Economic History - Final
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Lecture 5: Mass Migration
What are 2 key facts regarding mass migration between 1820s-1920s?

How did the social characteristics of migrants change throughout the period?

How would you describe the distribution of migration during this period?
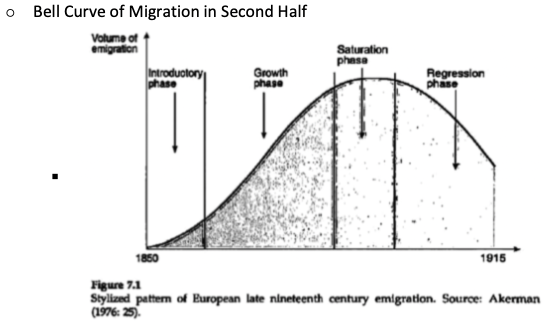
What were the push and pull factors?

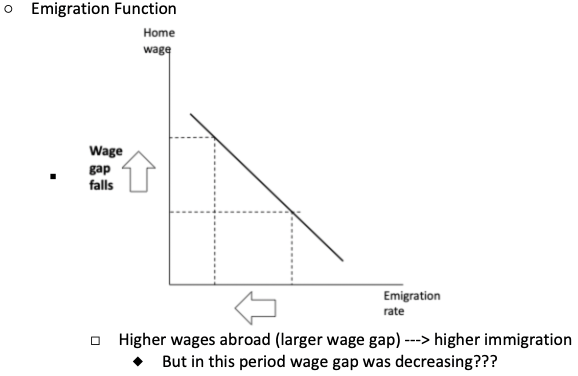
What is the basic emigration function? What is wrong with it?
What are the other 5 major factors that needed to be accounted for?

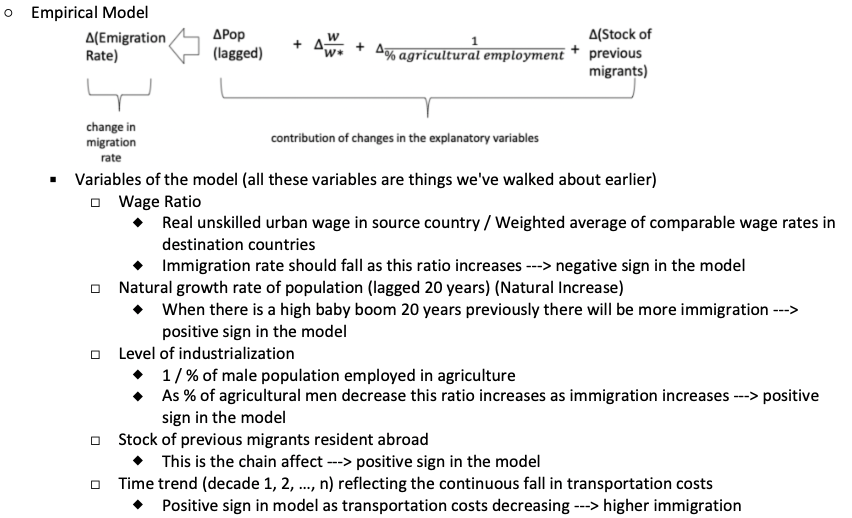
What is the empirical model and its 5 variables?
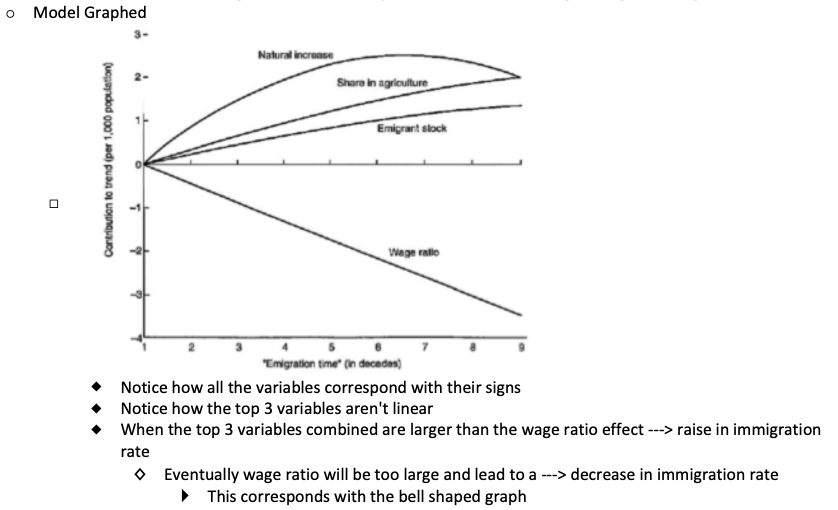
How does this model look like when it is graphed?
Turning back to the emigration function, how do you bring this all together?
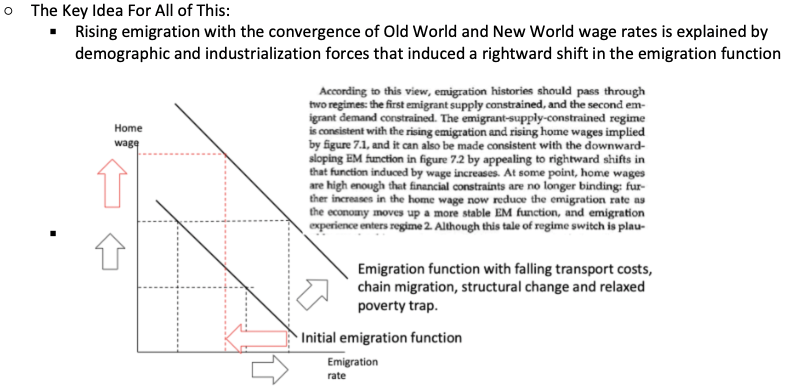
What made the Latins different?

What was the impact of migration on the labor markets at home? Short and Long-term.

How did immigrants face assimilation in destination countries?

How did destination countries fair in terms of absorption of immigrants?

