Chapter 21: Spirochete Diseases
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Syphilis
Most commonly acquired spirochete disease
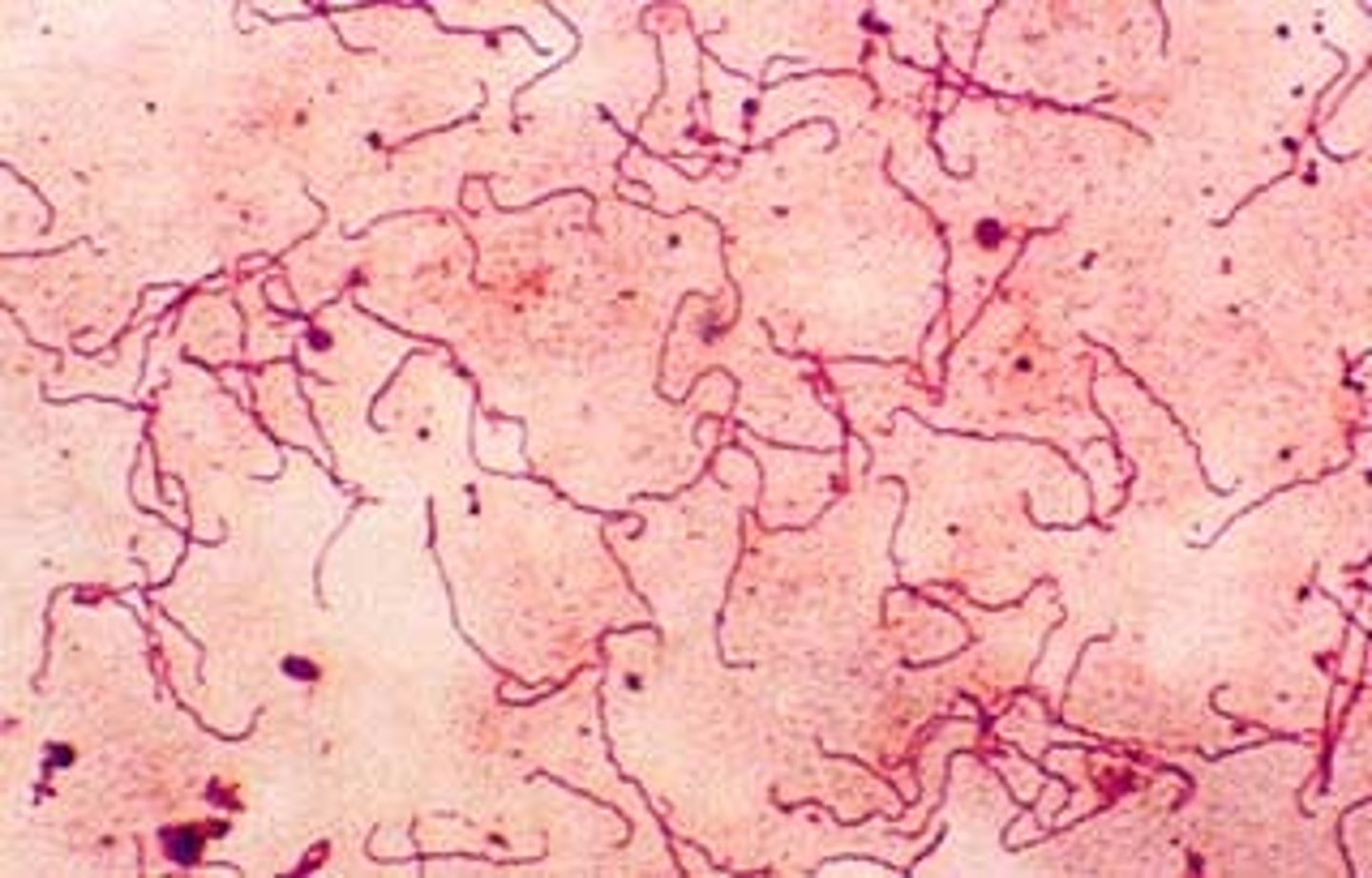
Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum
Causative agent of Syphilis
Treponema pallidum subsp. pertenue
Agent of YAWS (chronic nonvenereal disease of skin and bones)
Treponema pallidum subsp. endemicum
Agent of nonvereneal endemic syphilis
Treponema pallidum subsp. carateum
Agent of Pinta
Sexual transmission
