earth and space science mid term review 2026
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
when was the universe made
13 billion years ago
red shift
moves away
blue shift
coming closer
is the earth expanding? how?
yes because cosmic background show it
nuclear fusion
2 hydrogen make helium then turn into energy
what determines the way a star dies
mass
dark matter
pulls galaxies together (25%)
dark energy
pushes the universe apart (mostly made up of the universe; around 68%)
where in the sun does nuclear fusion occur
the core
conduction
convection
radiation
solids
liquids
how sunlight gets to earth
how are sunspots made
magnetic field lines pushes down/holds the heat creating sun spots
solar flares
occurs when sunspots energy gets too much then explodes
consequences of solar flares
fry communications, fry astronauts, and cause auroras in the sky
when was solar system made
4.6 billion years ago
how was the sun made
gas contracts then spins and gets hotter
accretion
when rocks meld together and create planets
kepler’s laws
further planet from the sun = longer year
eccentrecity
sun is at one foci
1= flat 0=circular
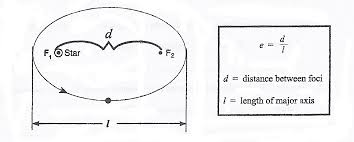
aphelion
furthest point away from the sun
perihelion
closest point from the sun
how was the moon made
piece of the earth came off and created the moon.
how many days does the sun to fully orbit earth
27.3 days
how many days does it take to go from one moon phase to another (full moon to next full moon)
29.5 days
why do we see the same side of the moon
revolution is the same time as rotation
why do we see phases of the moon
the moon revolves around the earth
solar eclipse (arrangement)
sun - moon - earth
