Anti-peptide , fungals - not done
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IPM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
How do antimicrobial peptides preferentially target microbes and not human cells?
Antimicrobial peptides selectively target microbes due to differences in cell membrane composition. Microbial membranes have more anionic phospholipids (negative ), attracting cationic peptides, while human membranes contain neutral phospholipids, making them less affected by the peptides
What are the biggest advantages of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)?
Broad-spectrum activity: AMPs can effectively target various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Lower risk of resistance: Their unique mechanisms make it difficult for microbes to develop resistance, ensuring prolonged effectiveness.
Immune modulation: AMPs enhance the immune response by recruiting and activating immune cells, aiding in infection control.
What are the disadvantages of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)?
Cost-effective synthesis: Producing AMPs can be expensive and complex, which may limit their availability and widespread use in clinical settings.
Cytotoxicity: Some AMPs may exhibit toxicity to human cells at higher concentrations, leading to potential side effects and limiting their therapeutic applicability.
Stability issues: AMPs can be susceptible to degradation by proteases in the body, which may reduce their effectiveness and require the development of modified peptides to improve stability.
Limited tissue penetration: Some AMPs may struggle to penetrate tissues effectively, which can hinder their ability to reach the site of infection and exert their antimicrobial effects.
Challenges of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
Limited Functionality: AMPs are often ineffective against certain bacteria, especially Gram-negative strains, due to their reliance on membrane disruption and instability in biological conditions.
Content Duplication: Developing AMPs involves extensive resource use in testing and optimization, which is inefficient and complicated by regulatory hurdles.
Design Constraints: Creating AMPs that are both effective and selective for pathogens without harming host cells is complex, requiring careful modeling
Limitations of Phage Therapy
Host Specificity: Phages target specific bacterial strains, complicating treatment for infections with multiple bacteria or unknown strains.
Resistance Development: Bacteria can quickly evolve resistance to phages, potentially requiring combinations of phages for effectiveness.
Immune Response: The human immune system may neutralize phages, limiting their therapeutic effectiveness and requiring higher doses.
Regulatory and Production Challenges: Phage therapy faces significant regulatory hurdles and complex manufacturing processes, hindering clinical use
What is CRISPR/Cas9 in bacteria, and how does it work?
Bacteria encounter a virus and incorporate unique segments of the viral DNA into their genome at a specific region called the CRISPR array (known as a spacer).
The CRISPR array is transcribed into long RNA, which is processed into shorter guide RNAs (gRNAs) that correspond to specific viral sequences.
Upon re-encountering the same virus, bacteria remember the previously integrated viral sequence in their CRISPR array, leading to transcription into gRNA.
The Cas9 protein is activated, which has the ability to break DNA strands.
The gRNA guides Cas9 to the virus, where it makes precise cuts in both strands of the viral DNA that match the gRNA sequence.
The virus cannot replicate because its DNA is rendered non-functional.
What are the challenges of using CRISPR technology in gene editing?- list 5
CRISPR/Cas9 technology faces several significant challenges:
Ethical Issues: The ability to edit human genes raises ethical concerns, especially with germline modifications that can be inherited. Issues surrounding consent and the potential for societal inequalities are paramount.
Long-Term Effects: The long-term impacts of gene editing are uncertain, with risks of unforeseen health issues
Off-Target Effects: CRISPR may modify unintended parts of the genome, leading to harmful mutations that could disrupt essential genes or regulatory elements.
Delivery Methods: Efficiently delivering CRISPR components to specific cells remains challenging, - to minimize immune reactions while maximizing targeting accuracy.
Technical Limitations: The precision of editing can vary significantly due to the complexity of the target gene's environment, making some edits more difficult to achieve.
Public Perception: Fear and misinformation surrounding gene editing can impede public acceptance and research funding, necessitating clear communication and education about the technology and its implications.
What are two different antibacterial ?
Anitmicrobial peptides +phages
Examples of Antimicrobial peptide
alpha helix - frog Magainin 2
Describe two types of antibacterial agents?
Peptide Antibiotics:
Small proteins that disrupt bacterial cell membranes (as it neg mem) , inhibit protein synthesis, or interfere with metabolic processes, effective against various bacteria.
Phage Therapies: Uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to specifically target and kill bacterial strains, minimizing damage to the microbiome. However it hard deliver as it needs to administered at the site of infection.
Can antimicribila peptide be synthesised without. source ?
Yes
Other sources u can get it from are diff organism. Then test the peptides against the desired bacteria.
What MOA of anibacterial peptide?