Primary mode of dissemination of pathogenic treponemes
Primary
Secondary
Latent
Tertiary
Stages of Syphilis
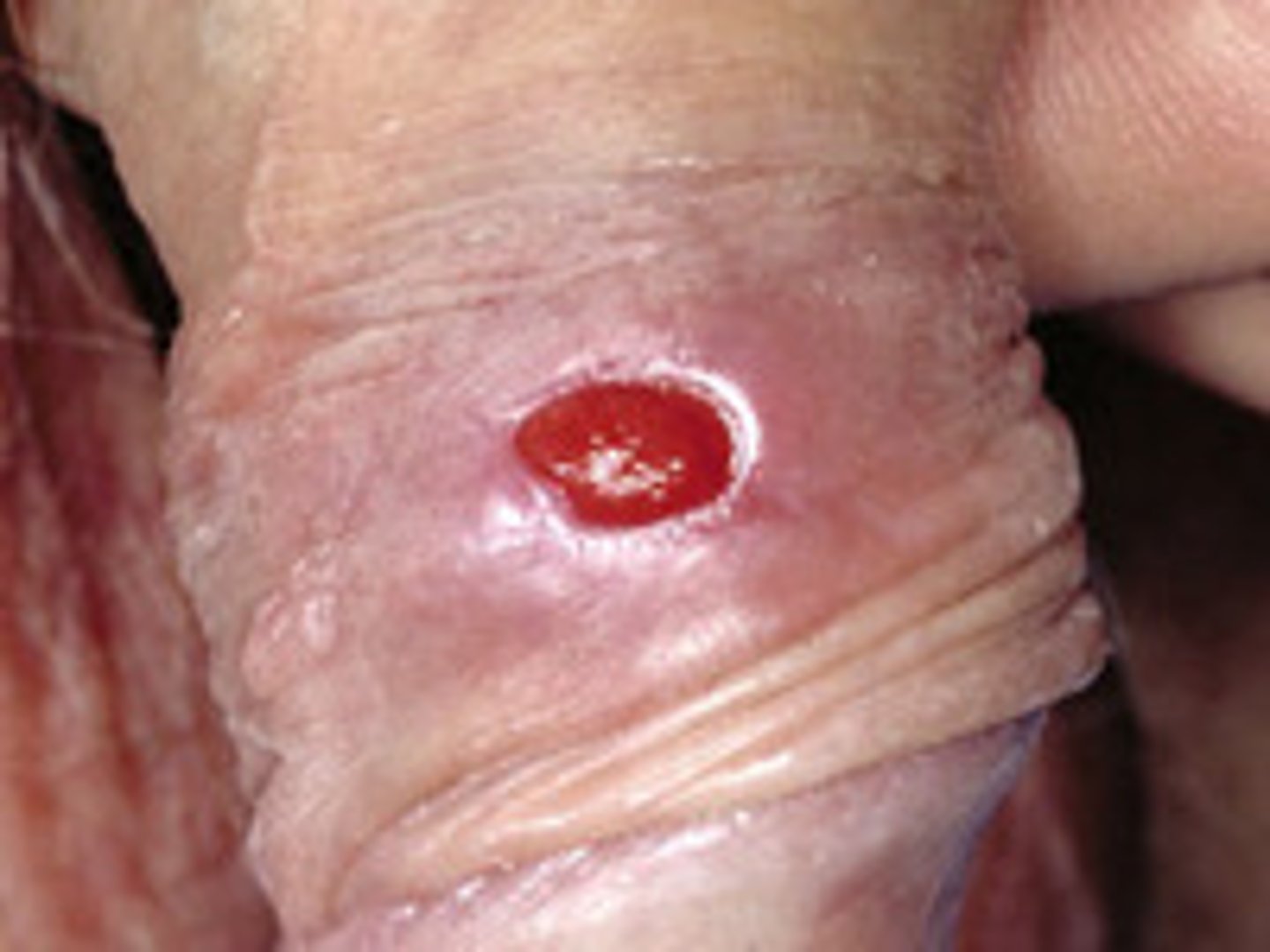
Chancre
A painless, solitary lesion characterized by raised and well-defined borders
Develops 10-90 days after infection (Ave: 21 days)
Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum
The Great Imitator
Gummatous syphilis
Cardiovascular disease
Neurosyphilis
Manifestations of Tertiary Syphilis
Note: This occurs 10-30 years following the secondary stage
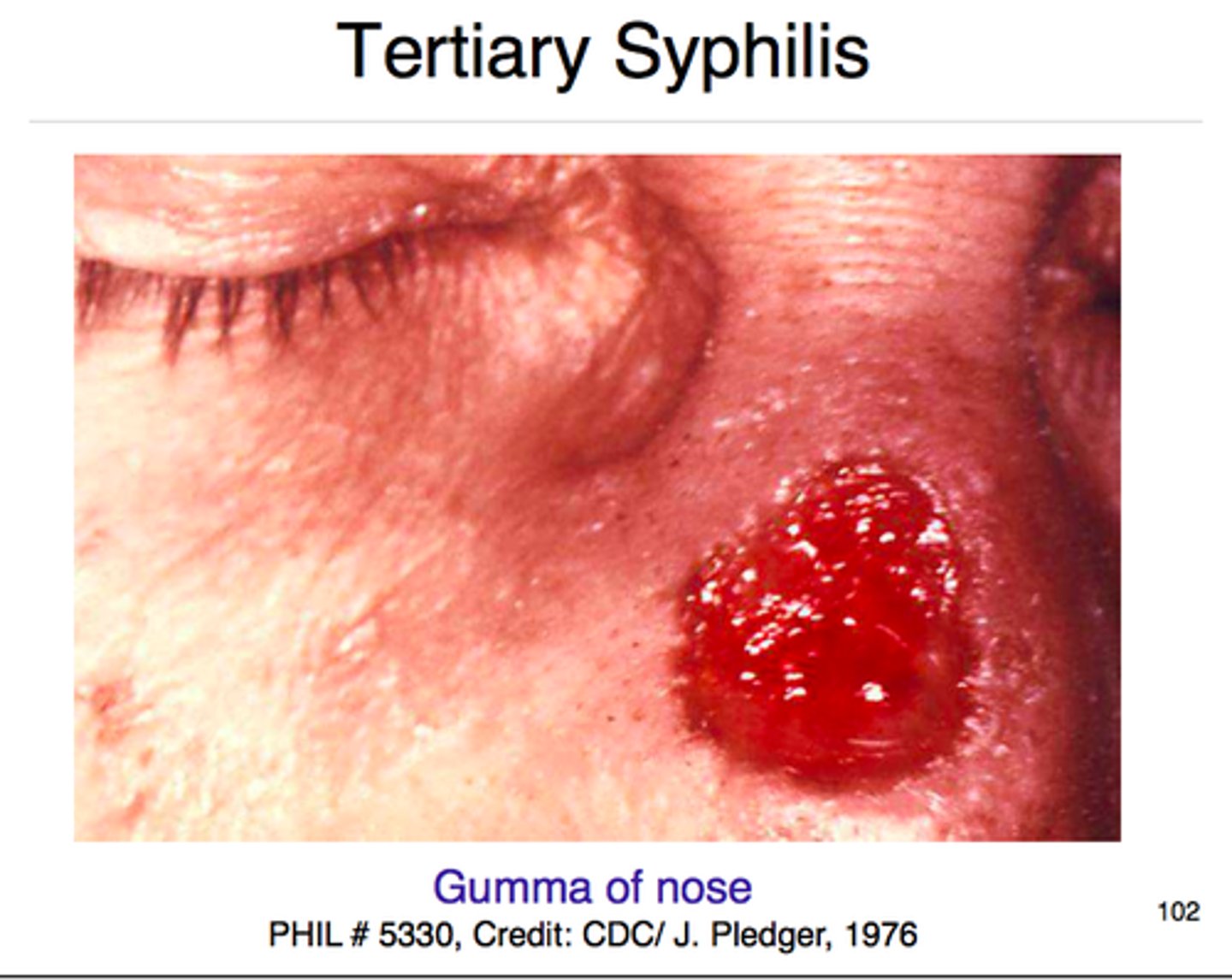
