1.6 ATP ❤️
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What does ATP stand for
Adenosine triphosphate
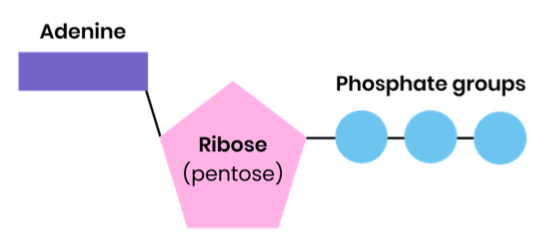
Describe the structure of ATP
ribose bound to a molecule of adenine (base) and 3 phosphate groups
Nucleotide derivative (modified nucleotide)
Draw the structure of ATP
.
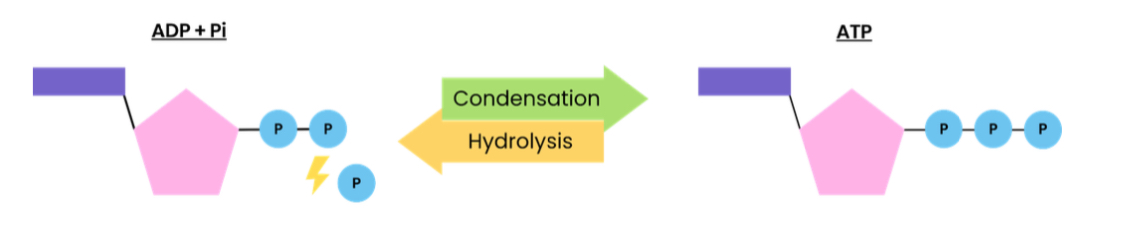
Describe how ATP is broken down
ATP (+water) —> ADP + Pi
ATP is hydrolysed using a water molecule
Catalysed by enzyme ATP hydrolase
What is ADP, what is Pi
ADP = adenosine diphosphate
Pi =inorganic phosphate
Two ways in which the hydrolysis of ATP is used
coupled to energy requiring reactions within cells (releases energy),e.g active transport, protein synthesis
Inorganic phosphate released can be used to phosphorylate other compounds, making them more reactive
How is ATP resynthesised in cells
ADP+Pi —> ATP (+water)
ADP + Pi is joined by a condensation reactions within cells, removing a water molecule
Catalysed by enzyme ATP synthase
During respiration and photosynthesis
Draw the reaction for ADP+Pi —> ATP
.
How do the properties of ATP make it a suitable immediate energy source
releases energy in small amounts, so little energy is lost as heat
Single reaction/ one bond hydrolysed to release energy so its an immediate release
Cannot pass out of cell