Cellular membrane damage : example
Creating hole or creating a port where u block the cell wall synthesis
Intercellular activity:
Inhibit the DNA duplication
Inhibit biological process by interacting with protein target like the ribosome so block the transcription + translation
Immune regulation : based on protein function + peptide can bind to these protein and
Reduce endotoxin induced inflammation respoonse
Induce pro-inflammatory factor synthesis
adjust adaptive immunity
Induce secretion of cytokines → macrophage recruits → immune modulatory effects
What are the characteristic of the bacteriophages ?
high host spescificty
Lytic (lysis of bacteria ) / non lytic phages
sensitive to heat
replicates : 2 form → lytic +lysogenic
applies in diagnostics +treatment
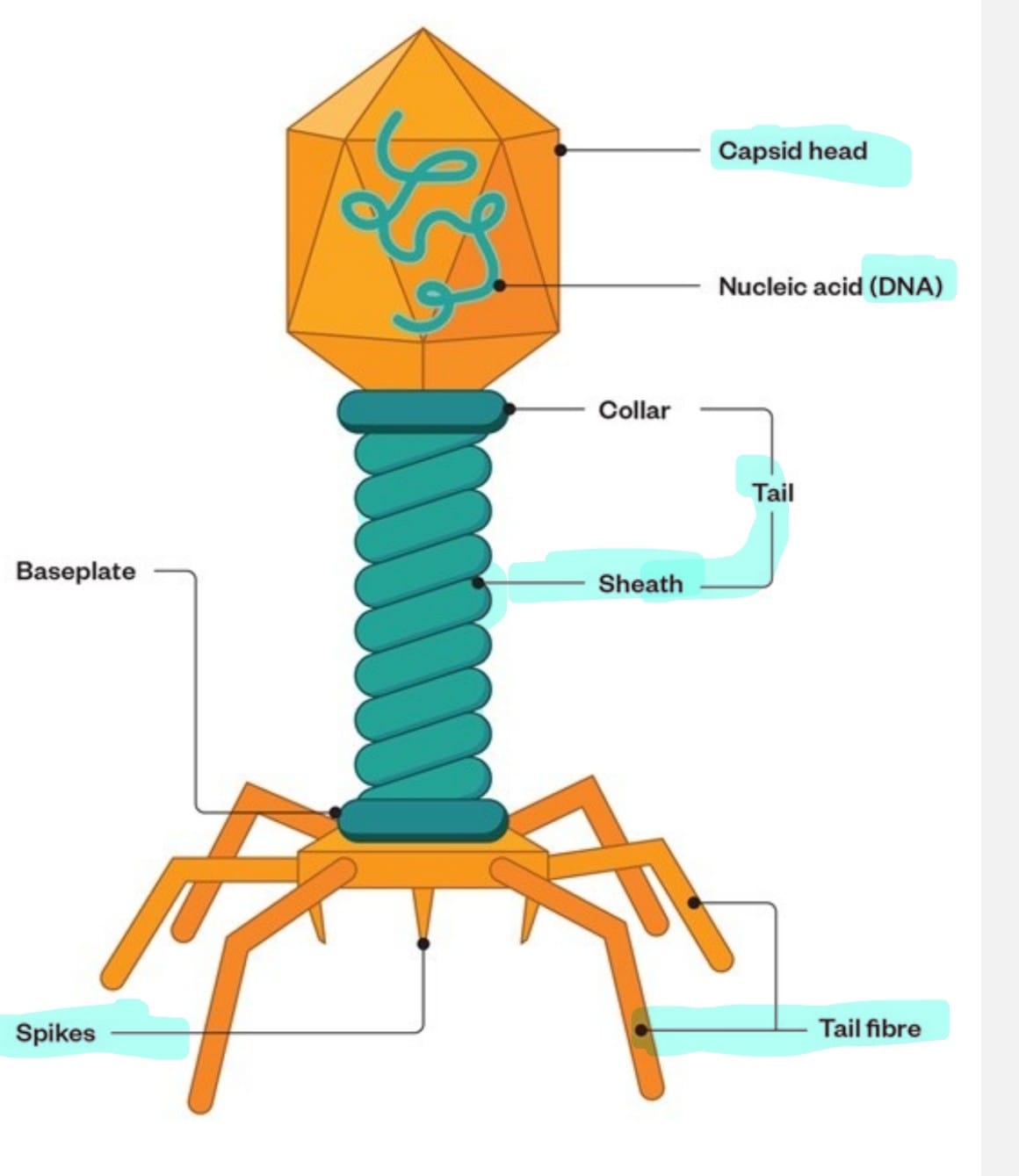
What are the feature highlighted used for when encountering bacteria?
Capsid head: hexagonal , compose of coat of protein ( quaternary structure ) encapsulate the phage DNA
Genome DNA: double strand DNA that codes for enzymes + protein for ti to replicate
Tail sheath : hollow core covered in contrails sheath where DNA travel from head to the bacteria through the sheath
Tail fibre : help to anchor the phage on it celll
Spike: protein complex tht penetrate the cell membrane and aids the phage DNA → host cell
When does the conformational change happen ?
when the phage encounters the bacteria the tail fibre aids in anchoring the phage to the bacteria. This attachment causes the conformational changes to the baseplate so the fibre attach irreversibly so the sheath contracts → spike to puncture the hole → DNA goes into the host
How does Lytic replication differ from Lysogenic replication
Lytic replican the DNA ISNOT INTERGRATED into host . immediately kills
Lysogenic DNA is integrated into the host therefore it says hidden in the bacterial while the bacterial divides then it penetrates out which cause the killing after a while.