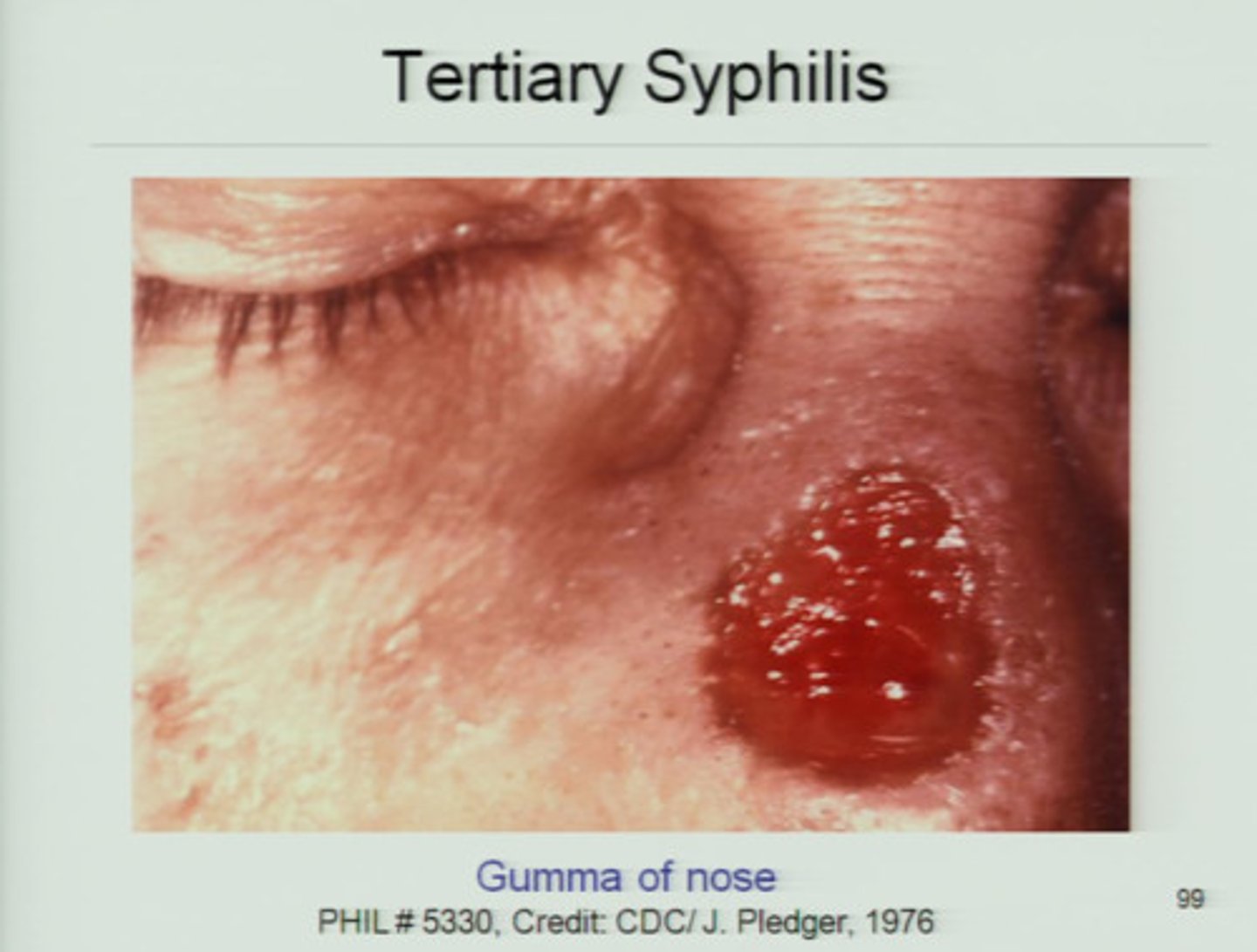
Gummas
Localized areas of granulomatous inflammation that are most often found on bones, skin or subcutaneous tissue
Congenital Syphilis
This occrs when a woman who has early syphilis or early latent syphilis transmits treponemes to the fetus
Direct detection
Nontreponemal Serological tests
Treponemal serological tests
Three main types of laboratory tests for Syphilis
Darkfield Microscopy
Fluorescent antibody testing
Direct Detection of Spirochetes is accomplished by means of ?