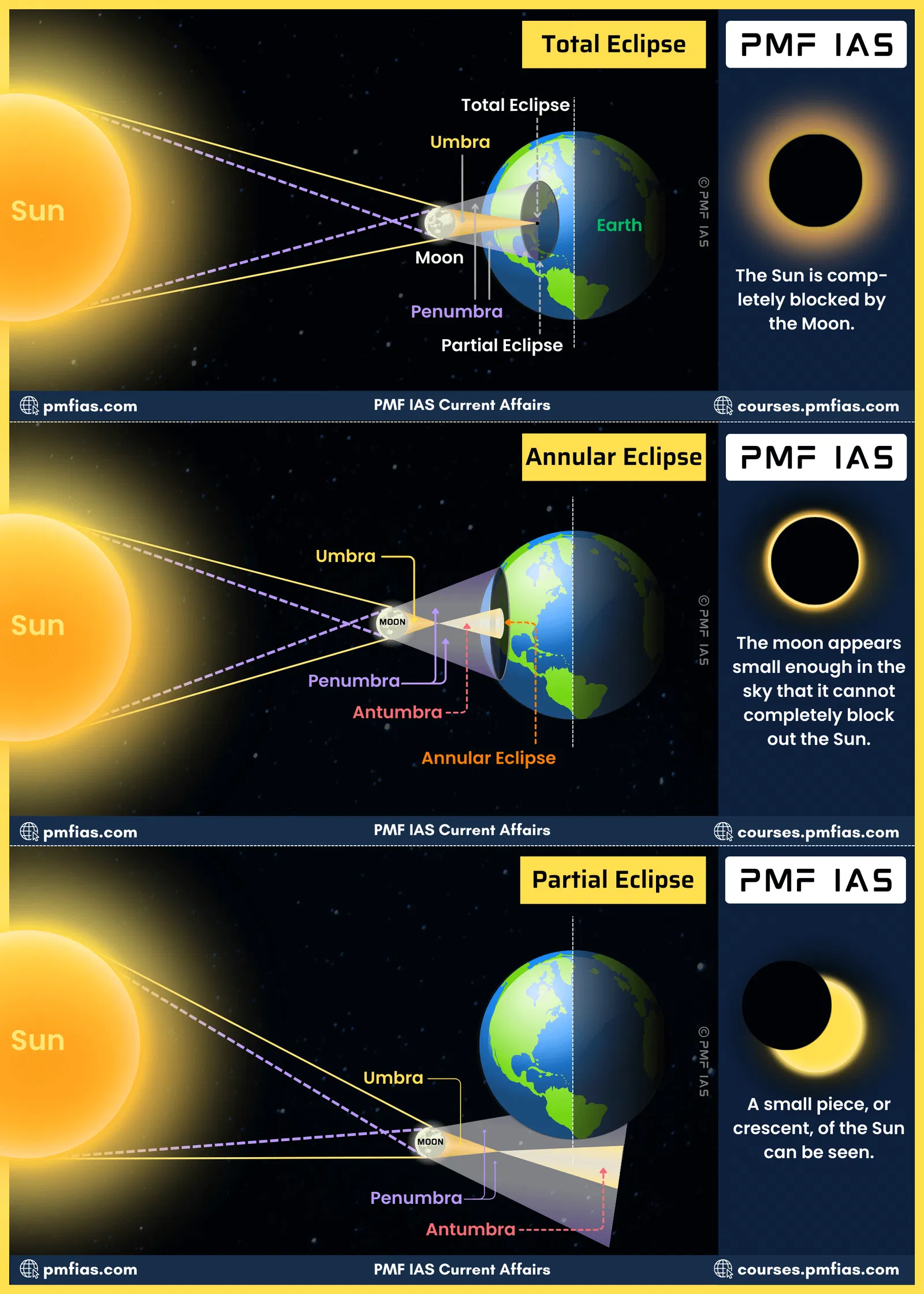
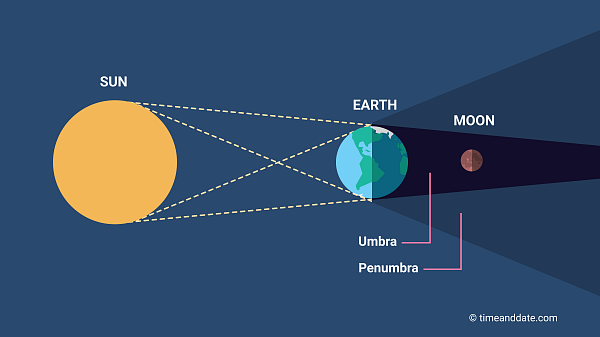
lunar eclipse (arrangement)
sun - earth - moon
whats a neap tide
90 degree angle
whats a spring tide
big difference of tides
cyclic changes
predictable changes
why do we have seasons
all because of the tilt of the earth and revolution
angle of insolation
angle
higher the sun = hotter
lower the sun = colder
duration of insolation
how many hours of sunlight and night time
tropic of cancer
june 21
sun above their heads
90 degrees = no shadow
tropic of capricorn
december 21
lowest point of the sun
equinox
equal 6 hour day light and 6 hour night
what color surface absorbs the most amount of heat
dark surfaces
what does the Foucault pendulum prove
that the earth spins on its axis
what is the coriolis effect
moving objects move because of the earth’s rotation on its axis
how many revolution degrees are there per day
1 degree
how much speed (in degrees) does the earth rotate per hour
15 degrees
why do we have seasons
because of the tilt of the earth
why do we see different constellations
because the earth is revolving around the sun
rocky planets
small dense planets (terrestrial planets)
composed of rocks and metals
surfaces with craters, volcanoes, and mountains
example: mercury, Venus, earth, mars
gas giants
massive planets mostly composed of hydrogen and helium
lacking solid surfaces
example: Jupiter, saturn
icy planets
surfaces of ice
large rocky/ice core
example: uranus and neptune
how long can carbon date things
recent objects
what does p waves go through
everything
(faster)
what does s waves go through
solids only
divergent boundary

convergent boundary
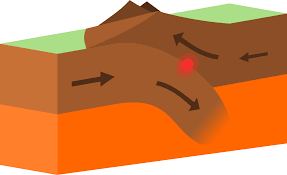
faults