Exam 3: Endocrine and Circuilatory
5.0(2)Studied by 134 people
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Last updated 7:15 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
Endocrine System’s Function
Excretion of hormones from endocrine glands into bloodstream, hormones act on target tissues that have receptors for specific hormones
2
New cards
Exocrine
External secretion of hormones (e.g. sweat)
3
New cards
Endocrine
Type of system that produces and secretes hormones into the bloodstream to regulate bodily functions and maintain homeostasis.
4
New cards
Paracrine
Paracrine signaling is a type of cell signaling in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells.
5
New cards
Autocrine
Type of cell signaling where a cell secretes signaling molecules that bind to its own receptors, triggering a response within the same cell.
6
New cards
Glands
Cells that secrete endo/exocrine chemicals
7
New cards
Leptin
Major hormone released by fat tissue
→ acts on hypothalamus to suppress appetite
→ acts on hypothalamus to suppress appetite
8
New cards
Glucocorticoids
Major hormone released by fat tissue
→ acts on liver and muscles to stimulate glucose metabolism
→ acts on liver and muscles to stimulate glucose metabolism
9
New cards
Epinephrine
A hormone released by the adrenal Medulla in response to stress.
→ Acts on heart, lungs, blood vessels to increase heart rate, blood pressure, and open airways
→ Acts on heart, lungs, blood vessels to increase heart rate, blood pressure, and open airways
10
New cards
Releasing/Inhibiting hormones
Produced by hypothalamus
→ Acts on anterior pituitary to induce secretion of anterior pituitary hormones
→ Acts on anterior pituitary to induce secretion of anterior pituitary hormones
11
New cards
Trophic hormones
Produced by anterior pituitary
→ acts on endocrine glands and other target organs to stimulate growth and development and secretion of other hormones
→ acts on endocrine glands and other target organs to stimulate growth and development and secretion of other hormones
12
New cards
Calcitonin, triiodothyronine (T3), and Thyroxine (T4)
Produced in Thyroid
→ acts on most organs to regulate Ca2+ levels, promote growth and development, and to stimulate basal metabolic rate (BMR)
→ acts on most organs to regulate Ca2+ levels, promote growth and development, and to stimulate basal metabolic rate (BMR)
13
New cards
Hypothalamus
Part of midbrain responsible for maintaining long-term homeostasis of the body
→ uses neural info from brainstem and chemical signals from pituitary to monitor vital signs
→ located in midbrain on top of pituitary
→ uses neural info from brainstem and chemical signals from pituitary to monitor vital signs
→ located in midbrain on top of pituitary
14
New cards
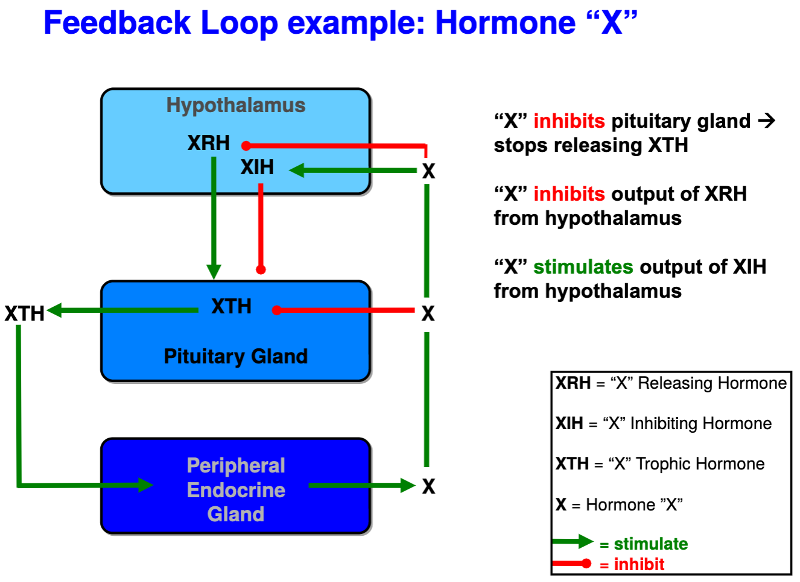
Endocrine feedback regulation
The mechanism by which hormones regulate their own secretion. Hormones produced by the endocrine glands inhibit or stimulate the production and release of other hormones. This feedback loop helps maintain hormonal balance in the body.
15
New cards
Can any endocrine cell produce any hormone?
No, most major hormones are cell-specific. When a certain endocrine cell is stimulated, it releases the hormone it produces and nothing else (normally).
16
New cards
Case study: Patient “a” is sick with an unknown hormonal problem and Patient “b” is well. If the problem with “a” resolves after recieving an injection of “b’s” blood, what was the root cause of patient “b’s” issue?
patient “a” has an issue producing certain hormones
→ if the injection did not solve anything, then “a” would most likely have an issue with their endocrine receptors
→ if the injection did not solve anything, then “a” would most likely have an issue with their endocrine receptors
17
New cards
When we learned the leptin hormonal pathway, what does it mean to be an ob/ob mouse?
Refers to a genetically obese mouse that lacks the ability to produce the hormone leptin but still has working leptin receptors, resulting in insatiable hunger and weight gain.
18
New cards
When we learned the leptin hormonal pathway, what does it mean to be an db/db mouse?
Refers to a genetically diabetic mouse that lacks the receptors to detect the hormone leptin but can still produce it, resulting in insatiable hunger and weight gain.
19
New cards
the more fat you have, the more (blank) you have and eating behaviors are (blank)
leptin, downregulated
20
New cards
what happens if you sew a “db” mouse to an “ob” mouse?
