Cardiac and Peripheral Vascular Examination Techniques
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Cardiac Auscultation
Listening to heart sounds using a stethoscope.

Point of Maximum Impulse
Location where heart's contraction is felt strongest.
Peripheral Vascular Exam
Assessment of blood circulation in extremities.
Capillary Refill
Time taken for color to return after pressure.
Peripheral Edema
Swelling due to fluid accumulation in tissues.
Deoxygenated Blood
Blood lacking oxygen, flows to right atrium.
Oxygenated Blood
Blood rich in oxygen, flows from left ventricle.
S1 Heart Sound
First heart sound; indicates ventricular contraction.
S2 Heart Sound
Second heart sound; indicates ventricular filling.
S3 Heart Sound
Rapid filling sound in a not empty ventricle.
S4 Heart Sound
Sound from a stiff ventricle being overfilled.
SA Node
Primary pacemaker initiating heart's electrical impulse.
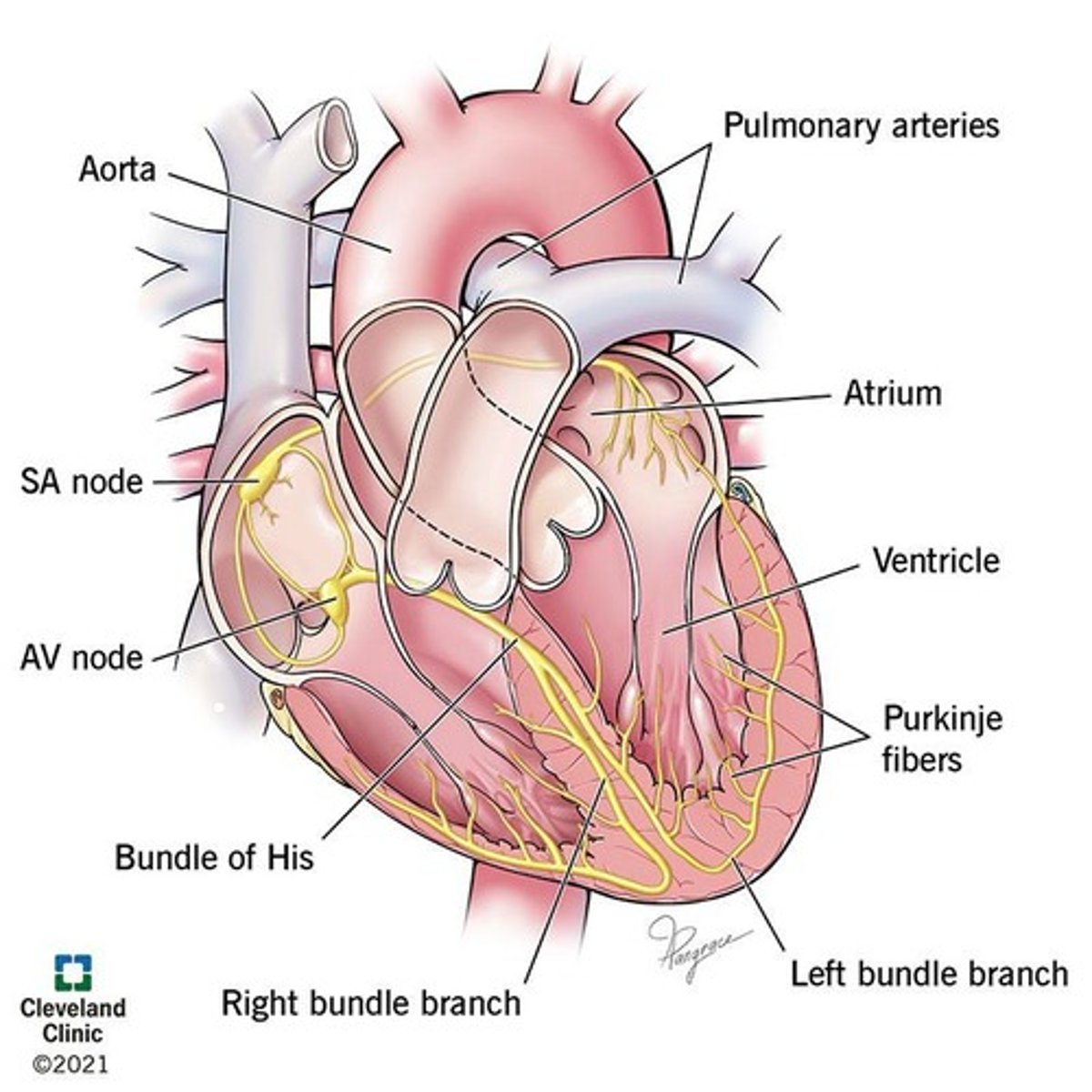
AV Node
Delays impulse before it reaches ventricles.
Bundle of His
Conducts impulses from AV node to ventricles.
Purkinje Fibers
Distributes electrical impulses throughout ventricles.