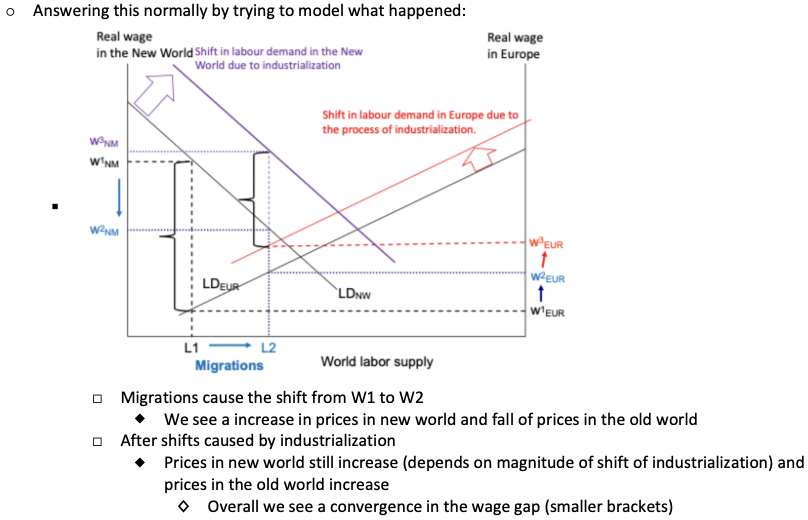
Describe the wage convergence model.
Describe the counter factual convergence model.
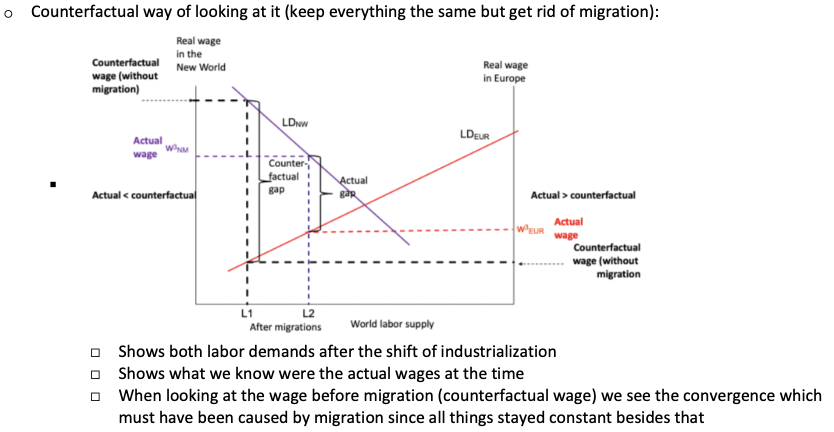
What is the main point on convergence?

Lecture 6: A World on Gold
What were the 3 key elements of pre-19th century money?
What was the dominate metal used for coinage until the 19th century?

What was a major change in economic policy that led to changes in monetary standards?

What were the different monetary standards in key countries before the 1860s?

Why was bimetallism controversial? How did this lead to the gold standard?
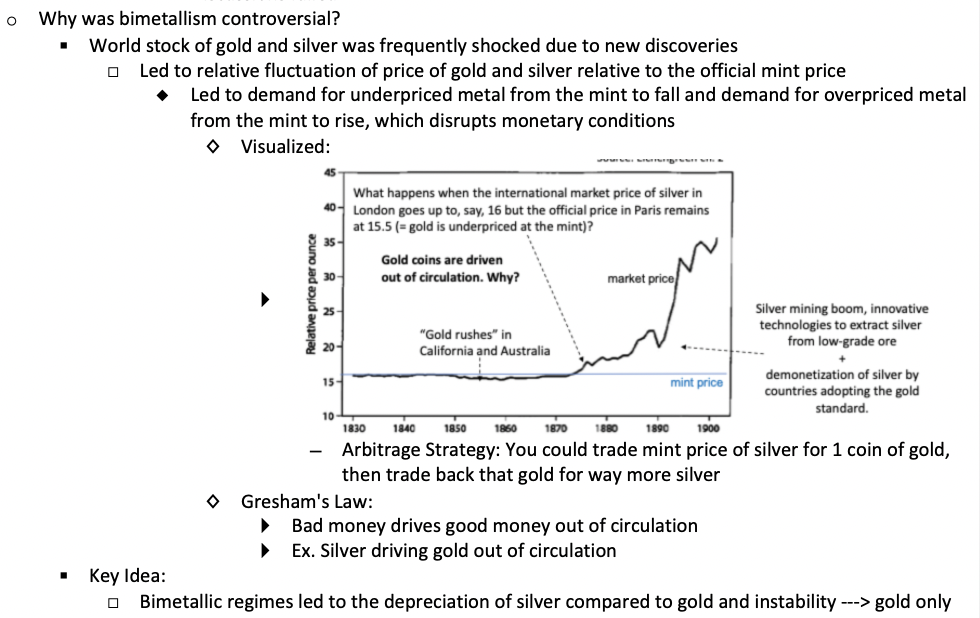
Why did most countries switch to the Gold Standard in the 1870s?

What are the basics of gold parity established by central banks?

What are the basics of banknotes and the banks that could issue them?

