Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are professional invaders
Pathogens that can infect healthy RT
Which pathogen adhere to normal mucosa
Respiratory virus, s pyogenes, s pneumoniae
Which pathogen interfere with cilia
Pertussis, mycoplasma pneumoniae, s pnuemoniae
Which pathogen have the ability resist destruction in macrophage
Legionella, TB
Which pathogen can damage local tissue
Corynebacterium diphtheriae, S pnuemoniae
What are some mechanisms professional invaders use
Adhere to normal mucosa, interfere with cilia, resist macrophage, damage local tissue
What are secondary invaders
Infect when host defense is impaired
What are some mechanisms used by secondary invaders
Initial infection by other virus, impaired local defense chronic issue, depressed immune response, depressed resistance
Which pathogen infect after other virus
S aureus, s pneumoniae
Which pathogen infect when local defense is impaired
S aureus, pseudomonas
Which pathogen infect with chronic bronchitis, local foreign or tumor
H influenzae, S pneumoniae
Which pathogen infect with depressed immune response
Pneumocystis jirovecii, CMV, MTB
Which pathogen invade with depressed resistance
S pneumoniae, S aureus, H influenzae
What are the causes of otitis and sinusitis
Viral: Mumps and RSV; Bacterial: S pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis
What is otitis externa
Swimmer’s ear; caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa and S aureus
What is acute otitis media
Fluid in ear = glue ear; found in 6-24 month olds
What are the causes of AOM
Bacteria: S pneumoniae, H influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis; Viral: RSV, corona
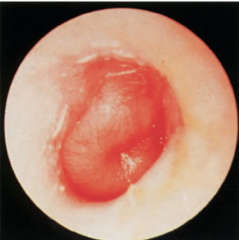
Bulging ear drum; AOM
What is mastoiditis
Found in kids <2 y/o; AOM complication
What is mastoiditis caused by
S pneumoniae, GAS, S aureus
What is sinusitis
Erythematous swollen nasal mucosa and pus; nasal congestion/blockage/discharge
Sinusitis cause
50% from RSV; other 50% from H influenzae, S pneumoniae, Moraxella Catarrhalis
What is parotitis
Caused by mumps
What causes oral cavity infection
Decreased salivary flow increases bacteria in saliva
What is oral candidiasis
Prolonged administration of BSA allows candida to fluorish; vit C def and HIV more susceptible
What are caries
Microorgs that form film (dental plaque); streptococci and anaerobic filamentous bacteria surround teeth
What is periodontal disease
Infection of gums; caused by actinomyces etc
What is rhinitis/acute coryza
Most common URTI; fever, nasal edema and increase in mucous secretion
Pathogenesis of common cold infection
Infection → Viral absorption → Viral replication → Virus shedding → Overgrowth of bacteria
Common pathogens that cause common cold
Rhinovirus, coronavirus, HRSV (adult), Parainfluenza, Influenza A and B
How does rhinovirus and enterovirus cause common cold
Capsid protein bind to ICAM-1 on cell
What is the difference between cold and flu
Cold are milder; flu can lead to severe illness and death
Flu complications
Sinus and ear infection, pneumonia; organ failure, inflammation of major organs
What is pharyngitis
Appearance of erythema and swelling of tissue; 10% caused by GAS
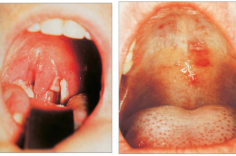
Pharyngitis
What is EBV
Saliva transmission, causes mono; latent in B lymphocyte
EBV diag
IgM Ab to erythrocyte (cold agglutinin); VCA, atypical lymphocytes
Mono diag sign
Mono characteristic = palatal petechiae in mouth
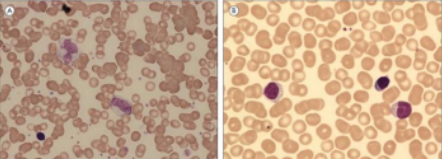
Atypical lymphocytes
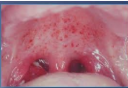
Oral petechiae
What cancers are associated with EBV
Burkitt lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, B cell lymphoma
What is CMV
transmit by saliva and sex; cause mono; similar to EBV; cause intellectual disability
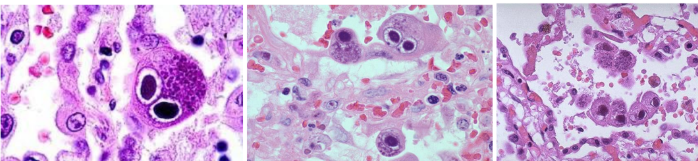
Owl’s eyes
Presence of owl’s eyes in BAL indicates what
CMV pneumonitis
What is bacterial pharyngitis
Caused by GAS, sometimes corynebacterium diphtheriae, N. gonorrhoeae if there was sexual activity
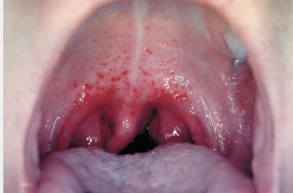
Bacterial pharyngitis
What is streptococcal pharyngitis
10% caused by GAS, transmit by saliva and direct skin contact
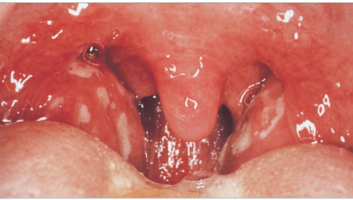
Streptococcal pharyngitis
What is diphtheria
Greyish/yellowish false membrane; highly infectious, NP diphtheria is most severe
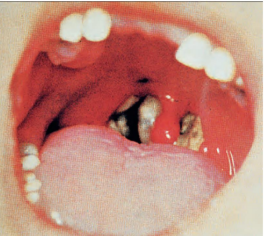
Pharyngeal diphtheria
What are the complication of diphtheria
Can cause fatal heart failure and polyneuritis
What is whooping cough
Caused by bordetella pertussis; paroxysm of coughing (100 day cough)
What is acute epiglottitis
Caused by Hib; emergency that NEEDS intubation and treatment with antibiotics
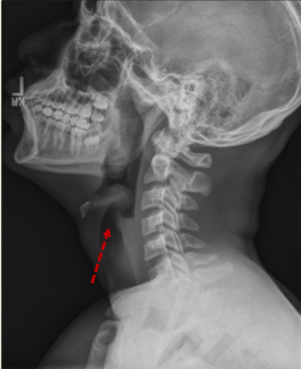
Acute epiglottitis thumb sign
What is laryngitis and tracheitis
Parainfluenza, C diphtheriae; easily obstructed in children