History of Present Illness (HPI)
Detailed account of patient's current health issue.
Myocardial Infarction
Heart attack caused by blocked blood flow.
Syncope
Temporary loss of consciousness; fainting.
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath; difficulty breathing.
Palpitations
Uncomfortable awareness of heart beating irregularly.
Clubbing
Bulbous swelling of nailbed; indicates chronic hypoxemia.
Bruit
Abnormal sound indicating turbulent blood flow.
Carotid Pulse Palpation
Technique to assess blood flow in carotid artery.
Diaphoresis
Excessive sweating, often linked to distress.
Edema Assessment
Evaluation of swelling in extremities for fluid retention.
Turbulent flow
Sound in blood vessels, like a soft whoosh.
Carotid
Major artery in the neck for blood flow.
Femoral
Artery supplying blood to the thigh and leg.
Aorta
Largest artery, carries blood from the heart.
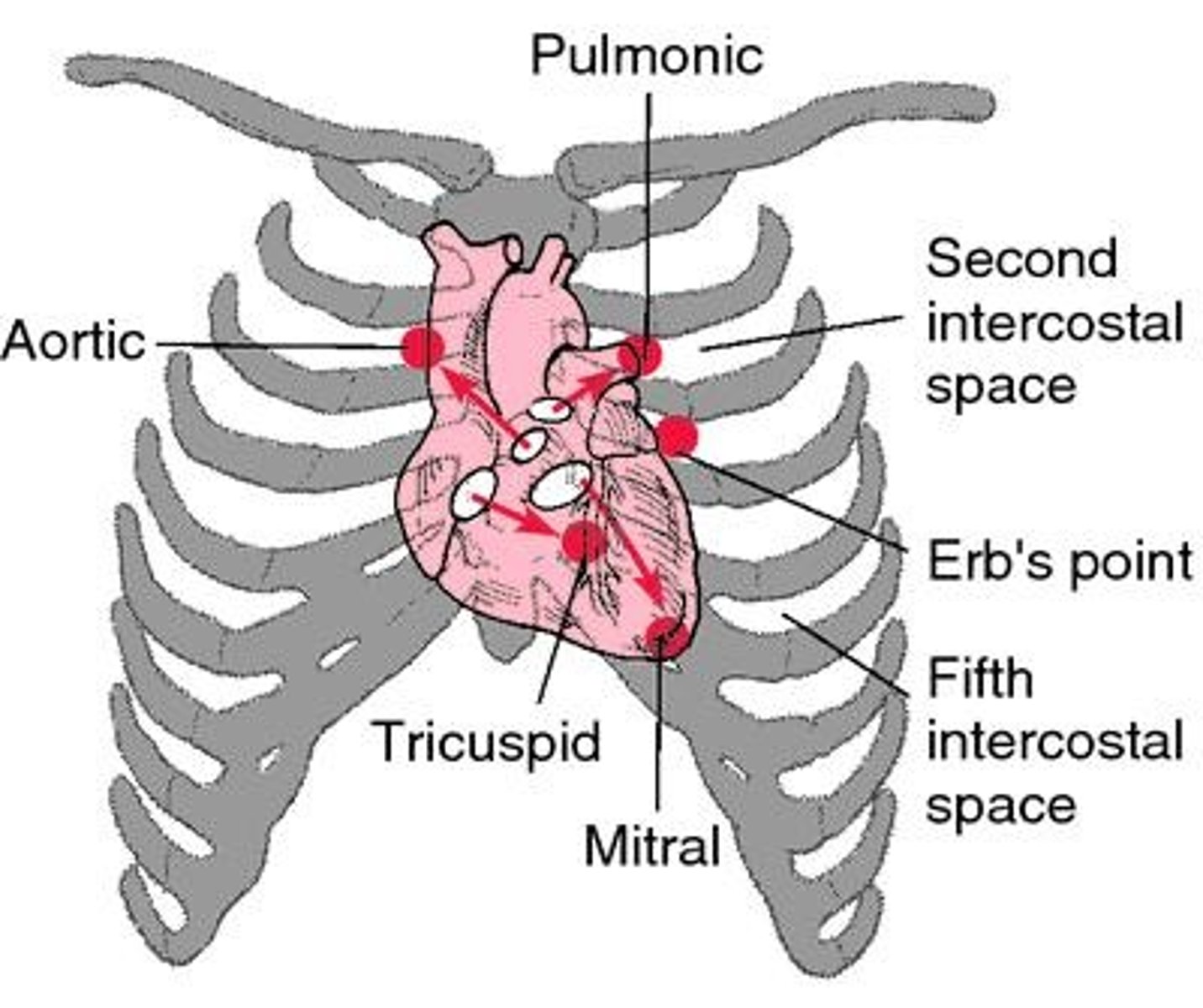
Aortic position
2nd right intercostal space (ICS) for auscultation.
