Geography IGCSE - Hazardous environments
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Hazards
An event that threatens, or actually causes damage and destruction, to people to their property and settlements
Natural hazards
A hazard produced by environmental processes and involves events such as storms, floods and earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
Why are some places more hazardous than others
some places, experience more than one type of natural hazard event, experience natural hazards more frequently, where the hazards are stronger and more destructive, are better able to cope with the damaging impacts of natural hazards
Geological hazards
Earthquakes, landslides, volcanic eruptions
Climatic hazards
storms, floods, drought
Biological hazards
fires, pests, diseases
Technological Hazards
nuclear explosions, accidents, pollution
Draw how tropical cyclones are formed
P.67 of Edexcel book
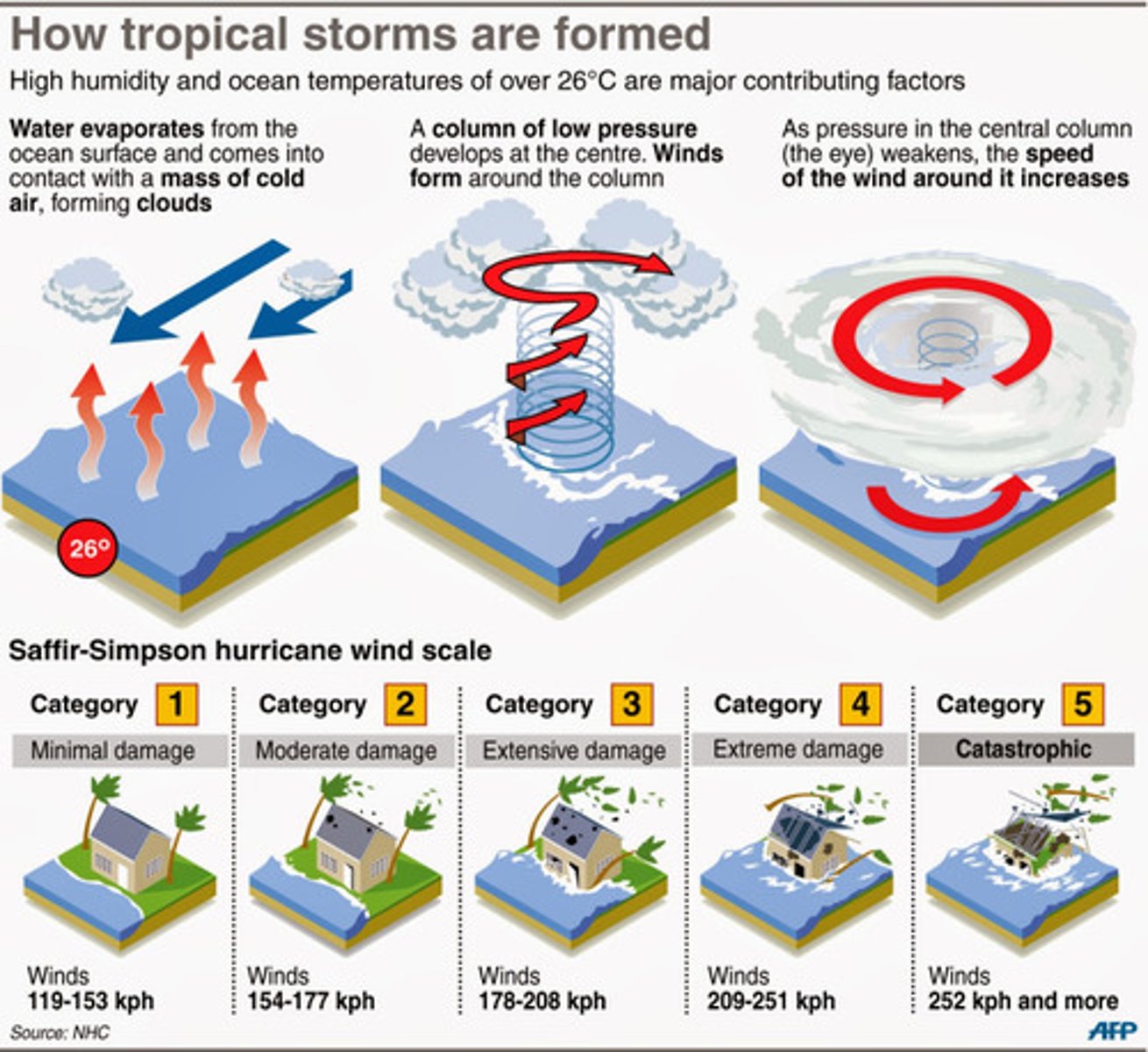
Conditions for tropical cyclone
deep layer of humid, warm (>27) and unstable air, supply of energy from surface of the sea, circular motion of the air, encouraged by Coriolis force, wind shear encourages the circulatory motion within the cyclone
Calmest part of a tropical cyclone
eye
Most destructive part of the eye
eye wall
Difference between hurricanes and cyclones
hurricanes in America, cyclones in Indian Ocean, typhoon in Pacific
effects of tropical cyclones
very strong winds, torrential rain, storm surges
Storm surges
rises in sea level associated with very low pressure, allows the sea to expand
Divergent/Constructive
When two plates are moving apart. Convection currents move plates. Up-welling of magma from the mantle creates new oceanic crust. Volcanic islands and mid-ocean ridge are created
Destructive/Convergent/Subduction
Convection currents in the upper mantle move plates. Denser oceanic plate is subducted beneath the continental plate. Ridge-push and slab pull forces pull the plate under and break it up. Increase in pressure causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
Conservative/Transform
Two plates move in opposite directions or in the same direction at different speeds. The friction may cause an earthquake
Collision
Two plates meet head-on and are of equal density and strength because of convection currents. The sediments between the two plates are squeezed upwards
Hotspots
location beneath the Earth's crust where strong and rising currents of magma occur
Different types of hazards from volcanoes
Lava flows, ash, gas emissions
Pyroclastic flows
a dense, destructive mass of very hot ash, lava fragments, and gases ejected explosively from a volcano and typically flowing at great speed
Earthquakes
Sudden and brief period of intense shaking of the ground
Measuring scale of explosivity
Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) which measures the volume of ejected material and eruption lava height
Scale of VEI
0-8
When magma erupts at the surface it can form different types of volcanoes depending on...
