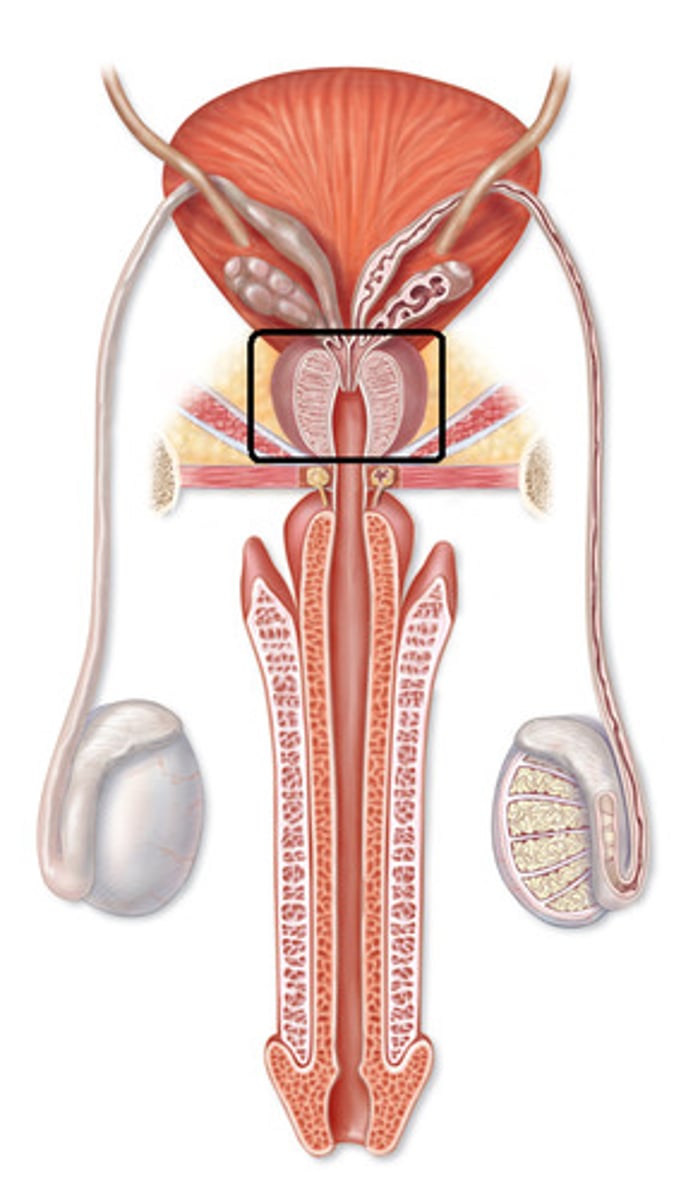
Male Reproductive Organs
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What all does the Male Reproductive System include:
- penis
- scrotum
- testes and epididymis
- spermatic cord
- prostate gland
- bulborethral glands
- seminal vessels
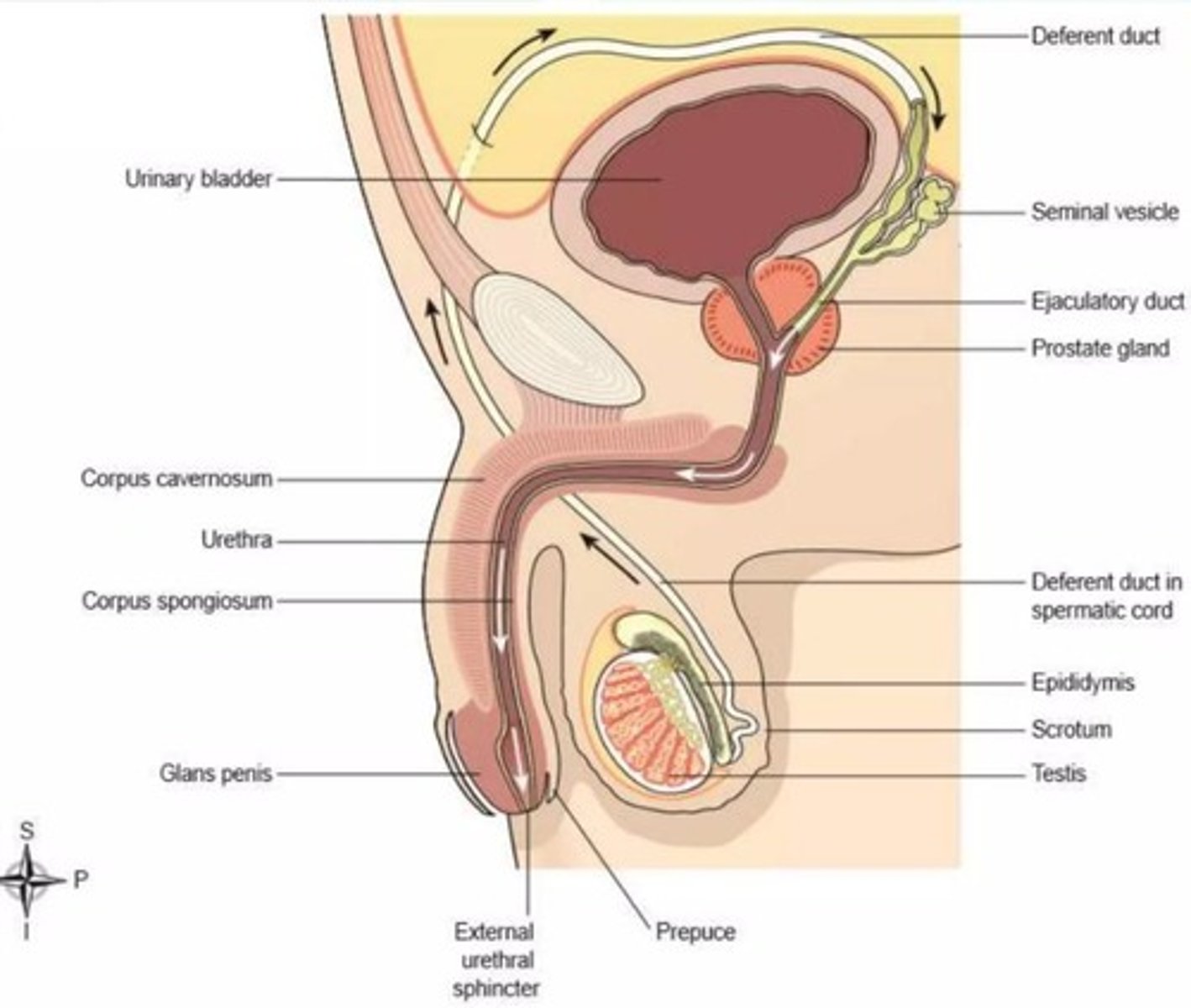
What are the 2 main functions of the Penis?
micturition and sexual intercorse
What is the Penis composed of?
erectile tissue, muscles, fascial coverings, and abundant vasculature
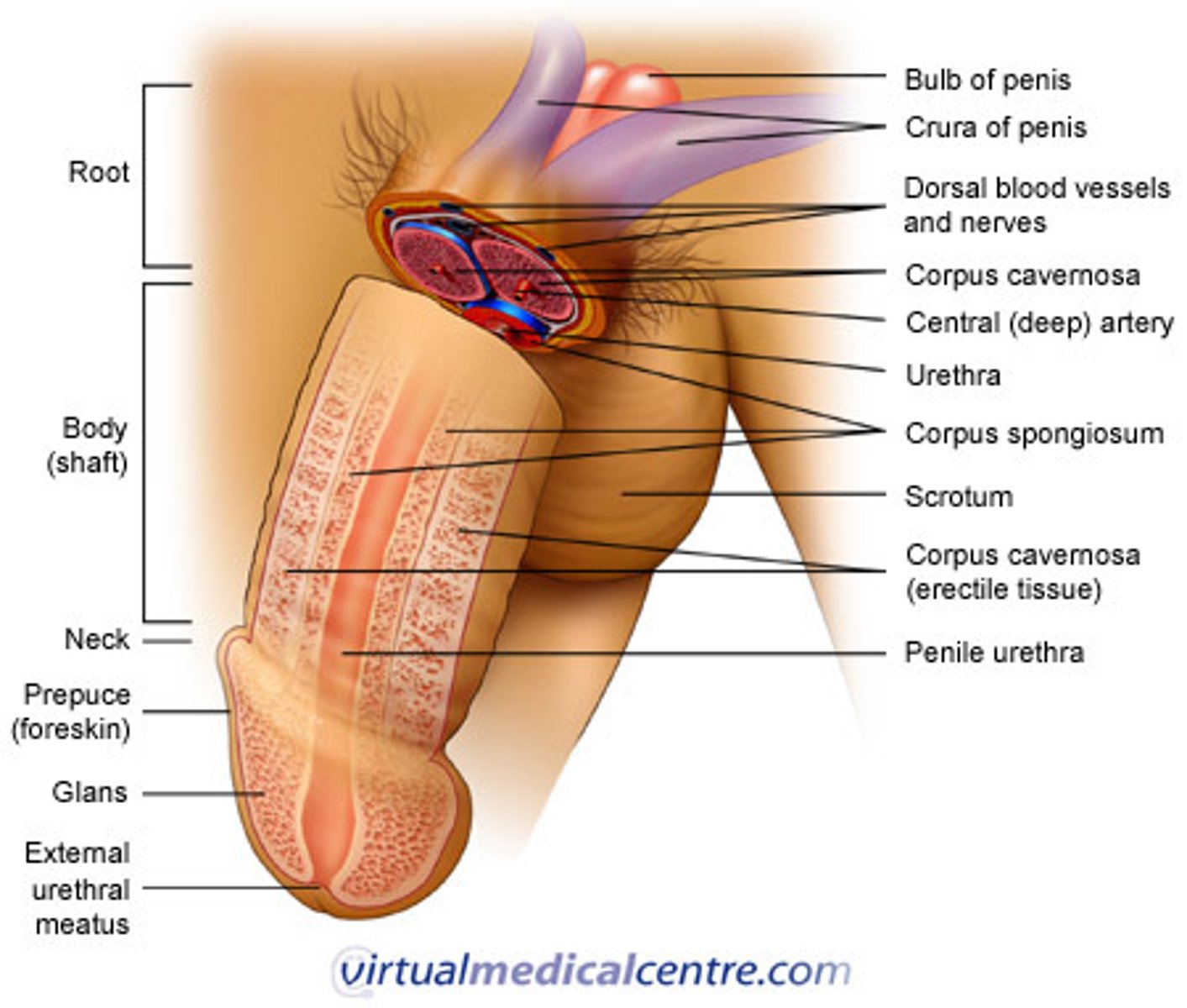
What are the 3 parts of the penis?
1. root
2. body
3. glans
Root of the penis
(fixed) found in superficial perineal pouch, contains 3 erectile tissues and 2 muscles
Body of the penis
(free) 3 erectile tissues protected by 3 layers of fascia and covered by skin
Glans of the penis
expanded corpus sppongiosum
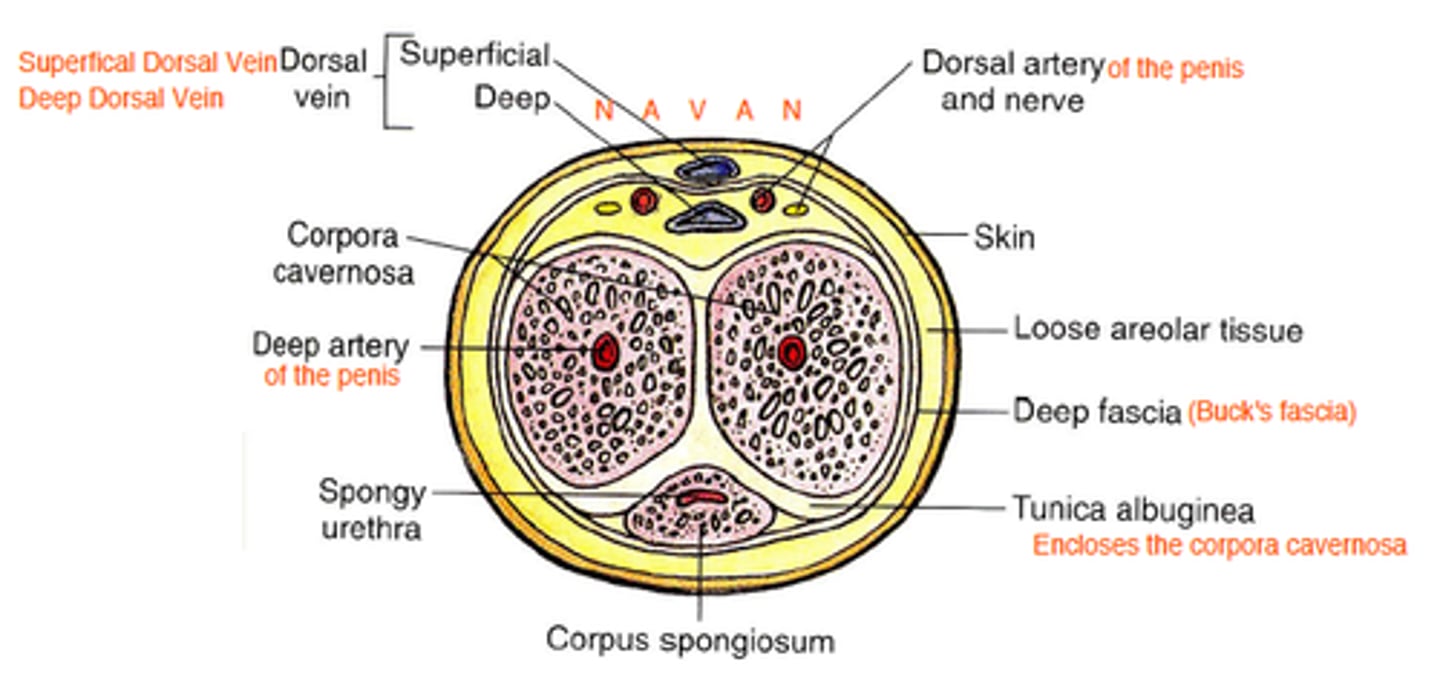
Erectile Tissue of penis
tissues that fill with blood during sexual arousal
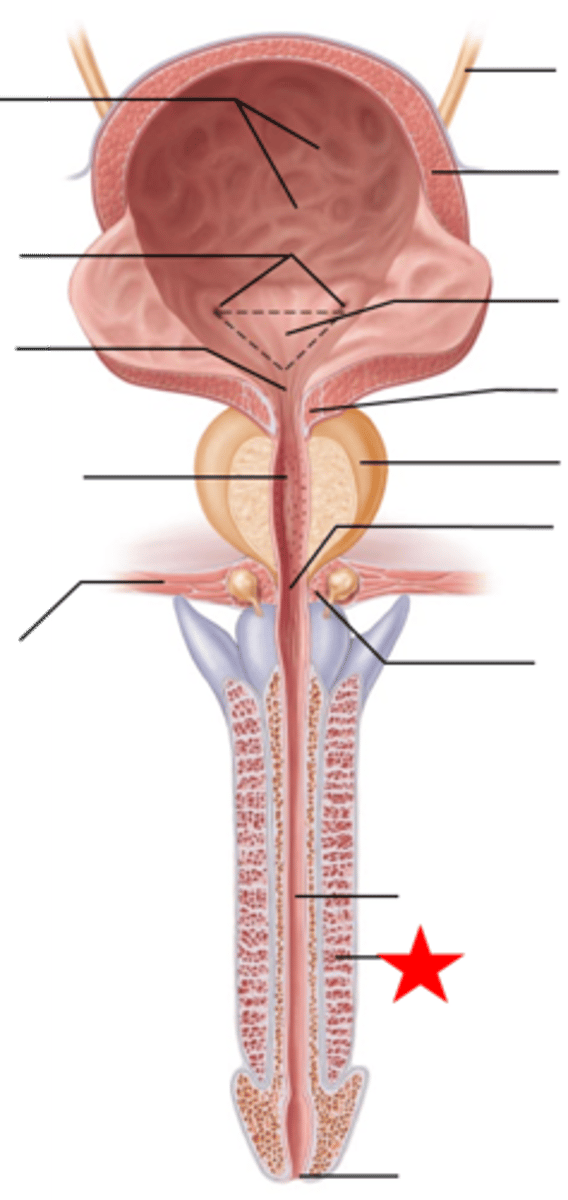
Erectile tissue in the root of penis
2 cura and a bulb
Cura
attached ipsilateral ischial ramus and covered by ischiocavernosal muscles
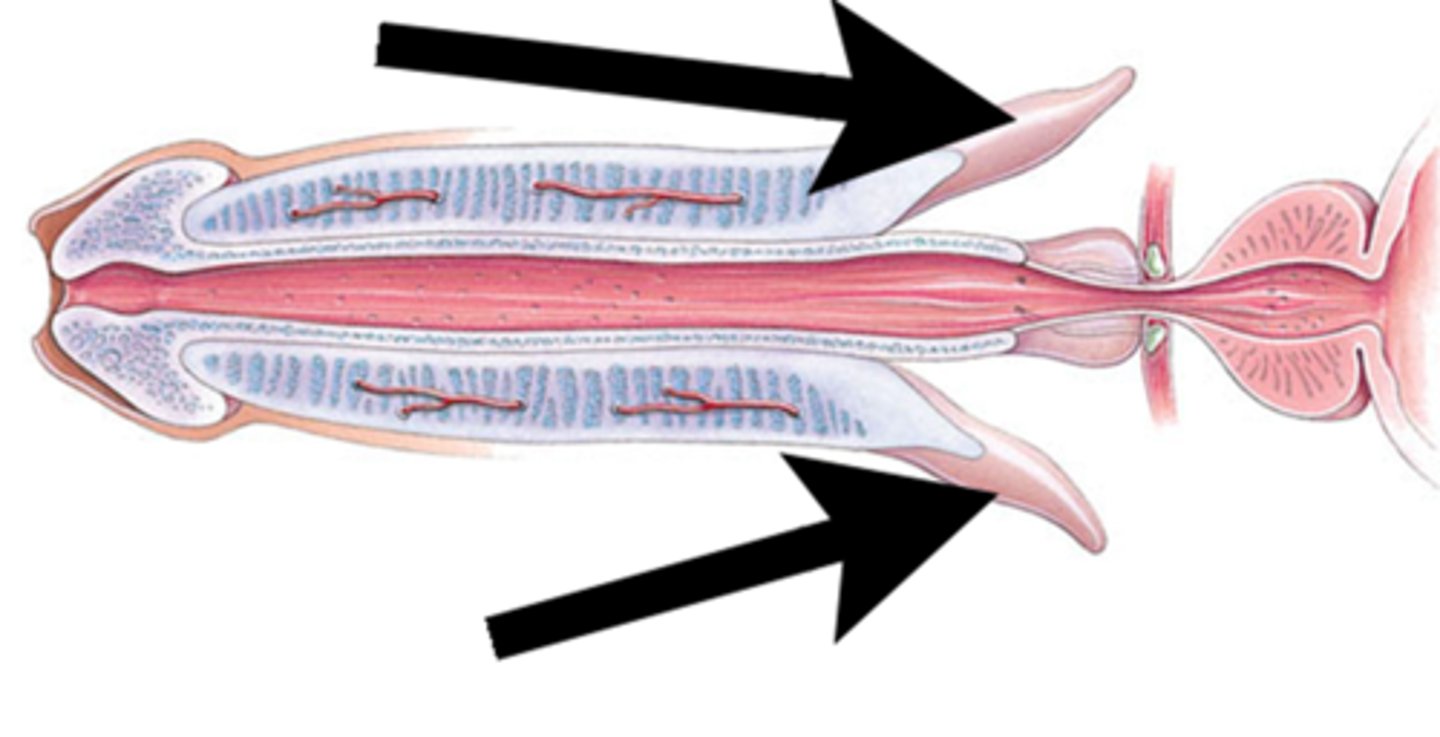
The two crura of the penis continue anteriorly to form what?
