neurophysiology lecture 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
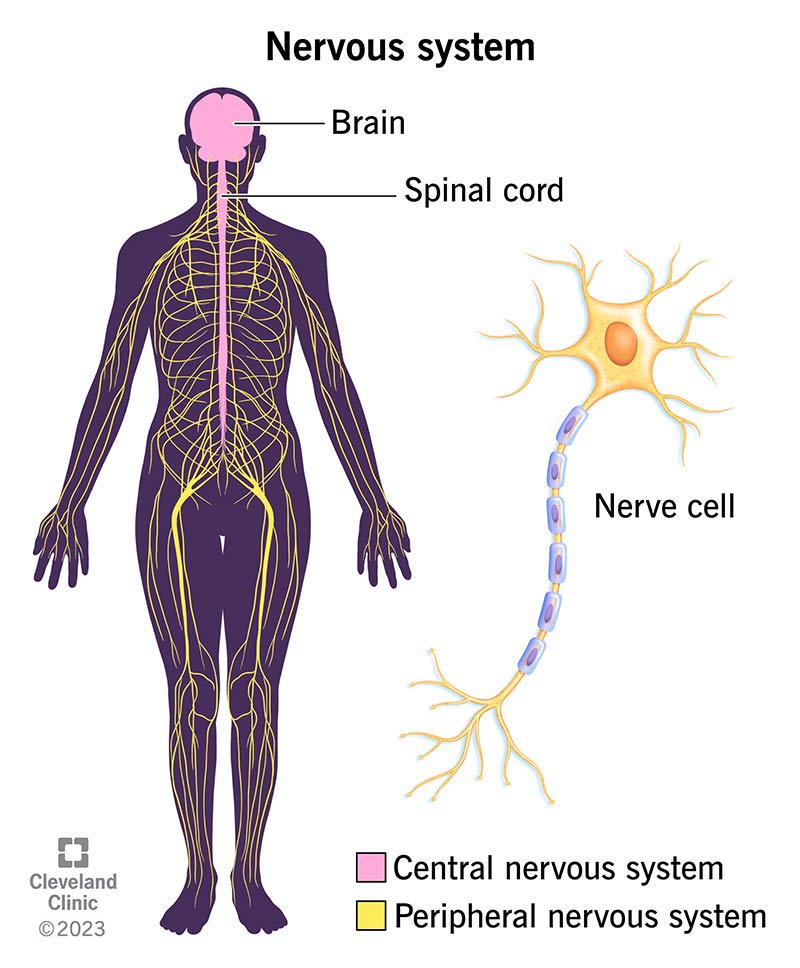
Nervous System
A complex, highly organized network of nerves and specialized cells (neurons and neuroglia) that facilitates communication between the brain and various parts of the body.
It controls bodily functions, sensory perception, and cognitive processes.
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and specialized cells, including neurons and neuroglia, responsible for communication between the brain and the body. It regulates bodily functions, processes sensory information, and supports cognitive activities.
It is essential for maintaining homeostasis and coordinating responses to stimuli.
Sensory Function
The ability of the nervous system to detect and monitor internal and external changes via sensory receptors.
These receptors respond to stimuli such as touch, temperature, light, and chemical signals, transmitting this information to the CNS.
allows the nervous system to interpret sensory information and facilitate appropriate responses, enabling an organism to interact effectively with its environment.
Integrative Function