Fluorescent Antibody Testing
A sensitive and highly specific alternative to dark field microscopy
Serological Tests
Key to diagnosis if patient has no active lesions in the case of Secondary and Tertiary Syphilis
Nontreponemal Tests
Traditional screening tests for Syphilis
Note: False-positive results are common because of the nonspecific nature of the antigens
Treponemal Tests
Positive results in nontreponemal tests must be confirmed by ?
August Paul von Wasserman
Developed the first nontreponemal Test
Complement Fixation
Principle of Wasserman Test
Nontreponemal Test
Tests that determine the presence of an antibody that forms against cardiolipin
Cardiolipin
A lipid materail released from damaged cells
Reagin
Antibody to Cardiolipin
0.03% Cardiolipin
0.9% Lecithin
0.21% Cholesterol
Composition of Antigen complex used in the reaction to detect the nontreponemal reagin antibodies in VDRL
Note: These abs are either IgG or IgM class
VDRL (venereal disease research laboratory)
RPR (rapid plasma reagin)
TRUST (Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test)
RST (Reagin Screen Test)
Most widely used nontreponemal tests
Flocculation Reactions
Principle of Nontreponemal Tests
Flocculation
A specific type of precipitation that occurs over a narrow range of antigen concentrations
1-4 weeks after the appearance of primary chancre
Nontreponemal test are positive within
Prozone phenomenon
Testing the sera of patients in secondary syphilis is subject to false negative due to
Prozone phenomenon
Lack of a visible reaction in antigen-antibody combination caused by the presence of excess antibody. This may result in a false-negative reaction.
Serial dilutions
Remedy if prozone phenomenon is suspected
VDRL
Both qualitative and quantitative slide flocculation test for serum that includes a modification for use on spinal fluid
Hamilton syringe
Instrument used to deliver one drop of VDRL antigen for the slide test
Alcohol and recalibrated
If the delivery of Hamilton syringe is off by >2 drops out of 60, the syringe must be cleaned with ____________?
Nonreactive
Minimally reactive
Reactive
Three control sera for VDRL
4 minutes
180 rpm
VDRL slide is rotated for __ minutes on a rotator at ____ rpm
Reactive
VDRL result: Medium to Large clumps
Weakly reactive
VDRL result: Small clumps
Nonreactive
VDRL result: No clumps or slight roughness
1:2 to 1:32
All sera with reactive or weakly reactive VDRL results must be tested using the quantitative slide tests with two-fold dilutions of serum ranging from ________________ are initially used
VDRL
Nontreponemal test that is read microscopically
Rapid Plasma Reagin
Modified VDRL test read macroscopically
Cardiolipin
Lecithin
Cholesterol
EDTA
Thimerosal
Choline chloride
Composition of RPR
Rapid Plasma Reagin
Nontreponemal Test that does not require heat inactivation before use
EDTA
Thimerosal
Choline chloride
Components of RPR that stabilize the antigen and inactive complement
Retesting using doubling dilutions in a quantitative procedure
All positive results in RPR should be confirmed by _______?
4
Inactivated serum for VDRL should be use within ______ hours
Beef Heart
Antigen source of VDRL
Cardiolipin source
56C for 10 minutes
Reinactivation of serum for VDRL Test is done at ________ when >4hrs has elapsed
18g
Gauge used for Qualitative VDRL and requires 60 drops of Ag suspension
19g or 23g
Gauge used for Quantitative VDRL and requires 75 and 100 drops of Ag suspension
21g or 22g
Gauge used for CSF VDRL and requires 100 drops of Ag suspension
Charcoal
Component of RPR that allows visualization of flocculation macroscopically
Choline chloride
Component of RPR that stabilizes antigen. Heating is not necessary because of this.