corpora cavernosa
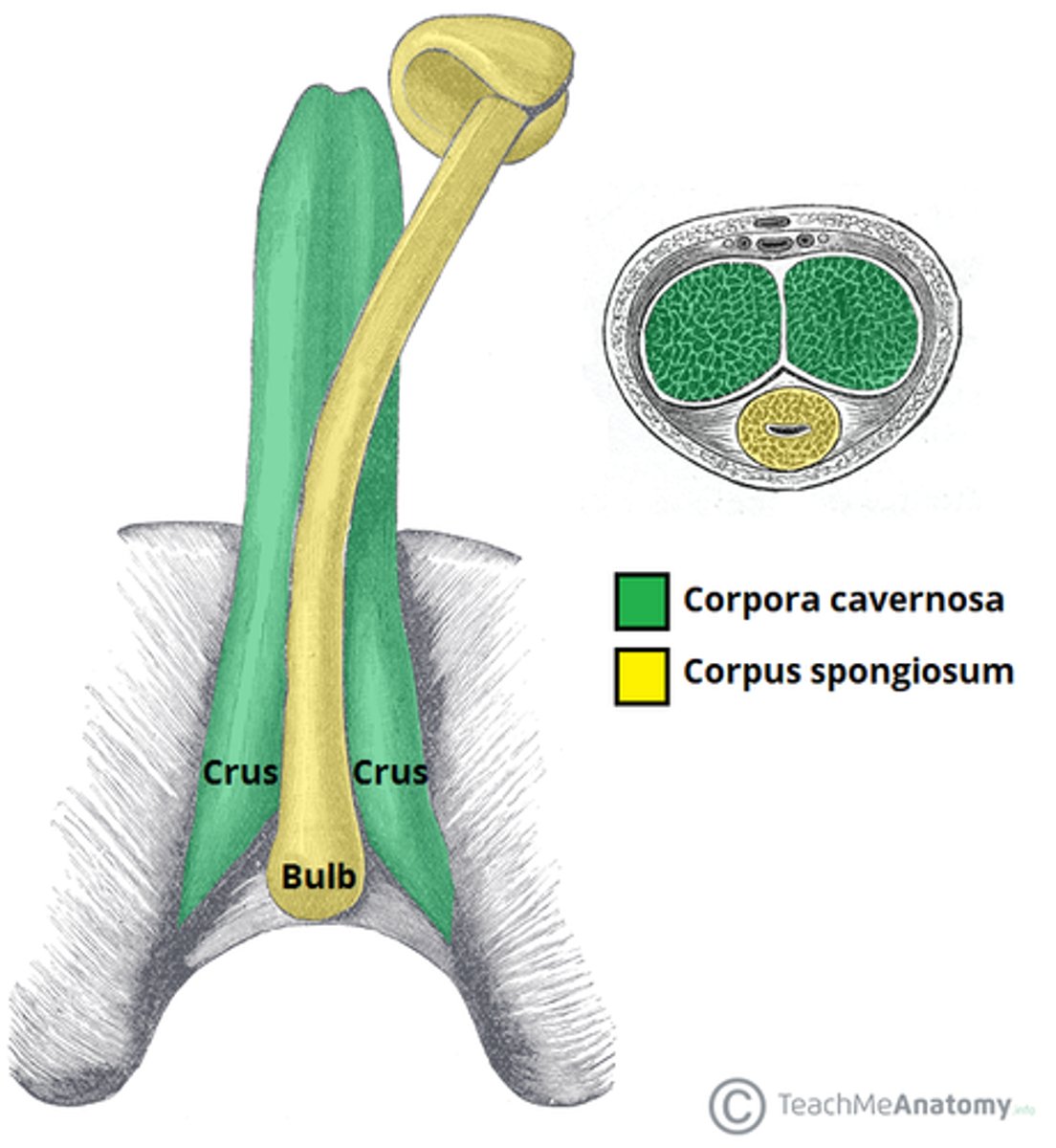
Bulb forms what?
corpus spongiosum (ventral)
Distally the corpus spongiosum forms what?
glans penis
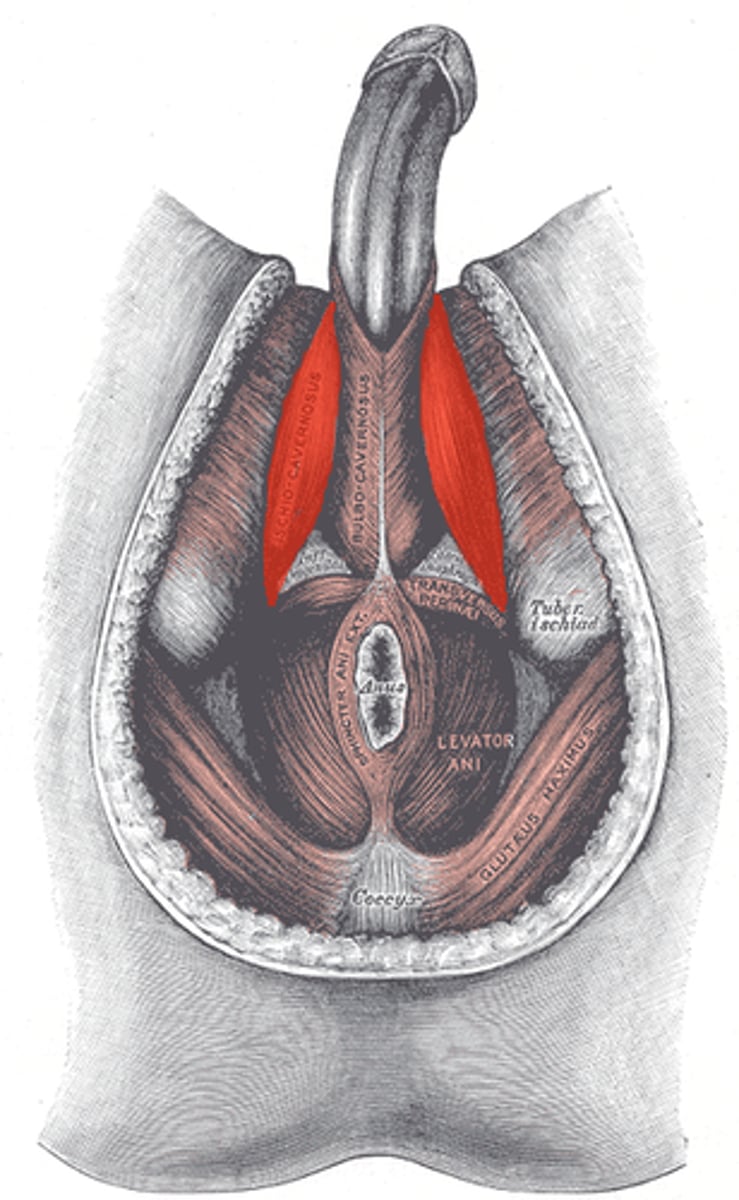
What are the 2 penis muscles?
1. bulbospongiosus muscle
2. ischiocavernosus muscle
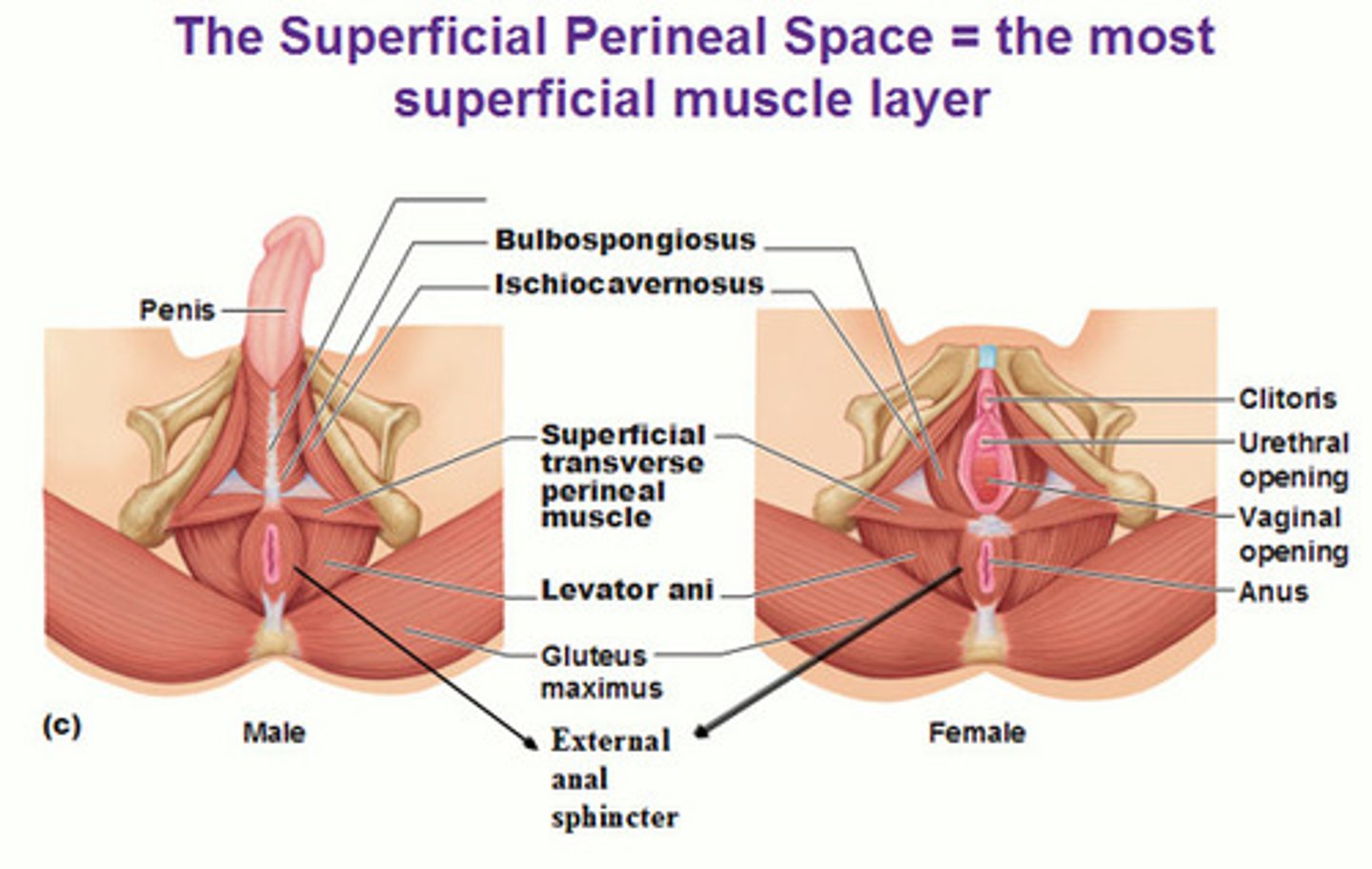
Bulbospongiosus muscle
contract to empty spongy urethra of residual semen and urine, maintain erection
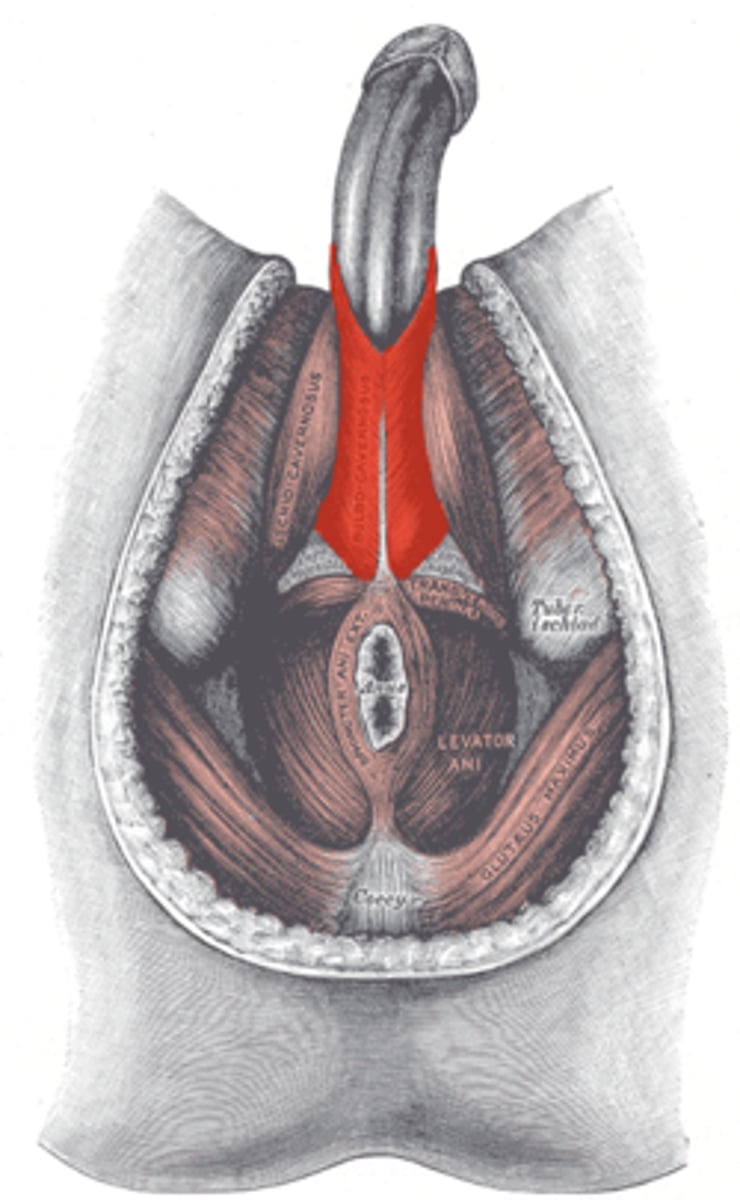
Ischiocavernosus muscle
contract to force blood from cavernous spaces in the crura into the corpora cavernosa
How many fascial coverings for each mass of erectile tissue is there?