What were the 3 ways that the central banks could circulate currency, regulated by law?
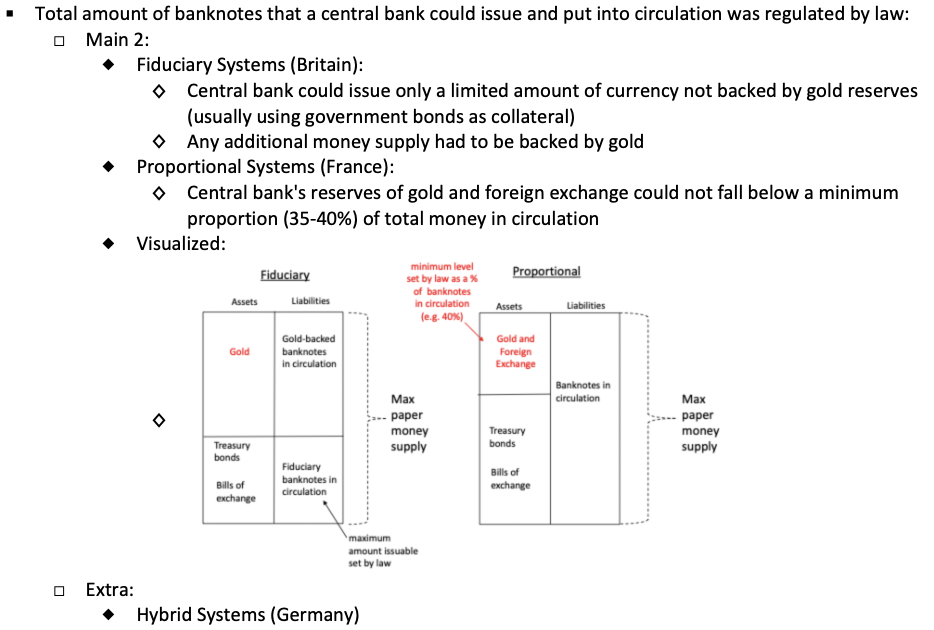
What is the key idea behind these 3 systems?

What was a solution to the acceleration of economic growth without an equal acceleration of gold supply?

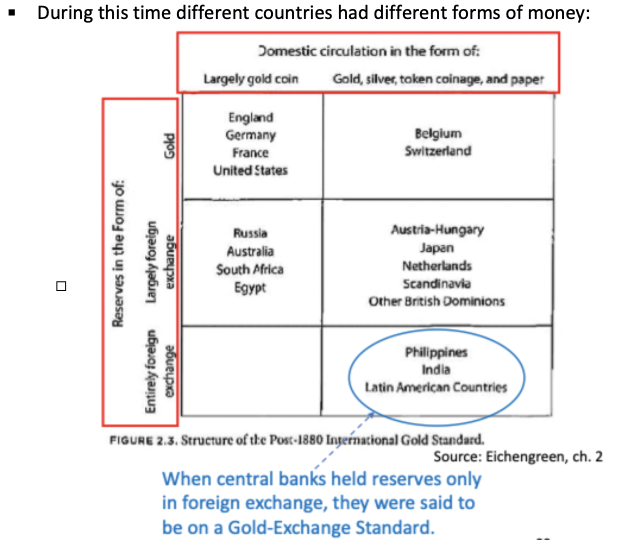
What were the different forms of money in different countries, and how it was backed by different countries?
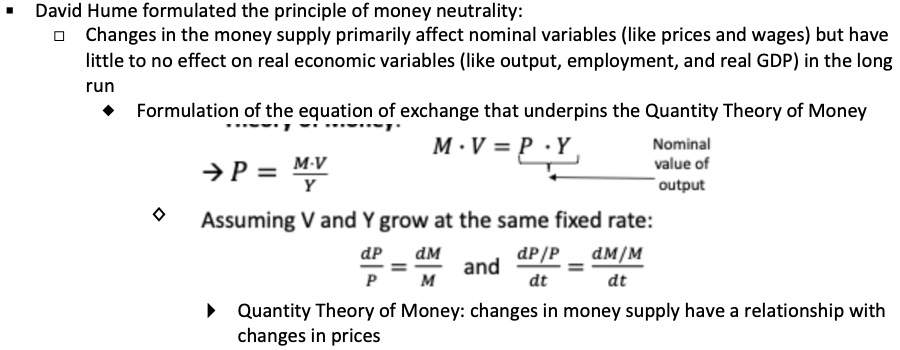
What were David Hume's findings in the principle of money neutrality and the Quantity Theory of Money?
Why is it a problem if a central bank follows an excessively lose monetary policy and how does the gold standard solve this?

What was the reality of monetary rules during this time?

What does the Quantity Theory of Money tell us about deflation during this period?

What was the traditional idea of external imbalances in a gold standard world system?

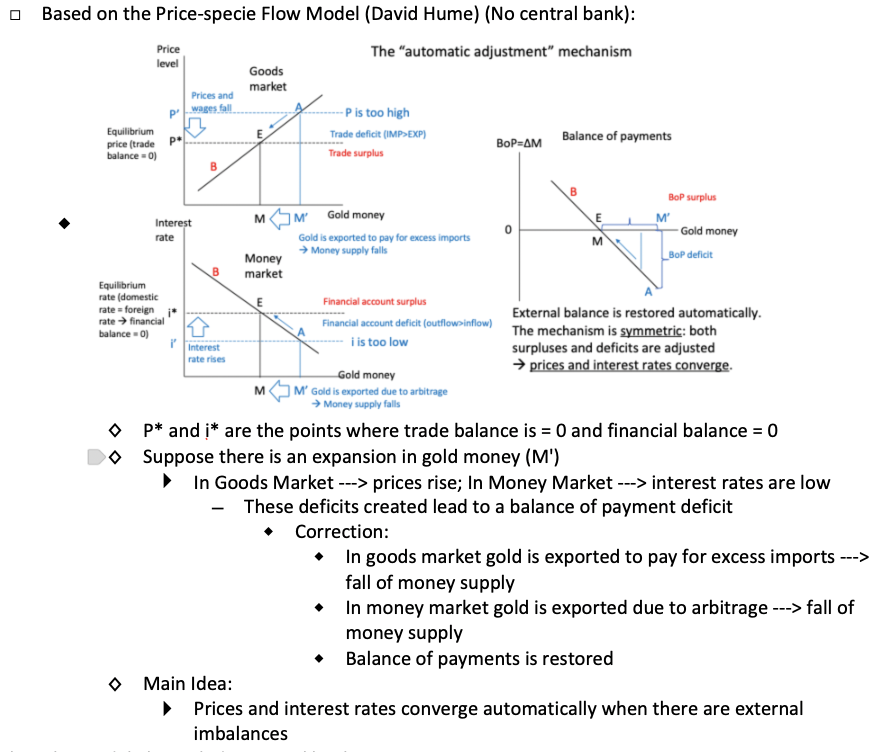
Explain David Hume's Price-Specie Flow Model and the key idea.
Describe the model when the central bank is involved.
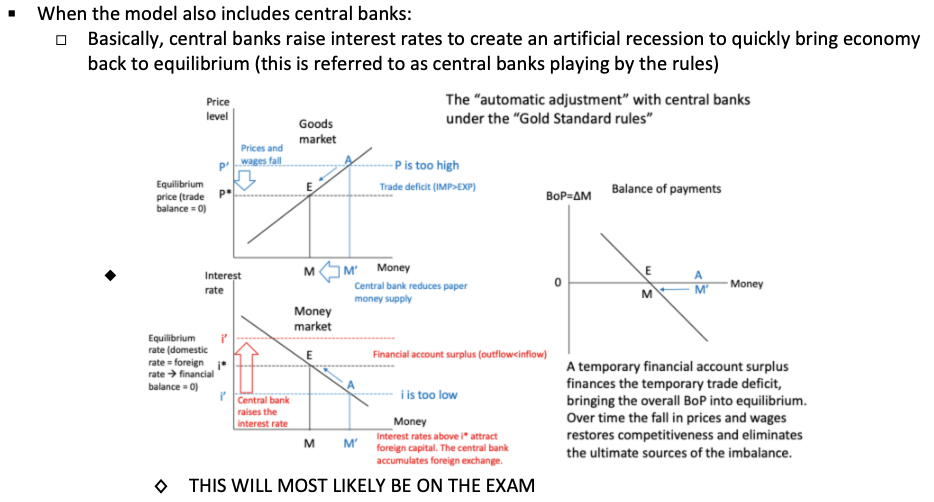
Did central banks play by the rules?