The nervous system's capacity to analyze, process, and interpret sensory input to determine an appropriate response. This involves decision-making within the CNS, integrating information from various sources to coordinate actions.
Motor Function
The capability of the nervous system to stimulate effectors—muscles and glands—through cranial (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs). This function allows for movement, secretion, and other bodily responses to stimuli.
Motor function is essential for maintaining homeostasis and interacting with the environment.
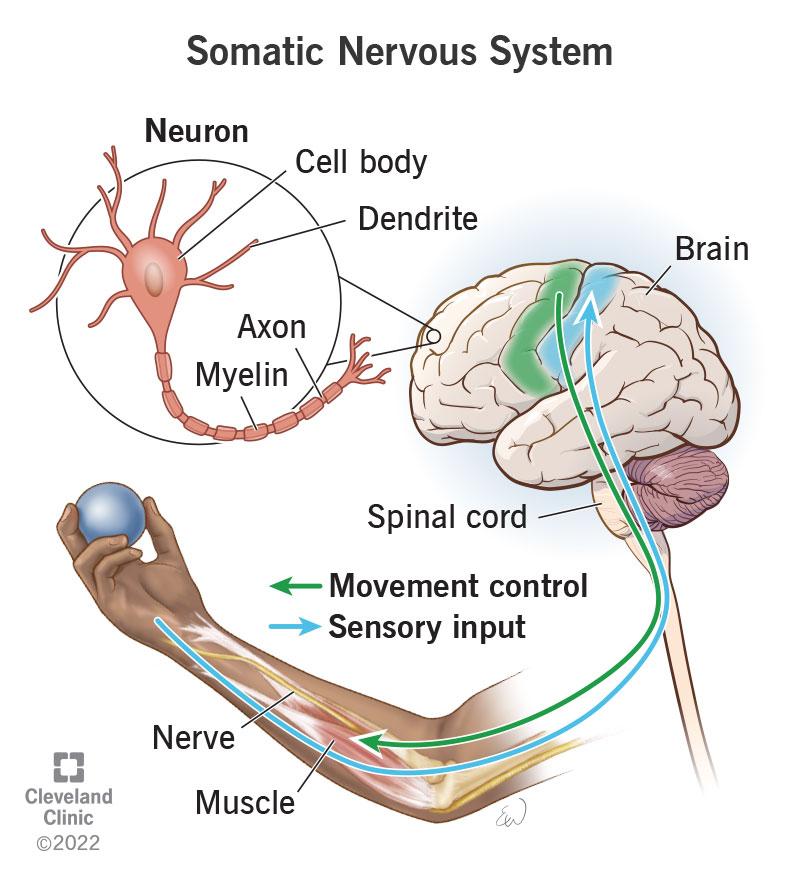
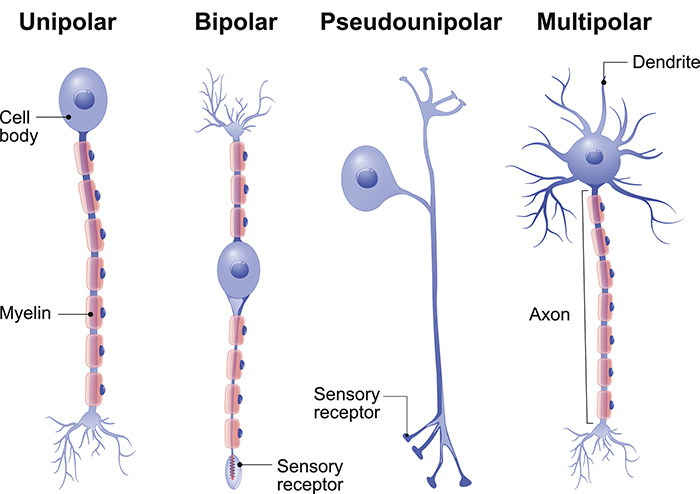
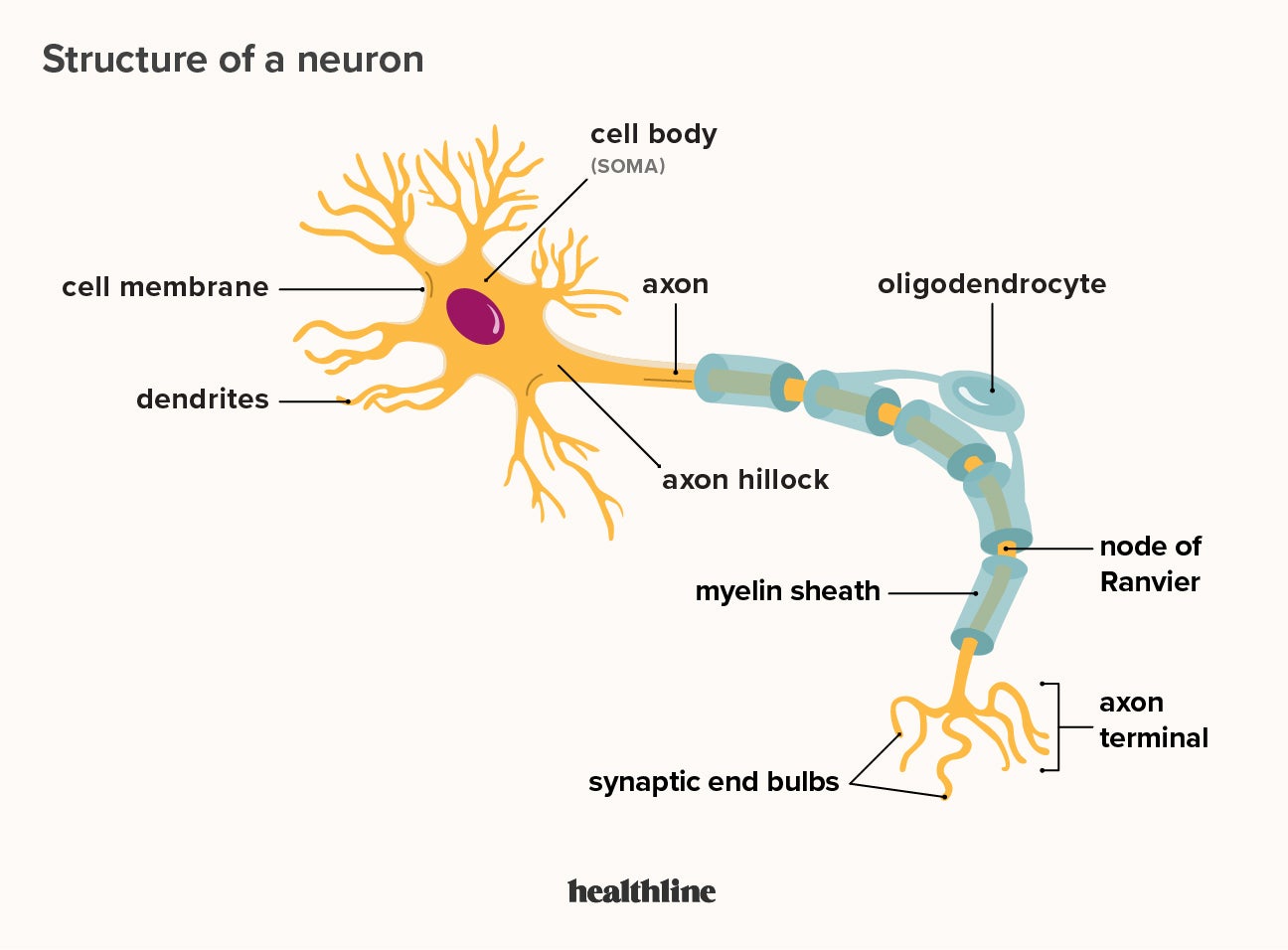
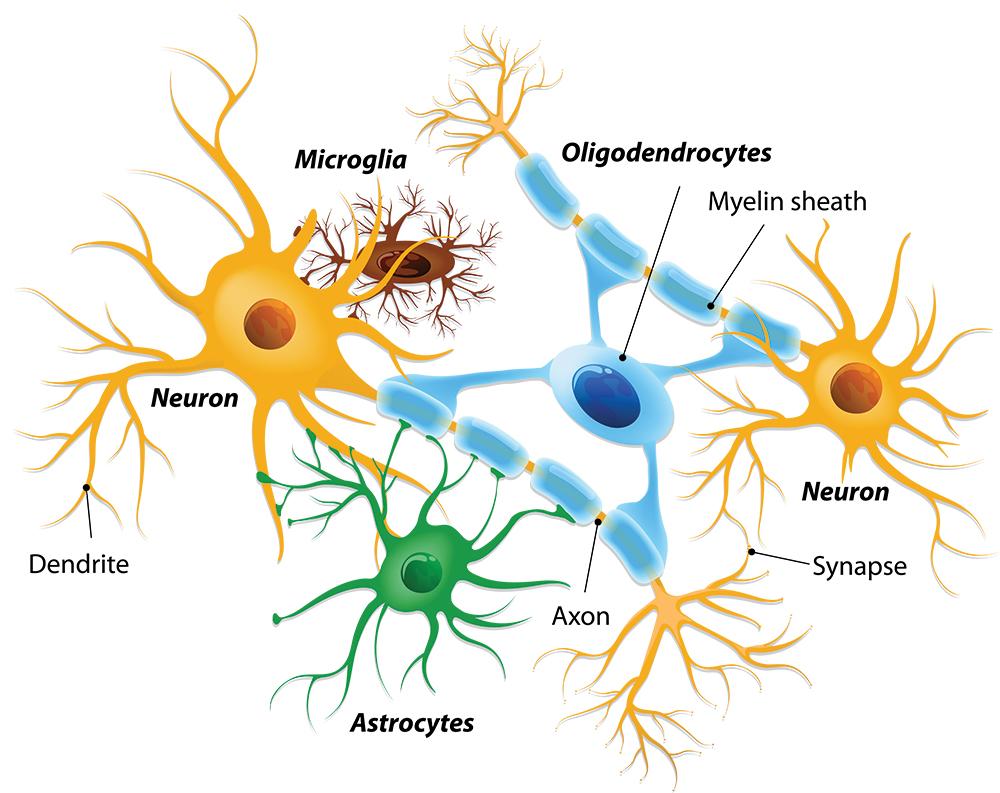
Neurons
The primary cell type in nervous tissue, responsible for conducting electrical signals (nerve impulses). Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which transmits signals).
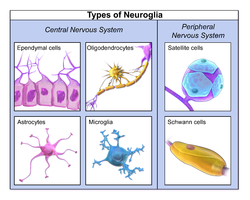
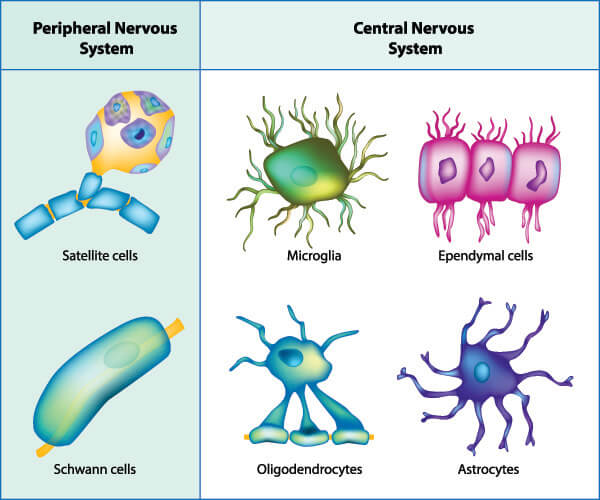
Neuroglia
Support cells found within nervous tissue that provide structural support, insulation, and protection for neurons.
Types of neuroglia include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells in the CNS, and Schwann cells and satellite cells in the PNS.
