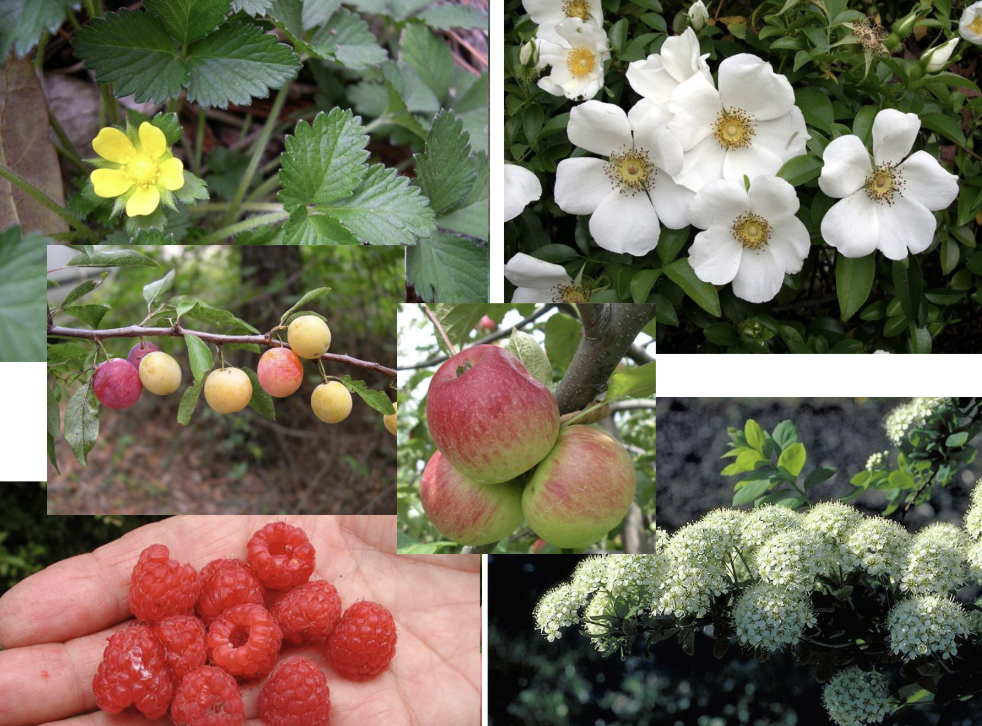

Family
Rosaceae
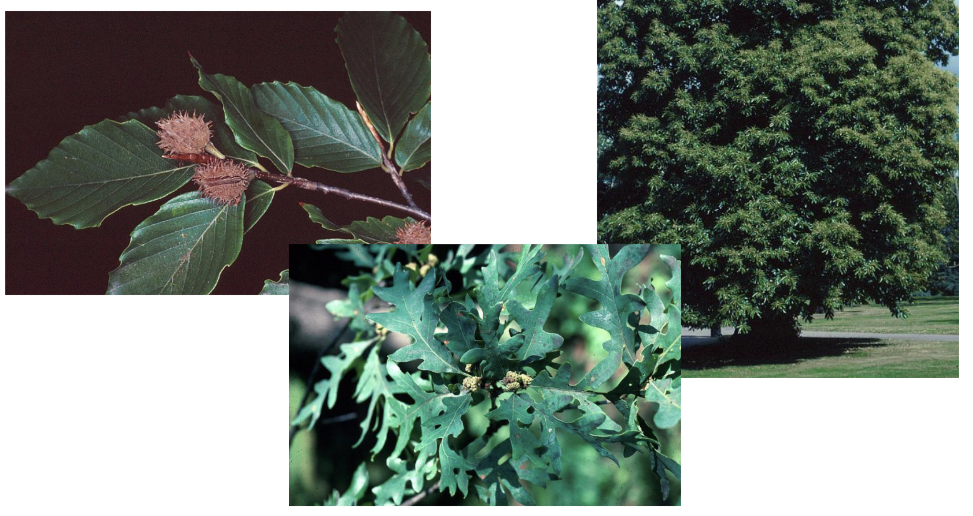

Family
Fagaceae
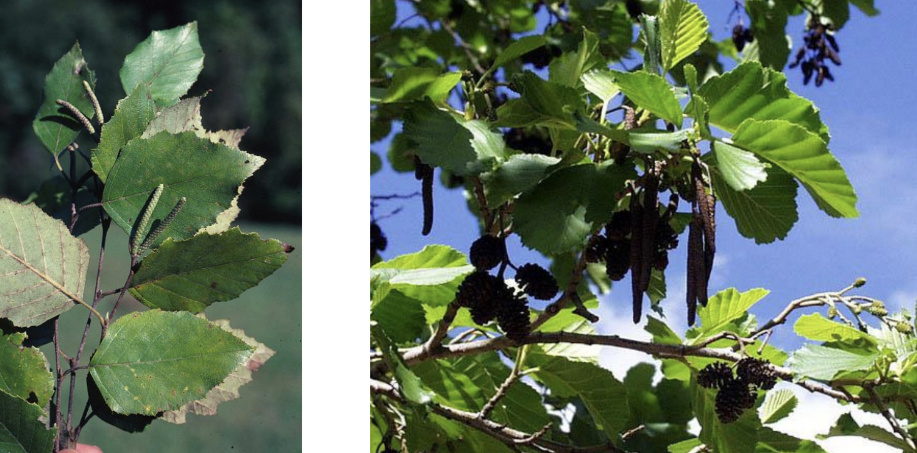

Family
Betulaceae

Family
Juglandaceae
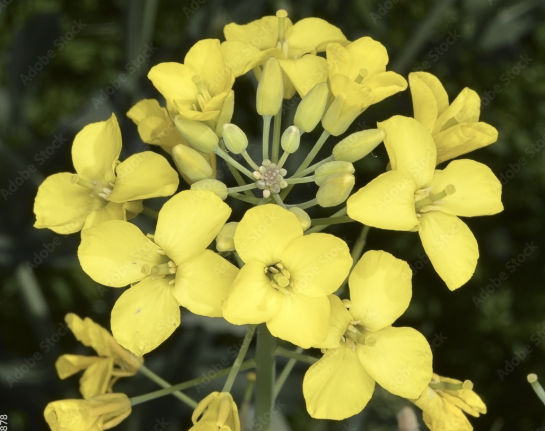