The “ob” mouse would become anorexic, because excessive amounts of leptin from the “db” mouse would down-regulate its need to eat.
21
New cards
what happens if you were to sew an “ob” mouse to a wild-type mouse?
the “ob” mouse would lose weight and be normal because of the regulated amount of leptin received from the wild-type mouse
22
New cards
What are the two main types of hormones?
1. Nuclear Receptor Hormones
2. Polypeptide Hormones
3. Glycoprotein Hormones
\

23
New cards
What are Nuclear Receptor Hormones?
steroids, thyroid hormones, retinoic acid
→ lipophilic, can pass through membranes
→ release regulated by synthesis
→ coordinate PNS and CNS response
→ can bind to DNA and impact gene transcription
→ lipophilic, can pass through membranes
→ release regulated by synthesis
→ coordinate PNS and CNS response
→ can bind to DNA and impact gene transcription
24
New cards
What are Polypeptide Hormones?
hormones made from chains of amino acids
→ e.g) ADH
→ e.g) ADH
25
New cards
What is a Glycoprotein Hormone?
hormone made up of protein and carbohydrate subunits
→ eg) FSH
→ eg) FSH
26
New cards
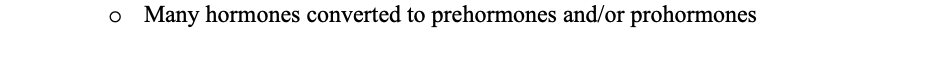
True or False: Many hormones converted to prehormones and/or prohormones
True: for example, Testosterone is a prehormone and can become a form of estrogen or DHT depending on the situation
27
New cards
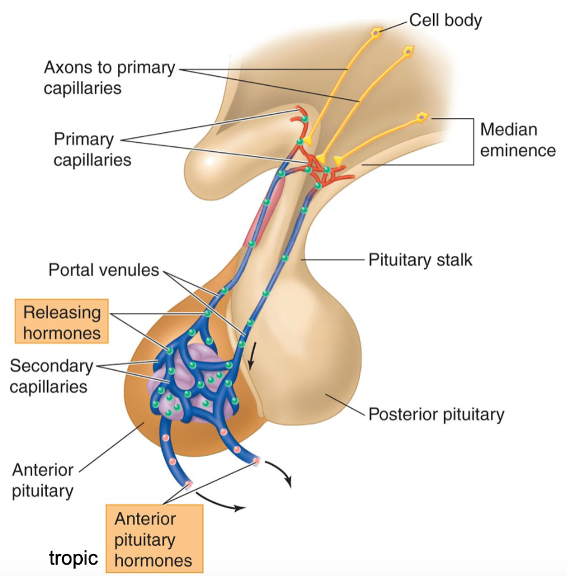
Pituitary Gland
attached to hypothalamus via infundibulum
→ functions to release hormones into bloodstream
→ functions to release hormones into bloodstream
28
New cards
Anterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland
Secretes Tropic and Trophic hormones into bloodstream
29
New cards
Tropic hormones
hormones that stimulate the release of other hormones
30
New cards
Trophic hormones
hormones secreted to · impact growth and development of other endocrine cells
31
New cards
Posterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland
contains ADH and oxytocin neuron axon terminals coming from hypothalamus; releases ADH and oxytocin into blood
32
New cards
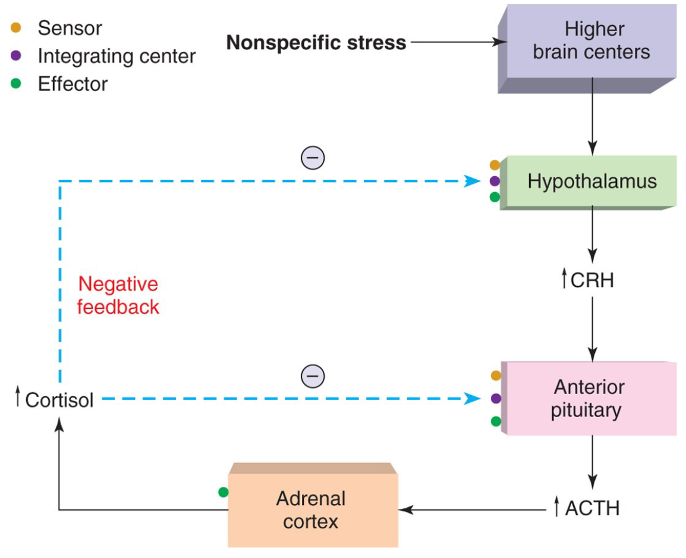
What is the Hypothalamic-pituitary axis?
It is a feedback loop between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands = **stress pathway**
→ responsible for regulating bodily functions using releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones
→ H releases CRH → P releases ACTH → reaches target gland: Adrenal Cortex → stimulates synthesis of corticosteroids (**stress**)
→ responsible for regulating bodily functions using releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones
→ H releases CRH → P releases ACTH → reaches target gland: Adrenal Cortex → stimulates synthesis of corticosteroids (**stress**)
33
New cards

What happens if you were to bisect the infundibulum (membrane connecting the pituitary and the hypothalamus)?