T. pallidum immobilization test
Most specific test for syphilis
Gummas
Localized areas of granulomatous inflammation that are most often found on bones, skin or subcutaneous tissue
0.03% Cardiolipin
Main reacting component of VDRL Antigen
0.9% Cholesterol
Component of VDRL Antigen that enhances the reacting surface of cardiolipin
0.21% Lecithin
Component of VDRL Antigen that removes anti-complementary activity of cardiolipin
EDTA
Component of RPR Antigen that prevents oxidation of lipids
100 rpm for 8 minutes
Rotation and time in RPR
Indirect Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption Test
Agglutination Test
Two main types of manual treponemal tests
Reiter strain
Sorbent used in FTA-ABS used to remove antibodies that cross-react with treponemes other than T. pallidum
Borrelia burgdorferi
Agent of Lyme disease
Willy Burgdorfer
First author and discoverer of the causative agent of Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Most common vector-borne disease in the U.S
Barbour Stoenner Kelly Medium at 33C
Culture medium for Borrelia burgdorferi
Erythema migrans (EM)
Clinical Hallmark of early infection of B. burgdorferi
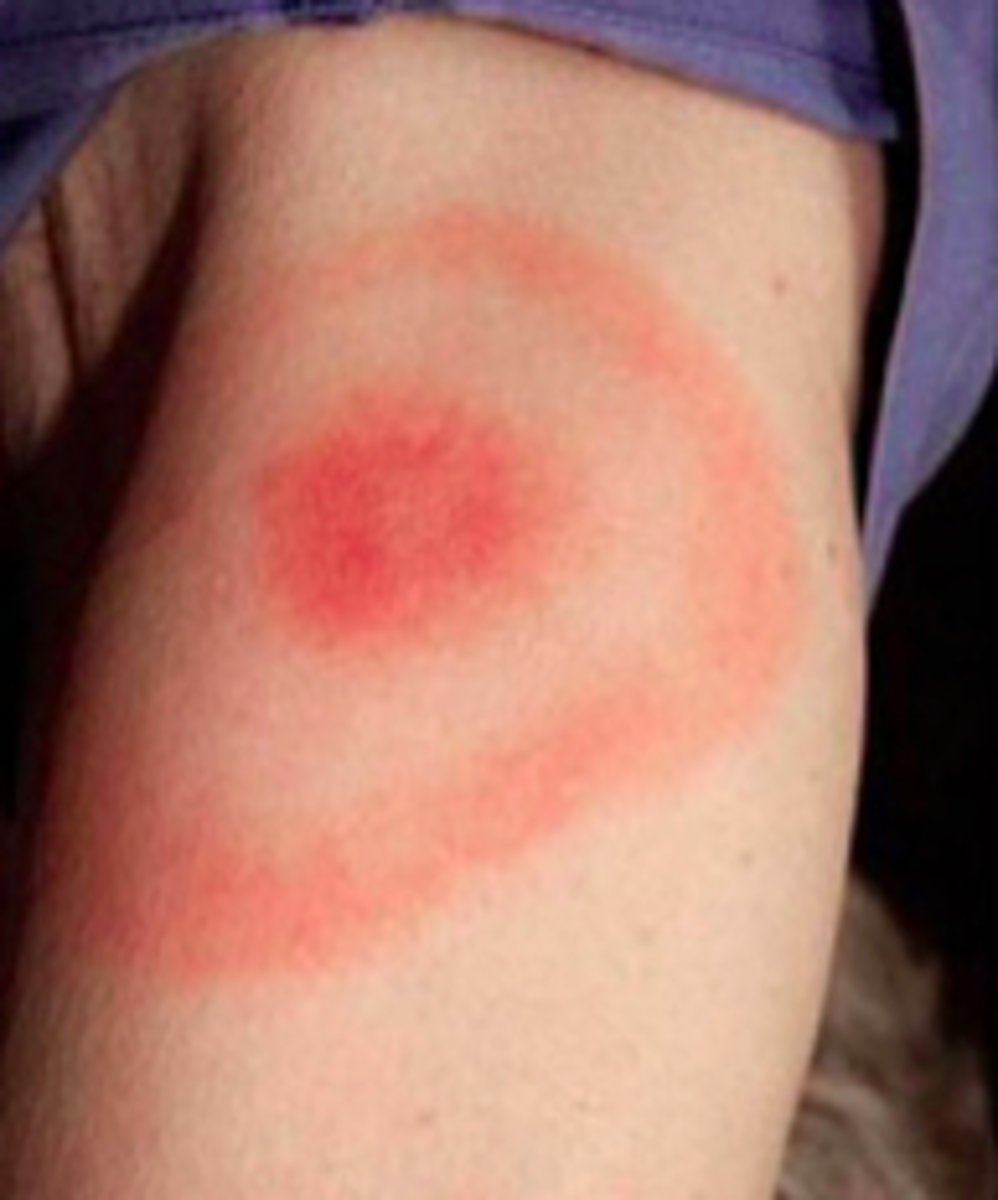
Facial palsy
Most common neurologic sign of Lyme disease
Facial palsy
A peripheral neuritis that usually involves one side of the face
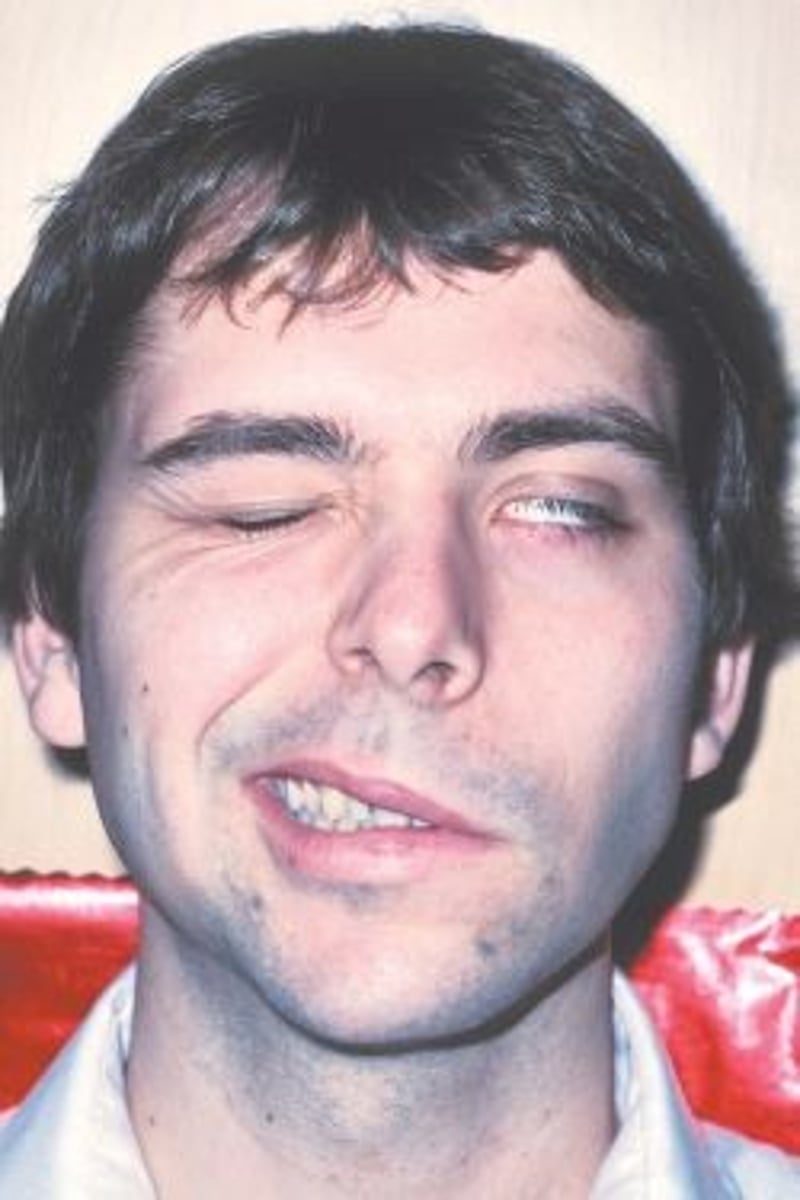
Arthritis
Peripheral Neuropathy
Encephalomyelitis
Major manifestations of late Lyme Disease
HLA-DRB alleles
HLA associated with treatment-resistant arthritis caused by Lyme disease
Immunofluorescence assay
Enzyme Immunoassay
Patients with clinical evidence of Lyme disease be screened with?
Western Blot
Supplemental test for Lyme diseases
