3 - Thermodynamics and molecular binding
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Define Gibbs free energy
how much energy is free in a system
List the 3 things Gibbs free energy is a function of
enthalpy (H)
entropy (S)
temperature (T)
Define enthalpy
the total heat content of a system in terms of bond breaking and making
Define entropy
measure of disorder in a system
State the Gibbs free energy equation
△G = △H - T△S
What explains a negative value of △G
the reaction is spontaneous and energetically favourale

What explains a positive value of △G
the reaction will not occur spontaneously and energetically unfavourale
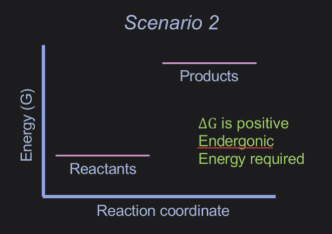
What explains a negative value of △H
the reaction is exothermic and releases heat energy
What explains a positive value of △H
the reaction is endothermic and absorbs heat energy
What is temperature measured in?
Kelvin
What explains a negative value of △S
reactants will have a higher entropy than products
What explains a positive value of △S
reactants will have a lower entropy than products
Enthalpy in protein folding
since H bonds are stronger in hydrophobic environments there will be increased enthalpy in proteins
Is entropy in a proteins primary structure high or low?
high as single bonds are free to rotate around themselves with lots of possible conformations
Is entropy in a proteins later structures high or low?
low as chains are folded in on themselves
Levinthal’s paradox
in an 100 residue protein if each amino acid can only adopt 1 of 3 conformations
the total number of possible structures would be 3100
if we also imagine it takes 10-13 seconds to sample each configuration
it would take 1.6×1027 years to search all conformations
Lowest energy state (2 points)
proteins gravitate energetically towards the lowest free energy conformations
however since there are several naturally found low energy conformations, the ultimately favoured one is dependent on the environments they’re in
Define a ligand/enzyme in terms of thermodynamics
a molecule that forms a complex with a receptor biomolecule to serve a biological purpose
Define a substrate in terms of thermodynamics
a molecule that binds to an enzyme and is converted into product
Define affinity in terms of thermodynamics
a measure of strength of an interaction between molecules
Write the association constant equation
[AB] / [A] + [B] = KA
where
[A] + [B] are concentration of reactants
[AB] is concentration of product(s)
What is association constant measured in?
M-1
What does a high KA value describe?
strong binding affinity between molecules
Write the disassociation constant equation
[A] + [B] / [AB] = KD
where
[A] + [B] are concentration of reactants
[AB] is concentration of product(s)
What is disassociation constant measured in?
M
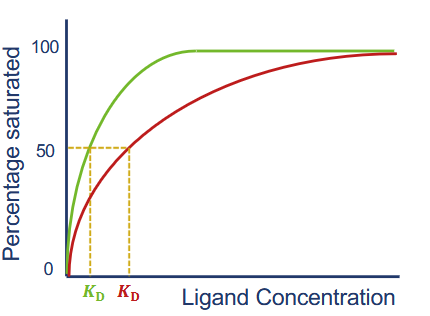
What does a low KD value describe?
strong binding affinity between molecules
How can KD be found on a graph?
read ligand concentration at which half of the receptor sites are occupied
Define cooperativity (2 points)
can occur when two or more molecules bind to the same receptor molecule
binding a molecule changes the affinity for the subsequent binding events

Define allostery
occurs when a molecue binding to a receptor molecule changes its affinity for a separate molecule