It causes all pituitary hormone levels to decrease *except* prolactin, which *increases*
→ symptoms include lactation
→ symptoms include lactation
34
New cards
What is the HPG (H-P-Gonadal) Pathway?
feedback loop between hypothalamus, pituitary, and the sex organs = **Reproduction Pathway**
→ H releases GnRH → P releases LH → reaches target gland: ovaries (females) /testes (male) → Stimulates estrogen/testosterone synthesis (**reproduction**)
→ H releases GnRH → P releases LH → reaches target gland: ovaries (females) /testes (male) → Stimulates estrogen/testosterone synthesis (**reproduction**)
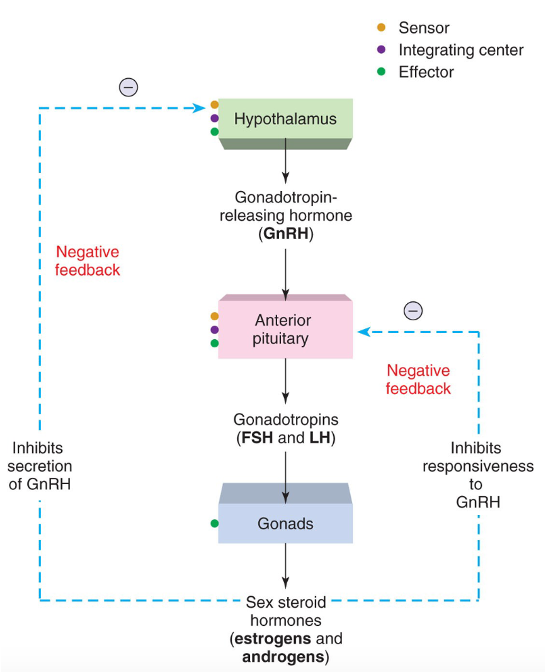
35
New cards
What is the HPT (H-P-Thyroid) Pathway?
feedback loop between hypothalamus, pituitary, and the thyroid = **Metabolism Pathway**
→ H releases TRH → P releases TSH → reaches target gland: Thyroid → Stimulates thyroxine synthesis (**metabolism**)
\
→ H releases TRH → P releases TSH → reaches target gland: Thyroid → Stimulates thyroxine synthesis (**metabolism**)
\
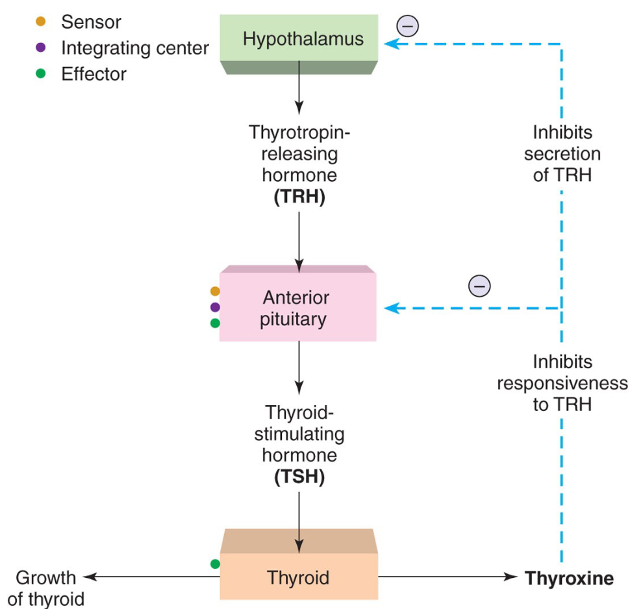
36
New cards
What can cause **hyper-secretion** of hormones in the endocrine system?
→ Tumors
→ damage to pathway eliminating negative feedback
→inappropriate hormone synthesis/degradation from precursor
→ damage to pathway eliminating negative feedback
→inappropriate hormone synthesis/degradation from precursor
37
New cards
What can cause **hypo-secretion** of hormones in the endocrine system?
→ missing releasing/tropic hormones
→ missing synthesizing enzymes
→ missing receptors for hormones
→ missing synthesizing enzymes
→ missing receptors for hormones
38
New cards
What is the general response to stress (cortisol) in the endocrine system?
→ increase in gastric and adrenal secretion in hypothalamus
→ suppression of immune system
→ suppression of immune system
39
New cards
What part of the nervous system is responsible for the **immediate response** to elevated stress levels?
Autonomic nervous system
40
New cards
What is the ANS’s **immediate response** to elevated stress levels?
*Hypothalamus* → brainstem → vagus → increased heart rate → sympathetic activation → spinal cord → splanchnic nerve → adrenal medulla
*Adrenal medulla* → EP and NEP released into blood → increases heart rate, blood flow, blood pressure → mobilizes glucose and increases metabolism
*Adrenal medulla* → EP and NEP released into blood → increases heart rate, blood flow, blood pressure → mobilizes glucose and increases metabolism
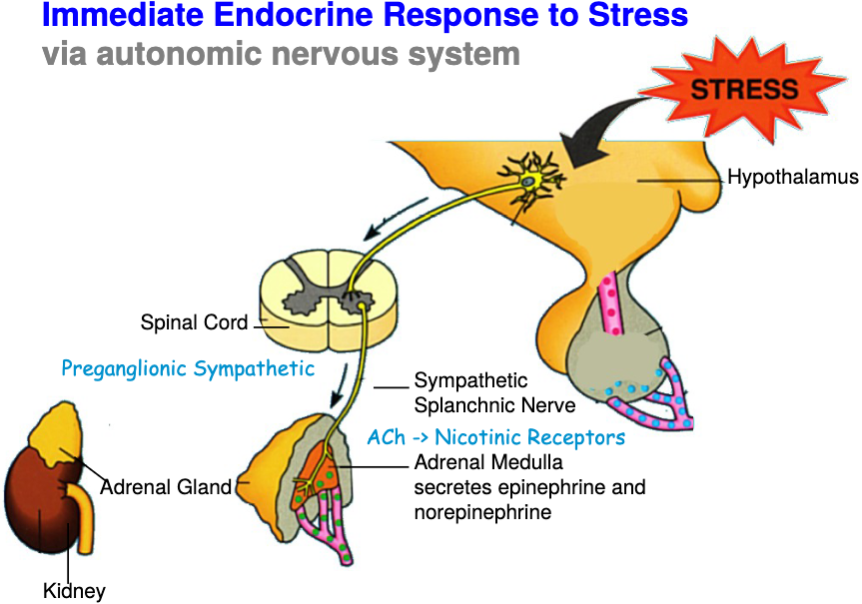
41
New cards
What part of the endocrine system is responsible for the **long-term** **transcriptional response** to elevated stress (cortisol) levels?