viscosity, stickiness, amount of gas, way it reaches surface
Two types of volcanoes
explosive, effusive
High viscosity
high explosivity
low viscosity
Effusive explosivity
Strato Volcano (composite cone)
viscous magma, explosive eruption
shield volcano
Low viscosity, effective eruption
Measure of earthquake
Richter scale
Epicentre
point on the surface directly above the centre
Focus
centre of the earthquake underground
Richter scale
used to determine the likely damage caused by an earthquake
The amount of earthquake damage depends...
on the depth of the focus and the type of rock
The worst damage occurs where the...
focus is closest to the surface and where rocks are soft
Shock waves...
liquefy soft rocks so they behave like a liquid. Rocks lose their load-bearing ability. The foundations of buildings and bridges collapse
The hazard threat of earthquakes lies in their ability to...
shake buildings so vigorously that they fall apart and collapse. The damage is worse than it should be because of poor building design. They also rupture gas pipes and break electricity cables
Mercalli scale
scale that is based on what people experience and the amount of damage done
Moment Magnitude Scale (MMS)
scale which measures the energy released by an earthquake on a logarithmic scale. (More accurate than Richter scale)
The amount of damage and destruction caused by a particular natural disaster does not just depend on its scale and destructive energy. Other factors are...
size of area affected/ density of population/ how long the event lasts/ degree to which people are warned in advance of event/ level of preparation/ ability of country or region affected to cope with aftermath of hazard
Primary effects of earthquake...
collapsed buildings and people killed by this/ broken water, gas and sewage pipelines/ downed electric power lines
Secondary effects of earthquake...
tsunamis/ aftershocks/ fires due to ruptured gas mains
Primary effects of volcanoes
Buildings, roads, crops are destroyed by lava flows; ash causes roofs to collapse; people and animals are injured/killed by lava and falling rocks; water supplies are contaminated; people, animals and plants are suffocated by volcanic gases
Secondary effects of volcanoes
Lahars, fires, psychological trauma
Richter Scale
The Richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake (how powerful it is). It is measured using a machine called a seismometer which produces a seismograph. A Richter scale is normally numbered 1-10, though there is no upper limit. It is logarithmic which means, for example, that an earthquake measuring magnitude 5 is ten times more powerful than an earthquake measuring 4.
Reasons people live in high risk areas such as volcanoes
fertile soils, farming, tourism, mining, geothermal power, family
Reasons people live in high risk areas such as tropical cyclones
warm seas, tourism, climate, family
Reasons people live in high risk areas such earthquakes
geothermal power, tourism, feeling of protection, family
major short-term impacts of tropical cyclones
damage of property, people killed or injured, disruption of communities, decline in quality of life, disruption and destruction of businesses transport links and services, landslides, soil erosion, flooding
what causes primary impacts in cyclones
high winds, torrential rain, storm surges
major secondary-term impacts of tropical cyclones
cost of repairing the damage to the spread of waterborne disease, loss of homes and personal possessions, transport lines being blocked by landslides
Reasons for why developed countries cope better with the impacts of natural hazards
better access to resources and technology, better emergency services, quicker recovery,
Scale to measure wind speed
Saffir-Simpson hurricane Wind Scale
Ways to reduce the possible impact of future tropical cyclones (adjustment/ mitigation)
building design, location, warning systems, education
Adjustments to buildings to protect against hazards
curved roof for typhoon protection, base isolation system for earthquakes, 3m columns for flood, water can easily run off grass
Coriolis Force
exerted by the spin of the earth on a rotating system causing it to be deflected to the right in the northern hemisphere and to left in the southern hemisphere
why is Indonesia at greater risk from volcanic hazards (physical)?
area one of the most seismically active areas on the planet, subduction on the Indian Ocean, islands were formed due to volcanic activity, Indonesia sits on top of the meeting point of several tectonic plates
why is Indonesia at greater risk from volcanic hazards (social)?
Jakarta has 10 million people, high risk of infectious disease, 300 different ethnic groups use more than 700 languages, rural areas 20% of population don't have clean drinking water, 32% of the population is involved with agriculture
why is Indonesia at greater risk from volcanic hazards (economic)?
GDP per capita is $11 700, Indonesia imports $144.4 billions of good including fuel, 32% of population live below the poverty line,