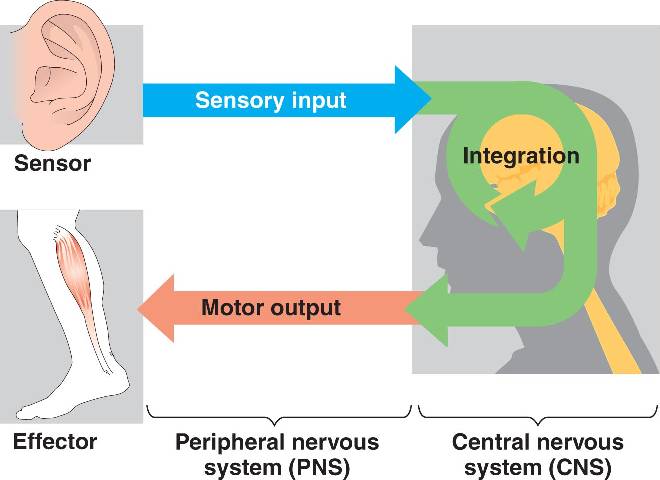
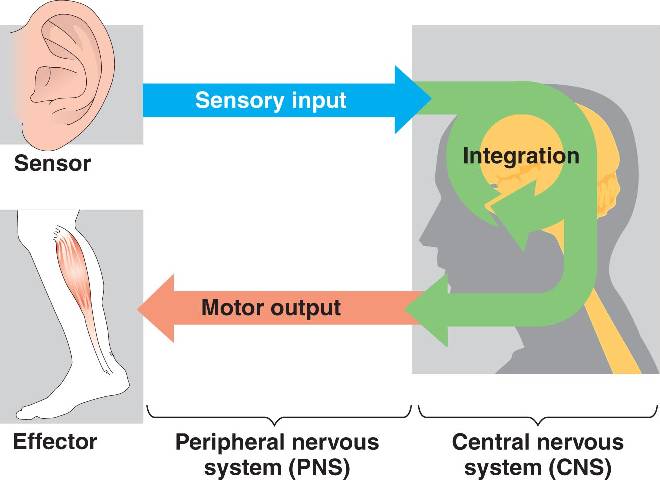
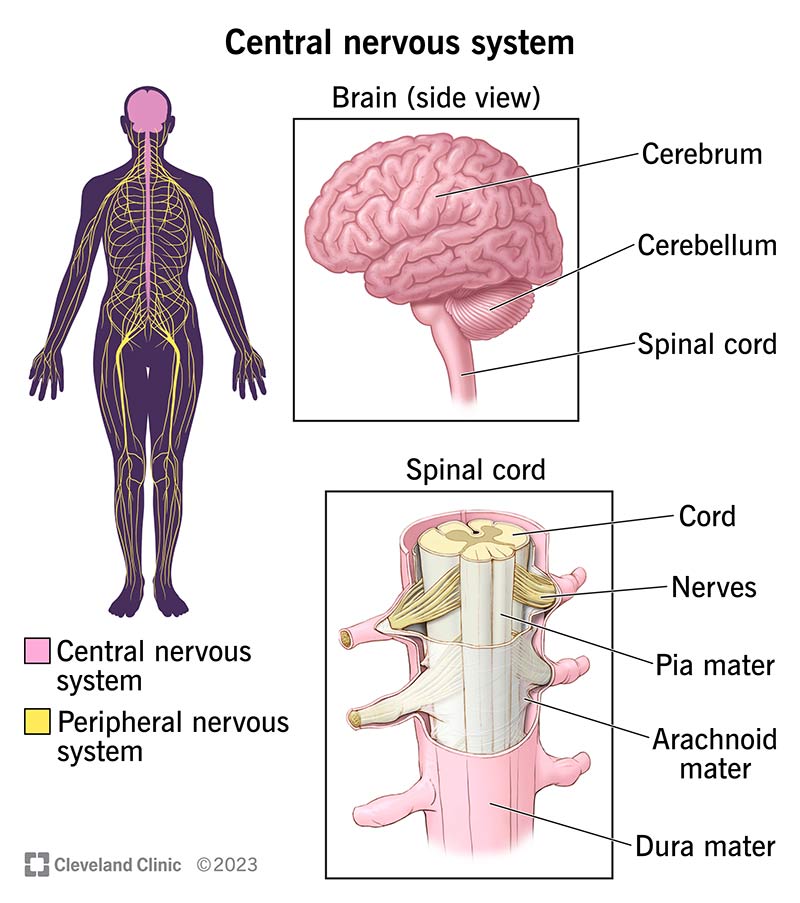
CNS
Central Nervous System; comprised of the brain and spinal cord.
The CNS receives sensory input from the PNS, processes information, and sends motor output back to the PNS to initiate actions.
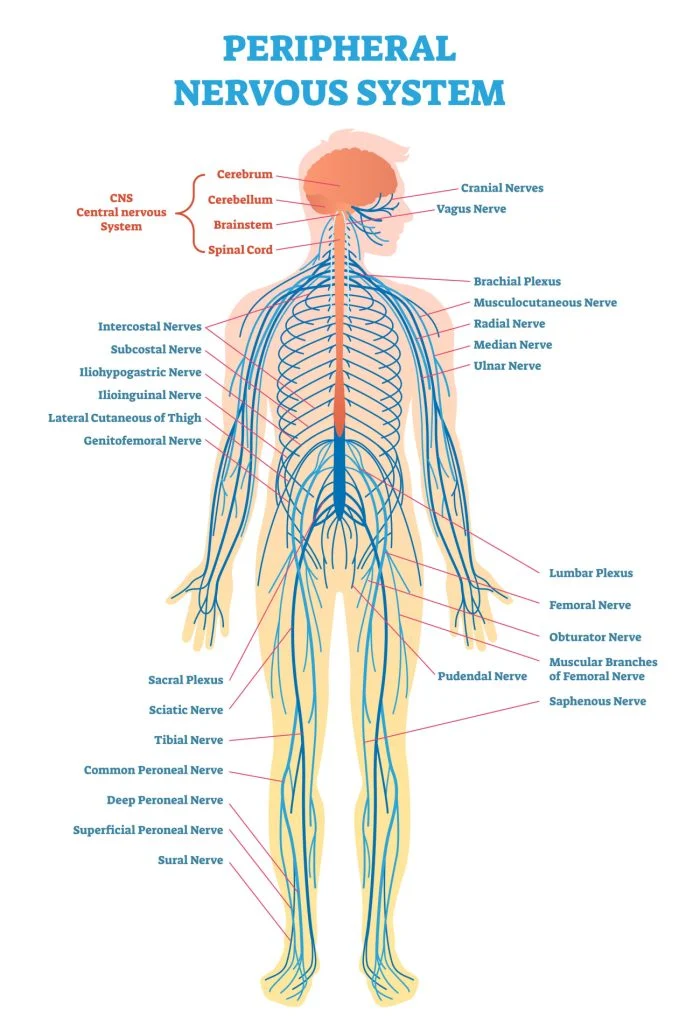
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System; encompasses all nervous tissue outside the CNS.
It includes the sensory (afferent) division, which carries sensory information to the CNS, and the motor (efferent) division, which carries motor commands from the CNS to effectors.
Somatic Nervous System
A division of the motor division of the PNS that is mostly voluntary and consciously controlled. It sends signals to skeletal muscles, enabling movement and conscious control of motor functions.