Mediated by glucocorticoids using positive feed forward loop
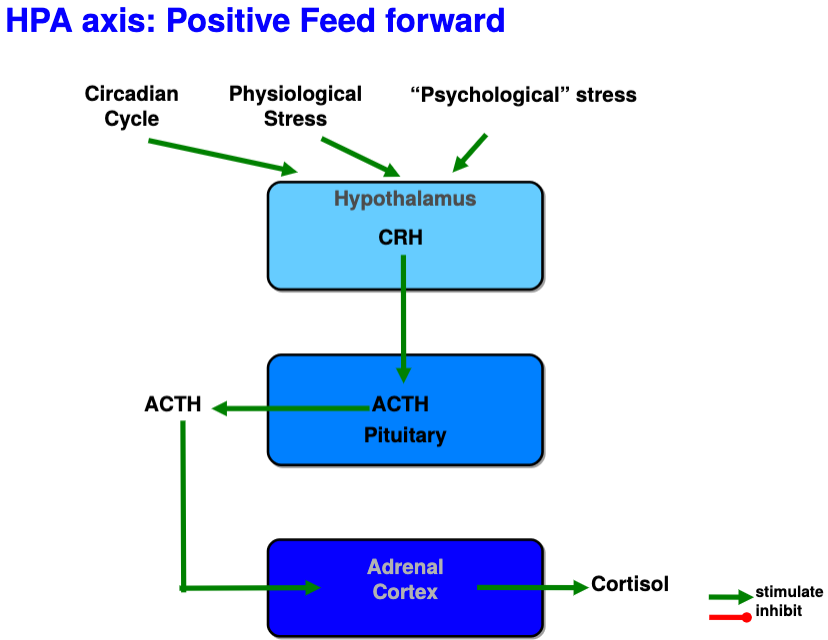
42
New cards
How is the long-term transcriptional response to elevated stress (cortisol) levels mediated by glucocoricoids?
*Corticotropin-releasing hormones from hypothalamus* → long portal vessels → anterior pituitary → corticotropes (pituitary cells) → adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
*ACTH in blood* → cortex of adrenal gland → ACTH receptors increase cAMP levels → increase in cholesterol conversion to cortisol via enzyme P450 in mitochondria and increased cortical growth
*Glucocorticoids* → transcriptional effects on cells expressing GC receptors
*ACTH in blood* → cortex of adrenal gland → ACTH receptors increase cAMP levels → increase in cholesterol conversion to cortisol via enzyme P450 in mitochondria and increased cortical growth
*Glucocorticoids* → transcriptional effects on cells expressing GC receptors
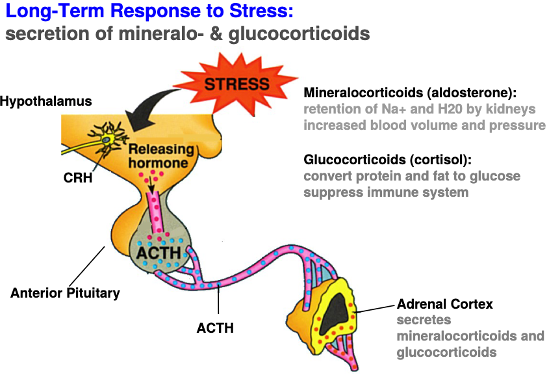
43
New cards
What is the main functions of glucocorticoids?
→ limit stress
→ suppress swelling, immune system
→ mobilize energy from muscle and fat cells
→ tells liver enzymes to detox poison, stress
→ suppress optional functions (growth, reproduction)
→ suppress swelling, immune system
→ mobilize energy from muscle and fat cells
→ tells liver enzymes to detox poison, stress
→ suppress optional functions (growth, reproduction)
44
New cards
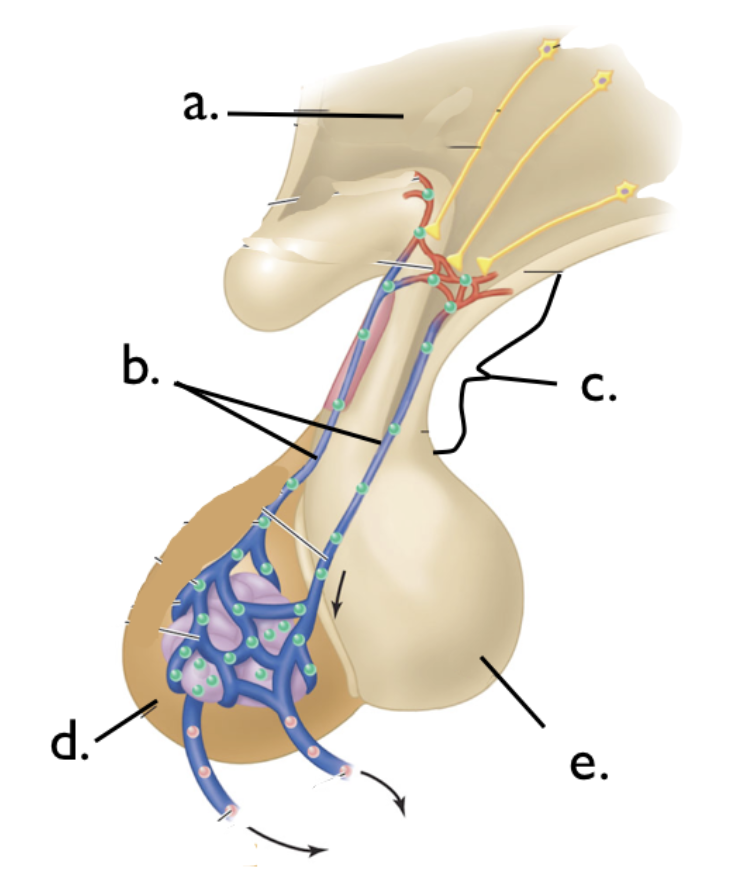
Label the parts of the pituitary gland
a: Hypothalamus
b: Portal Vessels
c: Infundibulum
d: Anterior Pituitary
e: Posterior Pituitary
b: Portal Vessels
c: Infundibulum
d: Anterior Pituitary
e: Posterior Pituitary
45
New cards
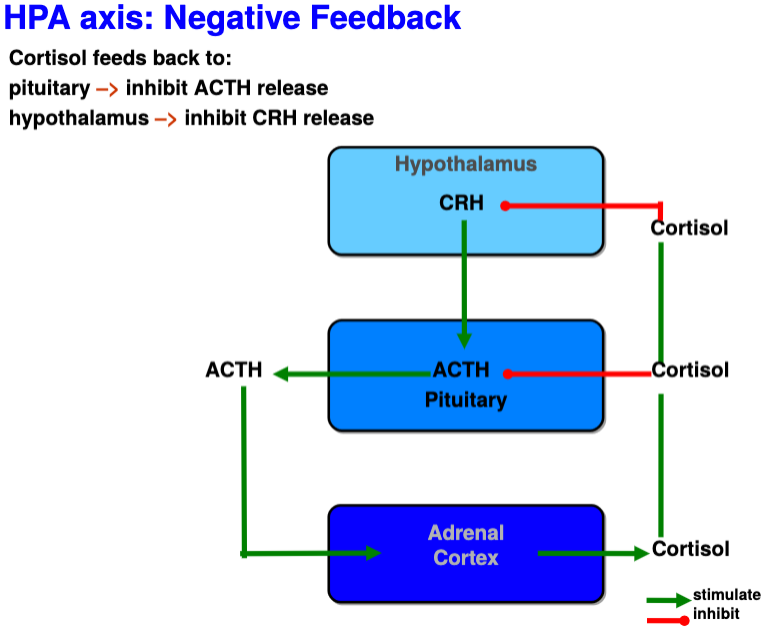
Negative feedback of cortisol onto hypothalamus and pituitary
* High levels of cortisol act on GC receptors in H and P to decrease CRH(H) and ACTH(P) synthesis/release
* Once excess GC are given, HPA detects increased negative feedback thus ACTH and cortisol levels drop
* Once excess GC are given, HPA detects increased negative feedback thus ACTH and cortisol levels drop
46
New cards
What is the dexamethasone suppression test?
It is a endocrine test where the patient is given a “fake” glucocorticoid (dexamethasone) to test if the HPA responds to negative feedback and is working correctly
