ch 17- endocrine system
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
endocrine system
comp of ductless glands that synthesize + secrete hormones
hormones released into blood
target cells
have specific receptors for a hormone
bind hormone + respond
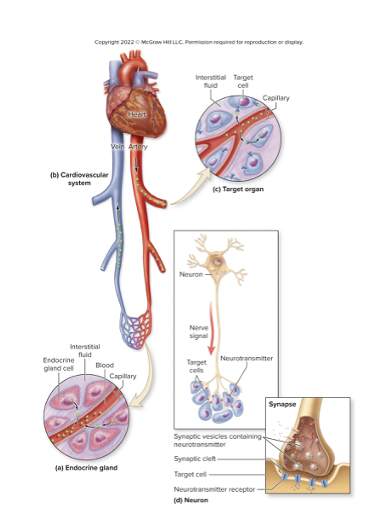
steps to hormone transport → target cells
hormones released → interstitial fluid→ blood→ transported w/in blood → leave blood + enter interstitial fluid → hormone binds to t. cell receptors
ligands
chemical messengers
bind to cellular receptor on t. cell
how does it differ from nervous system
exhibits longer reaction times
has longer-lasting effects (mins→ days→ weeks)
functions of endocrine system
regulating development, growth + metabolism
maintain homeostasis of blood composition + volume
controlling digestive processes
controlling reproductive activities
what kind of tissue does endocrine gland have
epithelial tissue that makes + releases hormones w/in a connective tissue framework
which are solely endocrine
pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal
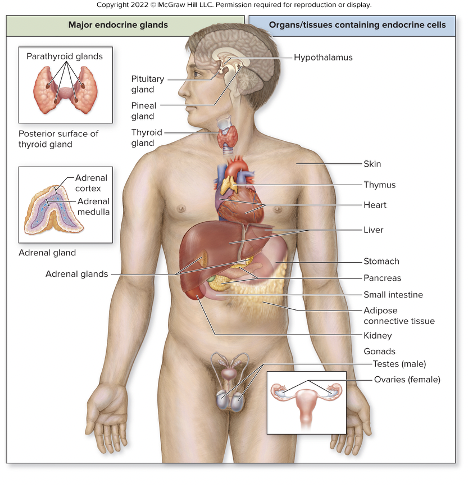
places w endocrine cell in clusters in organs
hypothalamus, skin, thymus, heart, liver, stomach, pancreas, small intestine, adipose CT, kidneys +gonads
hormonal stimulation
gland cell releases its hormone when some other hormone binds to it
ex: TSH stimulates thyroid gland
humoral stimulation
gland cell releases its hormone when there is a certain change in levels of nutrient or iron in the blood
ex: release of insulin when rise in glucose
nervous system stimulation
gland cell releases its hormone when a neuron stimulates it
steroids
lipid-soluble from cholesterol
ex: gonadal (estrogen), adrenal cortex (cortisol),
calcitriol is really a sterol
- vitamin D
biogenic amines (monoamines)
catecholamines, TH, melatonin
water-soluble except for TH
NP + lipid-soluble
proteins
most hormones in this cat.
water-soluble chains of amino acids
local hormones
signaling ‘cules’ that don’t circulate in blood
bind to cells
autocrine stimulation
a cell secretes a signal molecule that binds to receptors on the same cell
paracrine stimulation
cells release signaling molecules (paracrine factors) that travel a short distance and bind to receptors on nearby target cells, altering their behavior
eicosanoids
from fatty acids w/in phospholipid bilayer
synth. through enzymatic cascade
prostaglandins
stimulate pain + inflammatory responses
aspirin + other non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block prostaglandin formation
eicosanoid formation
phospholipase A2 removes arachidonic acid from phospholipid
other enzymes convert arachidonic acid to a subtype of eicosanoid
how do lipid-soluble transport in blood?