How were central banks able to not follow the rules?

How was the common level of interest rate determined?

What was the Baring Crisis and why was it significant?

What were the principles of peripheral economies in regards to banking and monetary system?

What is the Boom Bust pattern of peripheral economies?

What made the US's banking system unique?

What was the political controversy around the Gold Standard in the US?

Lecture 7: A World in Depression
What was the main target of central banks under the gold standard?

Explain what would happen to a countries goods and money market in the case of an expansionary monetary shock.
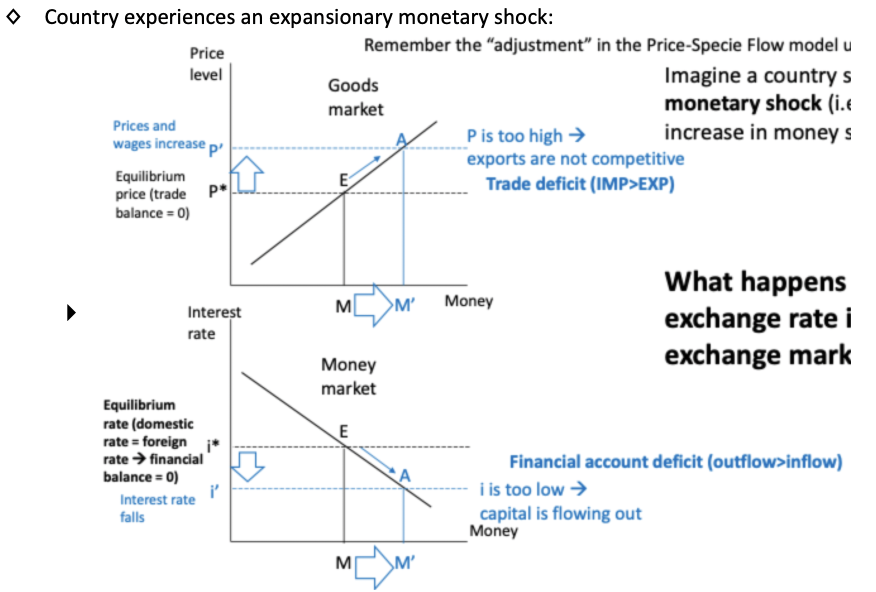
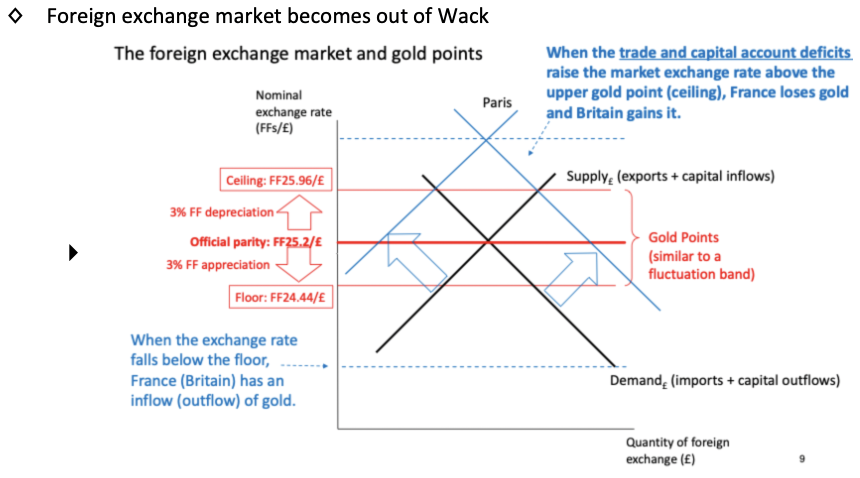
Explain what happens in the foreign exchange market when this expansionary monetary shock happens.
Explain how the central bank should react and how that changes the foreign exchange market.
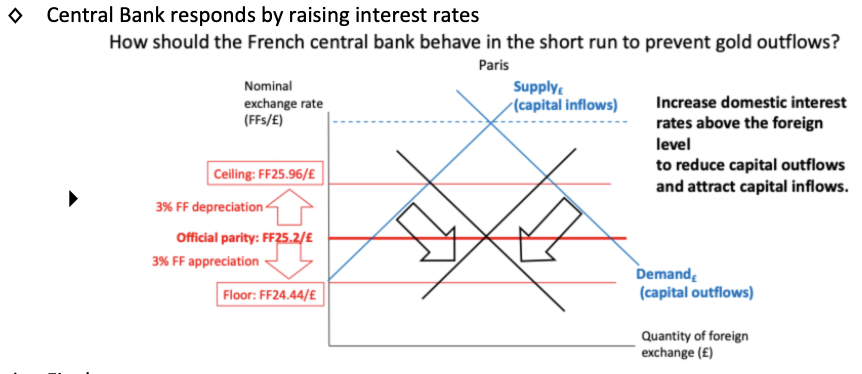
Explain what happens within the country's goods and money market when the central bank takes this action.
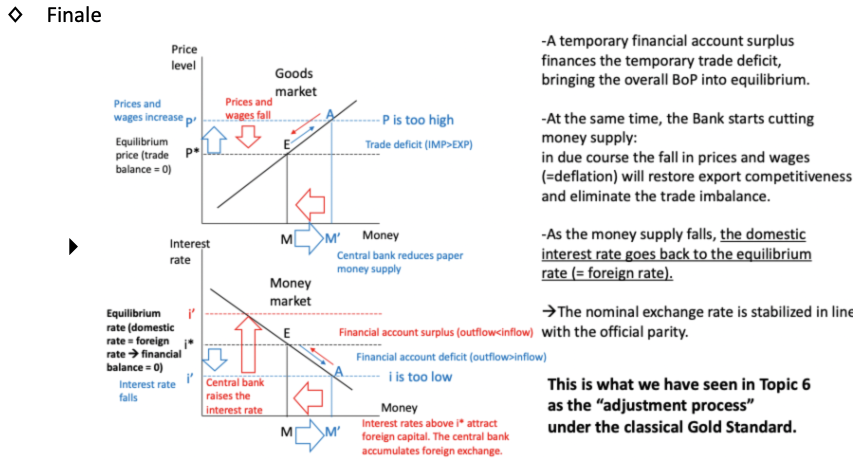
Explain what would happen if the central bank had done nothing.