47
New cards
If there was a defect in cortisol synthesis enzymes, what would be the effect on the negative feedback of cortisol onto hypothalamus and pituitary?
leads to the overproduction of mineralocorticoids (leading to high blood pressure) or too much sex steroids like progesterone (leads to masculinization)
48
New cards
What is Addison’s disease?
Occurs when an infection or the immune system damages the adrenal cortex leading to the loss of corticosteroids with an excess of ACTH
* intolerance to stress, loss of appetite, salt craving, hyperpigmentation in white people
* intolerance to stress, loss of appetite, salt craving, hyperpigmentation in white people
49
New cards
What is Cushing’s syndrome
Occurs when too much cortisol is being secreted leading to high output of ACTH
* loss of bone, muscle, connective tissue, fragile skin, abdominal obesity
* diagnosed using dexamethasone suppression test
* loss of bone, muscle, connective tissue, fragile skin, abdominal obesity
* diagnosed using dexamethasone suppression test
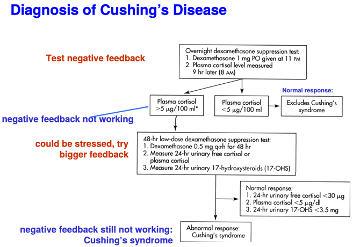
50
New cards
What is Cushing’s disease
its when Cushing’s syndrome occurs as a result of a tumor
51
New cards
What are Pheochromocytoma tumors
Tumors on the adrenal medulla
* cause hypersecretion of norepi/epi from adrenal glands
* leads to dramatic response to simple changes in homeostasis (ie. standing up)
* headaches, palpatations, chest pain, anxiety, impending sense of doom
* cause hypersecretion of norepi/epi from adrenal glands
* leads to dramatic response to simple changes in homeostasis (ie. standing up)
* headaches, palpatations, chest pain, anxiety, impending sense of doom
52
New cards
What does hyper-secretion of epinephrine cause
increased heart rate
53
New cards
What does hyper-secretion of norepinephrine cause
decreased heart rate
54
New cards
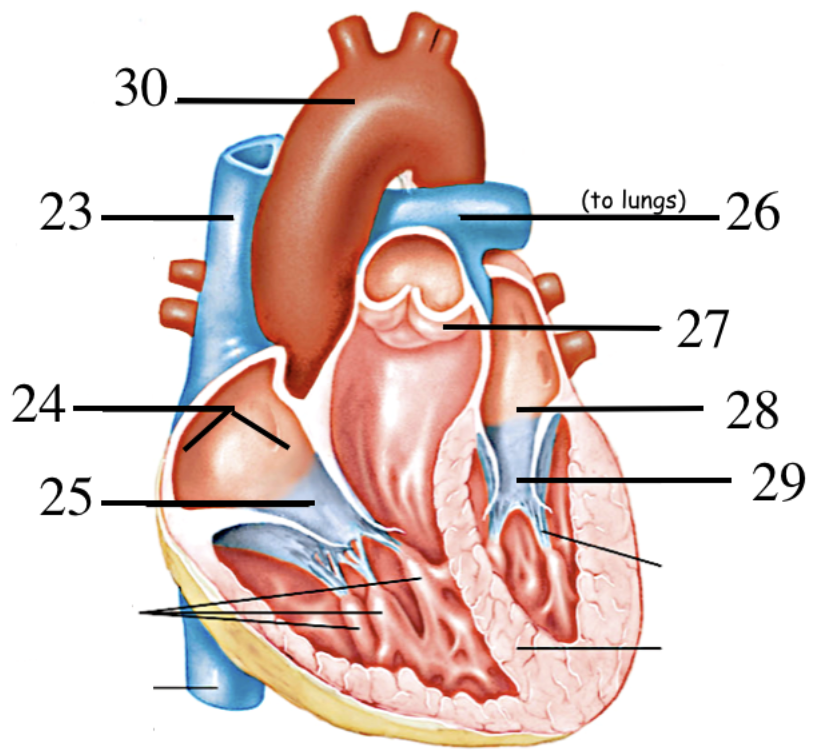
Label the parts of the heart
23. Vena Cava
24. Right Atrium
25. Tricuspid Valve
26. Pulmonary Vein
27. Semiluna valve
28. Left Atrium
29. Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve)
30. Aorta
31. \
55
New cards
What is the function of the atria?
recieve incoming blood from the body/lungs and transfer to ventricles
56
New cards
What is the function of the ventricles?