Note: This is done if the serology (IFA & EIA) is positive or borderline
1:256 or higher
Titer in IFA that is considered positive
B. reccurentis
T. denticola
RA
SLE
Causes biological false-positive to IFA for Lyme disease
Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
Serological test for Lyme disease best suited for low-volume testing
Beaded IFA pattern
IFA pattern of False positive to Lyme disease caused by biological false-positive causes
Western Blot/Immunoblotting
Confirmatory test for Lyme disease
2
Any of these; 23, 39, 41
Number of bands in Western Blot for Lyme disease to be considered positive for IgM antibody
5 of 10 proteins
Number of bands in Western Blot for Lyme disease to be considered positive for IgG antibody
Corscrew motility
Motility pattern of T. pallidum
Chancre
Specimen used in Direct Fluorescent Antibody Staining for T. pallidum
Darkfield Microscopy
DFAS
Levaditi's Silver Impregnation
Methods for Direct Microscopy of T. pallidum
Wasserman antigen
Other name of cardiolipin
Wasserman Complement Fixation Test
Oldest Test for Syphilis
0.9% Cholesterol
Component of VDRL antigen that is the center for absorption of tissue lipids to increase antigen size
0.12% Lecithin
Component of VDRL antigen that produces standard reactivity
60 +- 2 drops
Number of drops for Qualitative VDRL
Note: It uses 18 gauge
75 +- drops
Number of drops for Quantitative VDRL
Note: It uses 19 gauge
8 minutes at 100 rpm
Rotator setting for RPR
Nichols strain
T. pallidum strain seen on the slide in FTA-ABS
Green
Positive color in FTA-ABS
Serodia T. pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) Test
Treponemal test that uses a colored gelatin particles coated with treponemal antigens.