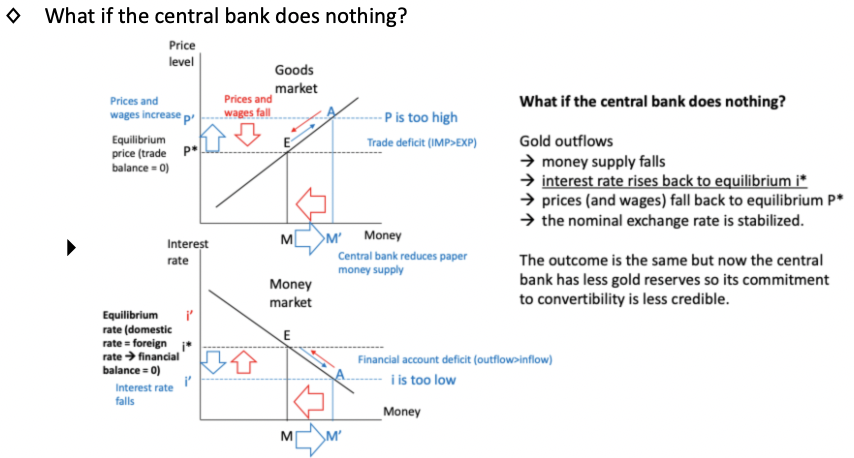
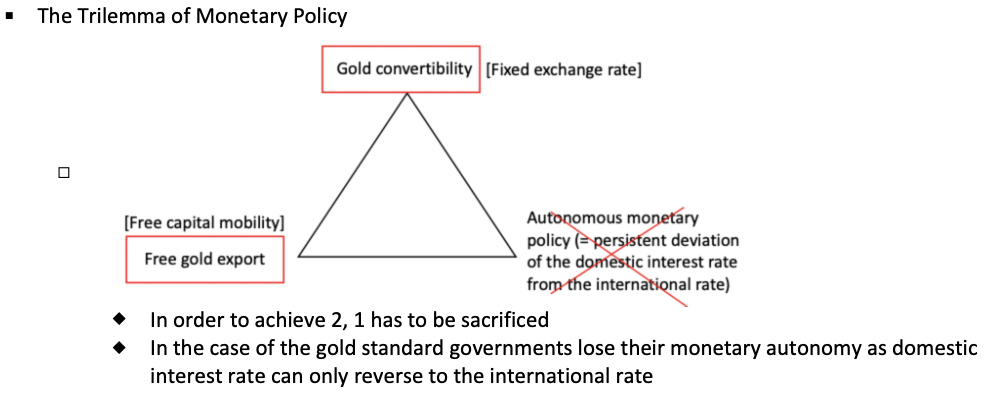
What is the Trilemma of Monetary Policy during this time?
What were the fiscal and monetary shocks as a result of WWI?

What were the 2 major characteristics immediately facing post-war economies?
Who were the deflationary and inflationary countries after WWI?

What were economic policies in all countries after WWI?

What were the 2 main ways that countries returned to gold convertibility?

What did the British case look like?

What did the French case look like?

How was the interwar Gold Standard different than before?

How did the Price-Specie Flow model say the international monetary system should work? Why did this fail during the interwar period?

How did peripheral economies fare during this period?

How did the Gold Standard make the global recession worse?

What are the options that central banks could do to respond to speculative attacks? Why did they choose what they chose and what was the result?

Why did Britain finally suspend gold convertibility?

Why did the US finally suspend gold convertibility?

