1-23. Test 2
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1. One feature of the GATT and now the WTO is that all member nations get the same treatment from their trading partners in terms of trade rules and restrictions. This provision is
the most favored nation clause
The escape clause in the U.S. trade law
permits the U.S. gov't to impose trade barriers if fairly traded imports are the cause of significant injury to a U.S industry and its workers
3. Section 201 of the Trade Act of 1974 allows tariffs to be applied when the U.S. International Trade Commission determines that:
a surge in imports threatens serious injury to a U.S. industry.
4. When President Trump imposed import tariffs on foreign goods, especially for products made in China, those foreign exporters:
imposed retaliatory tariffs on U.S. exports.
5. Foreign supply curves facing a large country differ from those facing a small country. Large countries face _____________ foreign supply curves, and small countries face ______________ foreign supply curves.
upward-sloping; perfectly price-elastic
6. When a large country imposes a tariff, the burden is often shared by:
domestic consumers and foreign producers
7. The United States applies a 25% tariff on imported pickup trucks (mainly from Japan). If the United States is considered a "large" country, then the U.S. price of imported Japanese pickup trucks will increase by:
less than 25%.
8. Suppose that the United States is a large country. In fall 2009, the United States imposed tariffs on tires imported from China. The deadweight losses of these tariffs were larger than the terms-of-trade gains to the U.S. economy. Who was better off and who was worse off as a result of these tariffs?
U.S. tire workers were better off; U.S. consumers and Chinese tire producers were worse off.
9. Suppose that: (1) the United States has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals; (2) Costa Rica has a comparative advantage in producing sugar; and (3) the United States imposes a quota on its imports of Costa Rican sugar. Now suppose that the United States eliminates its import quotas on Costa Rican sugar. Which of the following is MOST likely to occur for the United States?
Consumer surplus for American consumers of sugar products will rise.
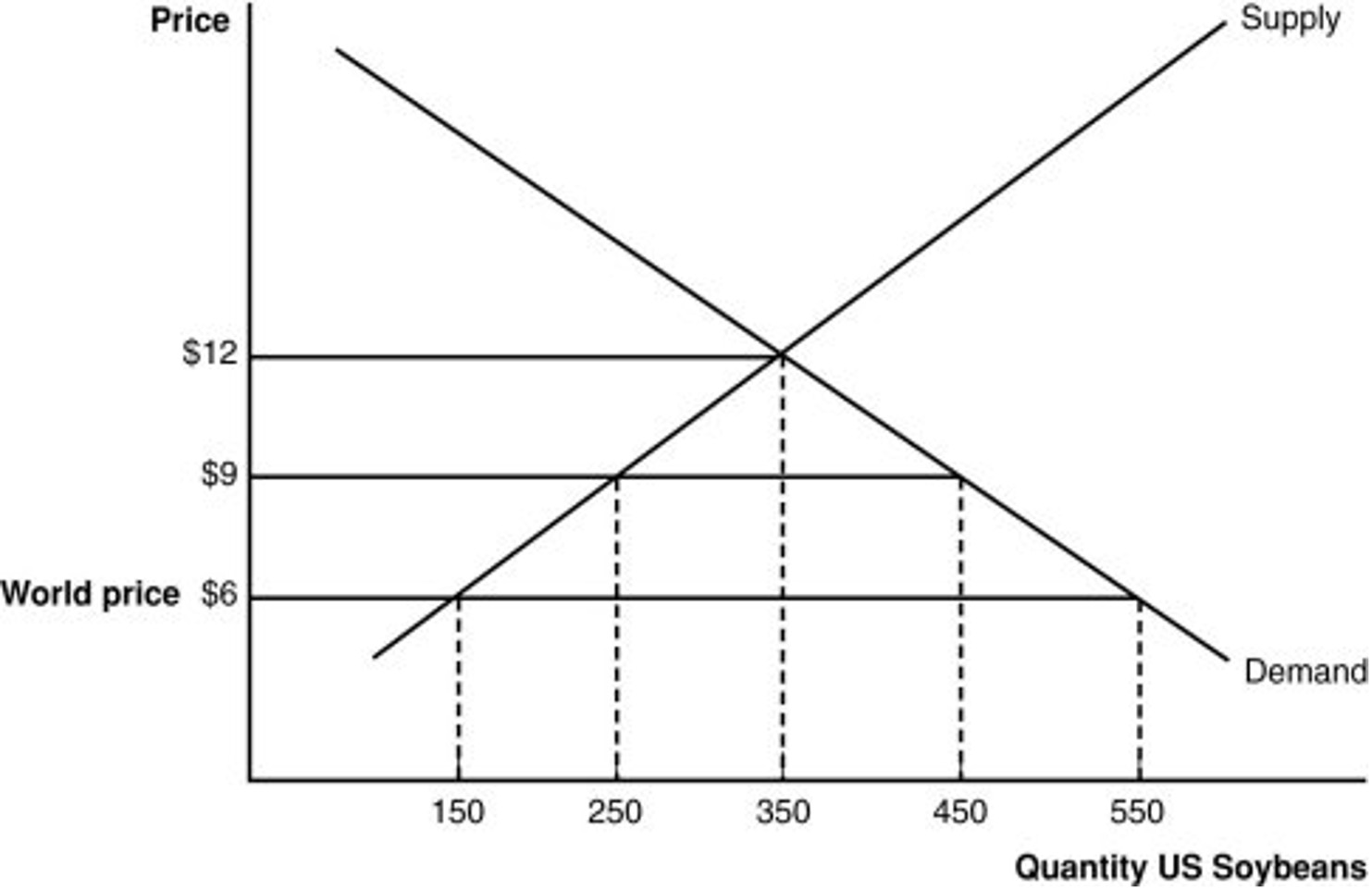
10. A quota generates a protective effect just like a tariff. Using the graph, calculate the "equivalent import tariff" that would produce the same result as an import quota of 200 units.