NEED A CARRIER PROTEIN
don’t readily dissolve in blood
carriers protect hormones from early destruction
are most hormones bound or unbound
most are bound
unbound (free) hormone
able to exit blood + bind to target cell receptor
how do water-soluble hormones travel?
travel through blood
don’t need a carrier protein
hormone release
positively related
an increase release results in higher blood concentration
ex: high blood sugar increase in insulin release
hormone elimination
enzymatic degradtion in liver cell
removal from blood via kidney excretion or t.cell uptake
faster the elimination rate, lower the blood concetration
half-life
time necessary to reduce a hormone’s concentration to half its original level
what happens to hormones with a short half-life
must be secreted frequently to maintain normal concentration
do water-soluble have a long half life?
no- have a short half-life
lipid-soluble hormones
diffuse across t. cell membrane
receptors in cytosol or nucleus
once hormone cell binds to receptor it forms hormone-receptor complex
Hormone-response element (HRE)
results in transcript of mRNA, which is translated to a protein
may have structural or metabolic effect
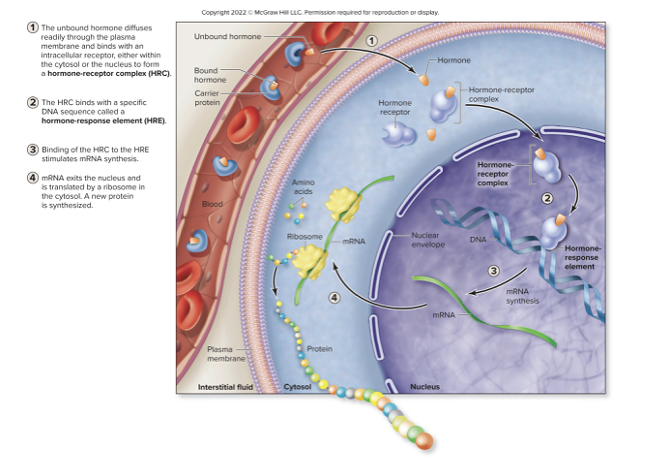
lipid-soluble will only bind to the outside of the cell receptors
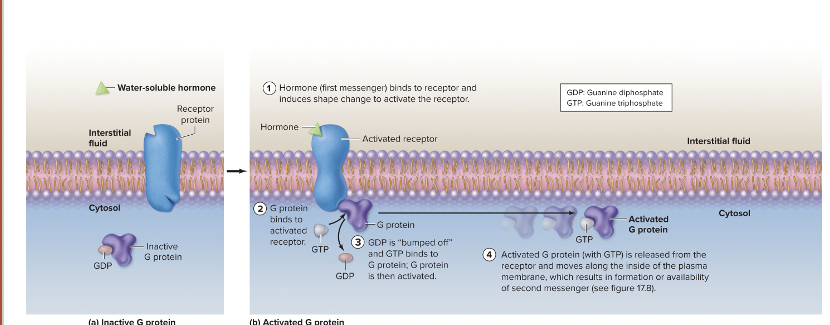
Signal transduction pathway
hormone is 1st messenger- intiates events by binding to receptor
binding activates a G-protein (internal membrane protein that binds a guanine nucleotide)
results in binding of GTP instead of GDP
G-protein activation causes activation of a membrane enzyme like adenylate cyclase or phospholipase C
second messenger- chemical modifies cellular activity
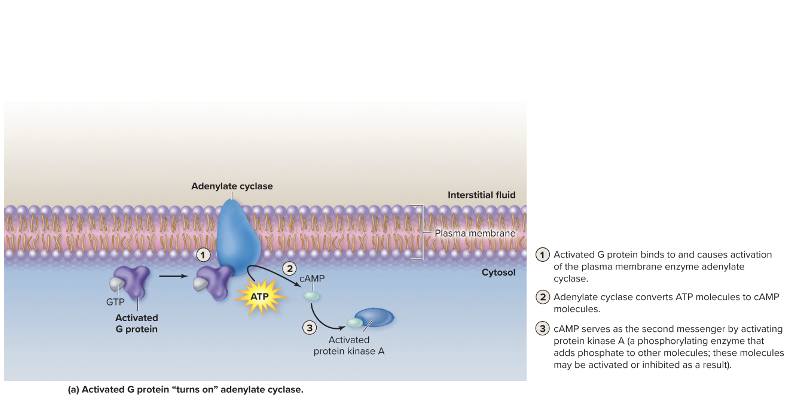
adenylate cyclase activity
after hormone (ex: glucagon) binds to its receptor G protein
activated G protein → adenylate cyclase
adenylate cyclase → cAMP
cAMP activates protein kinase (A)
protein kinase A phosphorylates other ‘cules’
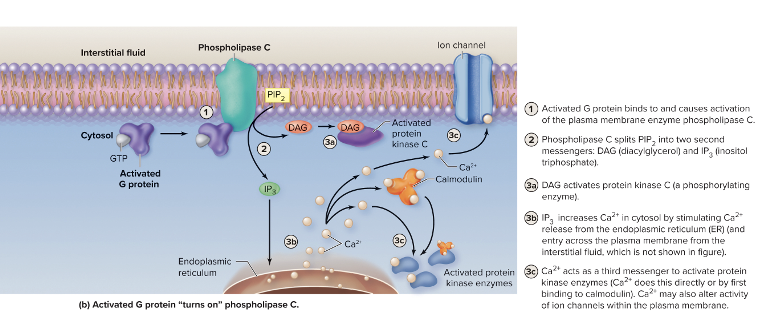
phospholipase C activity
binds to receptor, G protein
activated G protein → phospholipase C