2 - Colles and Buck's fascia
Colles Fascia of the penis
superficial layer that is a continuity of Scarpa's fascia (8)
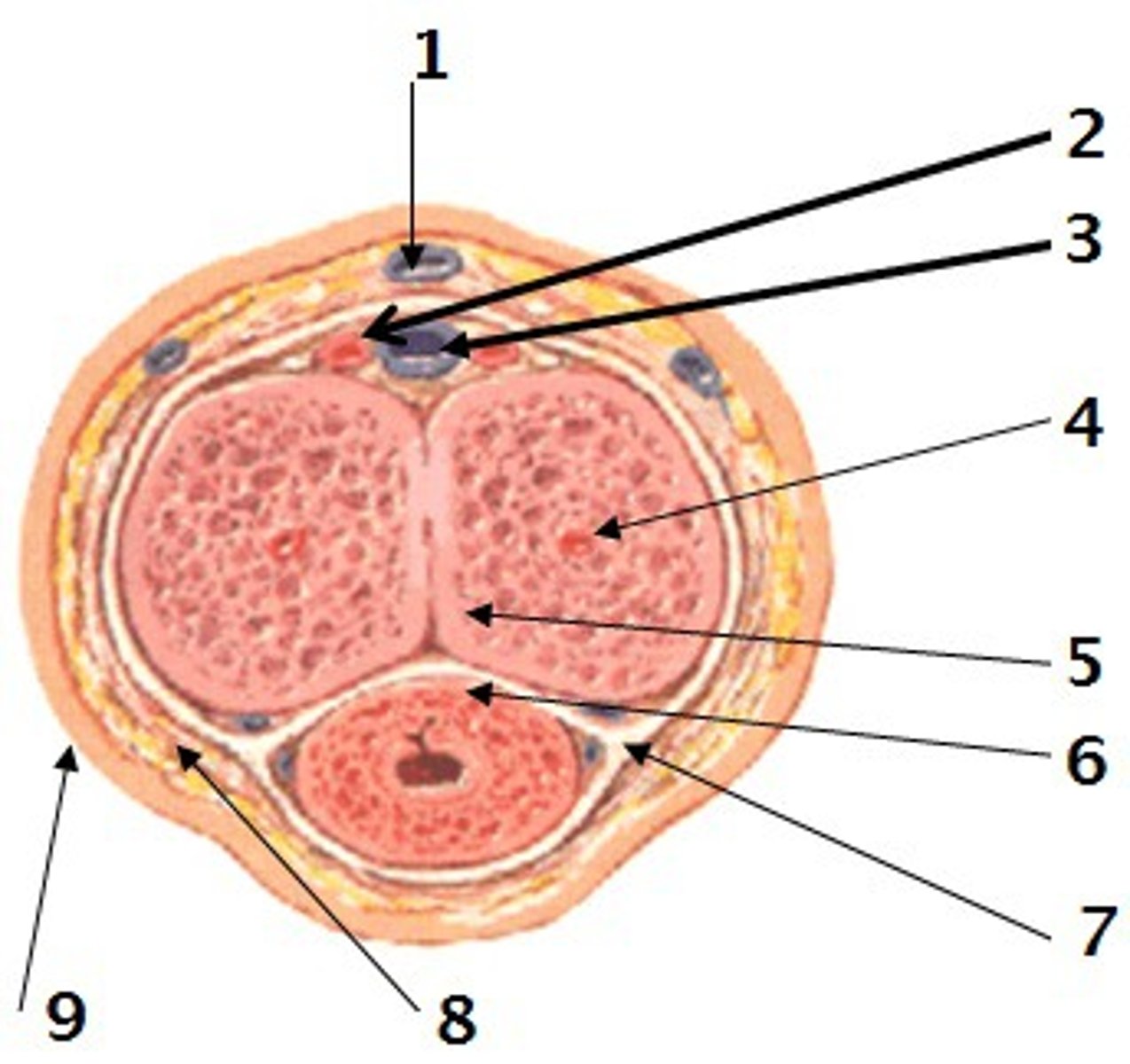
Buck's Fascia of the penis
deep layer that is a continuity of deep perineal fascia, holds all three erectile tissues together
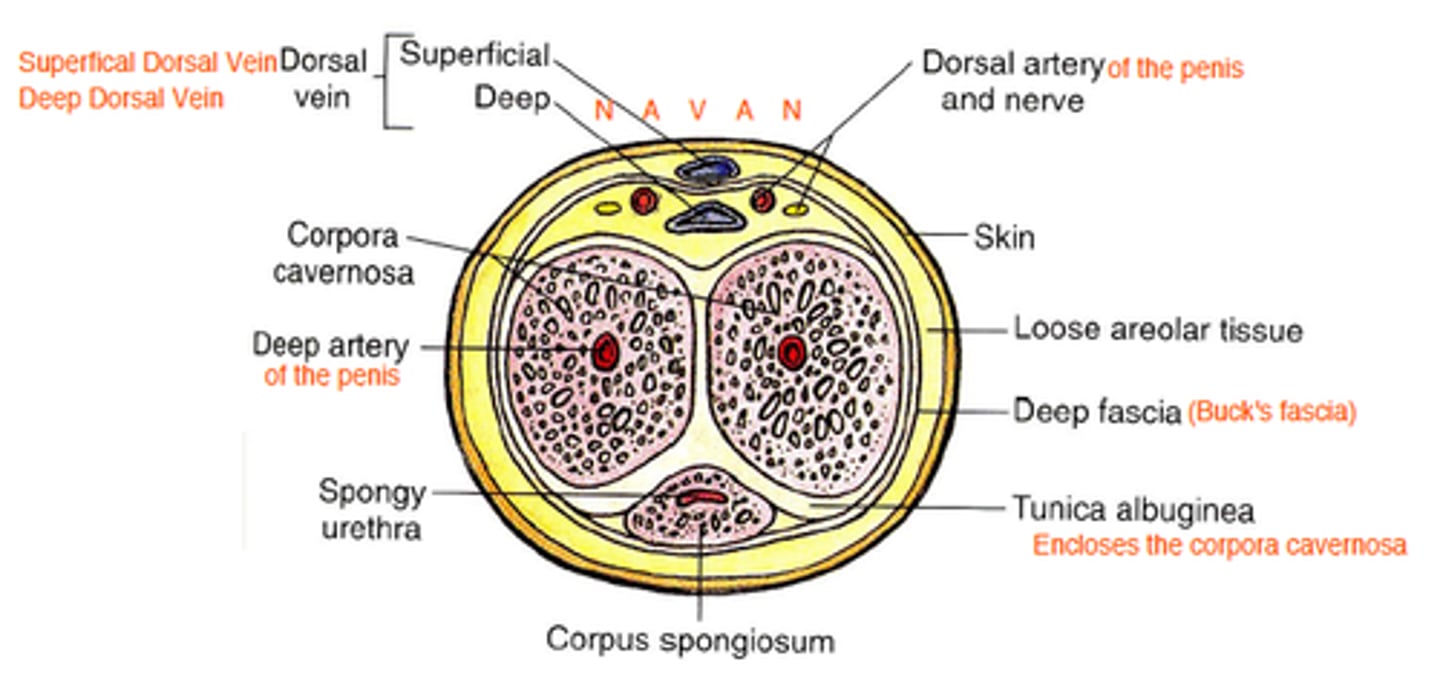
Tunica Albuginea
deep to buck's fascia and forms an individual covering around each cavernous body
What are the 2 penis ligaments?
1. suspensory
2. fundiform
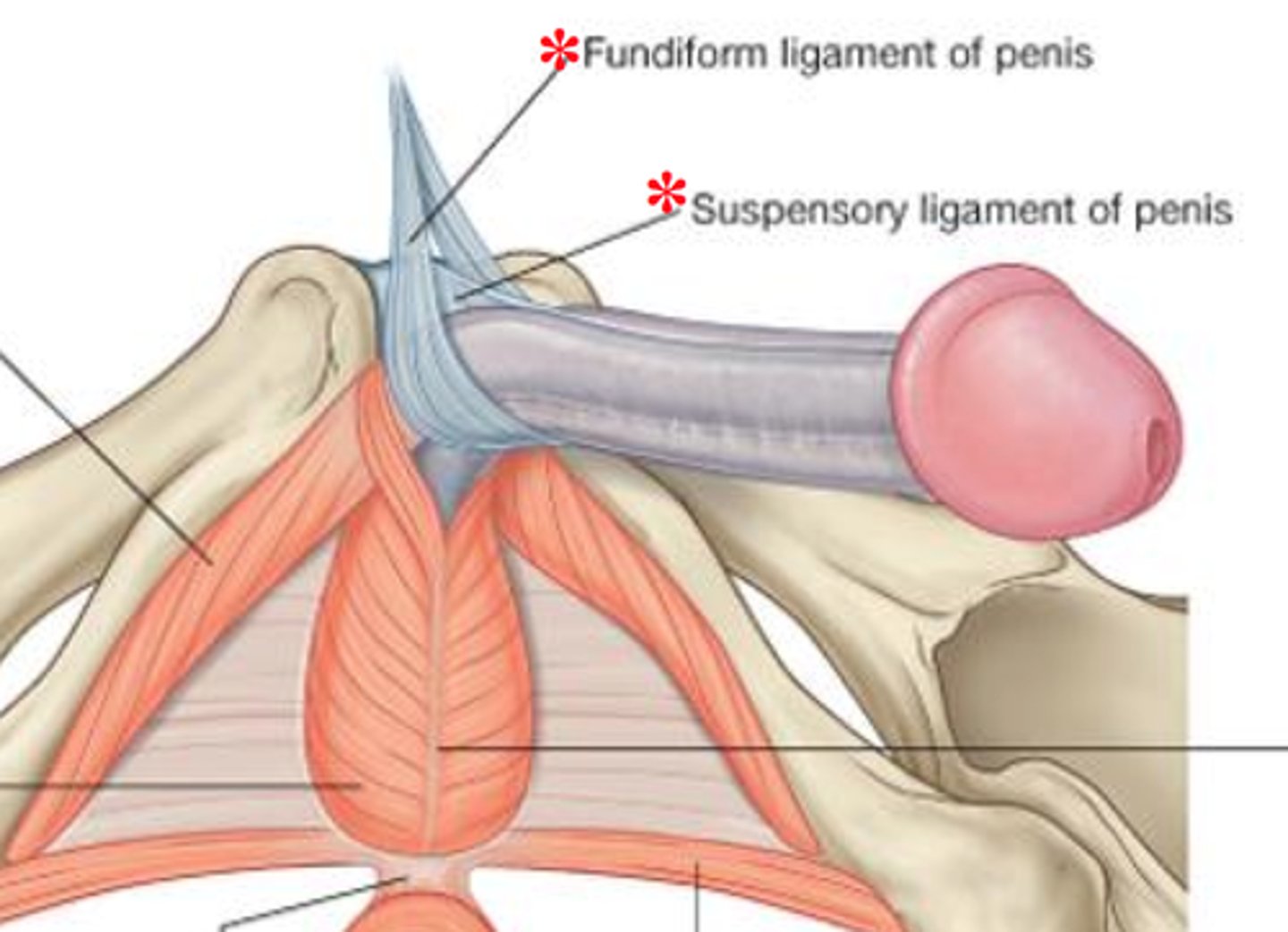
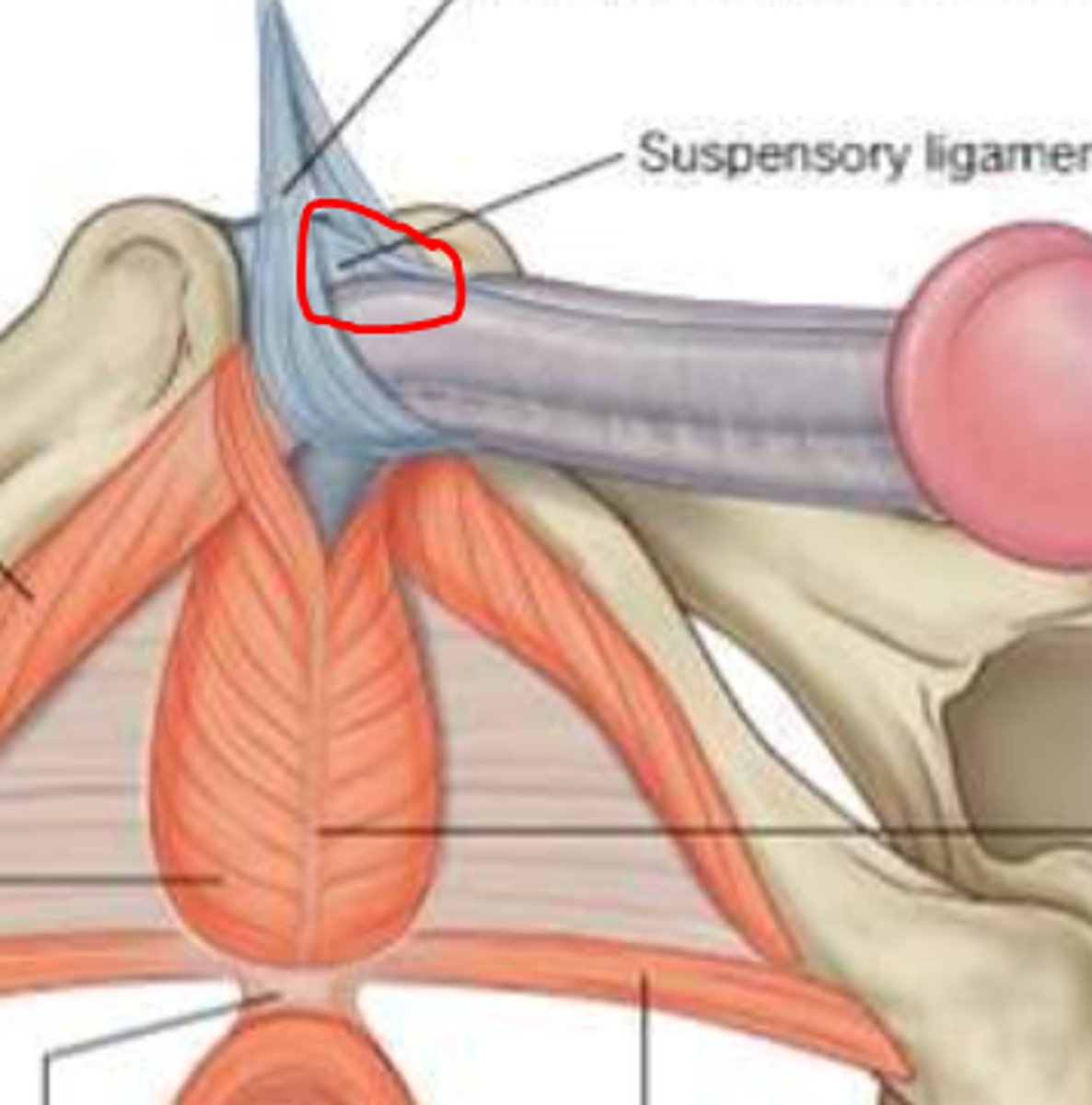
Suspensory Ligament of Penis
connects erectile body to pubic symphysis
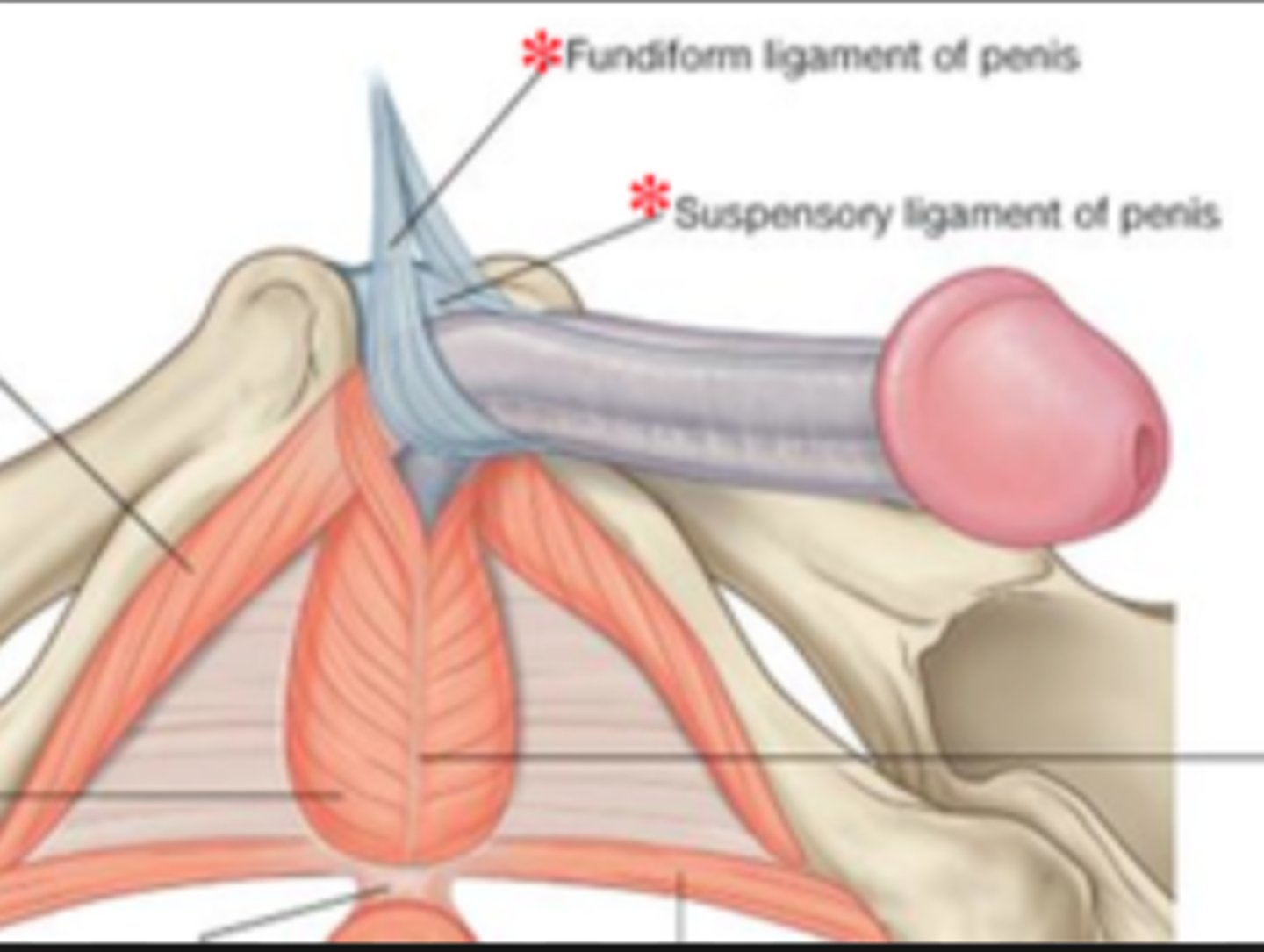
Fundiform Ligament of Penis
from linea alba slings around penis and attaches to symphysis pubis
Penis Vasculature
blood supply originates from internal pudental artery
Blood supply originates from internal pudental artery
1. dorsal arteries
2. deep arteries
3. bulbourethral arteries
Venous Drainage of penis
superficial dorsal vein and deep dorsal vein (prostatic venous plexus)
Penis Nerve Supply (Point & Shoot)
1. Parasympathetic supply - pelvic splanchnic nerves
2. Sympathetic supply - pudendal nerve
Parasympathetic supply - pelvic splanchnic nerves function
erectile function
Sympathetic supply - pudendal nerve function
ejaculation and also provides deep sensation
Skin and root for penis is innervated by?
