philosophy final
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
describe Douglas inductive risk
Inductive reasoning is inherently uncertain because it involves drawing general conclusions from specific observations (e.g., extrapolating from experimental results to general theories).
This uncertainty means there is always a chance of error: false positives (accepting a false hypothesis) or false negatives (rejecting a true hypothesis).
what are type I and type II errors
type one error is saying a drug is beneficial when it actually isnt and in order to avoid this you use a low significance level so you need a strong correlation for it to reject the null
type two error is saying there is no correlation when there actually is→saying a chemical is safe when it is not→using a high signicance level means any correlation in the data will be picked up
what are non epistemic values
moral and political values or social
what is the difference between the practice and context of science
the practice of science is the context of discovery and describes what we choose to study and the methods we imply→impossible to not be influenced by non-epistemic values such as funding and being humane in treatments
The content of science is how we interpret data providing evidence for a theory→standard thought is that this part of science is value neutral
describe underdetermination and provide an example
underdetermination is that evidence on its own can support multiple theories such as are children aggressive due to playing violent video games or are aggressive children more likely to seek out violent video games
what is the significance level in science
probability of the evidence being able to reject the null hypothesis
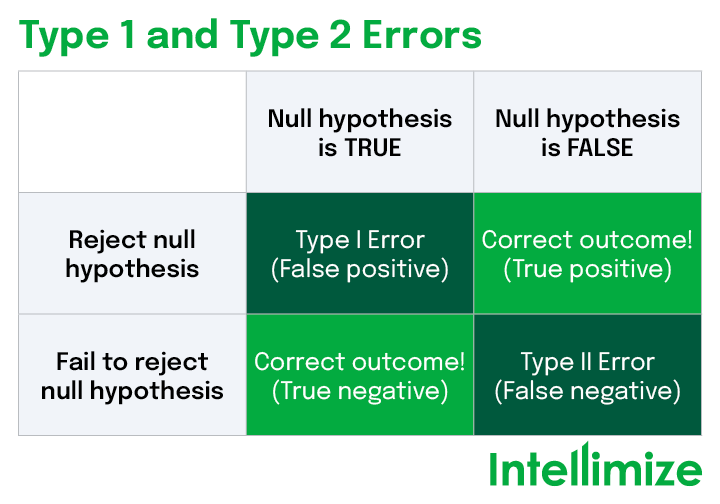
which error is rejecting the null when it is actually true and what significance level negates this
TYPE I and low significance level→takes a lot of evidence to prove that there is a correlation in the data
why does douglas say there are no value independent facts in science
because your conclusion of your data depends on how strongly you feel about being right or wrong
name a critique to douglas inductive reasoning
JEFFREY claims that scientists should report the probability that the hypothesis is true or the degree by which the data supports it however RUDNER responds to this by saying that even probabilistic claims require judgements and either way MAYO says scientists are the people who are informing policymakers so there conclusions will have non-epistemic consequences
what does Longino believe in response to Douglases inductive reasoning means there are always nonepistemic influences
Longino believes that even if the practice and content involve non epistemic values, communities of scientisits should still be held to a certain degree to practice good science
what are Longinos two aims for good science
scientists should subject there own assumptions and values to constant scrutiny for example gender bias and reevaluate their own hiring practices
encouraging criticisms from diverse viewpoints however determining these viewpoints can be contentious since this stands on the belief that science is always moving in a positive direction whereas it is often plagued by inhuman view points that may degrade it as a whole
what is a counterargument to douglas and who goes against that counter argument
Jeffrey claims scientists should report on probability and the degree to which data supports a theory
Rudner says that even making probabilistic claims still involves the inclusion of non-epistemic values since judgements about the data still need to be made
Mayo finally says that scientisits are the ones repsonsible for informing the policy makers and therefore need to understand the ramifications of their conclusion being right or wrong and weighing this with nonepistemic values
what does Longino say about non-epistemic values in science
Longino says that even if non-epistemic values have a place in science; as long as science aims to be good in its practice it can be truth seeking
assumptions should be subject to constant scrutiny→rejection of this is in Kuhns model of paradigm shifts where when science is in a normal stage there are accepeted theories that are not questioned and only when there are an abundance of anomamlies unexplainable by the normal science does it udnergo revolution
encouraging cristisms from diverse viewpoints amd the critisism of this is who are considered viewpoints to consdier
Van Fraasens realism stance
realism is not about what science achieves with the no miracles argument and the argument for theory change but rather its AIMS
Van Fransen and constructive empiricism
we want empirical adequacy to be able to explain our observations→noncognitivism in that we are not describing the world but rather seeking to have useful instruments such as with mathematics
what is a counterargument to van fraasen
MAXWELL how do we distinguish between observable and non observable
deontological and consequentialism
deontological is what we ought to do; KANT categorical imperative
consequentialism is outcome-based; maximizing benefit while minimizing harm→Bentham utilitarianism ; different from hedonism with having good things also including knowledge and beauty having intrinsic value
Wakefield affair related to ethics
The Wakefield affair was when doctor Wakefield, incorrectly reported data describing a correlation between mumps and measles and autism, which ended up being false and later retracted; the US Code of Research Integrity discusses falsification and fabrication
phlogiston theory and what does it relate to
phlogiston is a not real substance that is emitted during combustion and is used to defend the theory change argument from antirealists that theories we believed to be true in the past ended up being false therefore we cannot believe current theories to be true