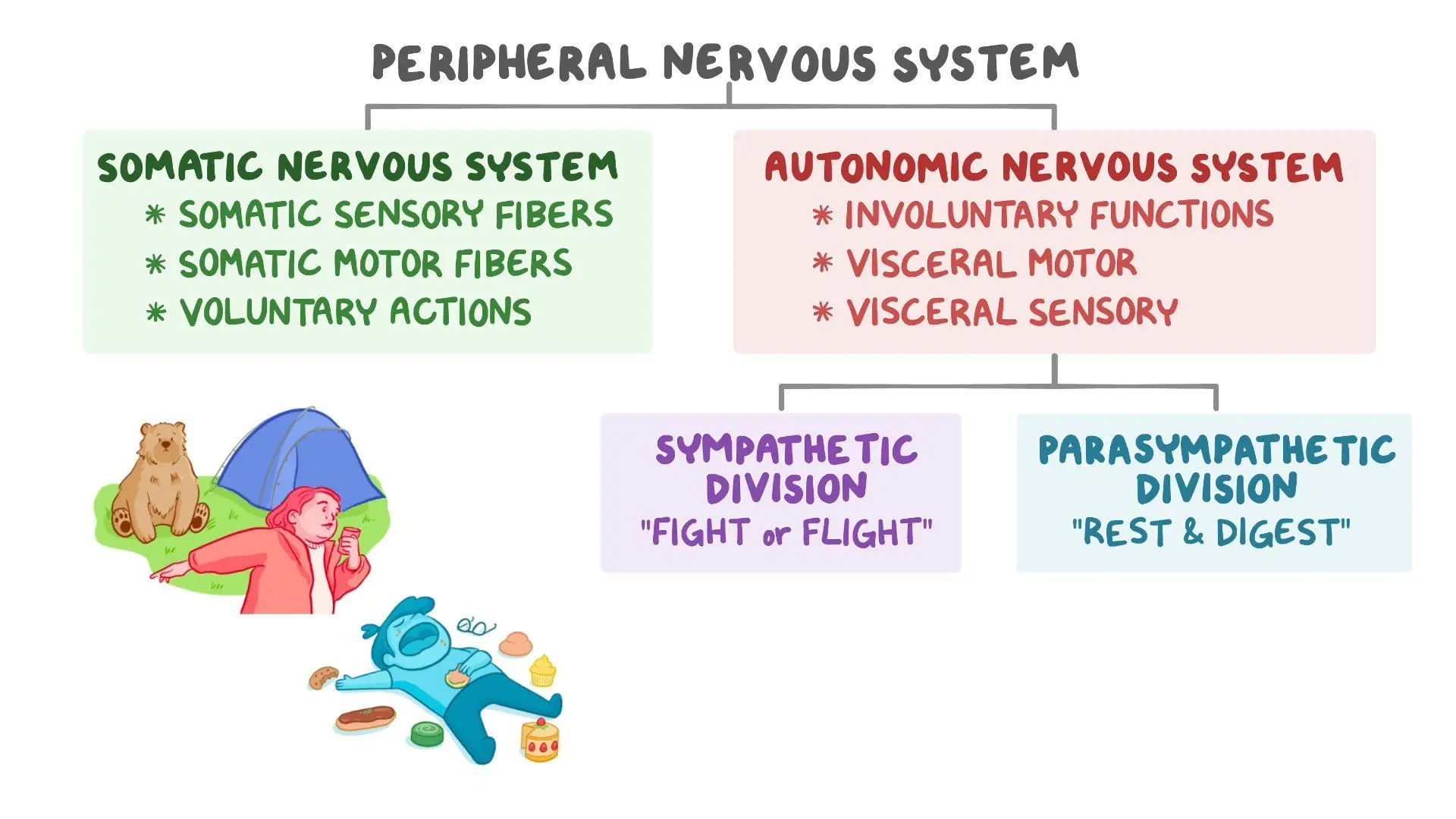
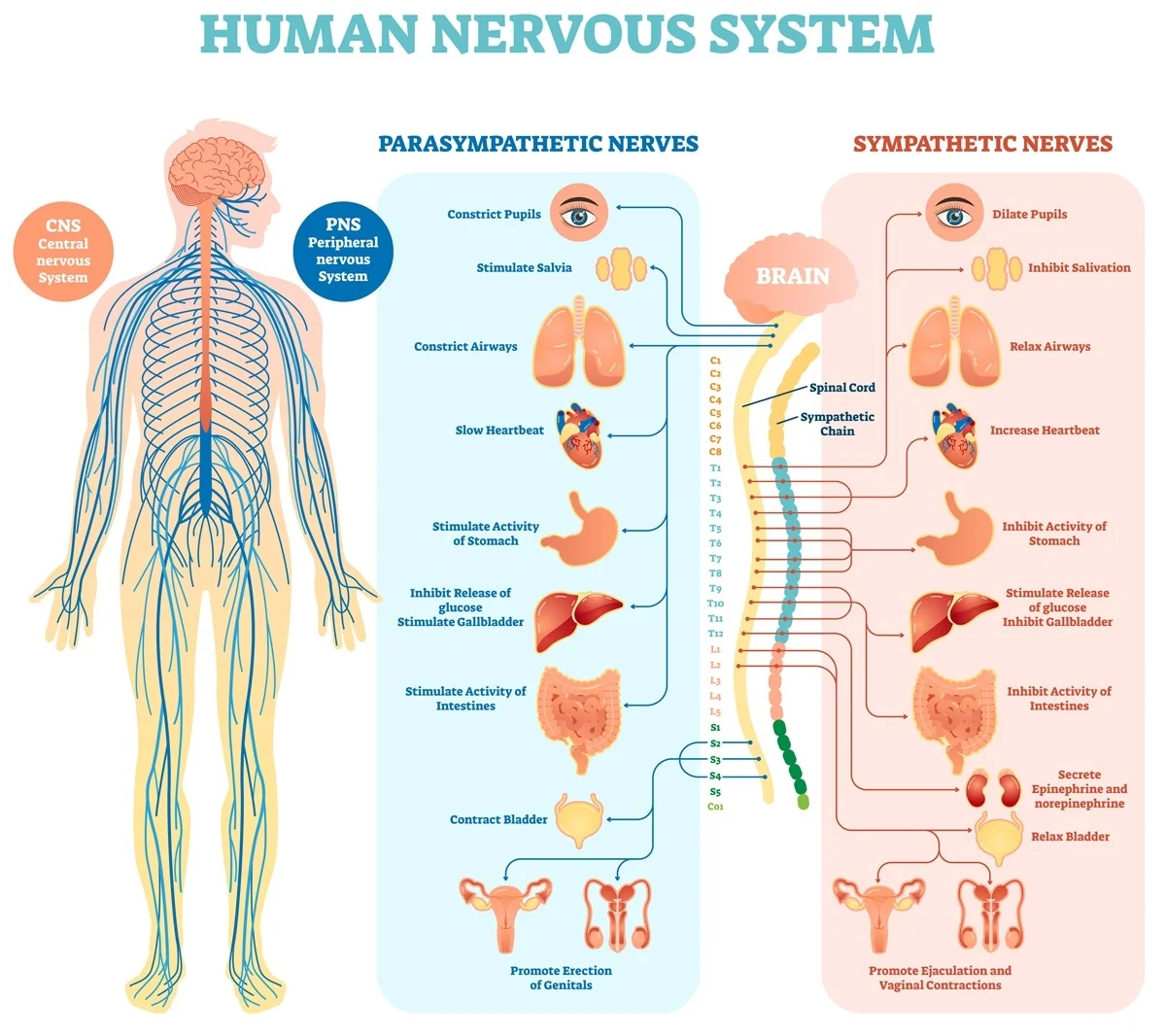
Autonomic Nervous System
A division of the motor division of the PNS that is involuntary and not consciously controlled. It sends signals to glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle, regulating functions such as heart rate, digestion, and glandular secretions.