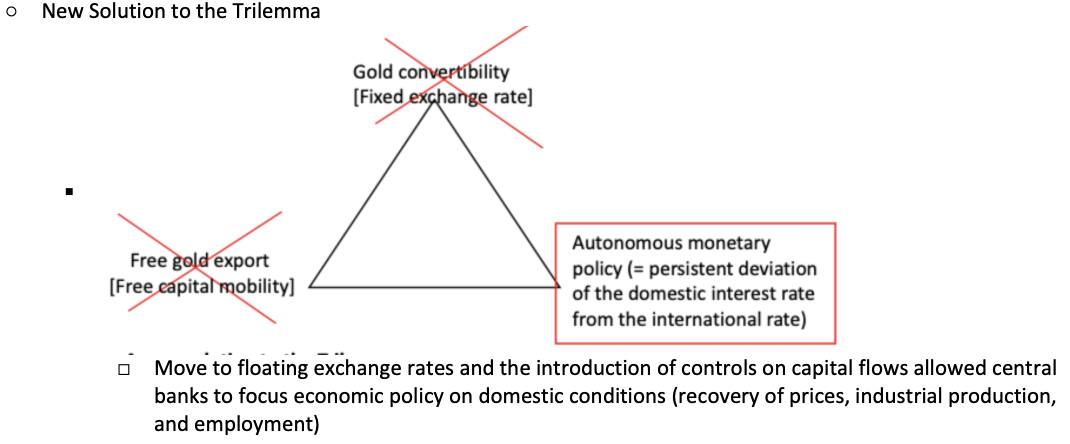
What was the new solution to the trilemma?
Lecture 9: US Hegemony
What was the ultimate objective of White's Plan?

What were the principles of White's Plan?

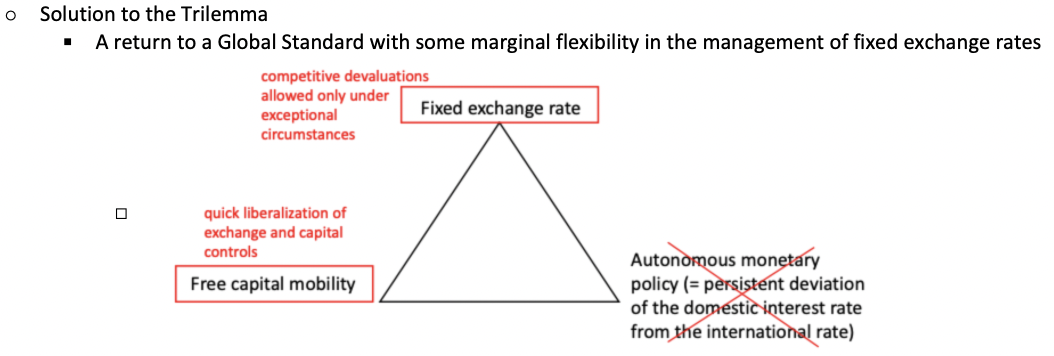
What was White's solution to the Trilemma?
What was the ultimate objective of Keynes' Plan?

What were the principles of Keynes' Plan?

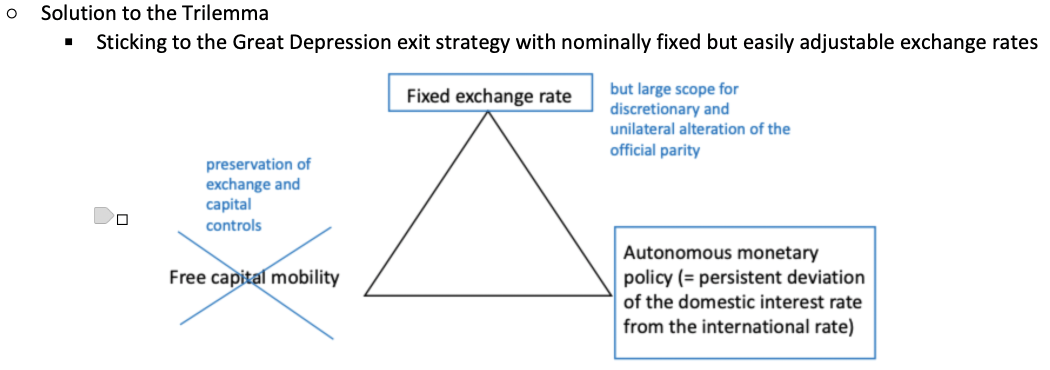
What was Keynes' solution to the Trilemma?
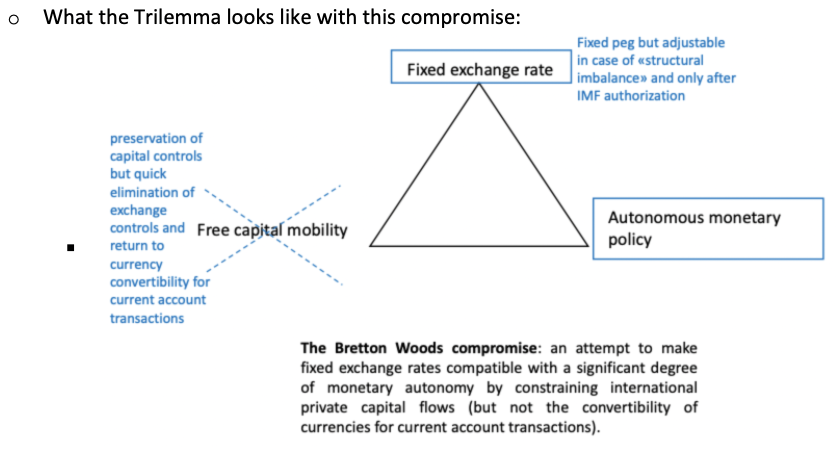
What were the 4 key compromises of the Bretton Woods declaration?