phospholipase C splits PIP2 into diacylglycerol (DAG) + inositol triphosphate (IP3)
DAG is a 2nd messenger of the membrane that activates protein kinase C
IP3 is a 2nd messenger leaves membrane + causes increase in Ca2+ in cytosol
ca2+ acts as a 3rd messenger, activating kinases → ion channels
action of water-soluble hormones
activation or inhibition of enzymatic pathways '
growth through cellular division
release of cellular secretions
changes in membrane permeability
muscle contaction or relaxation
Intracellular enzyme cascade
signal amplified at each step
few hormone ‘cules’ change many ‘cules’ w/in cell
signaling pathway controls
cells possess mechanisms to quickly inactivate intermediate
ex: break down 2nd messengers
how to target cells varies
number of receptors for the hormone
stimulates response to other hormones
up-regulation
increases # of receptors
increases sensitivity to hormone
sometime when blood levels are low
sometimes when development, cell cycle, cell activity
down-regulation
decreases # of receptors
decreases sensitivity to hormone
sometime when blood levels are high
sometimes when development, cell cycle, cell activity
ex: diabetes 2
synergistic interactions
one hormone reinforces activity of another hormone
ex: estrogen + progesterone
permissive interactions
one hormone requires activity of another hormone
ex: oxytocin milk ejection effect requires prolactin’s milk generating effect
antagonistic interaction
one hormone opposes activity of another hormone
ex: glucagon increase blood glucose while insulin lowers it
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
inferior to HT in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
connected to HT by infundibulum
split btw anterior + posterior
posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
smaller, neural part of PG
HT neurons project through infundibulum + release hormones in PP
somas in supraoptic nucleus + paraventricular nucleus
axons in hypothalmo-hypophyseal tract of infundibulum
synaptic knob w/in PP
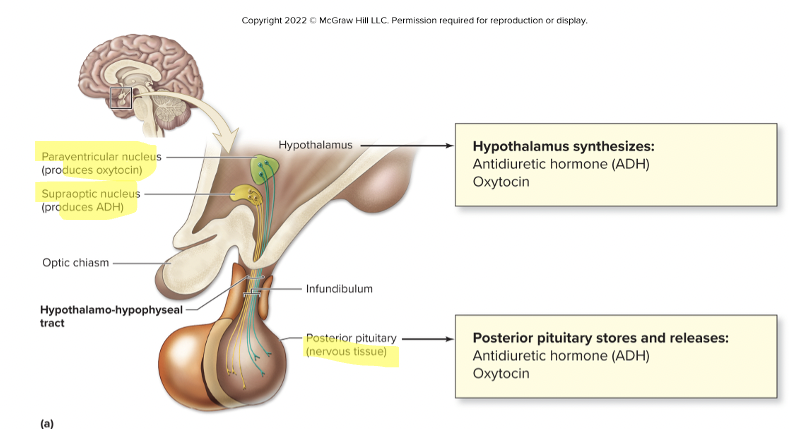
what does supraoptic nucleus produce?