Sympathetic Nervous System
The 'fight or flight' division of the autonomic nervous system. It prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, respiration rate, and blood flow to muscle
s, while reducing non-essential functions like digestion.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The 'rest and digest' division of the autonomic nervous system. It conserves energy by slowing heart rate, promoting digestion, and supporting processes that restore the body's resources.
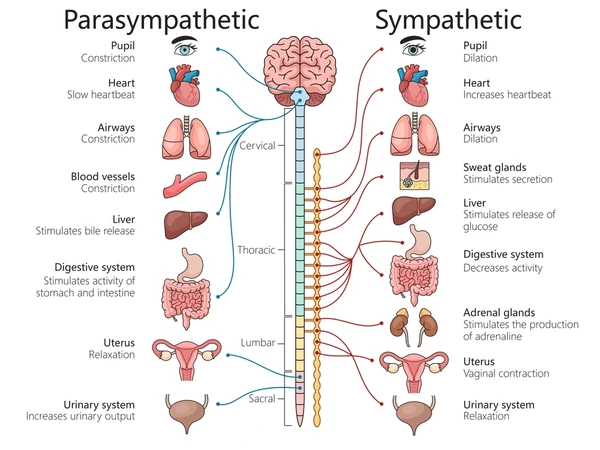
Enteric Plexuses
A network of neurons and glial cells within the walls of the digestive system. It operates independently of the brain and spinal cord to regulate digestive functions such as motility, secretion, and absorption.

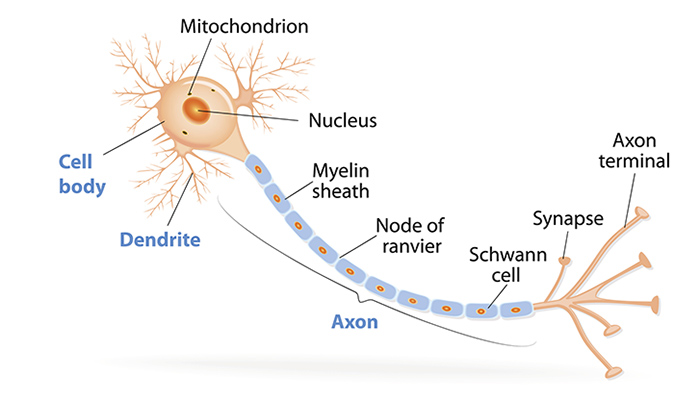
Cell Body (Soma)
Also known as the soma, it is the main part of a neuron that contains the nucleus, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, and various organelles. It integrates signals from dendrites and generates outgoing signals via the axon.
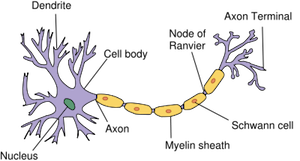
Dendrites
Branched extensions of the neuron cell body that receive input from other neurons. They contain receptors that bind neurotransmitters, initiating electrical signals that propagate toward the cell body.
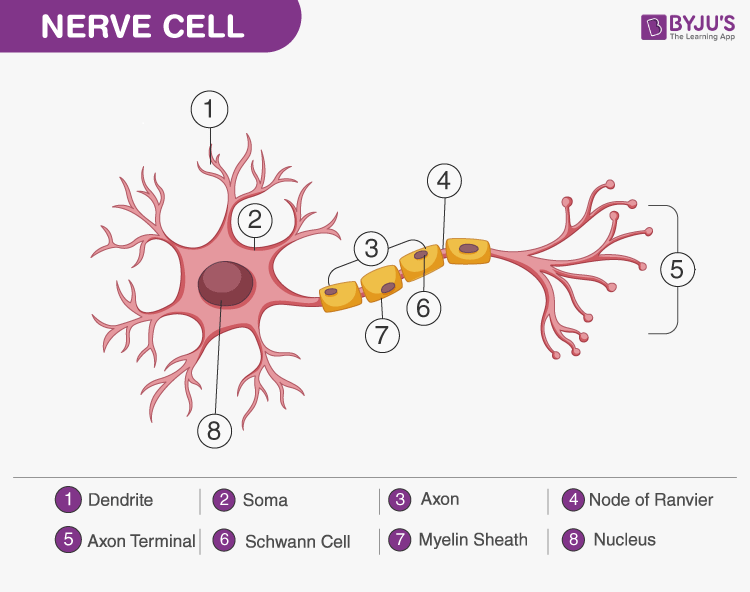
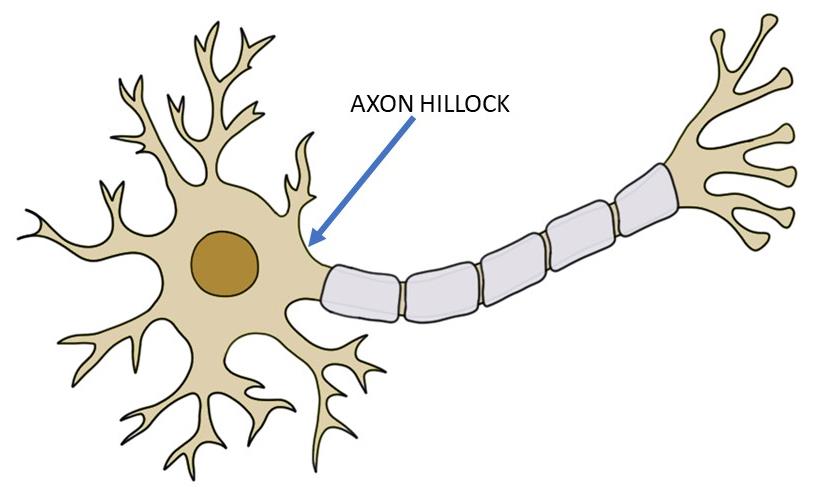
Axon
A single, long extension of the neuron cell body that transmits signals to other neurons or effectors. It originates at the axon hillock and terminates at the axon terminals, where neurotransmitters are released.