How does the Trilemma look with the Bretton Woods compromises?
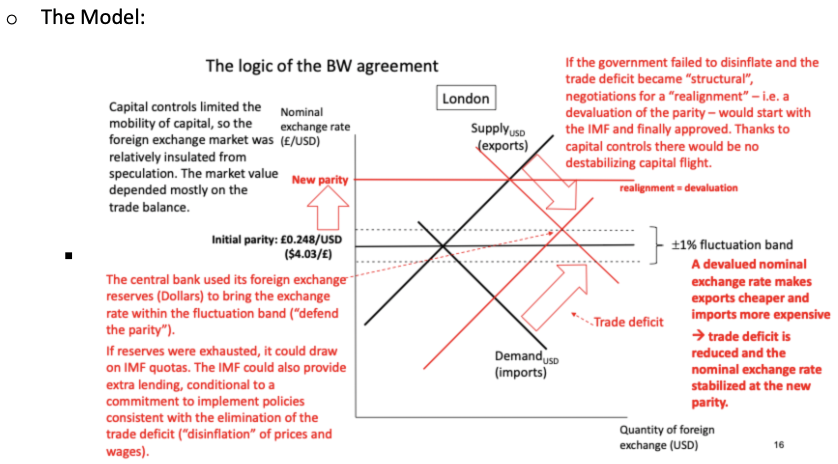
How does the model of USD foreign exchange look with the BW agreement?
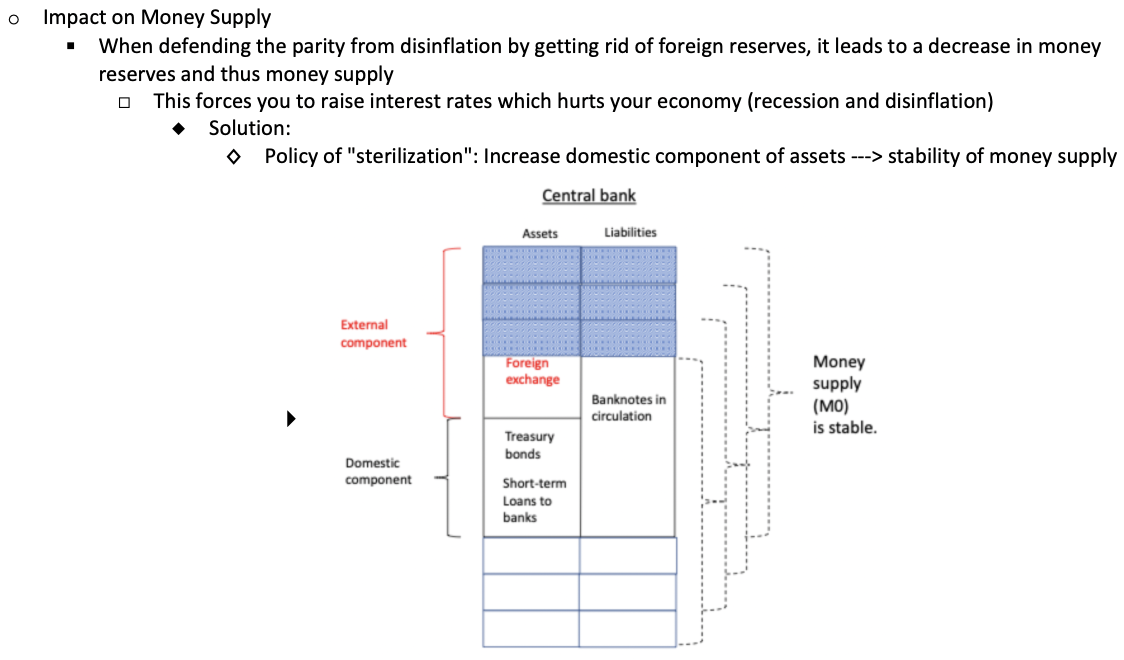
What is the impact of BW on money supply?
Why didn't the BW system work in the 1940s?

What was one potential solution to the BW system in the 1940s?

What was the first real used solution?

What was the second real solution?

What was the third real solution?

Why did trade liberalization make little progress during this period?

What is the European Miracle?

Why did the world go on the Dollar standard?

What are the 3 main reasons why Dollar dependency is a problem?