3
Because there is no government revenue as a result of the quota, one of the parties in the trade transaction makes a "return" equal to lost government revenue (P - MC) · Qimports. This is called:
a quota rent.
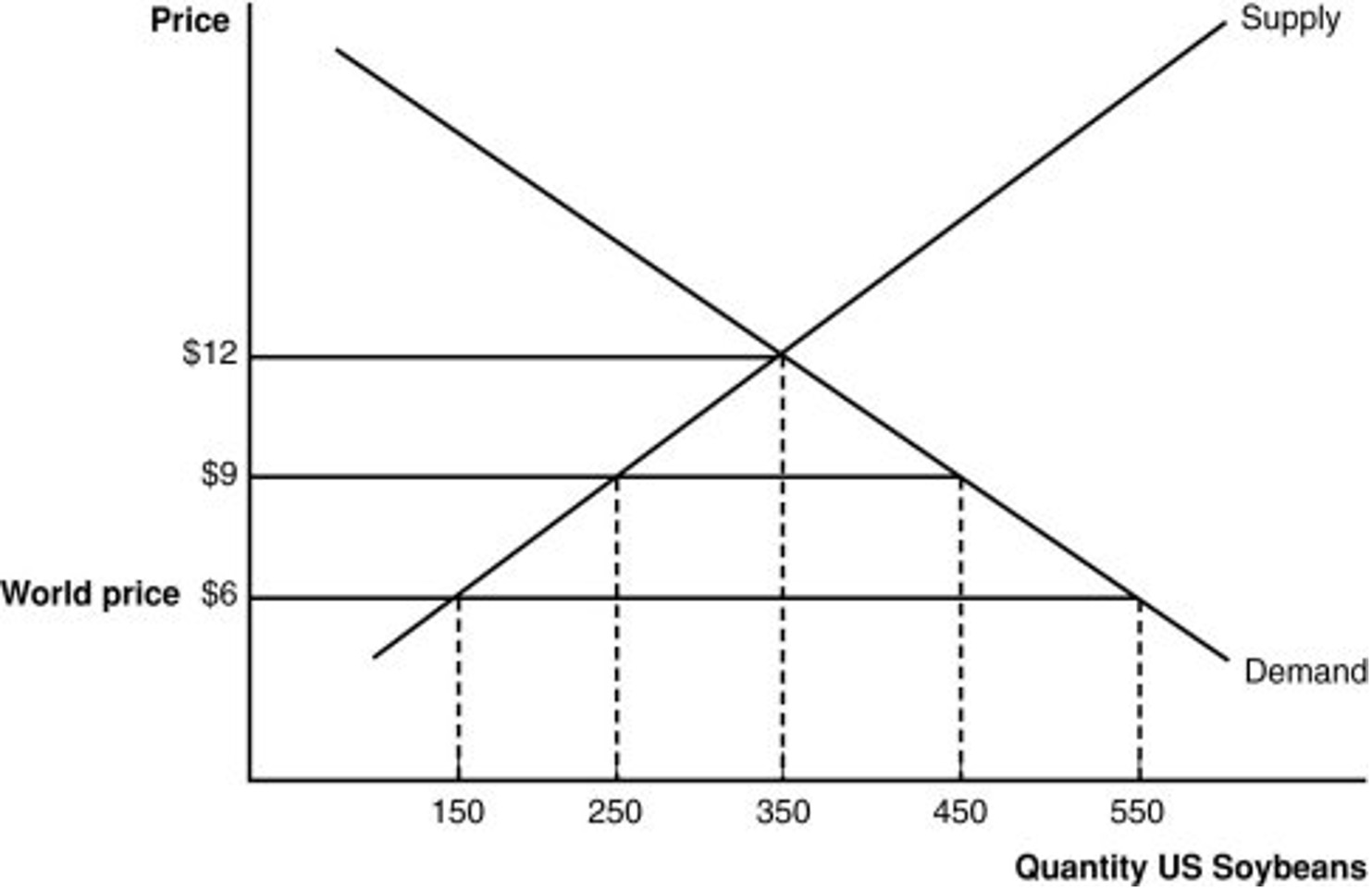
12. See figure above.
When an import quota is employed, the quota rents are calculated to be:
$600
13. Who collects quota rents when the government gives quota licenses to domestic firms?
domestic producers
14. Rent-seeking activities are:
bribery and lobbying activities to obtain quota licenses.
15. If rent seeking occurs, then a country's welfare losses from quotas will:
increase.
16. Suppose a nation agrees to limit its own exports by imposing quotas on its own firms in order to keep their revenues high, keep from breaking WTO rules, and pacify protectionist interests in the import nation. Which of the following terms describes this practice?
voluntary export restraints
17. What is the main difference between a quota and a voluntary export restraint?
