Diversity Midterm 2: Key Terms & Definitions in Sports
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Movement of xylem sap
goes against gravity
transpiration pull
force of pulling from the xylem tissue
Transiration-Cohesion-Tension-Theory
Evaporation from mesophyll cells in the leaves produces a negative water potential gradient that causes water and minerals to move upwards from the roots through the xylem
As leaf dries out...
film of water is thinner
autotrophs
draw simple molecules from environment for nourishment
photosynthesis
form carbs, respiration, cellulose
herbaceous plants
80-85% water
Dry weight of plants
95% carbs
Mineral deficiency symptoms
-little nutrient element
-mesophyll is yellow between veins
Parasitism in plants
roots of parasite plant grow into host plant, takes nutrients
most limiting mineral element
Nitrogen (78% in atmosphere), not usable by plants but useful in soil (be aware of nitrogen cycle)
Environment N adaptation
Bogs, acid soil (not much N), carnivorous plants
N adaptations
-symbiosis w N fixing bacteria
-specific angiosperms (legumes)
-Rhizobium bacteria
-convert N to ammonia
-plants give carbs to Rhizobium
Nodulation
is a symbiotic interaction between soil bacteria and plant hosts, most notably between rhizobia and legumes. This interaction is important for plant hosts, since it enables them to access atmospheric nitrogen made available by the bacteria.
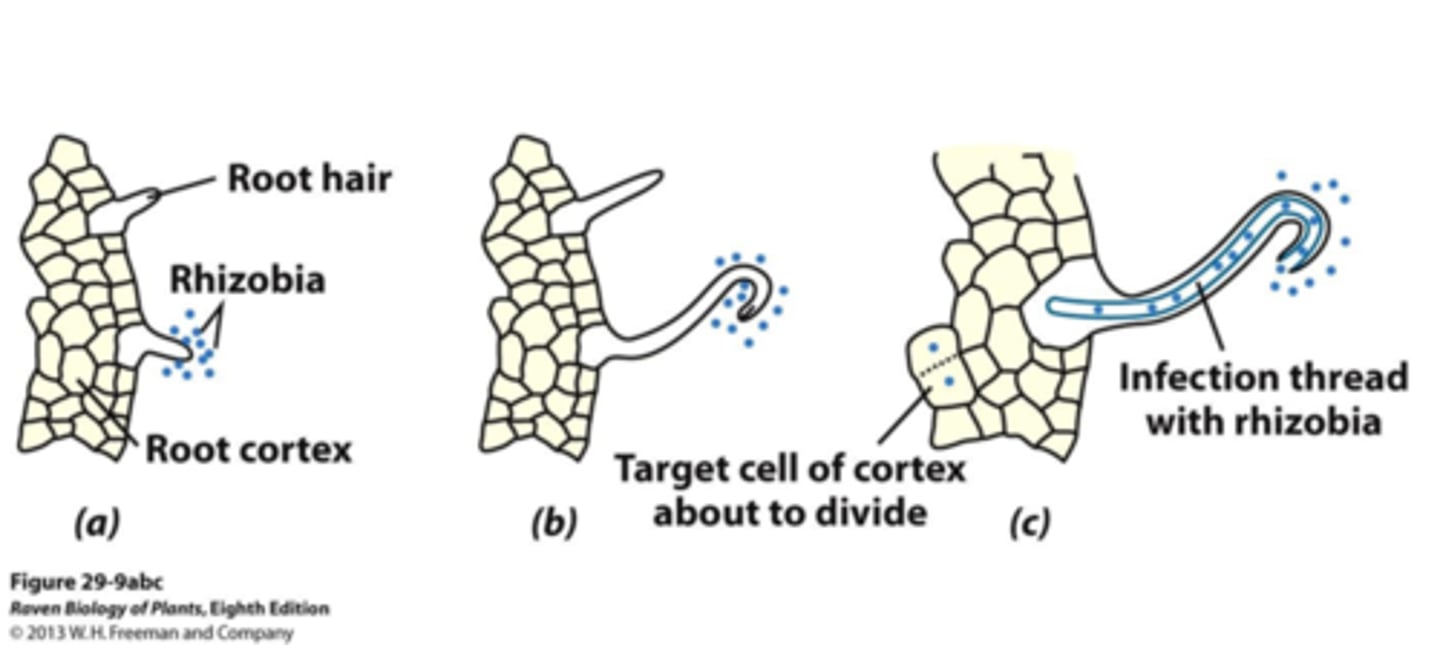
Rhizobium bacteria
bacterium found in soil that helps in fixing nitrogen in leguminous plants
Rubisco
enzyme that converts inorganic carbon dioxide molecules into organic molecules during the final step of the Calvin cycle (large subunit in plants)
male gametophyte (sperm)
pollen
female gametophyte (egg)
embryo sac
sepals (flower)
leaflike, protects flower bud
petals (flower)
attract pollinators
stamen (flower)
produces pollen
pistil (flower)
bears ovules --> ovules produce embryo sac
whorls (flower)
the formation floral organs are arranged in
angiosperm life cycle (step 1)
meiosis
angiosperm life cycle (step 2)
gametophyte development
angiosperm life cycle (step 3)
pollination
angiosperm life cycle (step 4)
fertilization
angiosperm life cycle (step 5)
embryo development
angiosperm life cycle (step 6)
seed formation
microspores
in anthers, develop into pollen
megaspores
in ovule, 3/4 abort, the surviving develop into embryo sac
pollination
transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of pistil
abiotic pollination
nontargeted - needs lots of pollen: wind, water, etc.
biotic pollination
targeted - less pollen, but needs pollinator: birds, insects, bats, etc.
outcrossing
self-pollinating plant (hermaphrodites) --> inbreeding (mutations)
monoecy
unisexual flower, plants that are hermaphrodites (corn)
dioecy
separate male and female plants (asparagus)
self-incompatibility
if too similar, fertilization is blocked
double fertilization
2 sperms in each pollen, only in angiosperms
2 sperm in each pollen
1 fuses w egg = zygote, 1 fuses w central cell = endosperm
embryogenesis
the formation and development of an embryo
ovule
seed, contains embryo and endosperm, seed coat covers ovule
ovary
fruit, "a ripened, mature ovary"
fruit development
promotes dispersal of seeds in nature, fleshy fruits = animal eats and moves seed, dry fruits = mechanical dispersal
dormancy
embryp becomes mature, loses water, slow metabolism