ADH
what does paraventricular nucleus produce?
oxytocin
Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
blood vessels connects HT to anterior pituitary
primary plexus
porous capillary network associated with HT
secondary plexus
capillary network associated with AP
hypophyseal portal veins
drain primary plexus + transport to secondary plexus
What does the posterior pituitary release
storage + release site for antidiuretic hormone ADH and oxytocin OT made in HT by neurosecretory cells
antiduretic hormone (vasopressin)
made in supraoptic nucleus
functions: decreases urine production, stimulate thirst, constrict blood vessels
oxytocin
made in paraventricular nucleus
functions: uterine contraction, milk ejection, emotional bonding
How does the HT and anterior pituitary gland interact?
HT hormonally stimulates anterior pituitary to release its hormones
HT secretes regulatory hormones
travel via portal blood vessels to pituitary
anterior pituitary secretes hormones into general circulation
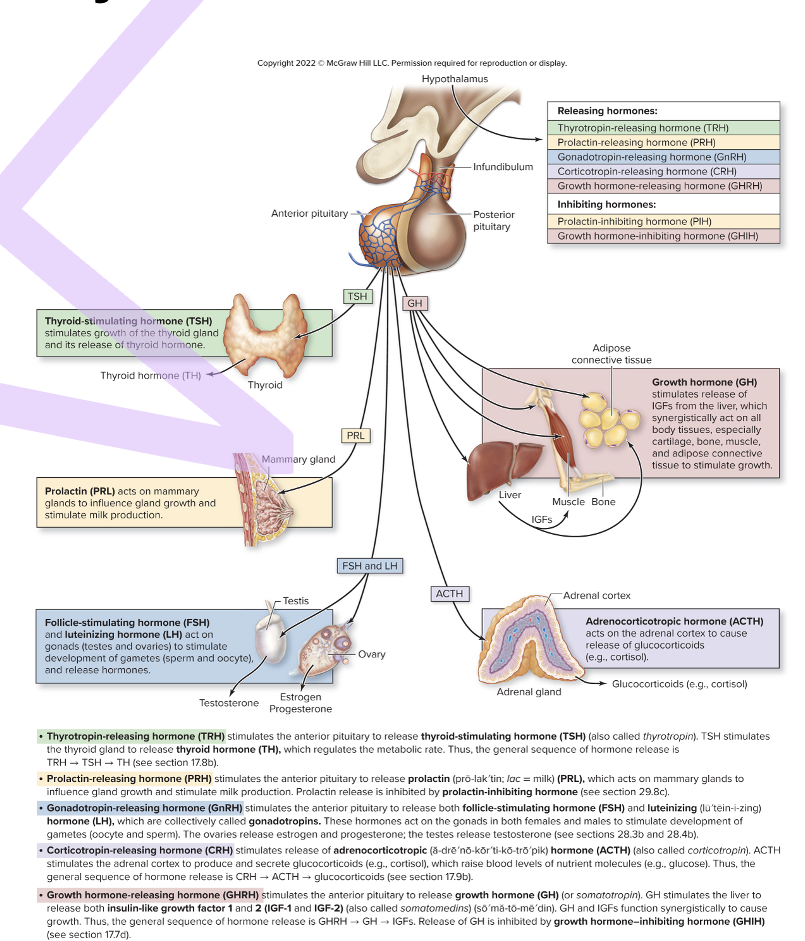
what are the inhibiting hormones?