to take the blood coming from the atria and pass to the body/lungs to oxygenate.
57
New cards
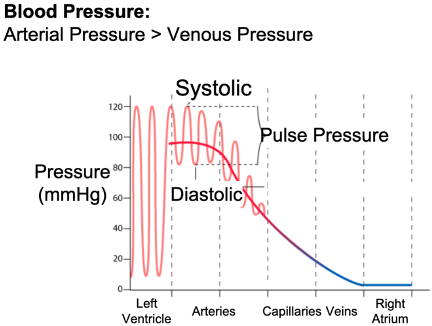
What does diastole mean?
chambers of the heart are relaxed, blood allowed to flow in
→ diastolic pressure (bottom BP #) = arterial pressure when ventricle relaxes
→ diastolic pressure (bottom BP #) = arterial pressure when ventricle relaxes
58
New cards
What does atrial systole mean?
atria contract, push blood into ventricles
59
New cards
What does ventricular systole mean?
ventricles contract with high pressure, push blood to lungs/rest of body
60
New cards
What is systolic pressure?
arterial pressure when ventricle contracts and pumps (top BP #)
61
New cards
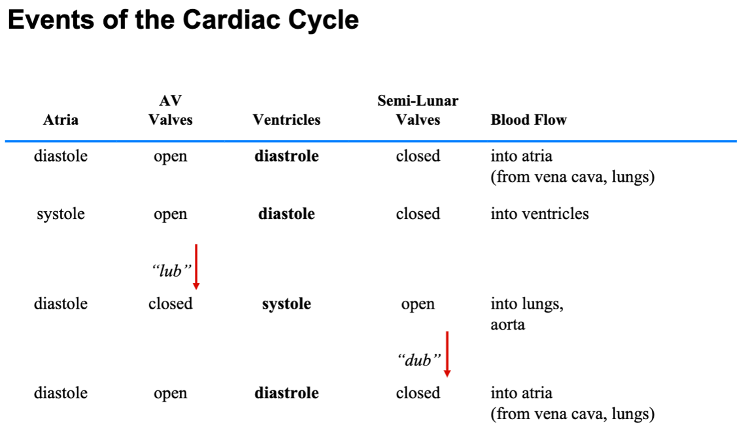
What are the events of the cardiac cycle?
1. Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium.
2. The right atrium contracts and pumps blood into the right ventricle.
3. The right ventricle contracts and pumps blood to the lungs.
4. The lungs oxygenate the blood.
5. Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium.
6. The left atrium contracts and pumps blood into the left ventricle.
7. The left ventricle contracts and pumps blood to the body.
62
New cards
What makes the “lub” noise in the heart?
It is caused by the closing of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves after blood flows from the atria into the ventricles.
63
New cards
What makes the “dub” noise in the heart?
it is caused by the closing of the aortic and pulmonary valves after blood flows out of the ventricles into the lungs and to the rest of the body.
64
New cards
What is the steps in the conduction of the AP across the heart and how does it correlate to the ECG?
1. The AP spreads from pacemaker cells in the SA node.
2. The myocardium forms a functional syncytium via gap junctions.
3. The AP spreads rapidly across the atria to cause depolarization and atrial systole (contraction).
4. The AP cannot cross directly to the ventricles, but must pass through the atrioventricular node (AV node).
5. Slow conduction through the AV node causes a delay between atrial and ventricular contraction, allowing for blood to flow.
6. The AP spreads from the AV node through the bundle of His and along Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles. The atria repolarize at this time.
