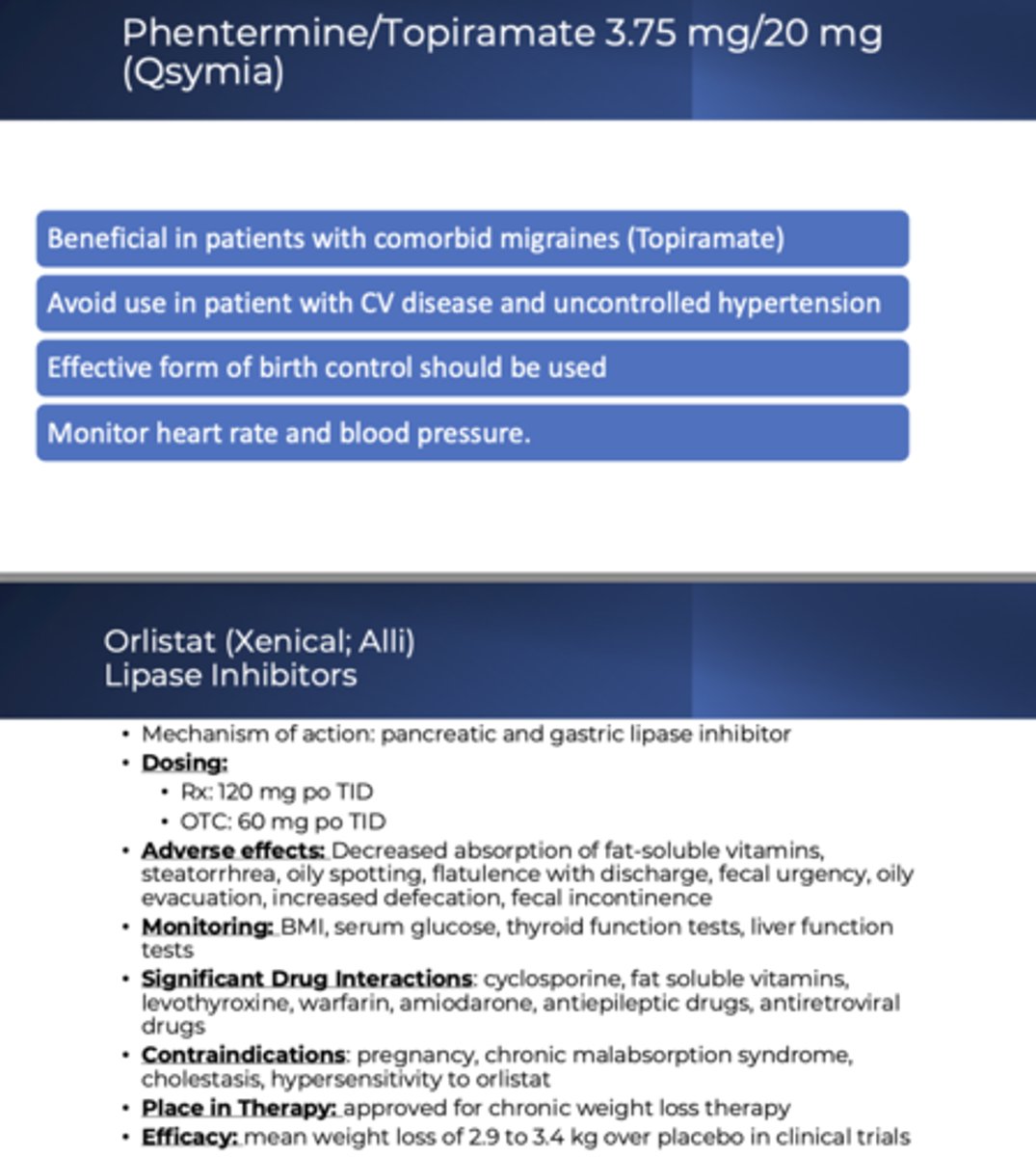
Obesity Therapeutics (Dr.Ezzo)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Background info.
Obesity Classifications
Class 1: BMI 30 to < 35
Class 2: BMI 35 to <40
Class 3: BMI ≥ 40
Risk factors of Obesity
- Genetics (leptin mutation)
- Medications
- Environmental
- Medical Conditions (Hypothyroidism, depression)
- Socioeconomic factors
- Age
- Lifestyle factors

List the medications that cause Weight gain
- Antidepressants
- Birth control
- Beta blockers
- Glucocorticoids
- Sulfonylurea
Non-pharmacological treatment
List Non-pharmacological treatment
- Nutrition & Diet
- Physical activity
- Behavioral modification
- Treat underlying condition
- Survey
Primary treatment for Children and Geriatric:
Lifestyle interventions
List Lifestyle interventions for Obesity (2)
- Calorie deficit of 500-750 kcal/day
- 150 minutes of physical activity
Explain Physical activity
- 150 minute of physical activity
- Aerobic exercise 3-5 days a week
- Resistance training 2-3 days a week
Pharmacological Therapy
When should you initiate pharmacotherapy for obesity (2)
- BMI ≥ 30
- BMI ≥ 27 + weight related complications
[weight related complications = lifestyle intervention did not work]
1st in line pharmacotherapy for Obesity
- Semaglutide
- Tirzepatide
- Liraglutide
[^GLP/GLP-1/GIP agonist^]
Monitoring of GLP/GLP-1/GIP agonist
BP
GLP/GLP-1/GIP agonist can cause a increase of _____
hypoglycemia in DM pts.
Which patient specific population should use GLP/GLP-1/GIP agonis with caution:
• Bulimia nervosa - medications are not to be used
• Binge eating disorder - monitor for worsening of behaviors
Common side effects of GLP/GLP-1/GIP agonist
N/V/D/C
Treatment of N/V in patients due taking GLP-1/GIP agonist
Short term antiemetics (Ondansetron)
Treatment of Dyspepsia in patients taking GLP-1/GIP agonist
PPI or H2 blockers
Treatment of Constipation in patients taking GLP-1/GIP agonist
- Increase fiber intake & hydration
- Bulk-forming laxative or Stool softeners or Osmotic agents