Note: It is more sensitive in detecting primary syphilis
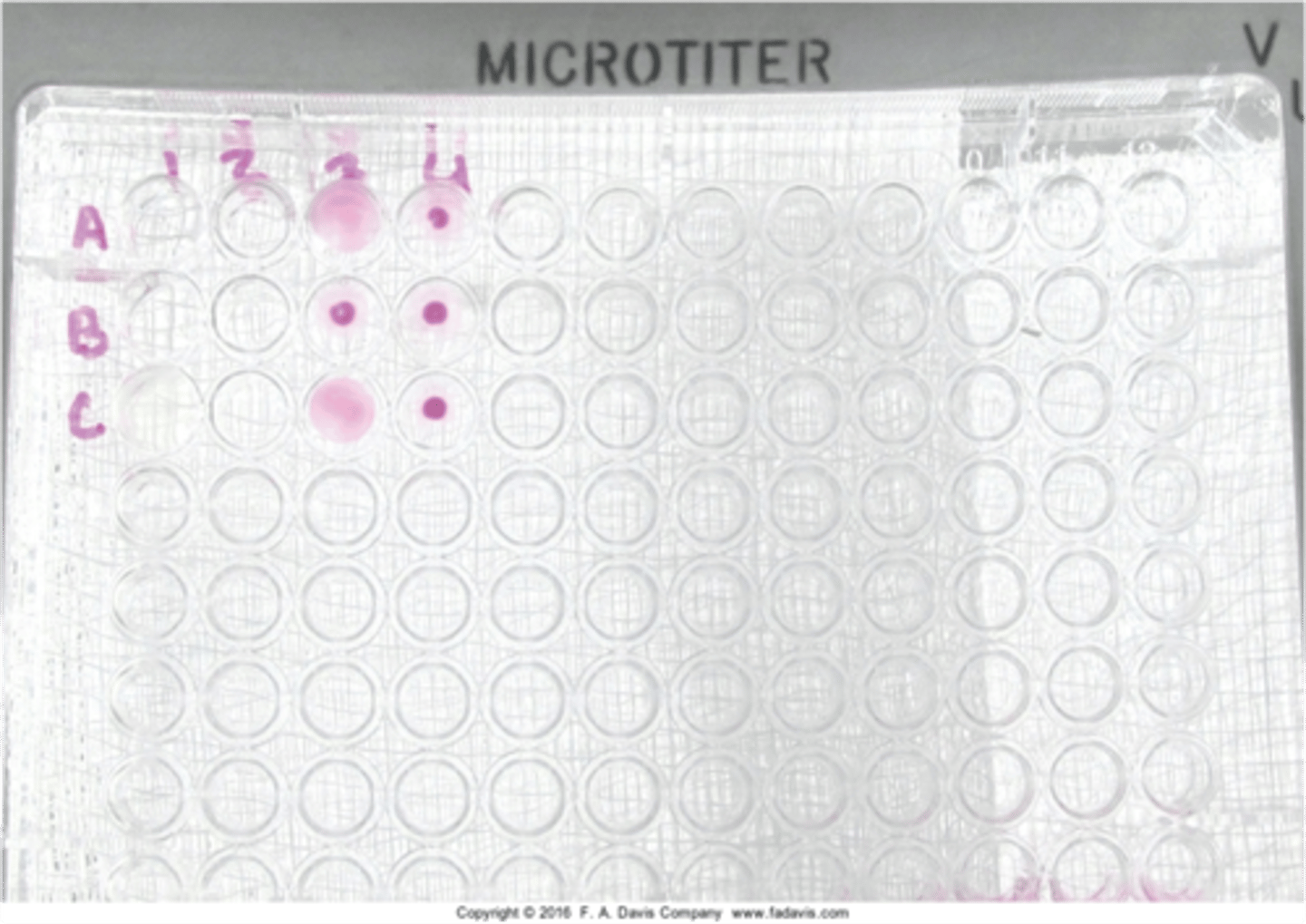
Neurosyphilis
Indication of positive VDRL in CSF
Treponema pallidum-Particle Agglutination
Assay for Syphilis that is excellent in resolving inconclusive FTA-ABS results