ilioinguinal nerve
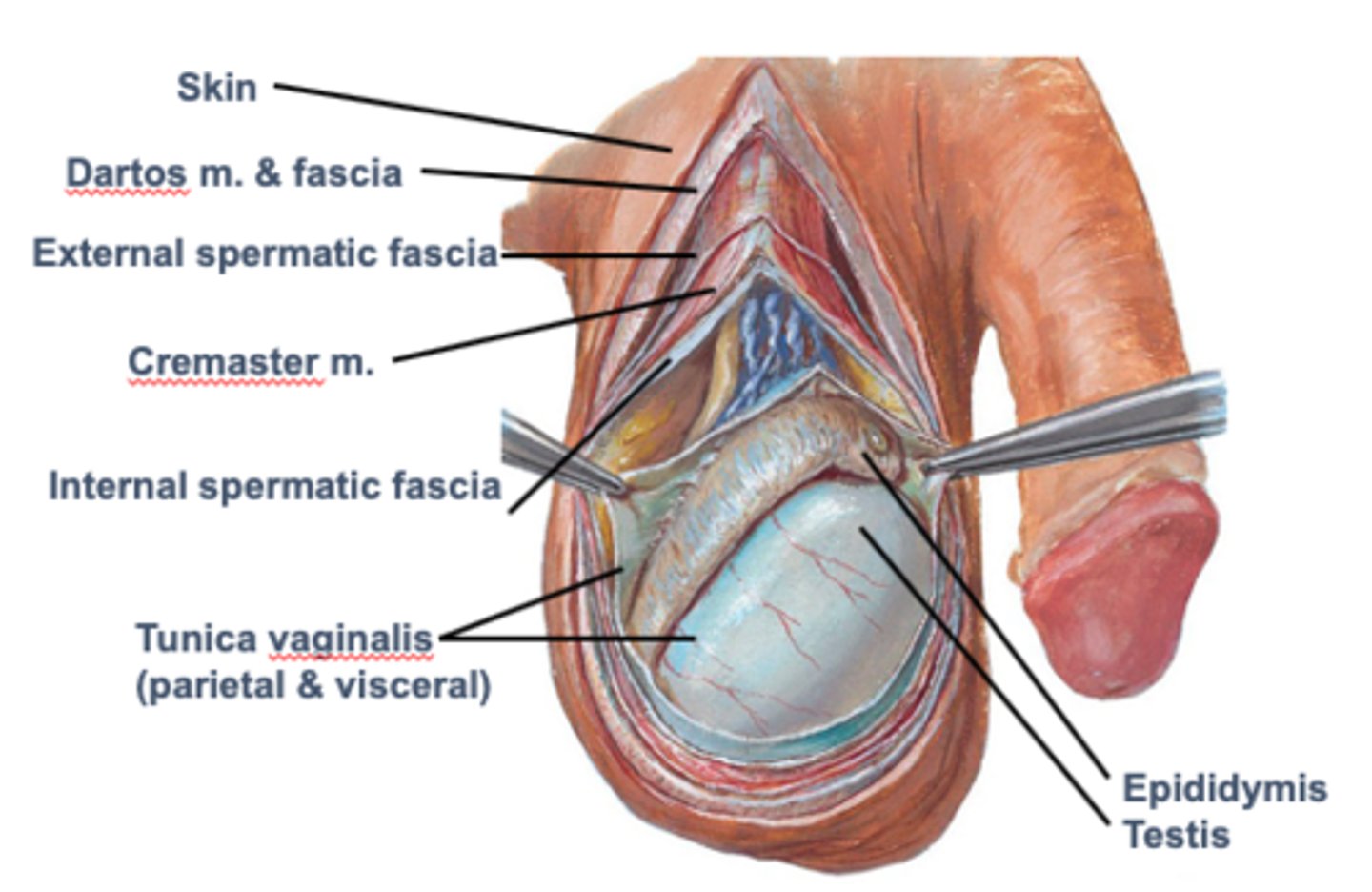
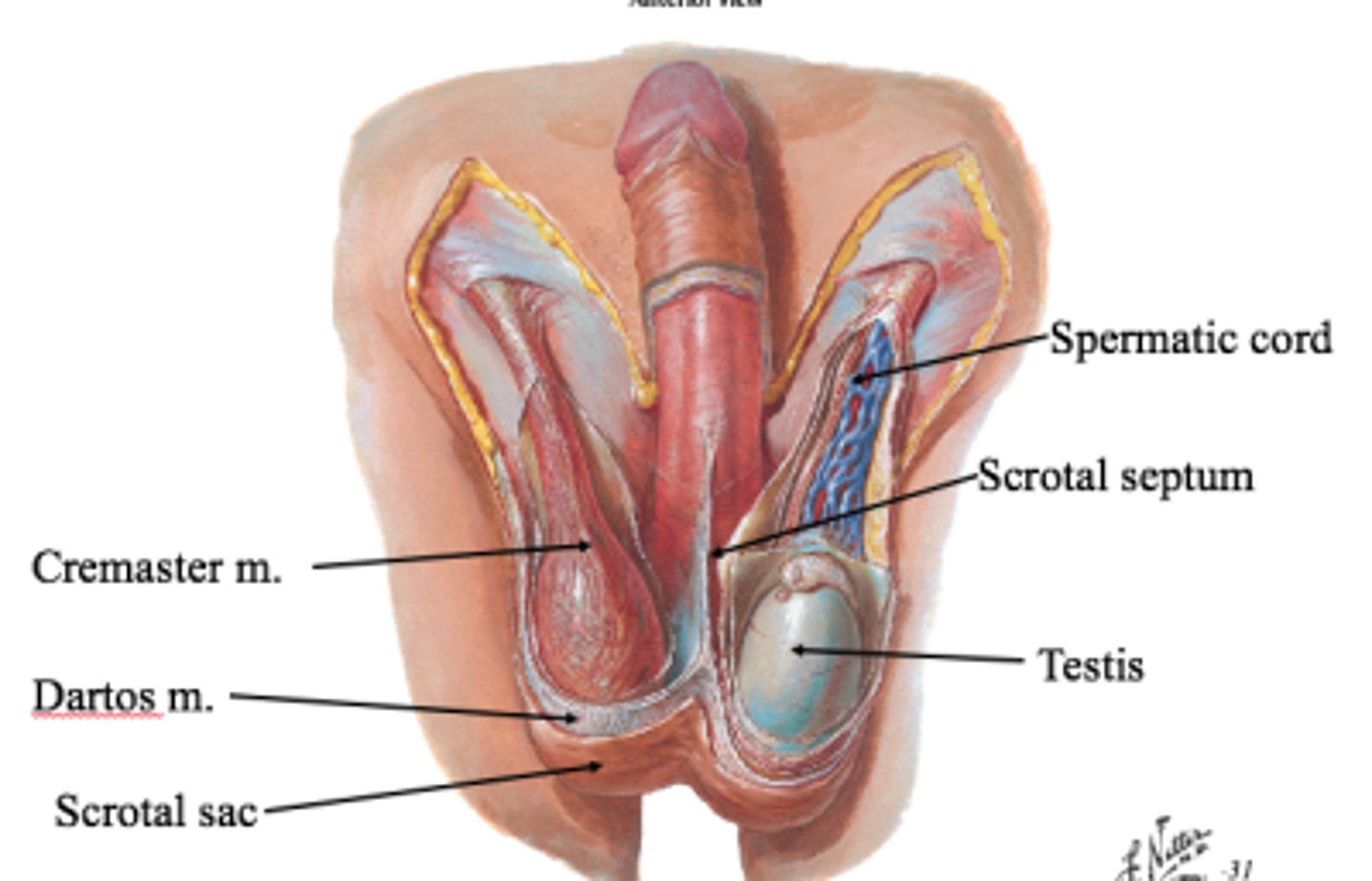
Scrotum
cutaneous sac that connects the testes to the lower parts of the spermatic cord
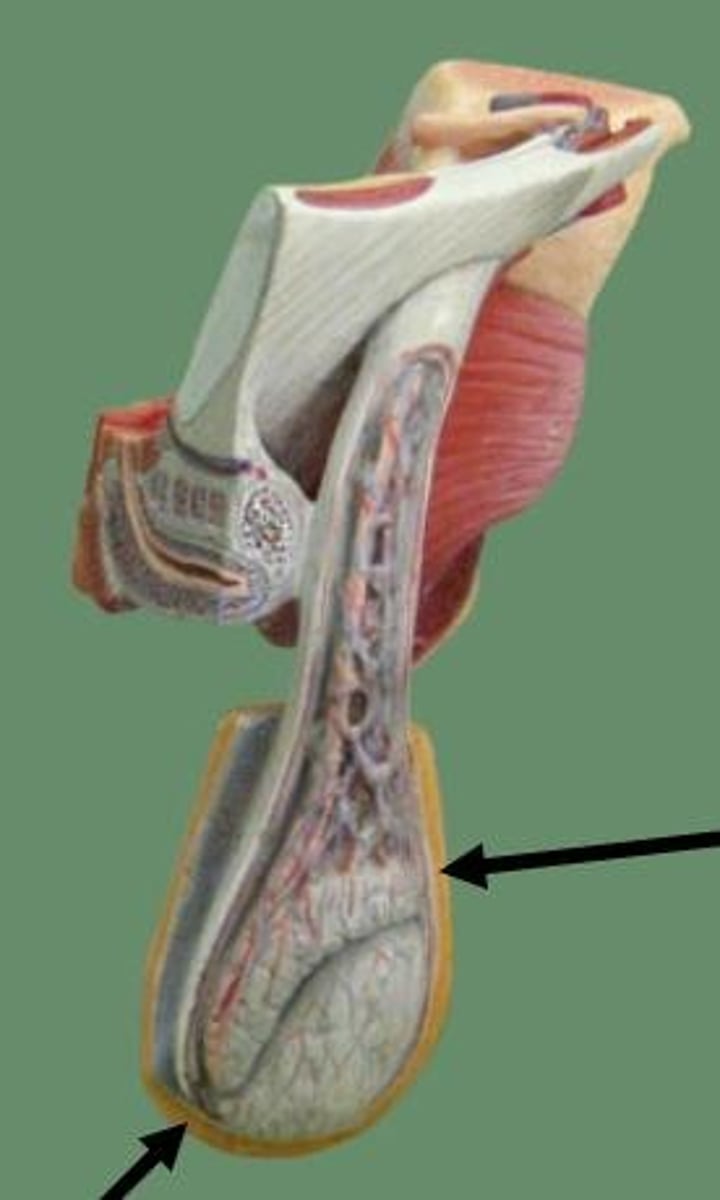
What are the contents of the Scrotum?
- testis
- epididymis
- spermatic cord
What is function of the Scrotum?
maintain adequate temperature for testes to produce sperm
What are the 2 layers of the Scrotum?
superficial skin and deeper dartos fascia
What are the 2 muscles of the Scrotum?
dartos muscle and cremaster muscle
The smooth muscle fibers of the dartos muscle go through what?
dartos fascia
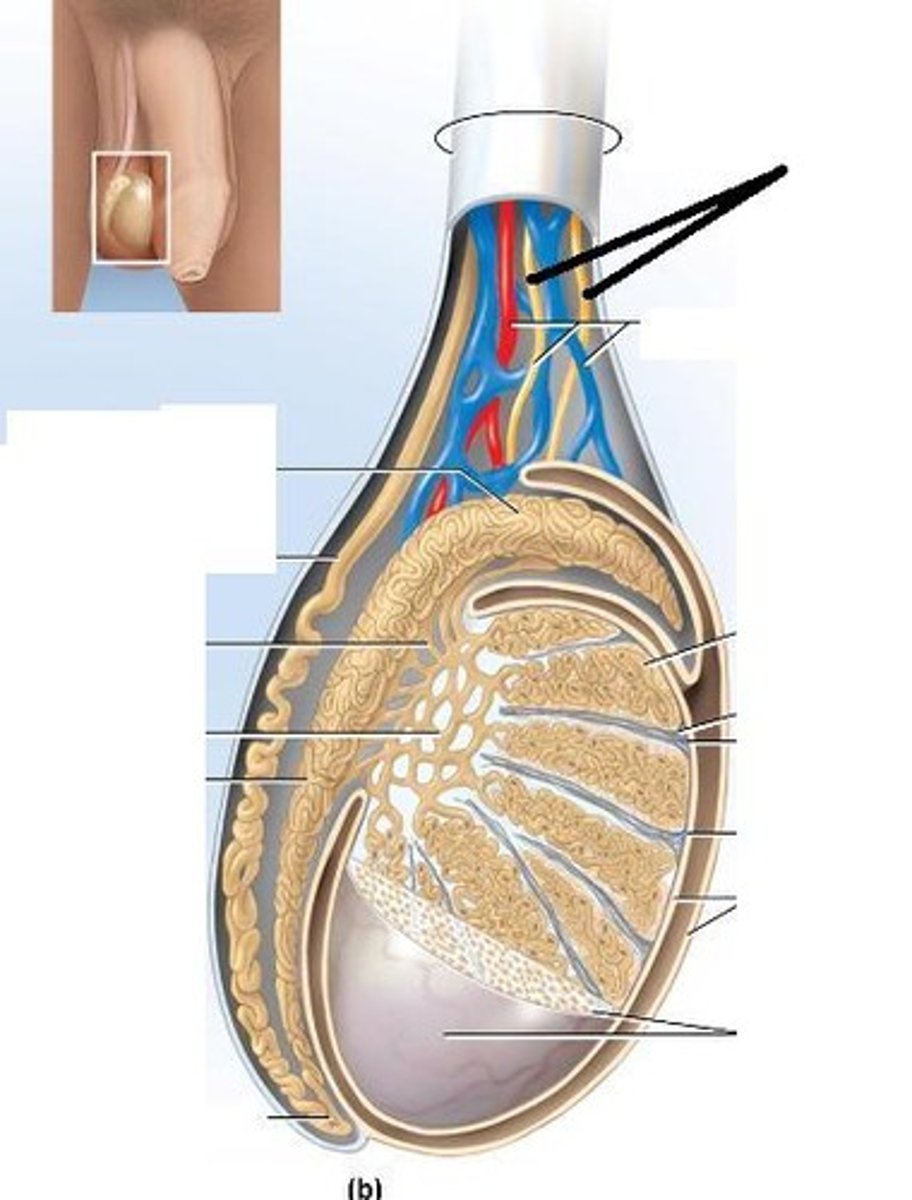
Testes
oval shaped gonads inside the scrotum, suspended from abdomen by spermatic cord
What do the testes produce?