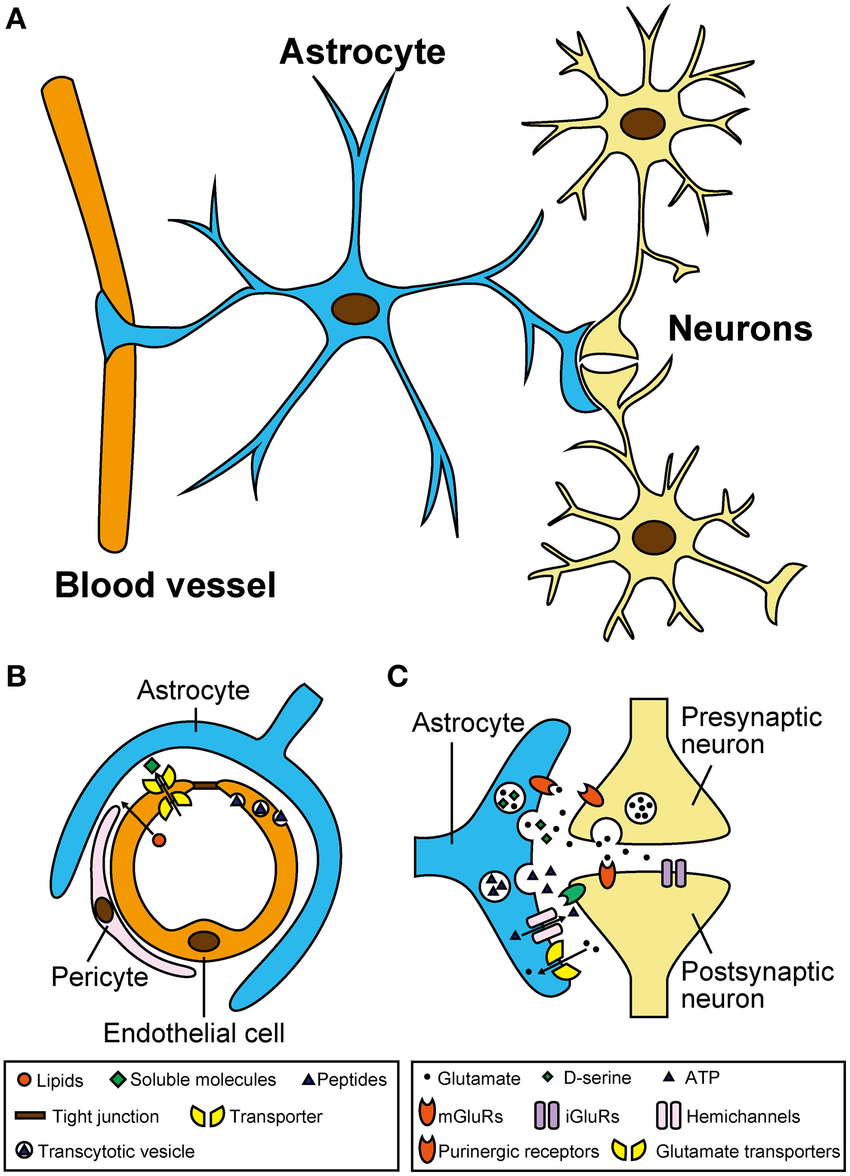
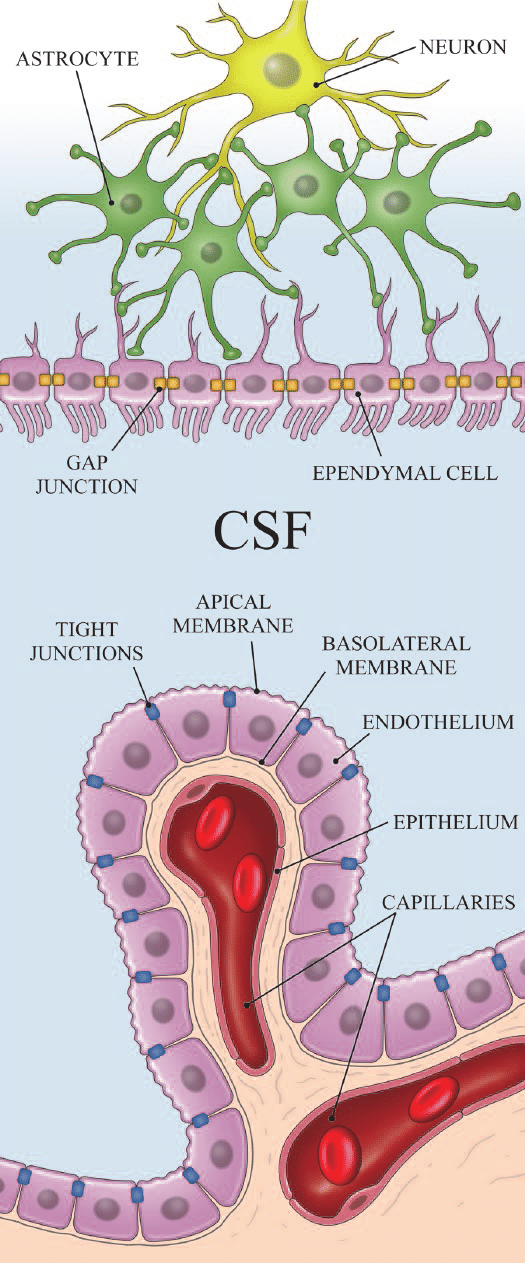
Astrocytes
A type of neuroglia in the CNS, characterized by their star-like shape.
They are the most abundant glial cells and come in two types: protoplasmic (found in gray matter) and fibrous (found in white matter).
Astrocytes support neurons, regulate the chemical environment, and form the blood-brain barrier.
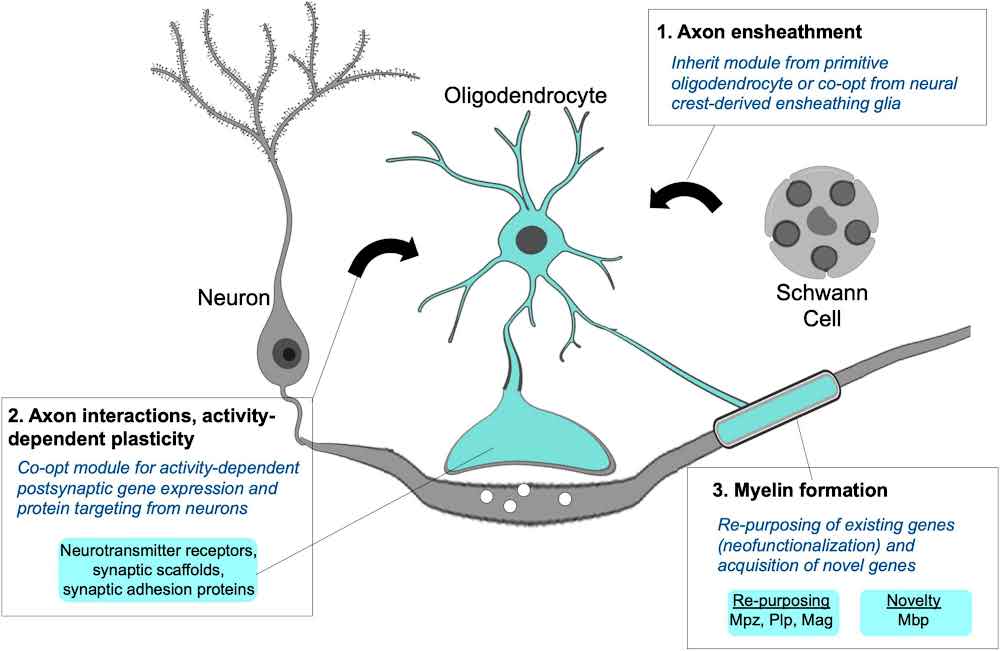
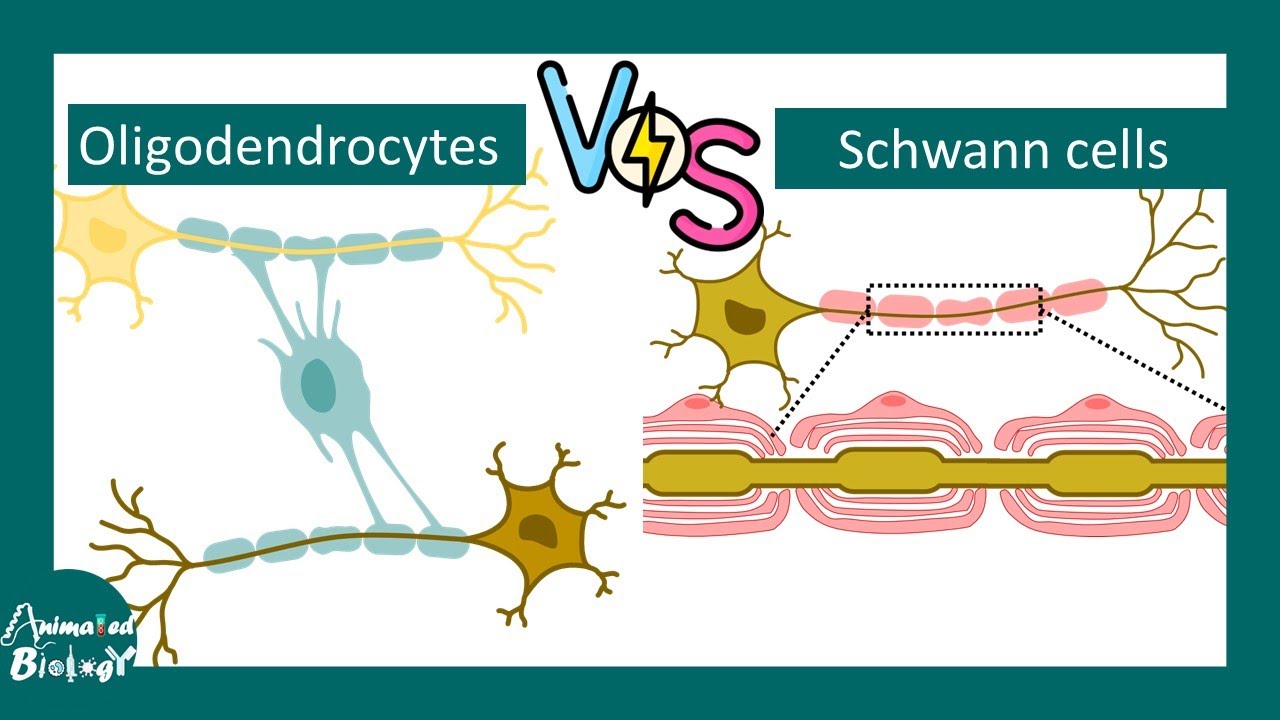
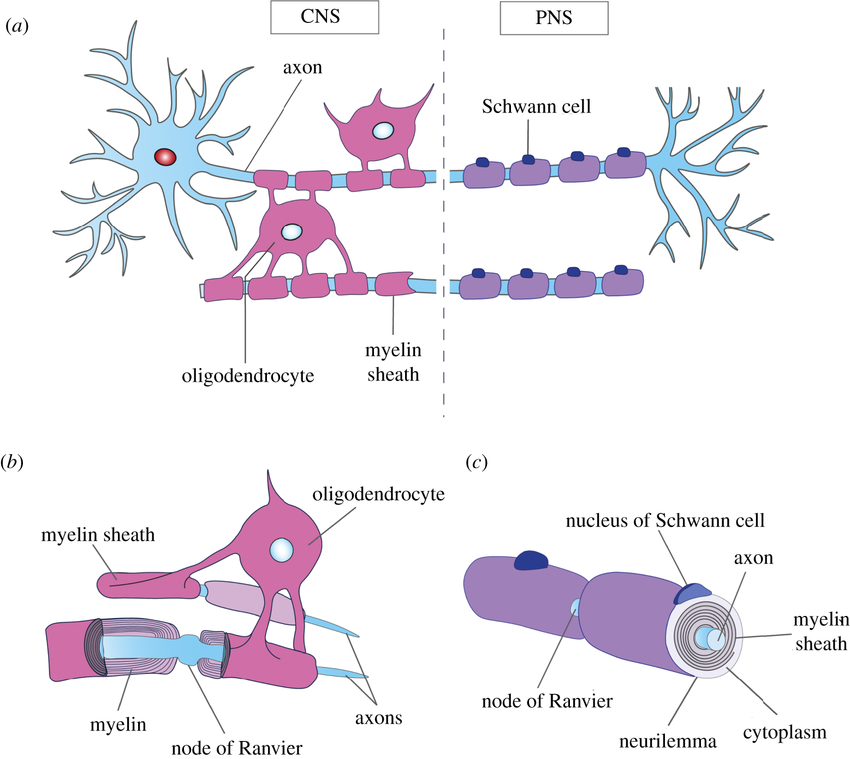
Oligodendrocytes
A type of neuroglia in the CNS that forms myelin sheaths around the axons of neurons.
One oligodendrocyte can myelinate multiple axons, providing insulation and increasing the speed of signal transmission.