Describe the haem cofactor
tetrapyrole ring molecule in association with an Fe2+ ion
What happens when oxygen binds to haem in haemoglobin?
Fe2+ moves into plane of tetrapyrole ring
Describe cooperative binding in haemoglobin (2 points)
binding of O2 to a haem cofactor in one subunit increases the affinity of O2 to others
binding of the last O2 is 200x more effecient than binding of the first
How does haemoglobin change upon binding?
α1β1 dimers rotate relative to α2β2 by 15o
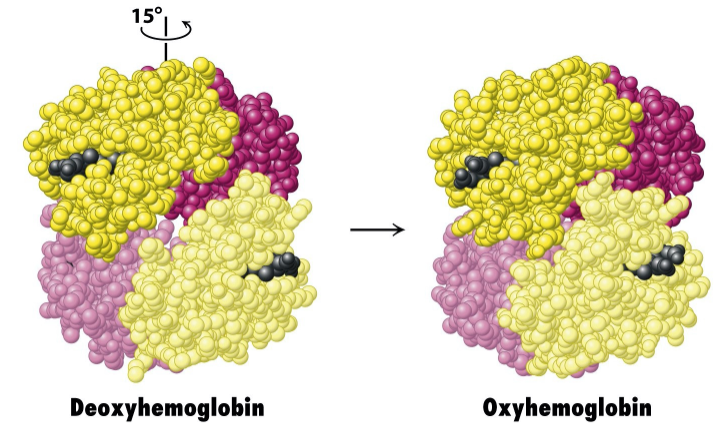
What is the deoxygenated form of haemoglobin known as?
T state (tense state)
What is the oxygenated form of haemoglobin known as?
R state (relaxed state)
State the two haemoglobin cooperativity models
concerted model
sequential model
Describe the concerted model of cooperativity
proposes that all subunits of hemoglobin switch between the T and R states simultaneously, affecting the entire molecule's affinity for oxygen
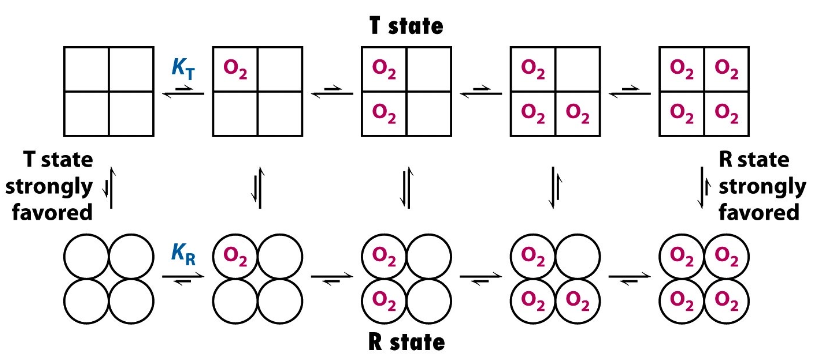
Describe the sequential model of cooperativity
suggests that binding of oxygen to one subunit increases the likelihood of neighboring subunits transitioning from the T state to the R state, leading to a gradual change in affinity.
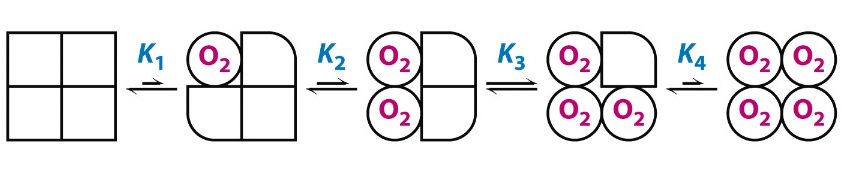
Describe allosteric control of oxygen binding to haemoglobin
2,3 Bisphosphoglycerate stabilises T state, making it harder to transition into R state
What reactions do oxidoreductase enzymes catalyse?
redox reactions
Give an example of an oxidoreductase enzyme
lactate dehydrogenase
What reactions do ligase enzymes catalyse?
formation of covalent bonds
Give an example of a ligase enzyme
DNA ligase
What reactions do transferase enzymes catalyse?
the transfer of functional groups between molecules.
Give an example of a transferase enzyme
kinases
What reactions do hydrolase enzymes catalyse?
hydrolysis
Give an example of a hydrolase enzyme
sucrase
What reactions do isomerase enzymes catalyse?
rearrangements of molecular structures
Give an example of an isomerase enzyme
alanine racemase
What reactions do lyase enzymes catalyse?
removes groups of atoms from molecules
Give an example of a lyase enzyme
oxalate decarboxylase