The importing country administers a quota; the exporting country administers a voluntary export restraint.
18. Who captured the quota rents of the 1980s U.S-Japanese voluntary export agreement for automobiles?
Japanese auto producers
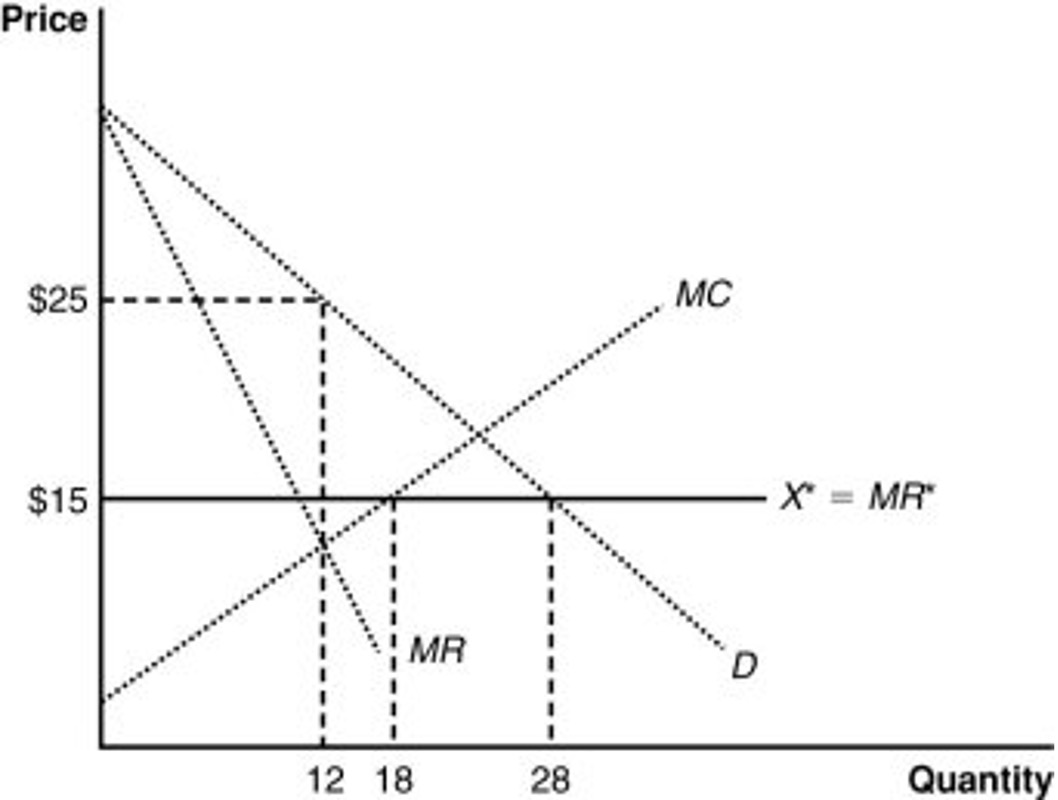
19. If the world price is $15, the domestic monopolist will produce ______ and the country will import ________.
12; 16
20. Because the small-country monopolist loses the ability to control the market price, consumers enjoy more quantity, competitive prices, and:
higher consumer surplus because the monopolist's producer surplus is reduced.
21. What is the outcome when the home nation imposes a tariff on a product currently produced by a home firm monopoly?
The home firm will be able to charge a higher price (world price + tariff), but it will become a price taker, just like a competitive firm.
22. For a home monopolist, a quota allows the firm to increase the price by _______________ it could with an equivalent tariff.
a higher amount than
23. Which of the following forms of protection will a home monopolist prefer?
a large quota