Microglial Cells/Microgliocytes
Specialized immune cells in the CNS that act as phagocytes, removing cellular debris, damaged neurons, and pathogens.
They are derived from monocytes and migrate into the CNS during development.
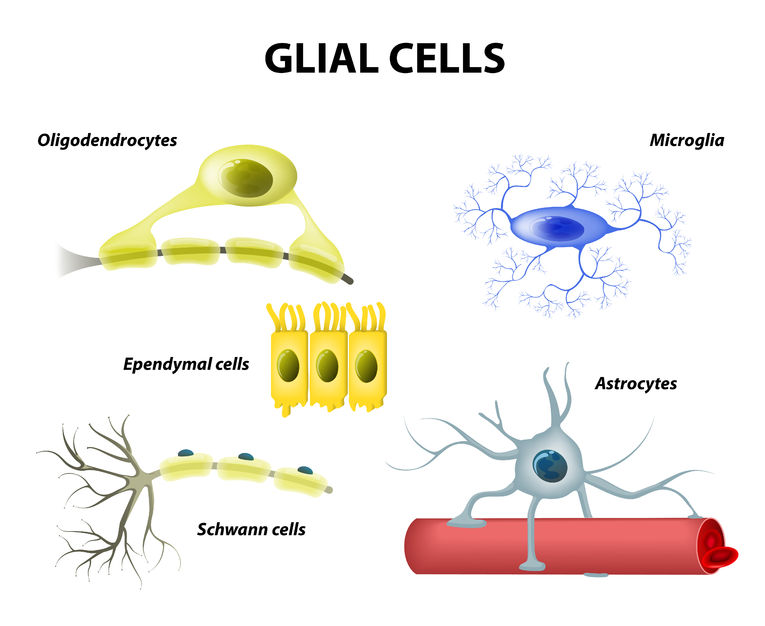
Ependymal Cells
A type of neuroglia in the CNS that lines the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord.
they produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and have cilia that help circulate the CSF.
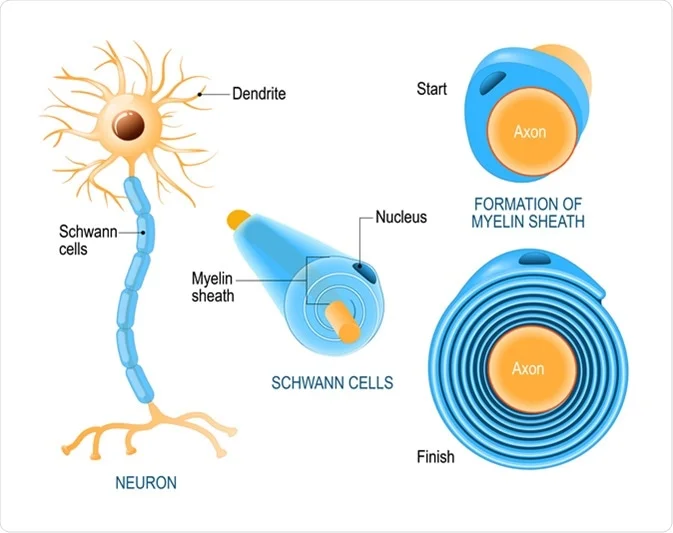
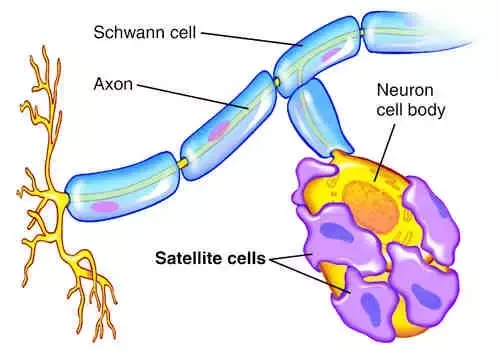
Schwann Cell
A type of neuroglia in the PNS that forms myelin sheaths around axons.