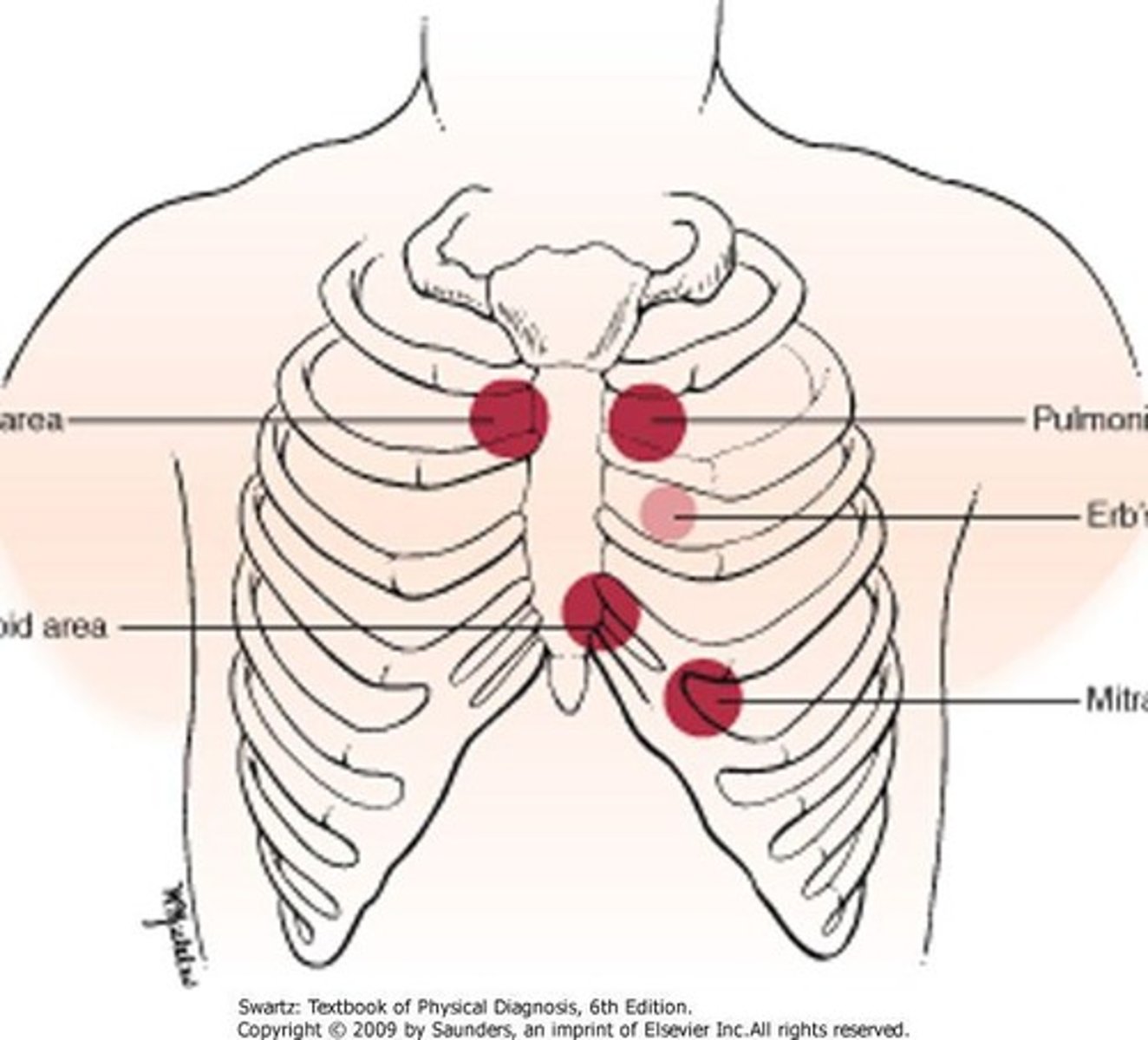
Pulmonic position
2nd left intercostal space (ICS) for auscultation.
Tricuspid position
4th or 5th left intercostal space (ICS) for auscultation.
Mitral position
5th ICS, midclavicular line for auscultation.
S1 sound
Closure of mitral and tricuspid valves; 'lub'.
S2 sound
Closure of aortic and pulmonic valves; 'dub'.
Split S2
Delay in P2 during inspiration; normal variant.
Gallops
Extra heart sounds S3 and S4 indicating issues.
Physiologic murmur
Normal flow murmur due to increased blood velocity.
Pathologic murmur
Turbulence from obstructed or leaky heart valves.
Systolic murmurs
Most common murmurs, occur with pulse.
Diastolic murmurs
Rare murmurs, always pathologic.
Point of Maximal Impulse (PMI)
Location where heart strikes chest wall.
PMI diameter
Normal size is less than 2.5 cm.
Peripheral pulses grading
0 to 4 scale for pulse strength.
Peripheral edema
Fluid imbalance causing swelling, often in legs.
Capillary refill
Time for color to return after blanching.
Normal capillary refill
Less than 3 seconds to return to normal.
Common abnormal findings
Signs of vascular disease in patients.