prolactin-inhibiting (PIH) and growth-inhibiting (GIH)
what are the releasing hormones?
thyrotropin-releasing (TRH), prolactin-releasing (PRH), gonadotropin-releasing (GnRH), corticotropin-releasing (CRH), growth hormone- releasing (GHRH)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
thyrotropin
release by TRH from HT
cause release of TH from thyroid gland
TSH→ HT→ TRH→ thyroid gland → TH
protecting (PRL)
release by PRH, inhibited by PIH from HT
causes milk production, mammary gland growth in females
PRH→PRL→ PIH from HT
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
corticotropin
release by CRH from HT
causes release of corticosteroids by adrenal cortex '
HT→ CRH→ ACTH→ adrenal cortex → corticosteroids
gonadotropins: follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
release by GnRH from HT
female: regulate ovarian development + secretion of estrogen + progesterone
male: sperm develp’t + secretion of testosterone
growth hormone (GH, somatotropin)
causes liver to secrete insulin-like growth 1 + 2
GH + IGFs function synergistically to stimulate cell growth + division
hypophysectomy
surgical removal of PG bc of tumors
various H’s need to be replaced + their level need to be monitored
where do GHRH + GHIH come from?
the HT
the amount impacts a person’s age, time of day, nutrient level, stress + exercise
effects of GH
stims release of IGFS from liver
all cells have receptors for GH, IGFs or both
H stimulate increase protein synth., cell division, cell differentiation
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen into glucose
gluconeogenesis
conversion of nutrients to glucose stimulated
glycogenesis
synthesis of glycogen inhibited
lipolysis
breakdown of triglycerides stimulated
lipogenesis
formation of triglycerides inhibited
Pituitary dwarfism (GH deficiency)
littlee= GH production
from HT or pituitary problem
short stature + low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
pituitary gigantism
too much GH
excessive growth + increased blood sugar
acromegaly
excessive GH in adult
enlargement of bones, face, hands + feet
increase release of glucose + organ increase
from loss of negative feedback
anatomy of thyroid gland
inferior to thyroid cartilage of larynx, anterior to trachea
midline by isthmus
Follicular cells
cuboidal epithelial cell that surround a central lumen, synthesize thryroglobulin (TGB)
produce + release TH
Parafollicular cells
cells btw follicles, make calcitonin
hormone decreases blood Ca levels
Hypthalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis
cold temp, pregnancy, high altitude, hypoglycemia or low TH cause HT to release TRH
TRH → AP→ TSH
TSH binds to follicular cell → release Th
T3
triiodothyronine
more active
T4
tetraiodothryronine
more abundant
Effects of TH
increases metabolic rate + protein synthesis in targets
stims. sodium-potassium pump in neurons
calorigenic: generates heat, raises temp
stims. increased amino acid + glucose uptake
increase # of cellular respiration enzymes w/in mitochondria
what do hepatocytes do?
stim. increase blood glucose
TH causes increases in glycogenolysis + gluconeogenis, decreased in glycogenesis
what do adipose cells do?
stim. increase blood glycerol + fatty acids
TH increase in lipolysis + decrease in lipogenesis
save glucose for the brain
How does TH affect the heart?