7. The ventricles depolarize and contract (QRS wave), which is heard as the "lub" sound.
8. The ventricles repolarize (T wave), which is heard as the "dub" sound.
65
New cards
What is an Ischemia?
Blockage of the blood vessels leading to/from the heart → causes depression of S-T interval
* main cause of damage to heart
* formation of plaques due to cholesterol build up
* main cause of damage to heart
* formation of plaques due to cholesterol build up
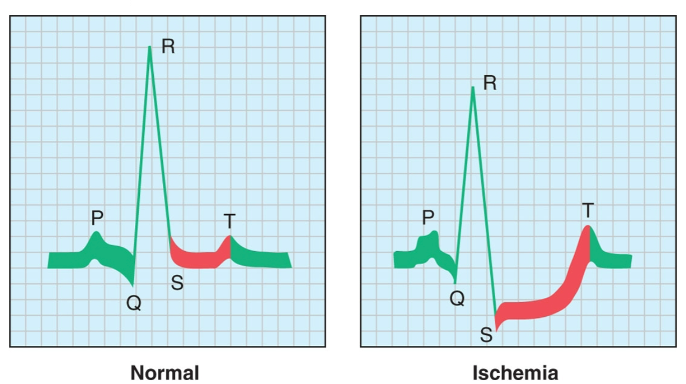
66
New cards
What is bradycardia?
slowed heartbeat
67
New cards
What is tachycardia?
rapid heartbeat
68
New cards
what is fibrillation?
“quivering” of myocardium; uncoordinated contraction of valves
69
New cards
what is arrhythmia?
loss of rhythm
70
New cards
What is a circus rhythm?
ischemia causes damage to purkinjie fibers, leading to parts of ventricle to contract out of step with rest of heart
71
New cards
What happens when there is an AV Node Block?
Damage to the AV Node slows or blocks pacemaker signal from the atria. P-waves occur, sometimes without QRS-waves.
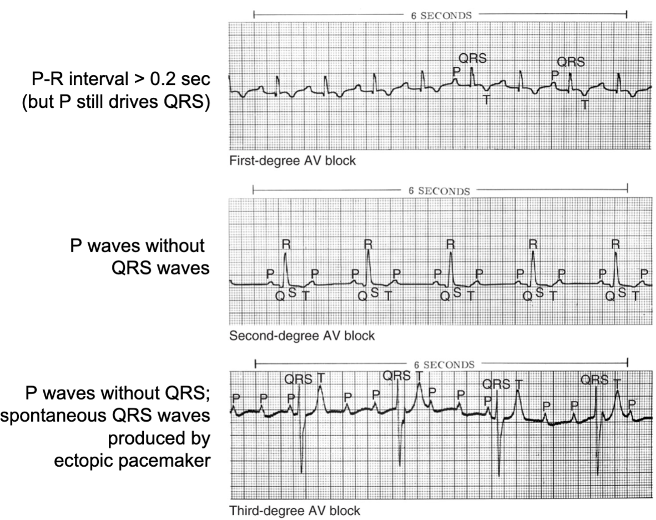
72
New cards
What happens during ventricular fibrilation?
ventricles of the heart quiver
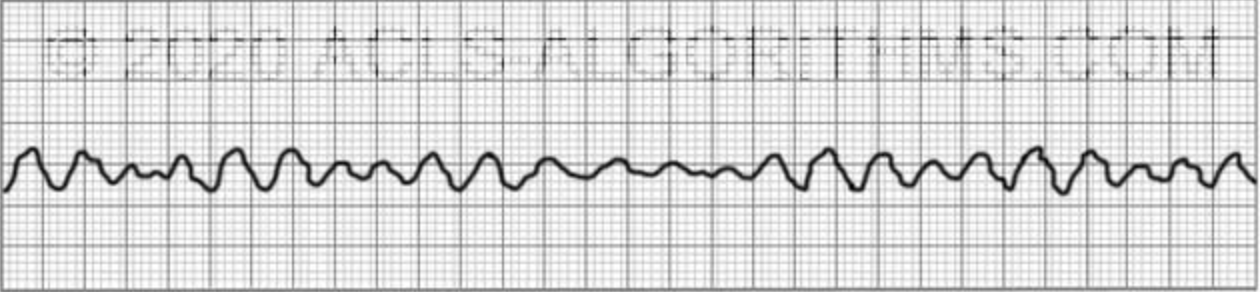
73
New cards
What are arteries?
carry oxygenated blood outwards from the heart towards the rest of the body
→ thick muscular walls contract to maintain high pressure to pass blood
→ thick muscular walls contract to maintain high pressure to pass blood
74
New cards
What are veins?
blood vessels carrying deoxygenated blood towards the heart from the body.
→ thin walls have a lower pressure, valves ensure passage of blood in one direction
→ thin walls have a lower pressure, valves ensure passage of blood in one direction
75
New cards
What are capillaries?
blood vessels carrying oxygenated/deoxygenated blood between the networks of arteries and veins.
→ much smaller than other vessels (up to 1 blood cell wide)
→ much smaller than other vessels (up to 1 blood cell wide)
76
New cards
What are the 4 main components of blood?
1. Red blood cells
2. White blood cells
3. Platelets
1. Plasma
77
New cards
What is the function of red blood cells?
Use hemoglobin protein to transport oxygen and CO2
78
New cards
What is the function of white blood cells?
provide immune response, source of DNA for PCR analysis of blood
79
New cards
What is the function of platelets?