sperm and testosterone
What does the Testes consist of?
intricate network of tubules and secretory cells
What are the network of tubules in the testes?
seminiferous tubules and rete testis
What are the secretory cells in the testes?
leydig and sertoli
What is the parenchyma of the Testes protected by?
tunica albuginea
What are the testes covered almost entirely by?
tunica vaginalis
Epididymis
single heavily coiled duct that is posterior to testes
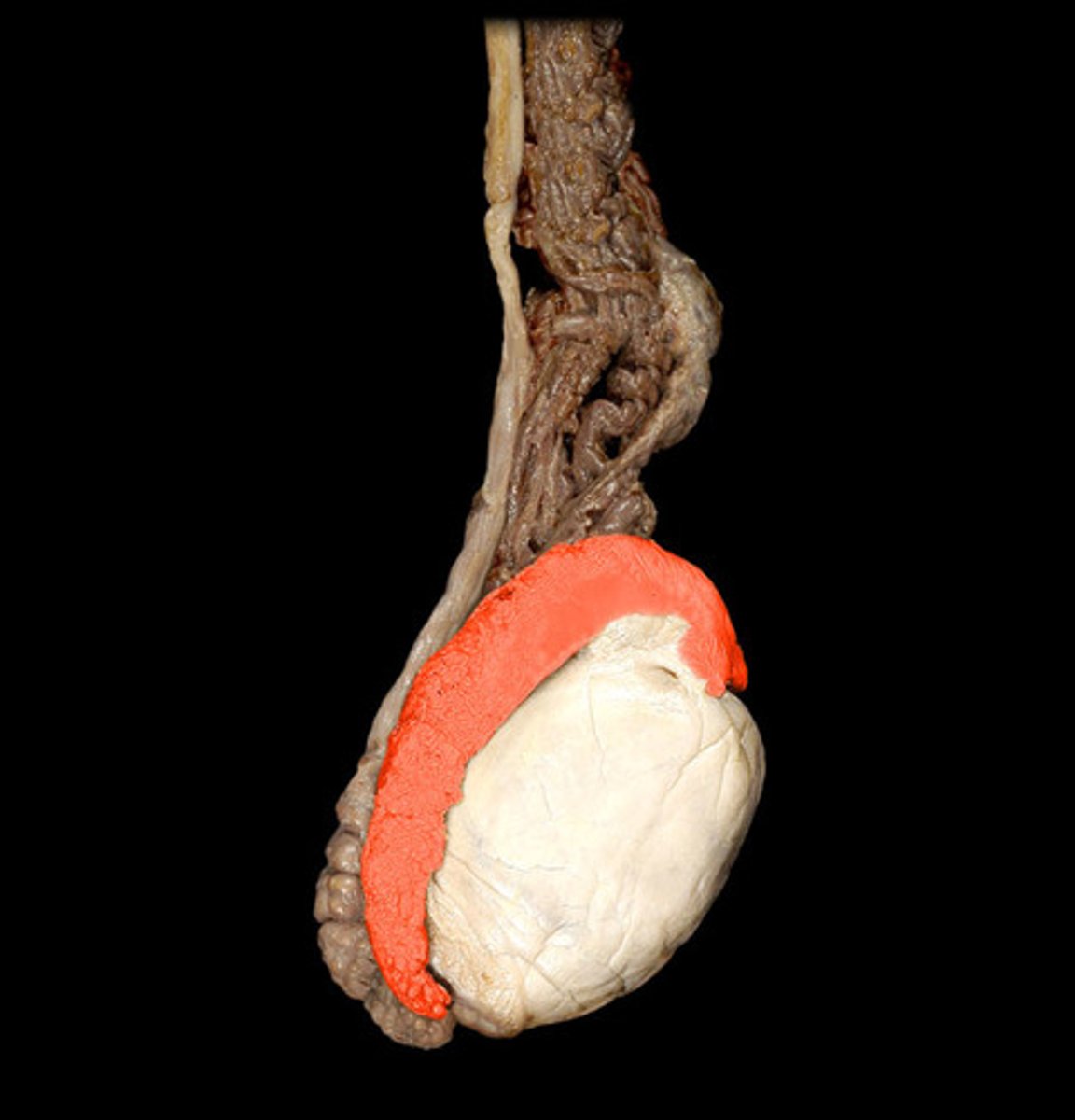
What is the function of the Epididymis?
storage and maturation of spermatozoa
What are the sections of the Epididymis?
head, body, and tail
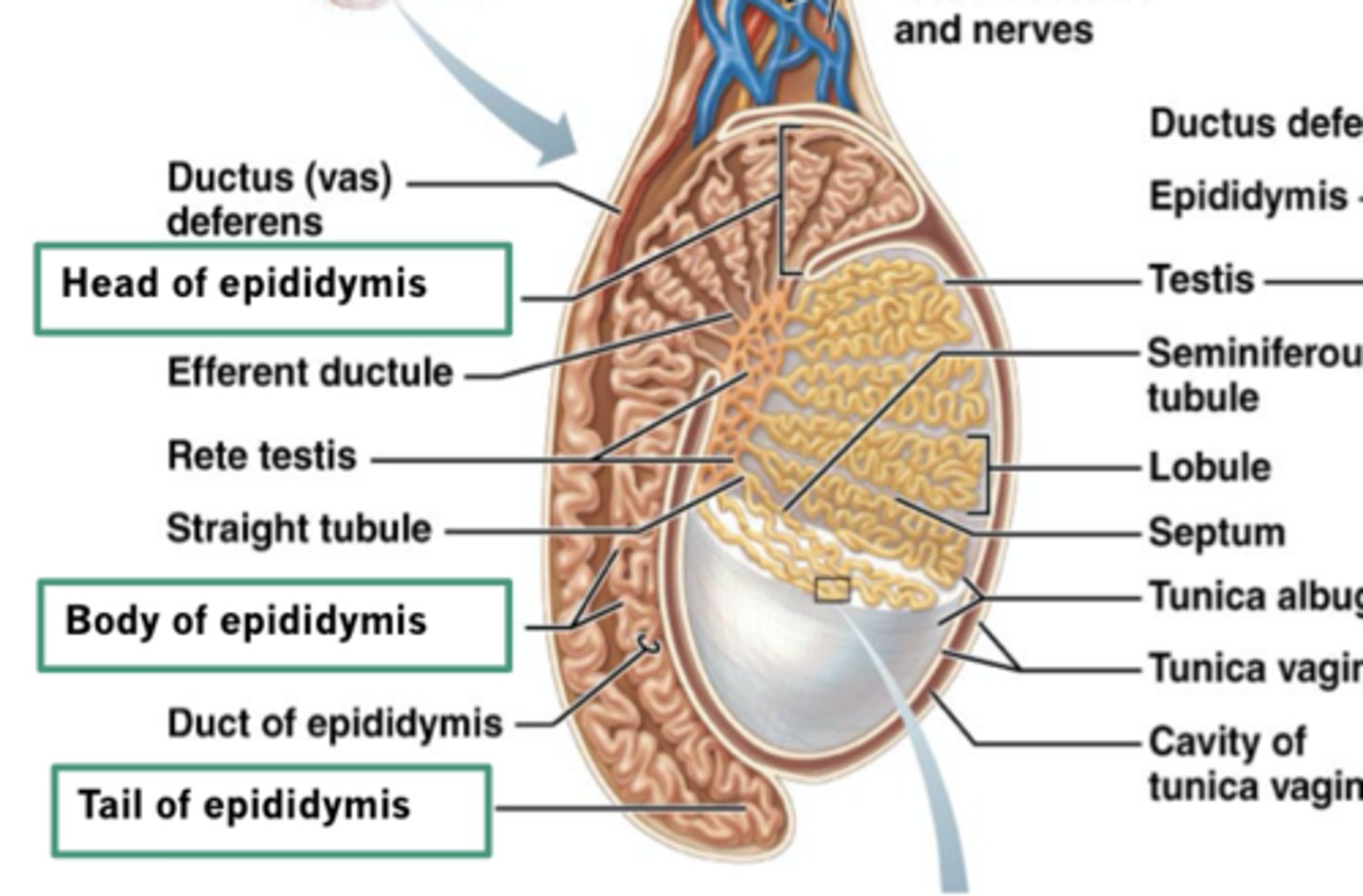
What does the Epididymis drain into?
ductus deferens
What is the blood supply to the testis and epididymis?
from paired testicular arteries by branches of cremasteric artery and artery of vas deferens
What is the Testicular veins?
formed from pampiniform plexus - right/left are different
Left testicular vein drains into?
left renal view
Right testicular vein drains into?
IVC
Varicocele
tortuous dilation of the veins draining the tests
- "bag of worms" in scrotum
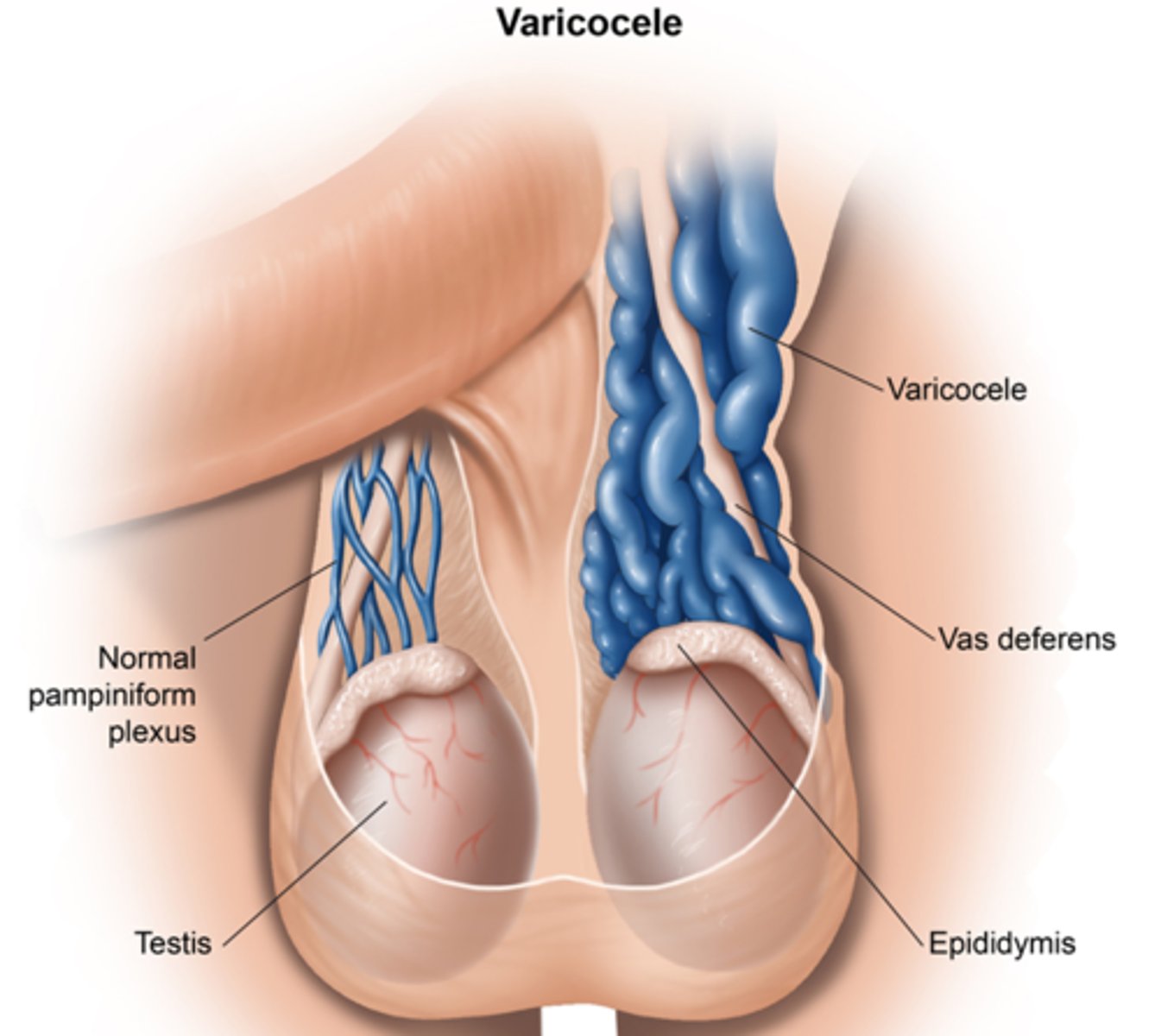
What Testicular vain is longer?
left which is why Varicocele is the most common in this one
Spermatic cord
Bundle of arteries, nerves, pampiniform plexus, ductus deferens, lymphatic vessels and tunica vaginalis
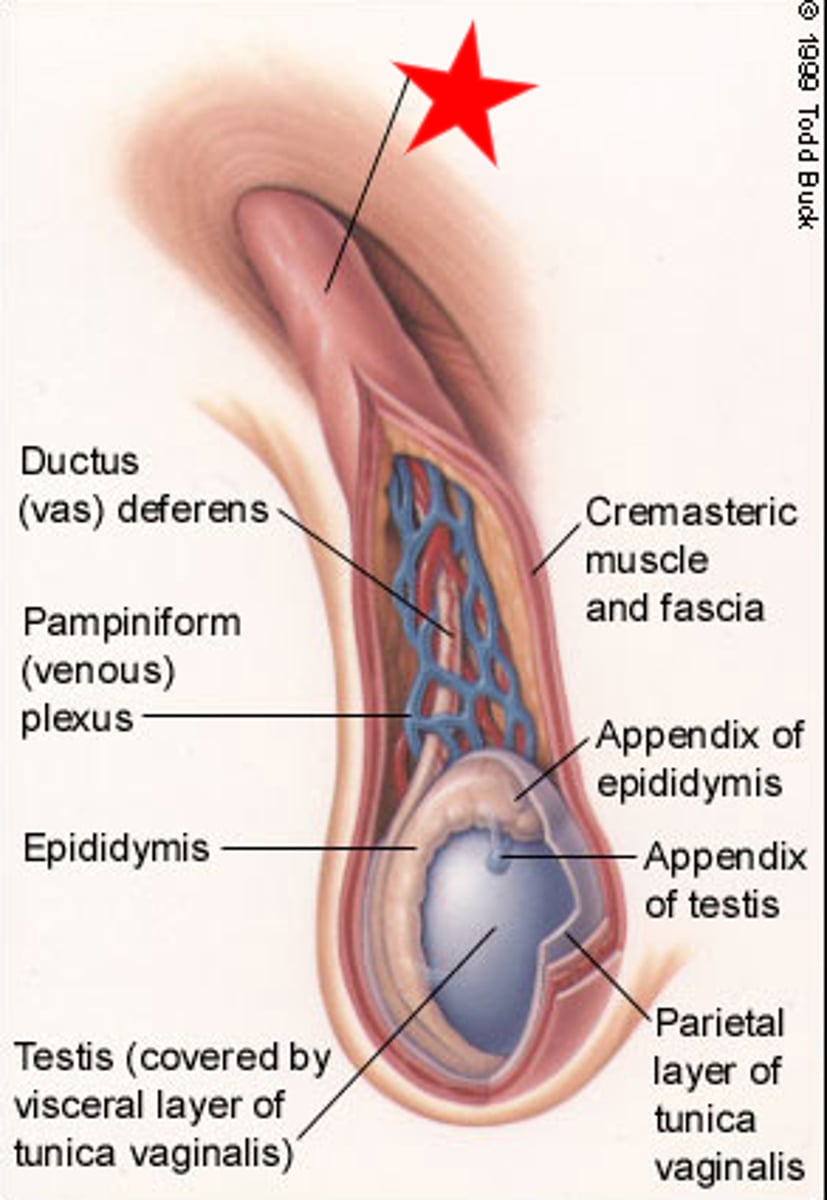
The Spermatic Cord travels in what?