Family
Brassicaceae

Family
Viscaceae

Family
Caryophyllacceae

Family
Cactaceae

Family
Droseraceae

Family
Ericaceae
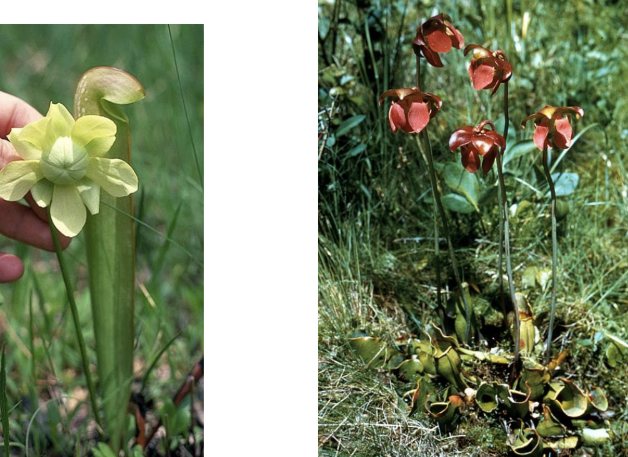

Family
Sarraceniaceae
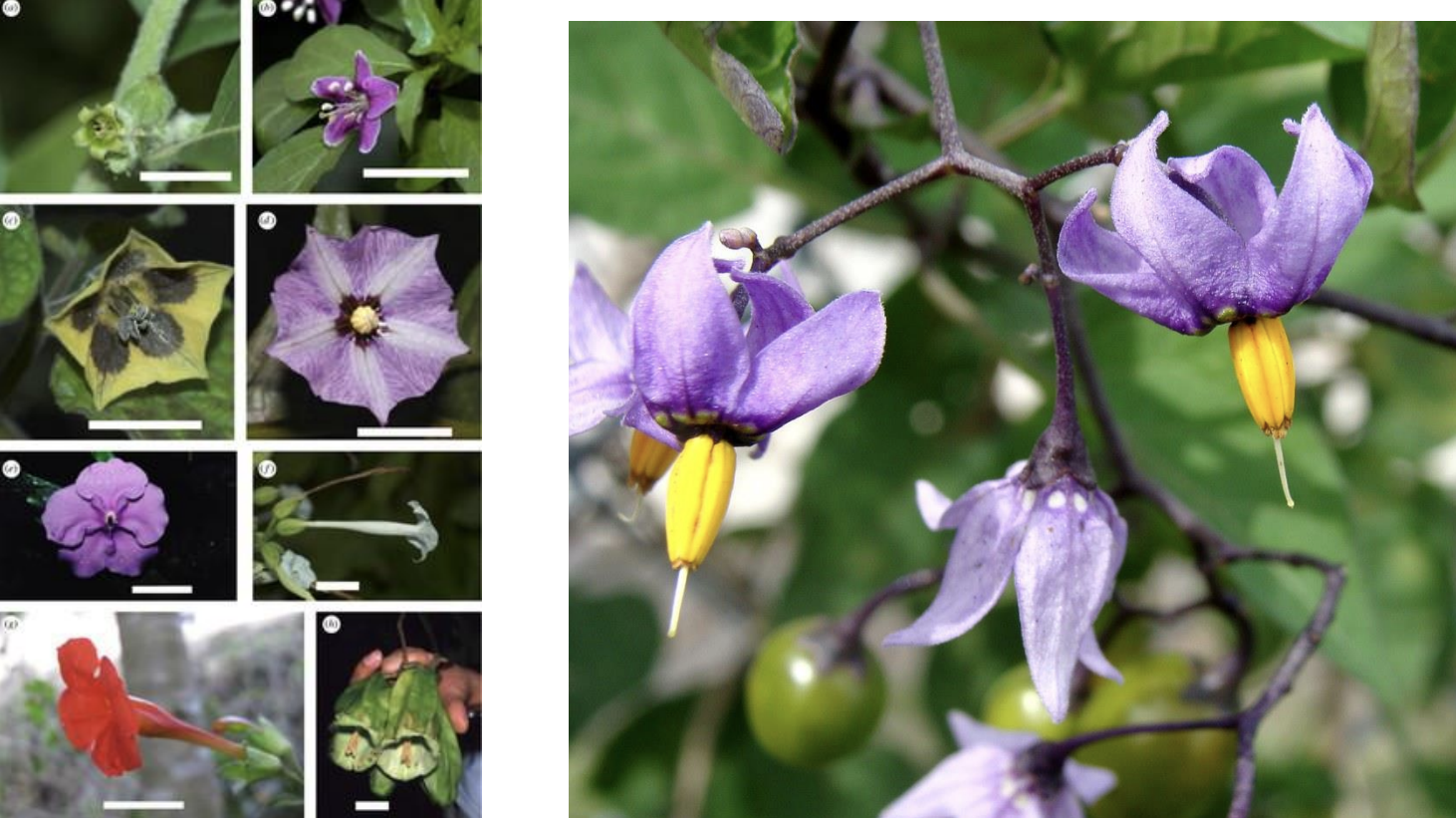

Family
Solanaceae

Family
Convolvulaceae
What does nyctinastic mean and what family is it in?
Circadian rhythm movement in Fabaceae
What does thigmotropic mean and what family is it in?
Touch movement in Fabaceae