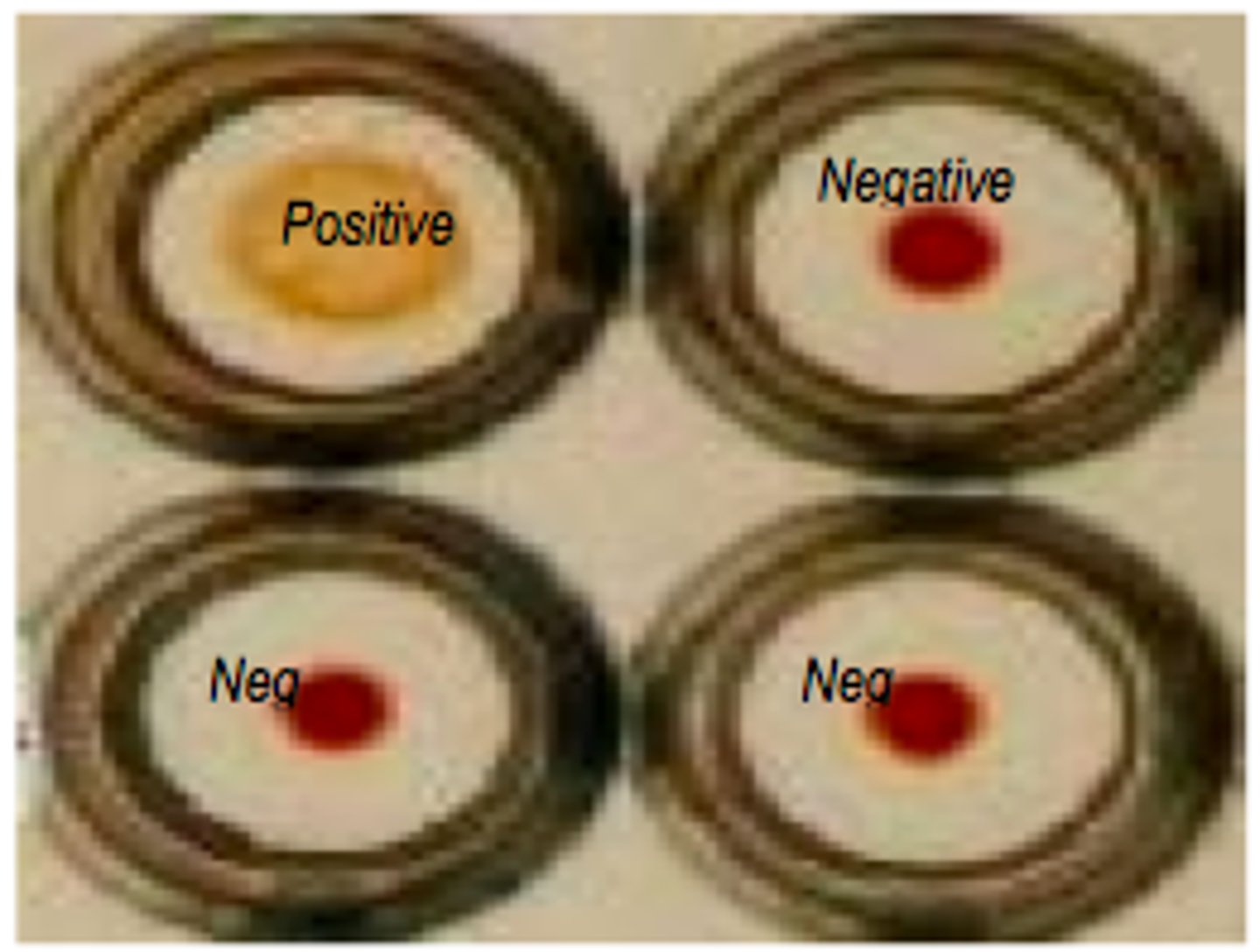
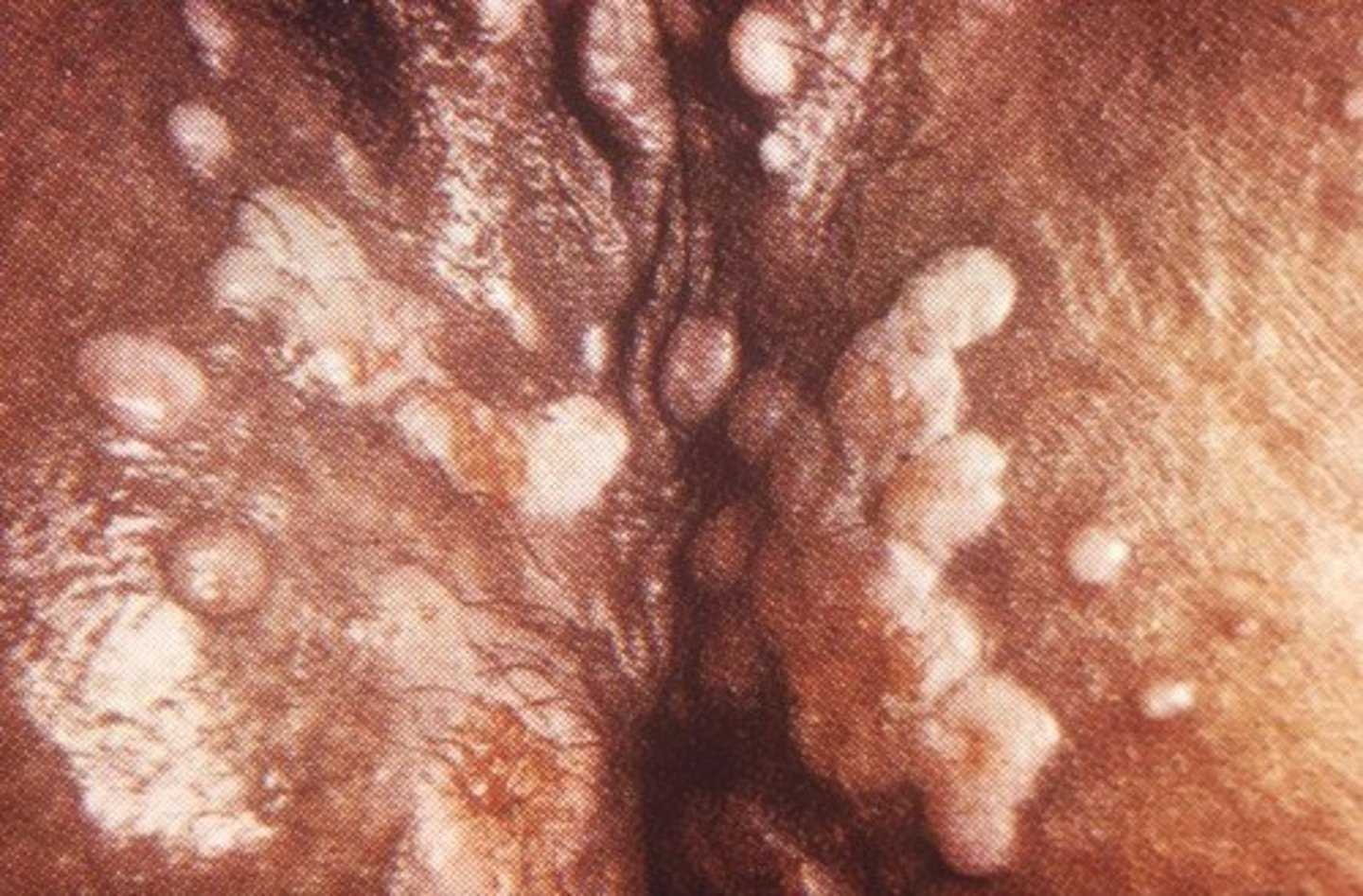
Condyloma lata
These are flat lesions resembling warts that are seen most commonly in moist areas of the body.
It is seen in secondary syphilis
Treponemal Tests
Most sensitive tests for primary syphilis