Unlike oligodendrocytes, each Schwann cell myelinates only one segment of a single axon.
They also surround unmyelinated axons, providing support and protection.
Satellite Cell
A type of neuroglia in the PNS that surrounds neuron cell bodies in ganglia.
They regulate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between neurons and the interstitial fluid.
Myelin Sheath
A multilayered lipid and protein covering around some axons, formed by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS.
It insulates the axon and increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
Ganglion
A cluster of neuronal cell bodies located outside the CNS in the PNS.
Ganglia serve as relay points for nerve signals.
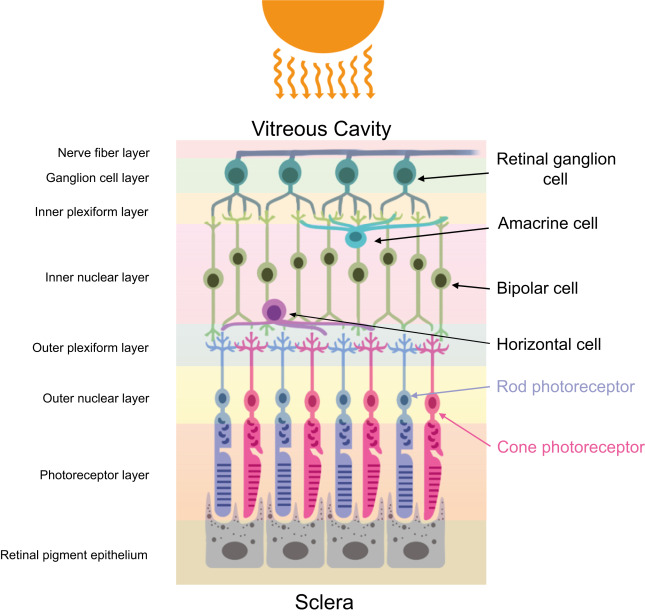
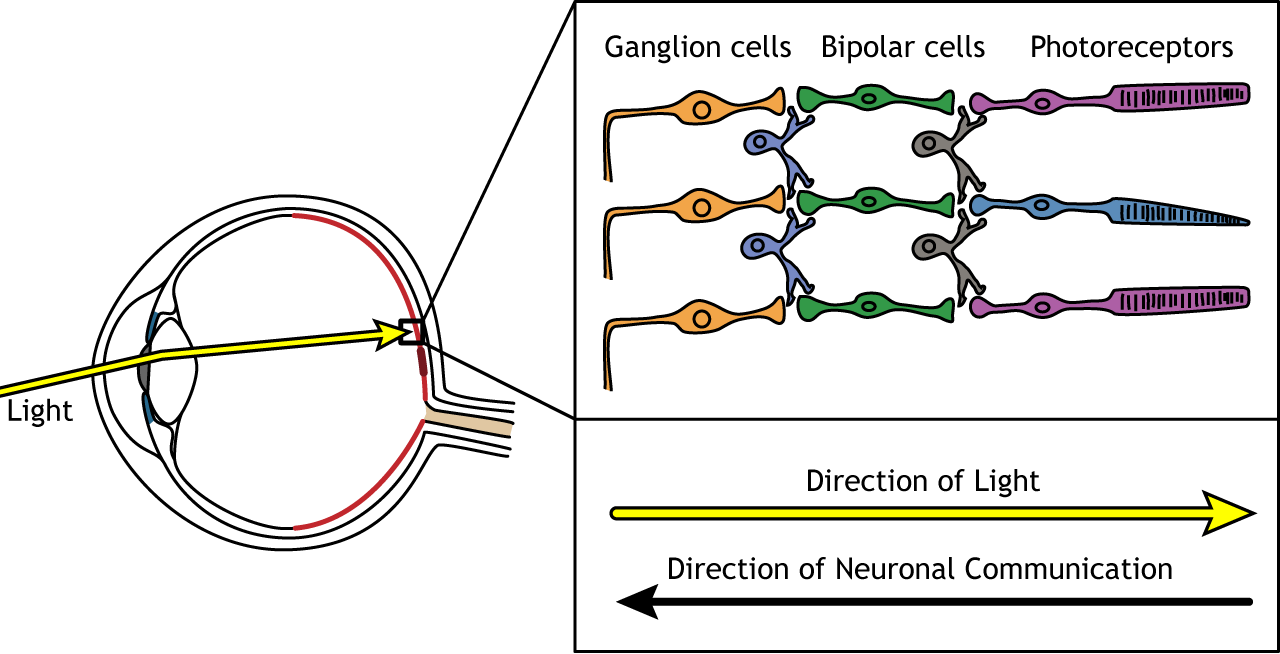
Nucleus
A cluster of neuronal cell bodies located within the CNS.
Nuclei are involved in various functions, such as sensory processing, motor control, and autonomic regulation.
Nerve
A bundle of axons located outside the CNS in the PNS. Nerves transmit signals between the CNS and the body.
Tract
A bundle of axons located within the CNS.
Tracts connect different regions of the brain and spinal cord, facilitating communication between them.
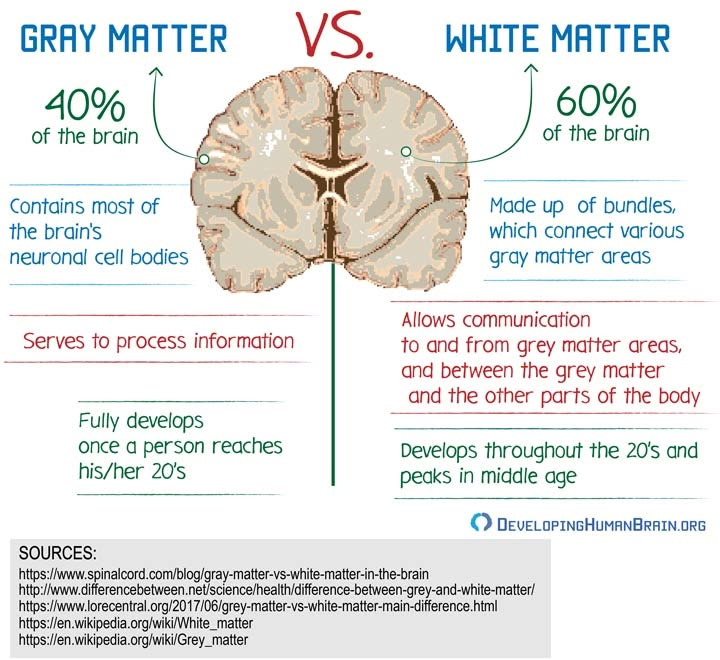
Gray Matter
Nervous tissue that primarily contains unmyelinated axons, dendrites, cell bodies, axon terminals, and neuroglia.
It is abundant in the cerebral cortex and central portions of the spinal cord and is involved in processing and integration of information.
White Matter
Nervous tissue that primarily contains myelinated axons.
It forms the major tracts within the brain and spinal cord, facilitating communication between different areas