inguinal canal to the scrotum and contents disperse around testes and scrotum
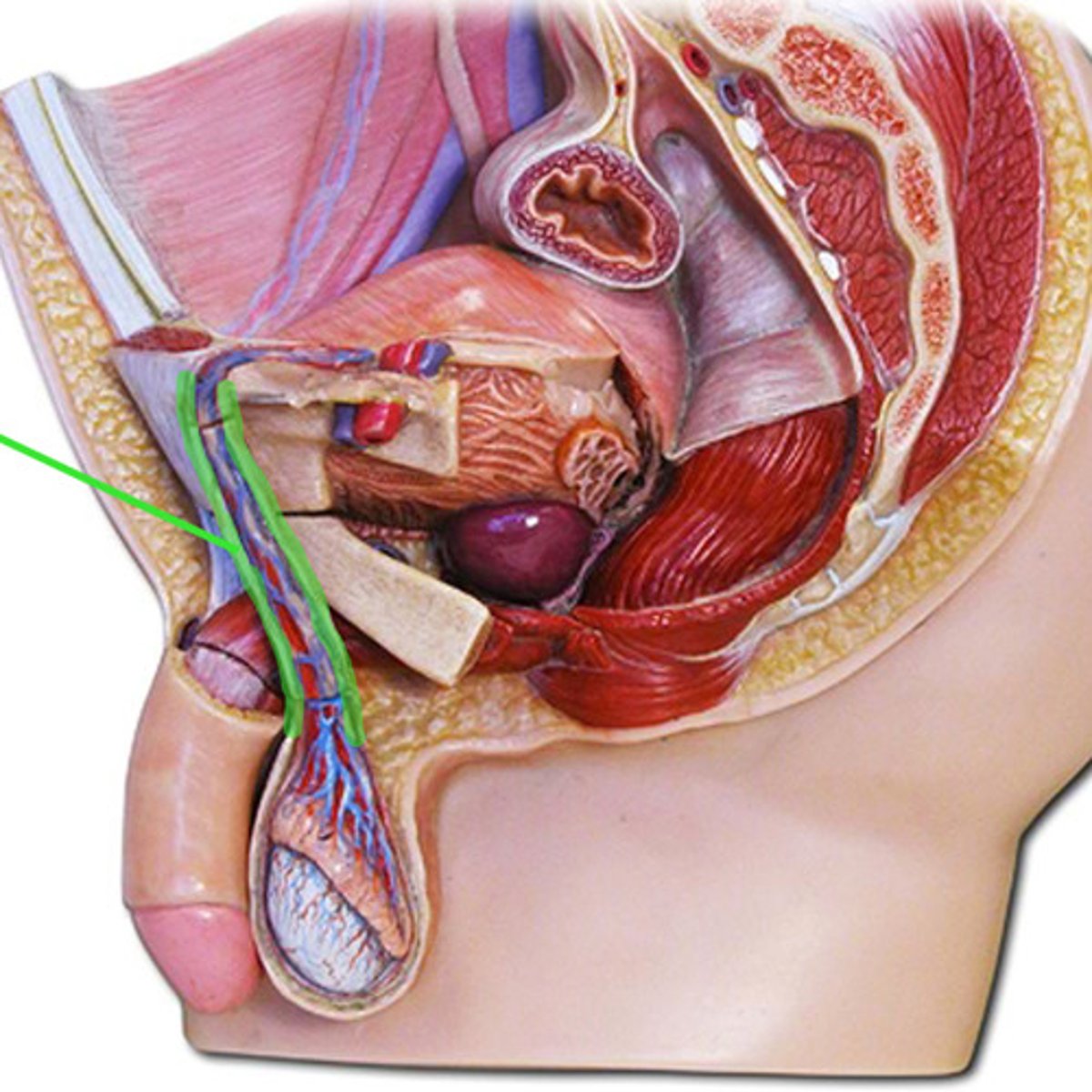
What are the 3 layers of the Spermatic Cord?
1. External Spermatic Fascia
2. Cremaster muscle
3. Internal spermatic fascia
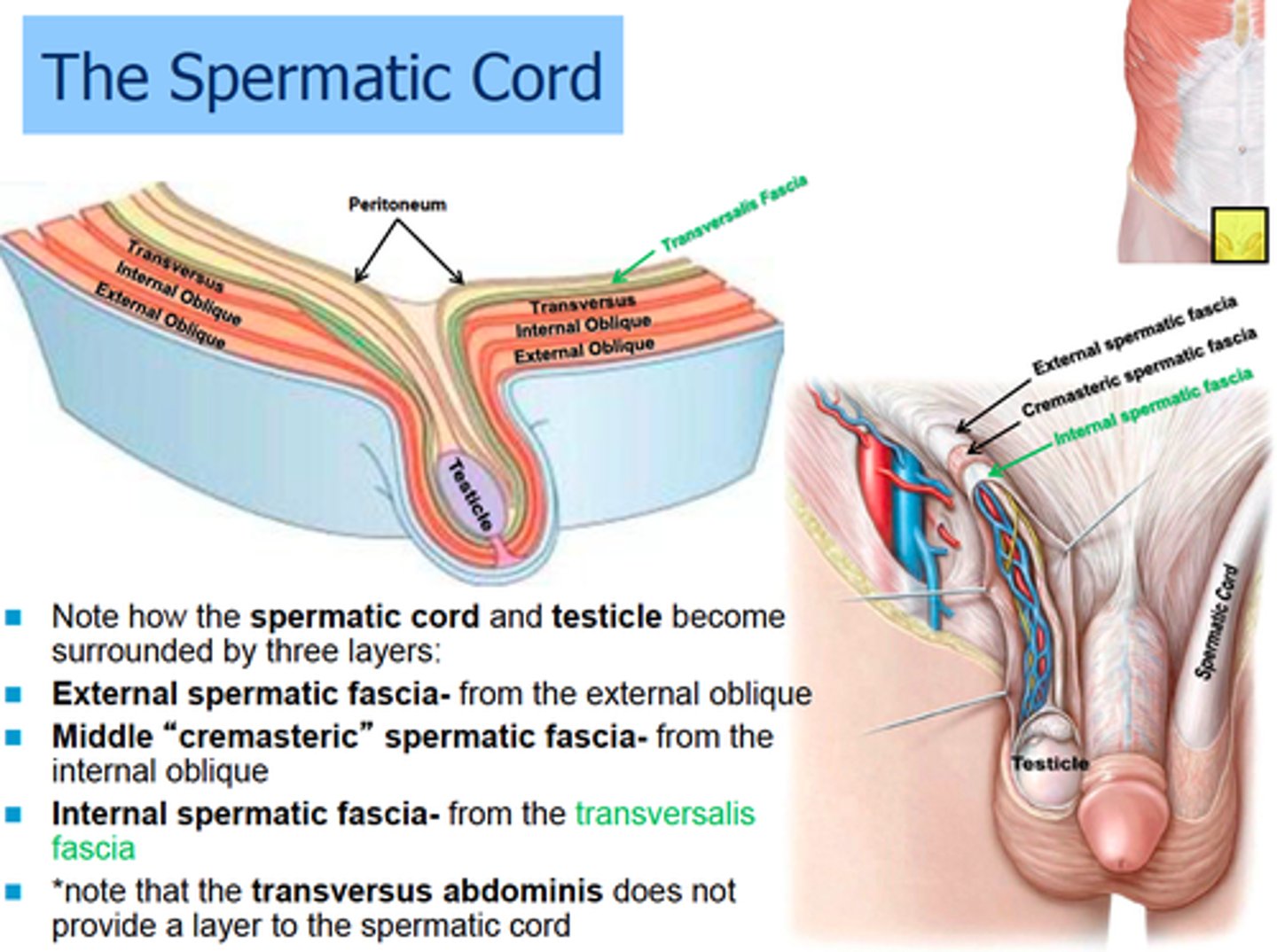
External Spermatic Fascia is from what muscle?
external oblique muscle
Cremaster muscle is from what muscle?
internal oblique muscle
Internal Spermatic fascia is from what?
transversalis fascia
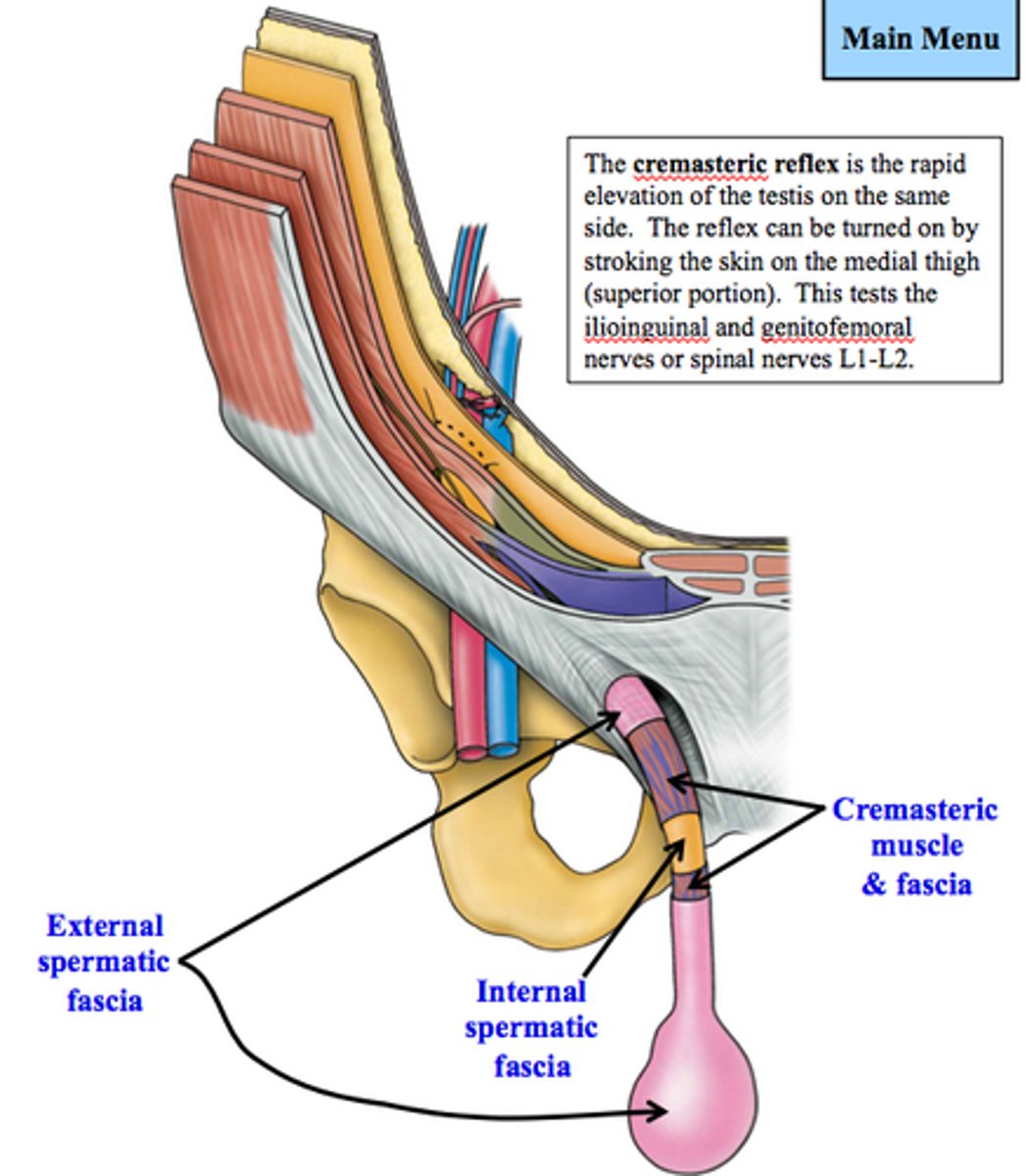
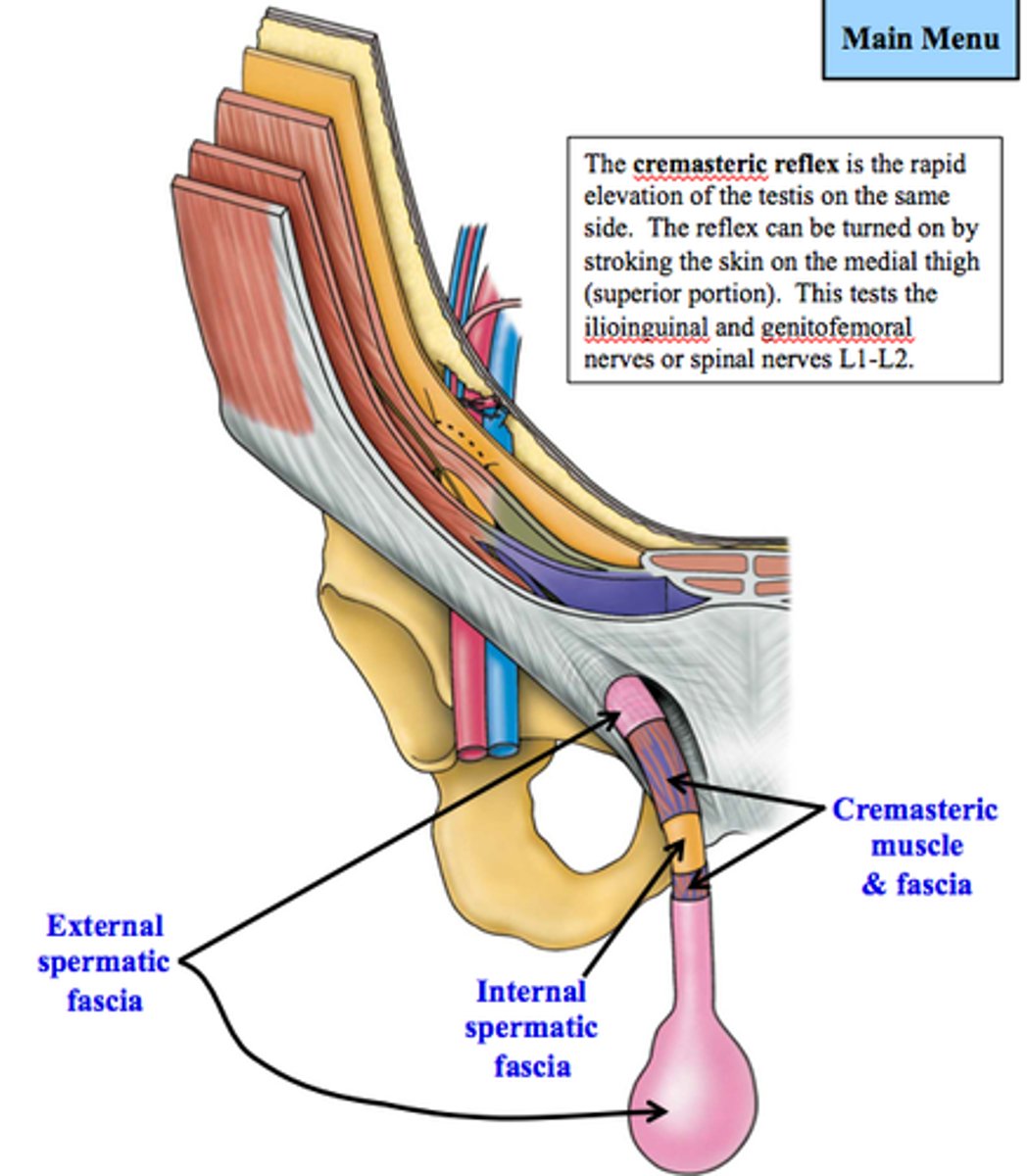
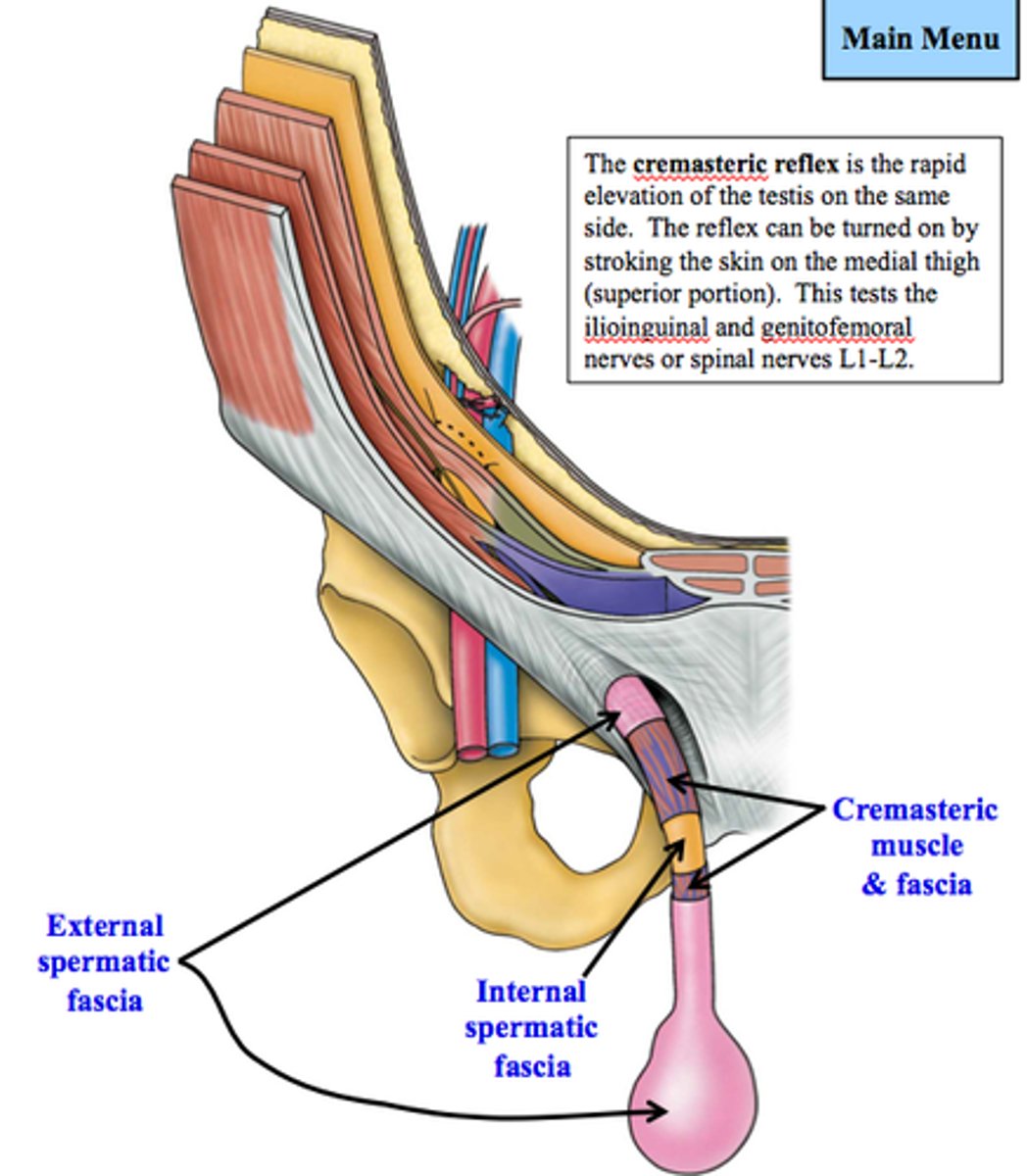
What elevates the testes?