Cell fragments that help in the clotting process
80
New cards
How does the blood clotting pathway behave when blood vessels are intact?
endothelial cells inhibit platelet aggregation
* platelets are physically separated from collagen
* prostacyclin and nitric oxide to cause vasodilation
* CD39 enzyme breaks down ADP in blood
* platelets are physically separated from collagen
* prostacyclin and nitric oxide to cause vasodilation
* CD39 enzyme breaks down ADP in blood
81
New cards
When a blood vessel is damaged, how does the blood clot?
1. Platelets bind to collagen and von Willibrand’s factor
2. Platelets release chemicals to recruit more platelets to plug up the damaged area
3. Serotonin causes vasoconstriction to decrease bleeding
4. Platelets activate plasma clotting factors, converting soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin which further helps to plug up damaged areas
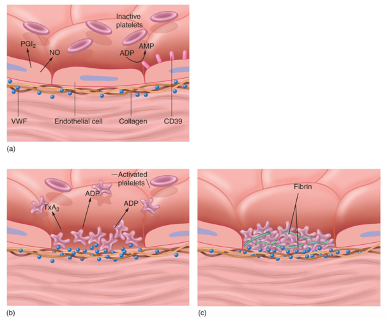
82
New cards
Once a clot has fulfilled its purpose, how does it dissolve?
1. Factor XII activates kallikrein enzyme.
2. Kallikrein converts plasminogen into plasmin enzyme.
3. Plasmin digests fibrin to dissolve clot.
83
New cards
What happens to the clotting pathway when you have a vitamin K deficiency?
Body cannot produce adequate clotting factors
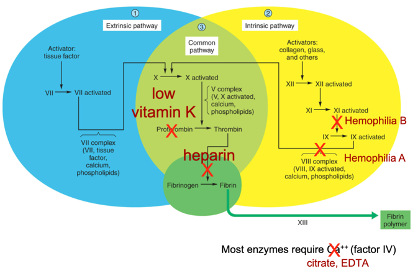
84
New cards
What is hemophila A?
X-linked recessive genetic disease where pathway to factors VIII, IX, Ca++ and phospholipids is not functioning correctly.
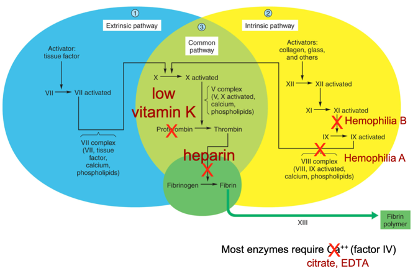
85
New cards
What is hemophilia B?
X-linked recessive genetic disease where pathway to activate clotting factor IX is not functioning correctly
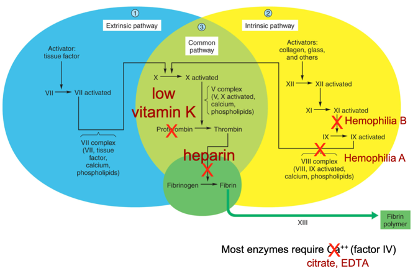
86
New cards
What would happen if you mixed hemophilia A and hemophila B blood?
there would be better blood clotting than when separate because each provides the factors that the other is missing
87
New cards
What is Von Willebrand’s disease?
disease that makes it hard for platelets to adhere to collagen during clotting
88
New cards
How does aspirin impact clotting?
causes defective platelet release, inhibiting clotting.
89
New cards
How does coumarin impact clotting?
inhibits the activation of vitamin K, inhibits production of clotting factors.
90
New cards
How does heparin impact clotting?
inhibits the activity of thrombin, inhibiting clotting.
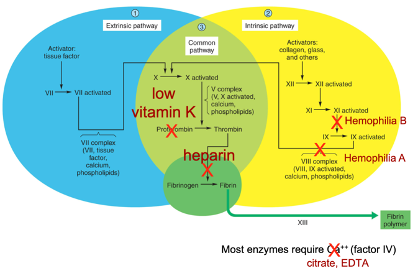
91
New cards
how does citrate impact clotting?
combines with Ca2+ to inhibit activity of clotting factors
92
New cards
why is it important to keep blood pressure constant?
to ensure blood reaches all of the tissues (fails when too low) and blood vessels are not damaged (fails when too high)
93
New cards
What is the equation for arterial blood pressure?
Arterial blood pressure = Cardiac output × Total peripheral resistance
94
New cards
What is cardiac output?
volume of blood pumped each minute by each ventricle
95
New cards
how is cardiac output changed by the body?
1. changes of heart rate → stroke volume and ventricle contractility
2. changes of the vasculature (squeezing/releasing arterial muscles)
96
New cards
How does blood flow to different body parts change during high cardiac output (exercise)?
* Blood flow to nonessential parts of body decrease (digestion, kidneys, etc.)
* Blood flow to musculature is increased
* blood flow to brain remains constant
* Blood flow to musculature is increased
* blood flow to brain remains constant
97
New cards
What is the equation for cardiac output?
Cardiac output(ml/min) = Cardiac rate(beats/min) × Stroke volume(ml/beat)
98
New cards
What does it mean to be in cardiac failure?
Cardiac output is too low to maintain the current amount of blood supply in circulation
99
New cards
How does the nervous system monitor blood pressure?
Baroreceptor neurons in the aorta report blood pressure to the brainstem medulla
100
New cards
How does the SNS increase heart rate?
1. Norepinephrine (NE) from sympathetic nerves and epinephrine (EPI) from the adrenal medulla bind to beta-adrenergic receptors on the SA node.
2. Binding of NE and EPI to beta-adrenergic receptors increases the concentration of cAMP in the SA node.
3. Increased cAMP opens HCN channels in the SA node.
4. Opening of HCN channels depolarizes the SA node, leading to a faster heart rate.