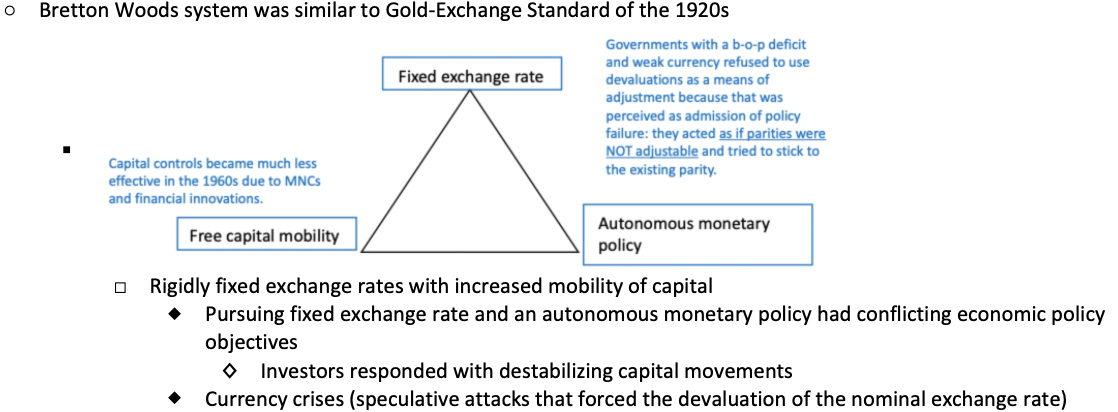
How was the Bretton Woods system similar to the Gold-Exchange Standard of the 1920s? Explain both the Trilemma involved and the key problems with it.
Explain the crisis that Britain faced due to the BW system between 1964-1967.
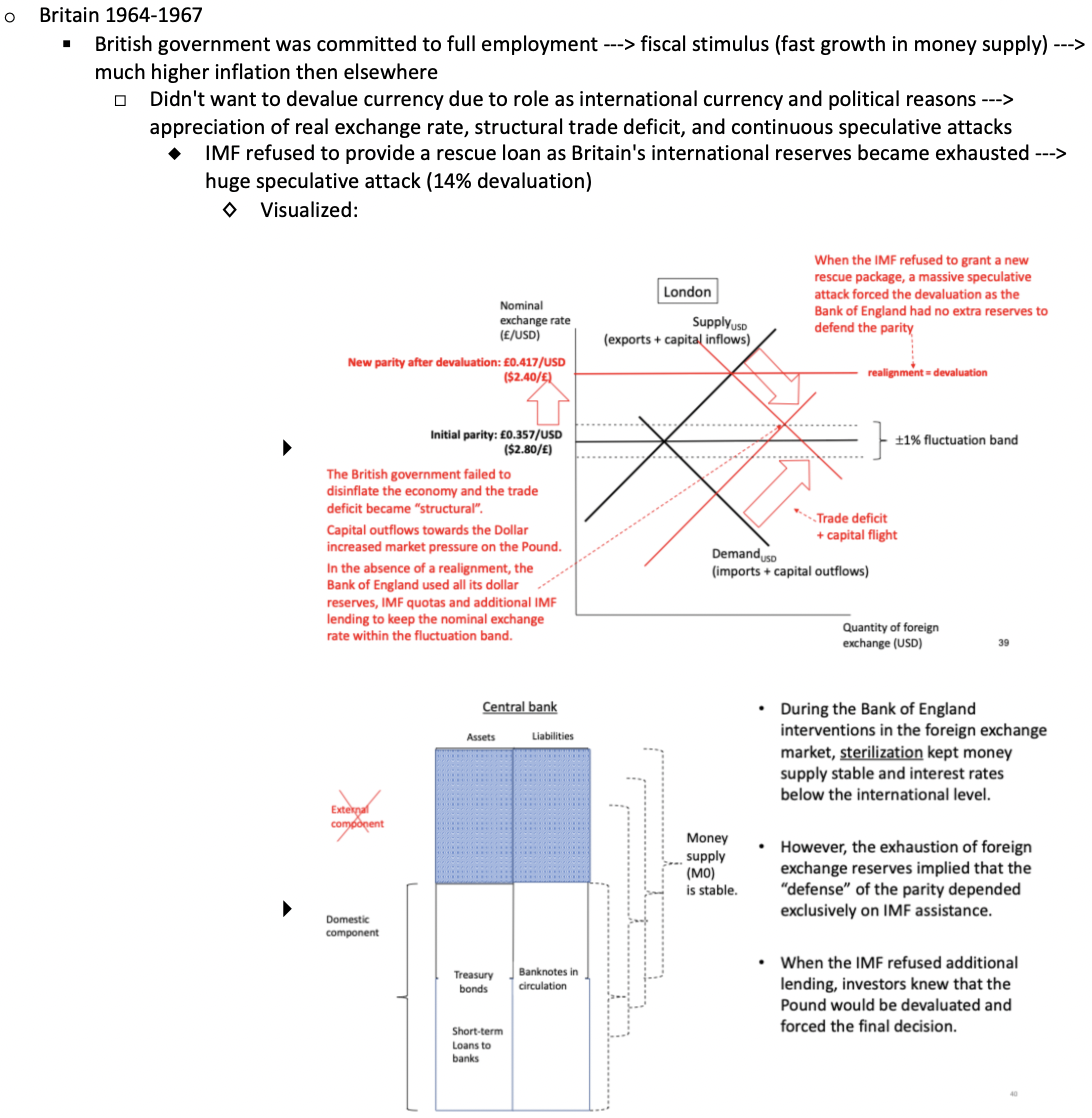
How does the US having the anchor currency mess up monetary policy autonomy?

Why was USD seen as an increasingly weak currency during the 1960s?

What was the US's attempted solution to solve this?

Describe how the weak dollar was a problem for West Germany.
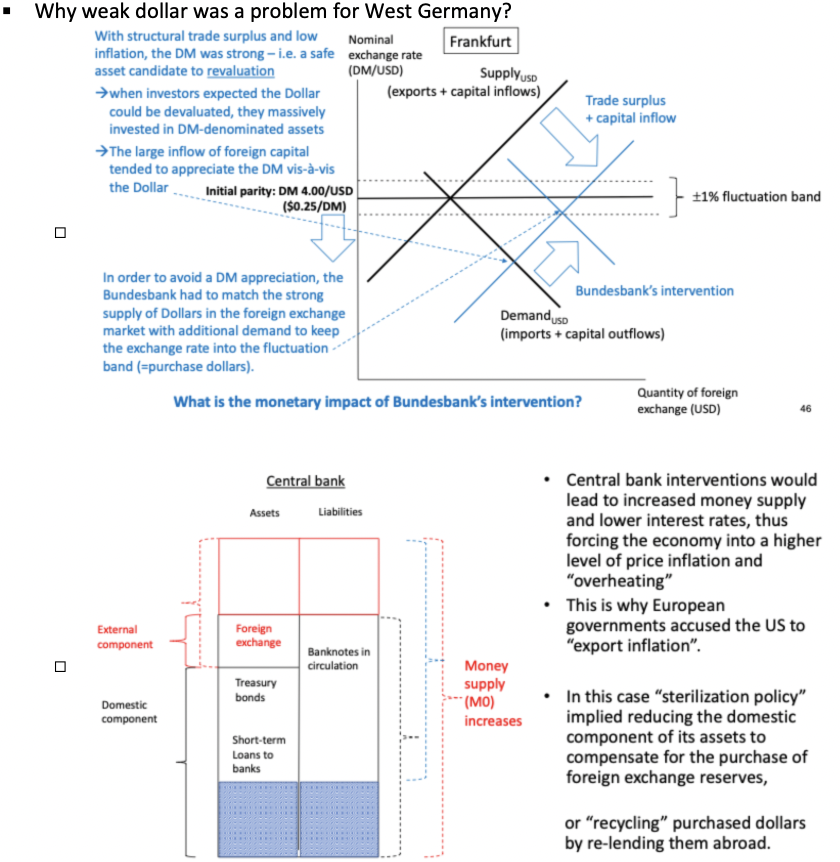
Describe the steps after this that led to essentially the end of the BW system.

What are the 4 key lessons from Bretton Woods?

Lecture 9: Multiple Choice
At the Bretton Woods conference, the main objective of the “clearing union” proposed by the British delegation was:
to oblige surplus countries to lend directly to deficit countries in order to facilitate their balance-of-payments adjustment
In the Bretton Woods’ Articles of Agreement, the scarce-currency clause:
gave the IMF the power to authorize deficit countries to introduce controls on imports from countries with persistent payments surpluses
The European Payments Union (1950–58):
facilitated the financing of intra-European trade deficits and the liberalization of inter-European trade