cremasteric reflex (cremaster muscle)
Skin of superomedial thigh is innervated by what?
ilioinguinal nerve
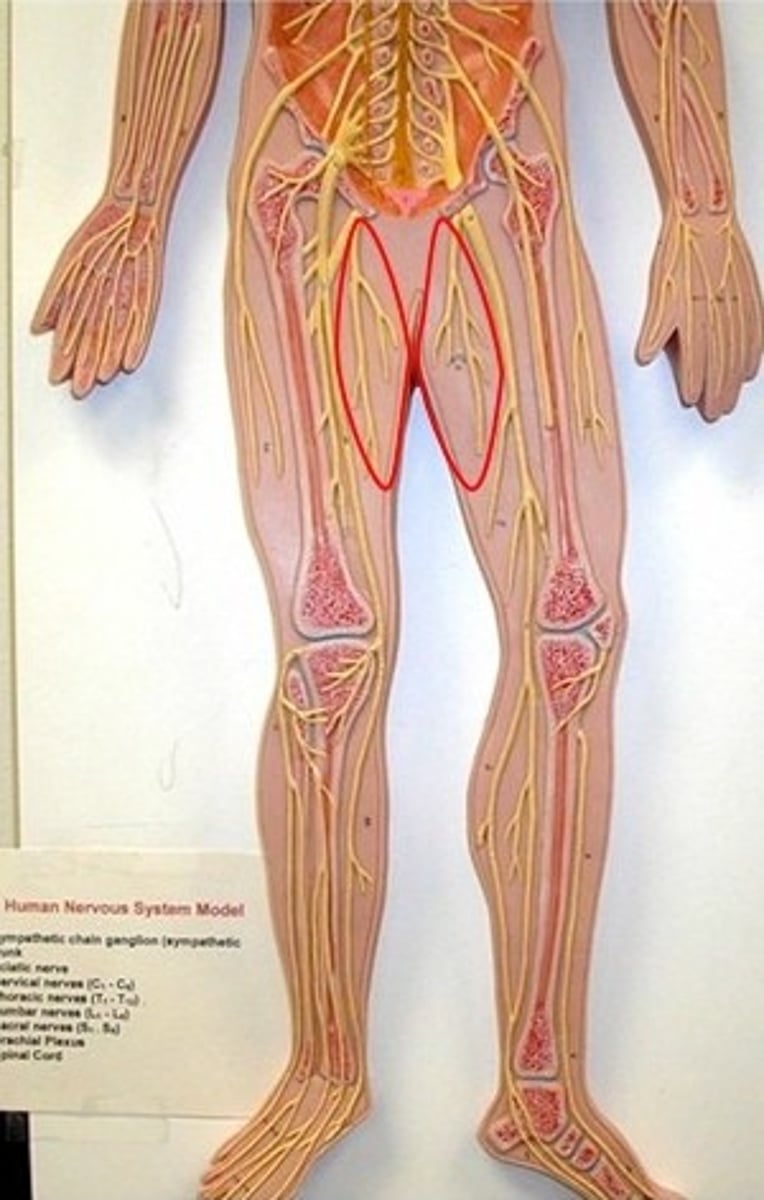
Cremaster muscle is innervated by what?
genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
Blood Vessels of the Spermatic Cord include:
- testicular artery
- cremasteric artery and vein
- artery to vas deferens
- paminiform plexus of testicular veins
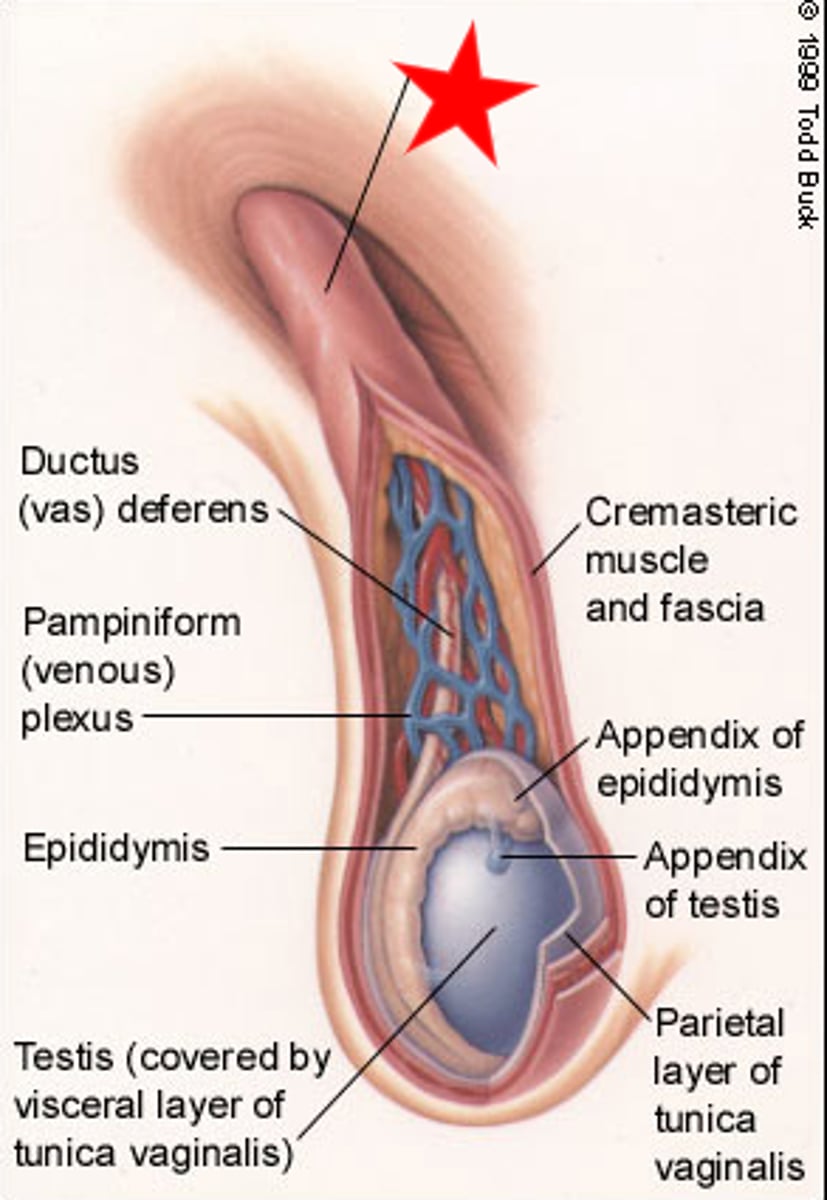
Nerves of the Spermatic Cord include:
- genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
- autonomic nerves
Other contents of the Spermatic Cord:
- vas deferens
- Procesus Vaginalis
- Lymphatics
Testicular Torison
twisting of spermatic cord upon itself
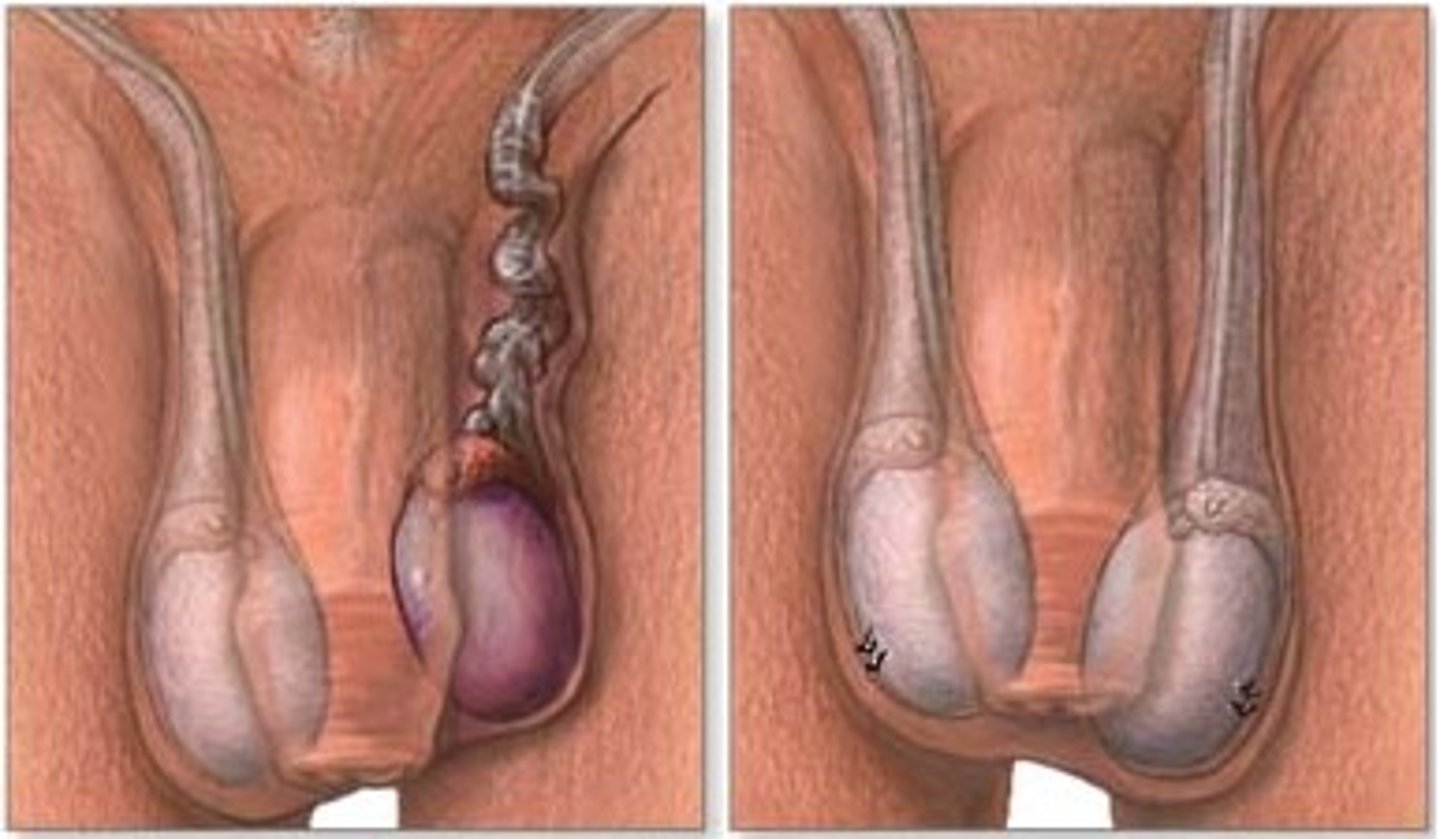
What happens to the affected testis of Testicular torsion?
the affected testis lies higher and due to the stragnulation of testicular artery it causes necrosis of the testis which is considered a surgical emergency
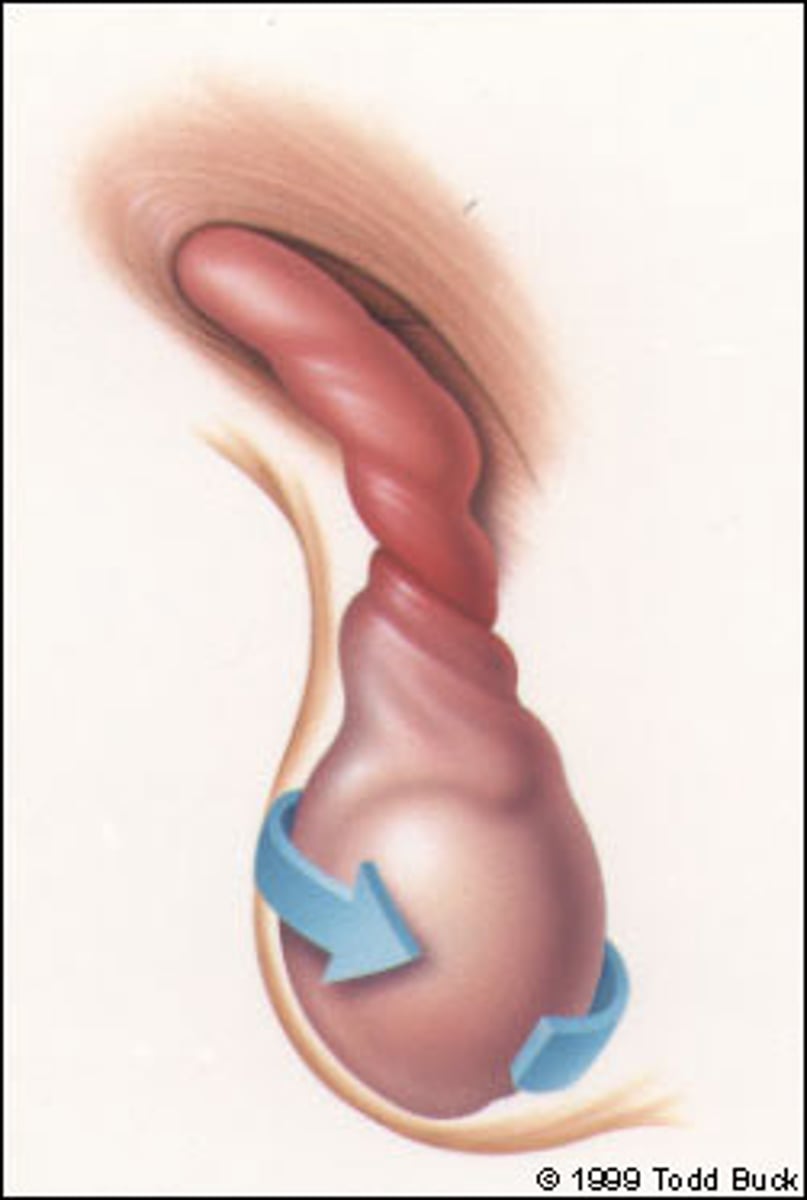
What is the cause of Testicular Torsion?
spasm of cremasteric muscle fibers or loos testicle in large tunica vaginalis which when done causes severe sudden pain in affected testis
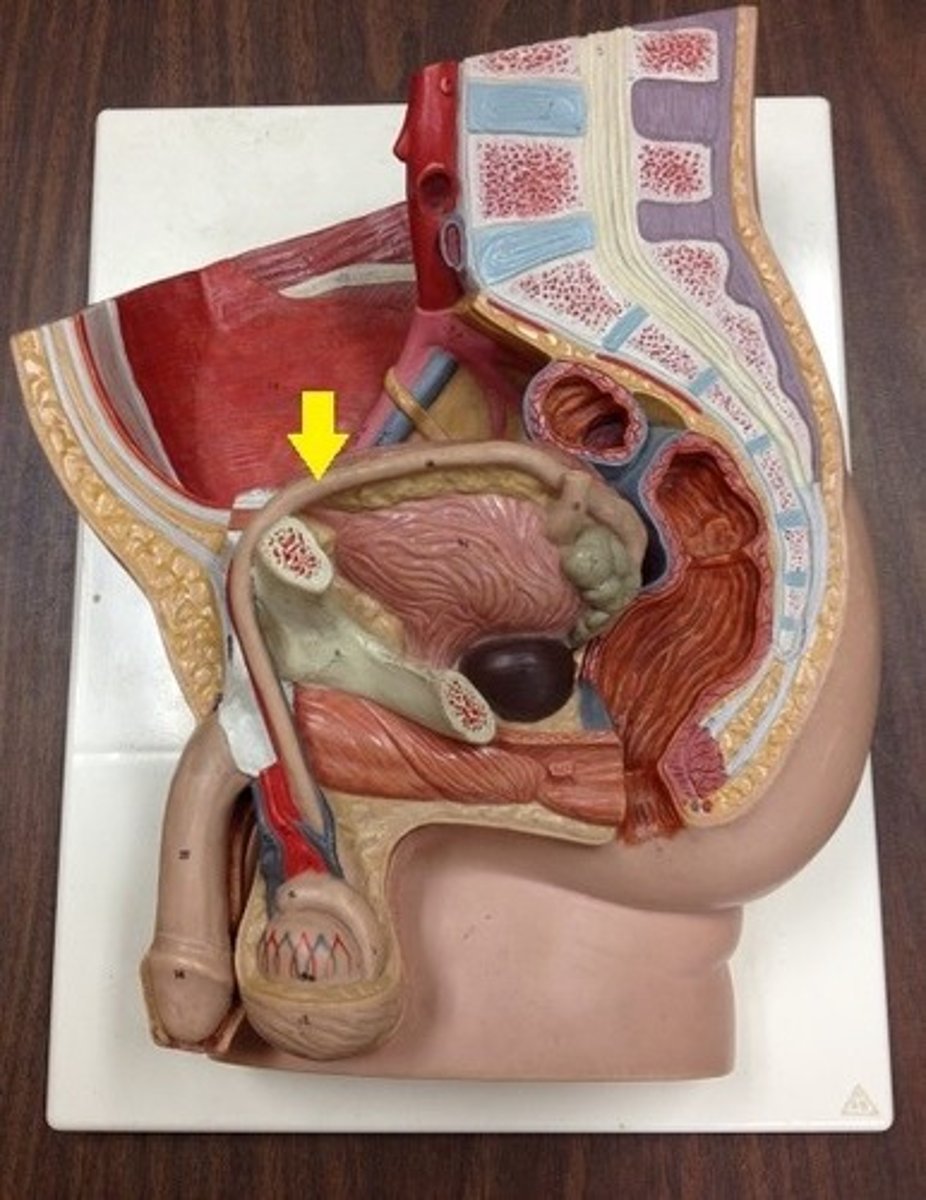
Vas Deferens
straight thick muscular tube that conveys sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct (vas deferens + seminal vesicle duct)
What are the 3 layers of smooth muscle in the Vas Deferens?