increases heart rate + force contraction
increased blood flow tp deliver more nutrients + oxygen
causes heart to increase receptors for epinephrine + norepinephrine
HYPERthyroidism
excessive production of TH
increased metabolic rate, weight loss, hyperactivity, heat intolerance
caused T4 ingestion, excessive stimulation by pituitary or loss of feedback control in thyroid (Graves disease)
HYPOthyroidism
decreased prod. of TH
low metabolic rate, legsrthy, cold intolerance, weight gain
caused by decrease Iodine intake, loss of pituitary stimulation of thyroid, postsurgival or immune destruction (HASHIMOTO )
goiter
enlargement of thyroid
lack of dietary iodine preventing iodine from producing thyroid hormone
Calcitonin
released from parafollicular cells of thyroid gland
stimulus: high blood Ca++ or stress from exercise
acts to decrease blood Ca++
inhibiting osteoclast activity
stimulate kidney to increase excretion of calcium in urine
adrenal medulla
inner core of gland
releases EPI + NOR w sympathetic stimulation
adrenal cortex
has 3 regions + synthesizes more than 25 corticosteroids
mineralocorticoids
regulate electrolyte levels
ZONE GLOMERULOSA: thin, outer layer
aldosterone fosters Na+ retention + K+ secretion
Glucocorticoids
regulate blood sugar
ZONA FASCICULATA: middle layer
cortisol increase blood sugar
gonadocorticoids
sex hormones
ZONA RETICULARIS: thin, inner
androgens: sex h’s by adrenal
made into estrogen
what do cortisol and corticosterone do?
increase nutrient level in blood
resist stress + repair injured tissue
What is regulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
stress, late stages of sleep, low levels of cortisol to release CRH
cortisol travels through blood attached to carrier proteins
regulated by negative feed back
cortisol inhibits release of CRH from HT + ACTH from AP
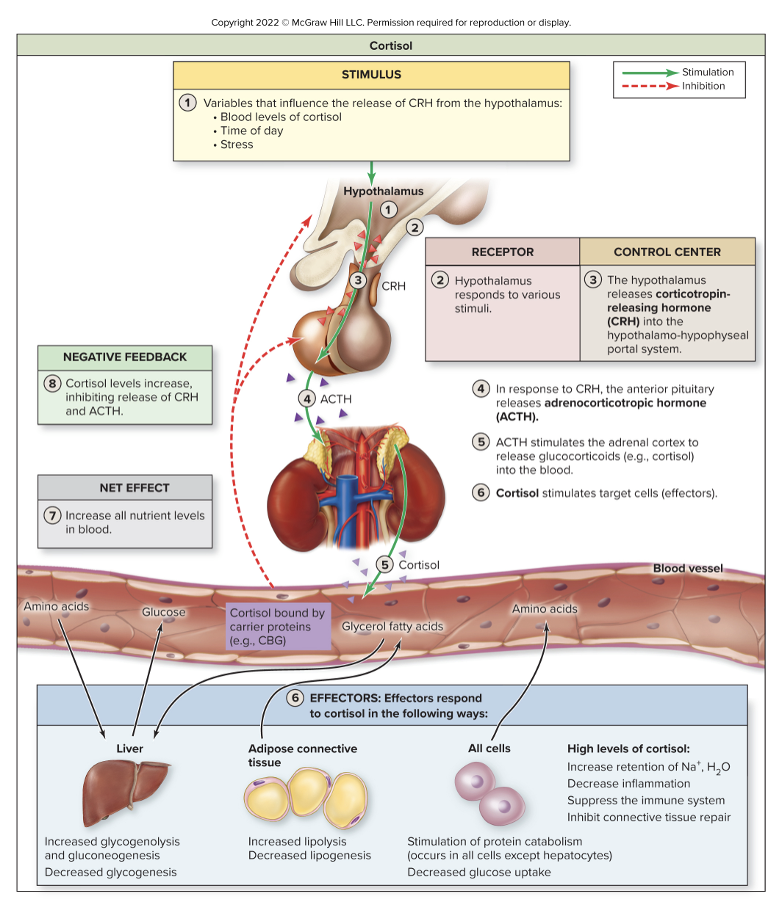
uses of cortisol or corticosterone
inflammation
inhibits inflammatory agents + suppress immune system
high doses: increase risk of infection, cancer, retention of Na + H20, inhibits CT repair
Cushing syndrome
chronic exposire to excessive glucocoticoid H in ppl for corticosteroid therapy
obesity, hypertension, hirsutism (male-pattern hair growth) kidney stones, menstrual irregularities
Addison disease
form of adrenal insufficiency
when adrenal gland fail
weight loss, fatigue + weakness, hypotension + skin darkening