1. inner longitudinal
2. outer longitudinal
3. immediate circular
What does the rich autonomic innervation of the Vas Deferens permit?
fast movement of sperm towards the ejaculatory duct
Vas Deferens Anatomical Course
1. tail of epididymis
2. Through inguinal canal
3. down lateral pelvic wall close to the ischial spine
4. turns medially to pass between the bladder and the ureter
5. down posterior surface of bladder
6. joins seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory duct
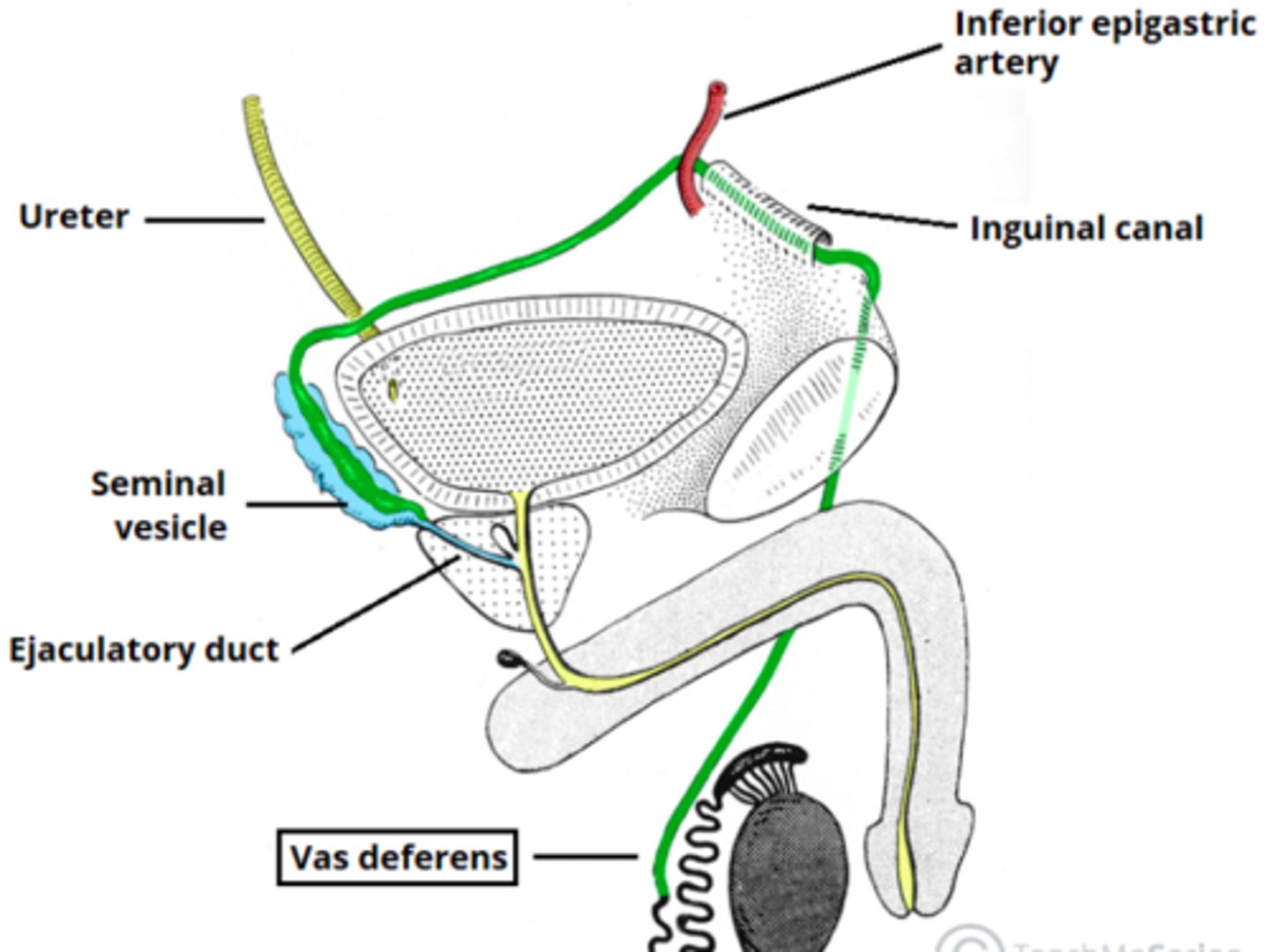
Seminal Vesicles
5cm long tubular glands that is between the bladder and rectum
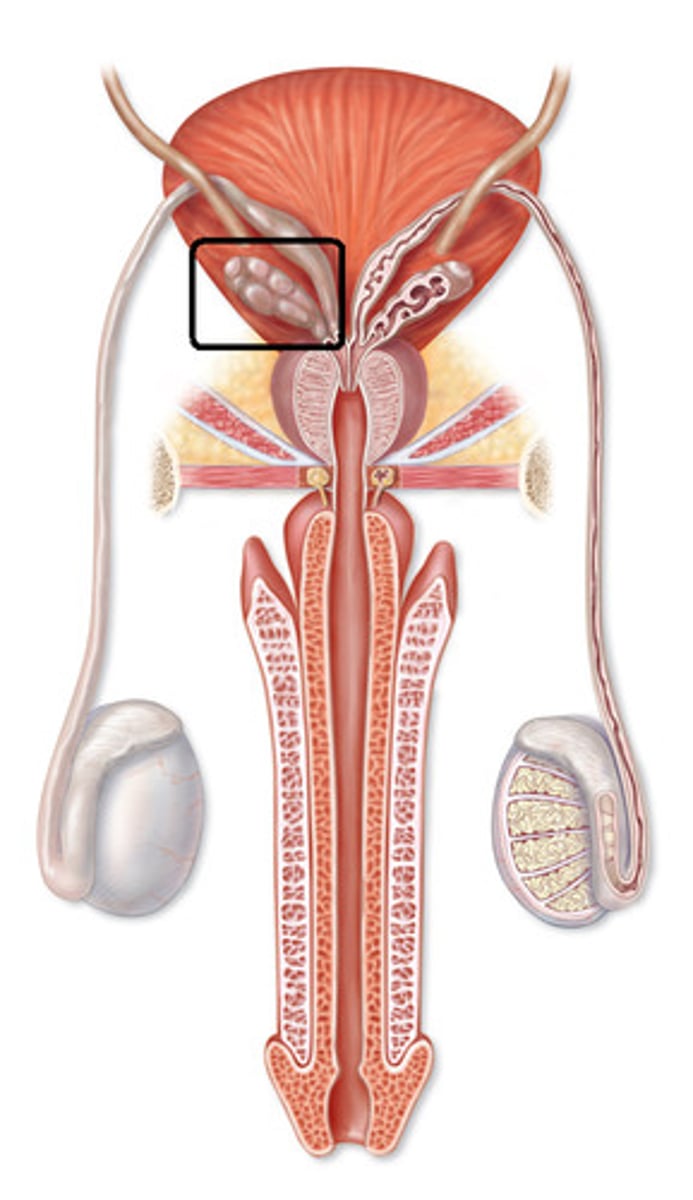
Seminal Vesicle secretions have a key role in what?
the normal functioning of semen that makes of 70% of its total volume
Seminal Vesicle late ejaculate fractions:
alkaline fluid, fructose, prostaglandins, clotting factor
The seminal vesicles and the ductus deferens form what?
the ejaculatory duct
Bulbourethral (Cowper's glands)
pair of pea shaped exocrine glands located posterolateral to teh membranous urethra
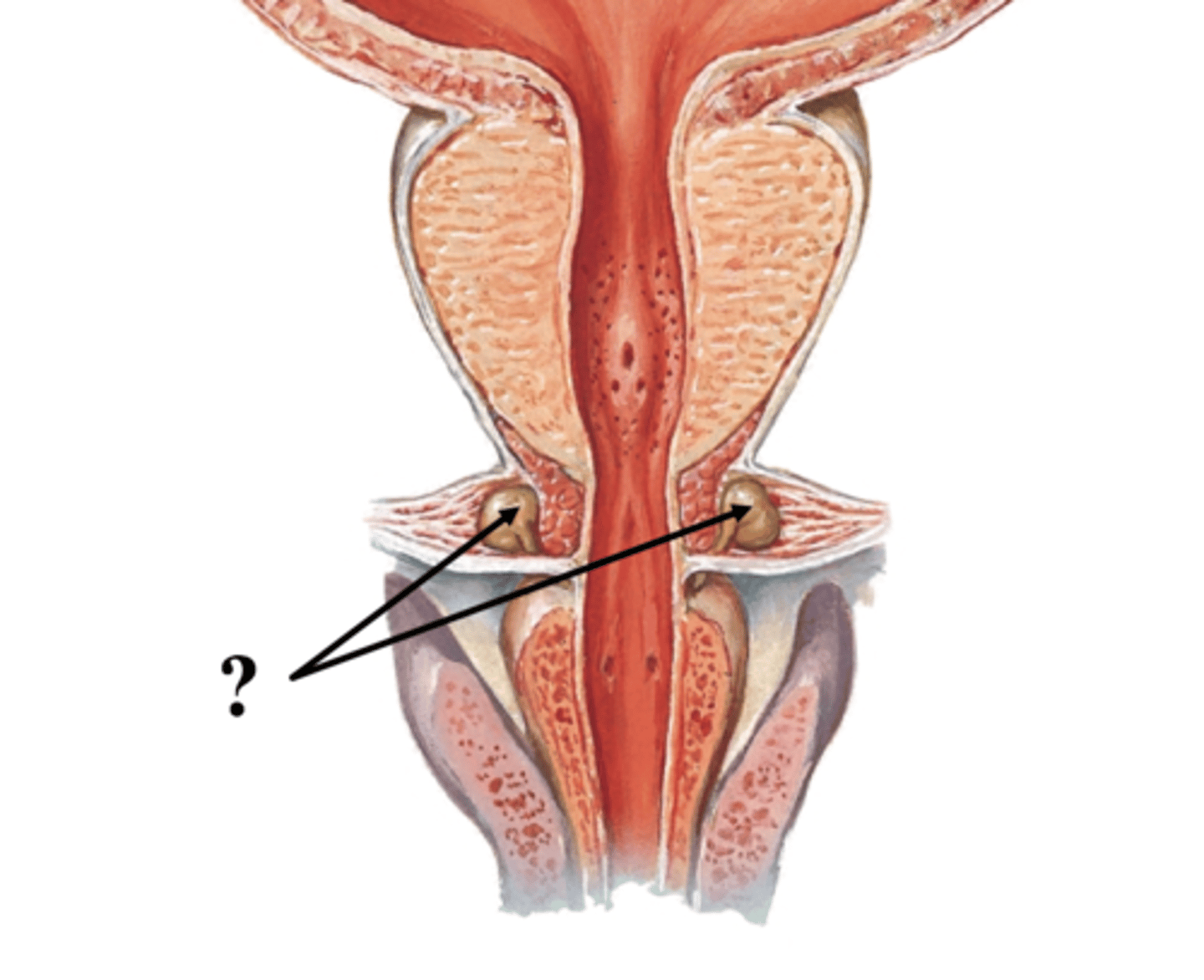
Function of Bulbourethral (Cowper's glands)
contribute to the final volume of semen by producing a lubricating mucus secretion containing glycoproteins
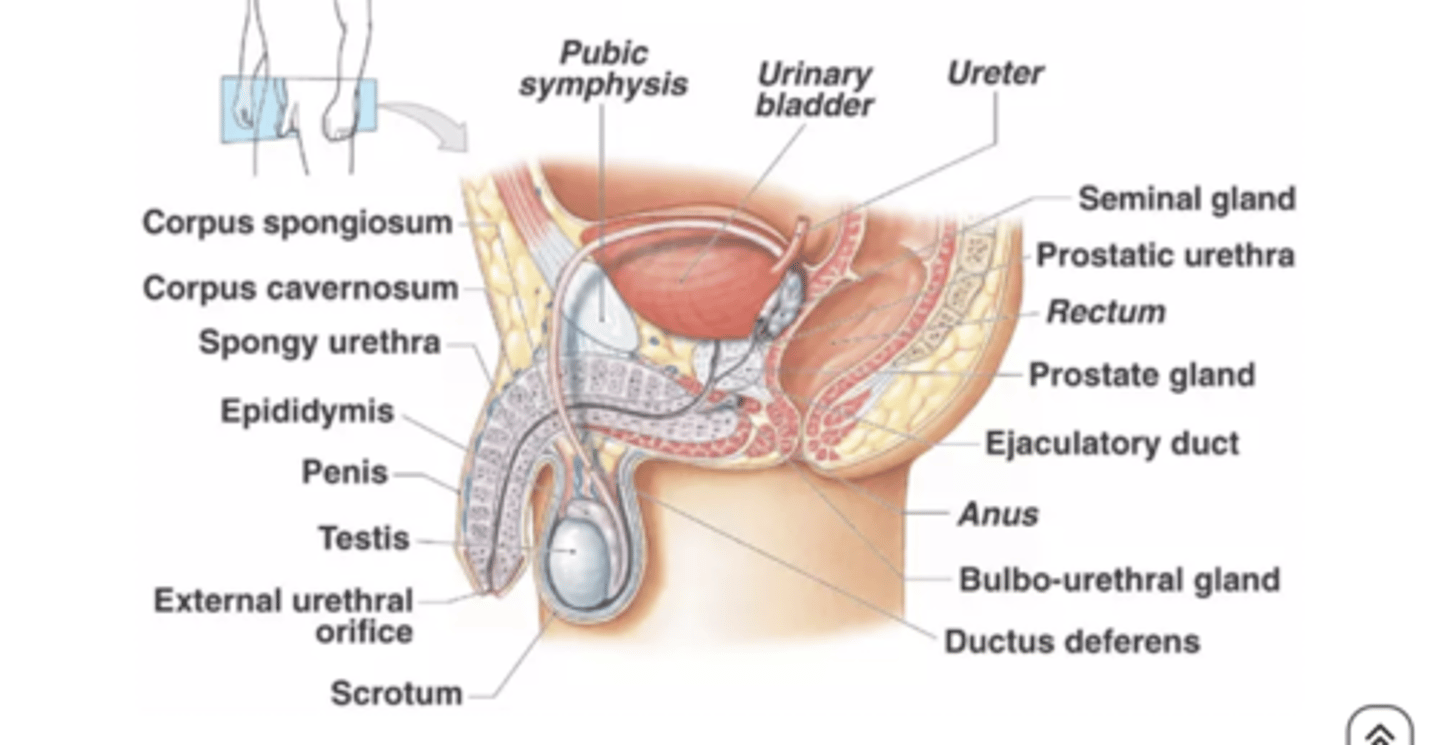
What is the largest accessory gland in the male reproductive system?
prostate
Prostate
found inferior to EUS with levator ani muscle inferolateral to it and anterior to rectum
What does the Prostate secrete?
proteolytic enzymes into the semon