IDing histamine structures Metcalf
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
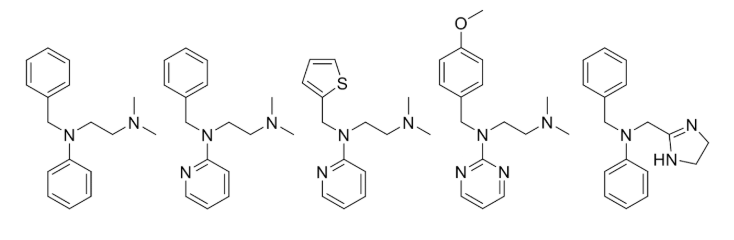
Ethylenediamines
1st gen H1 antihistamines
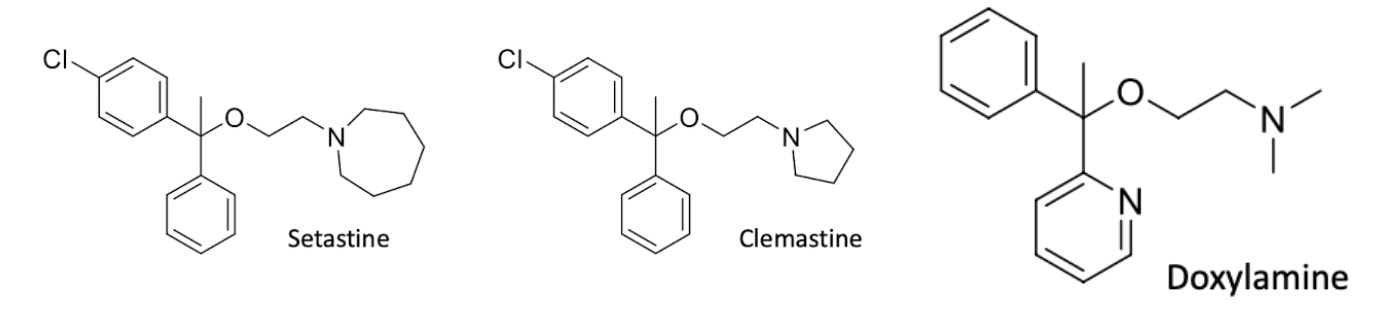
Ethanolamine ethers
1st gen H1 antihistamines
Alkylamines
1st gen H1 antihistamines
Piperazines
1st gen H1 antihistamines, multiple effects
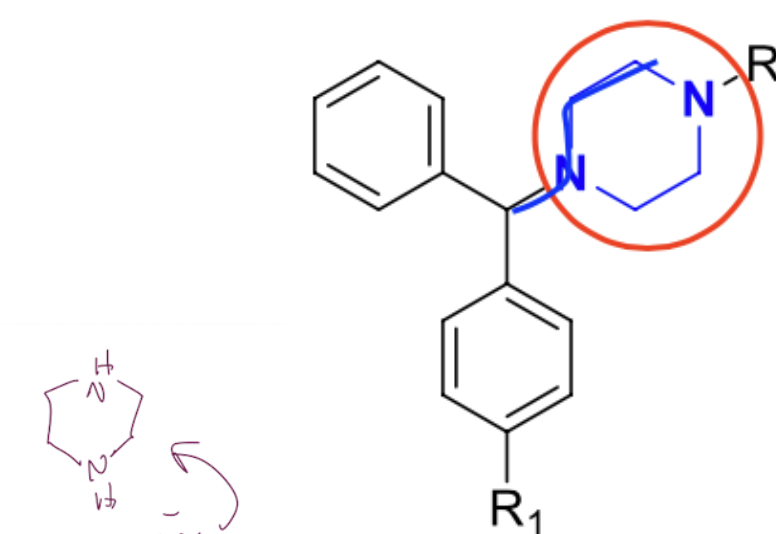
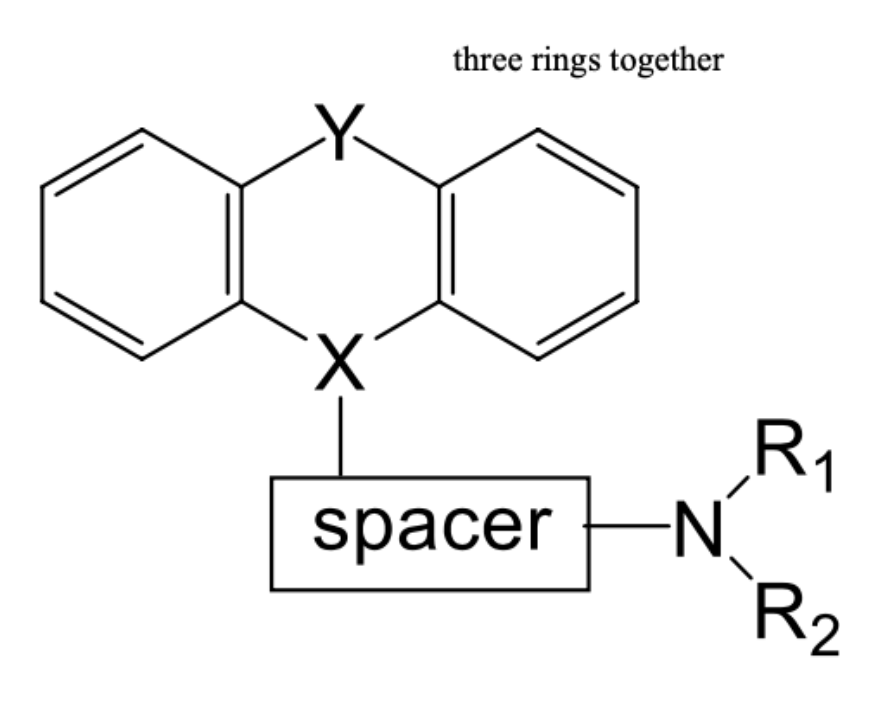
Tricyclics
1st gen H1 antihistamines, multiple effects
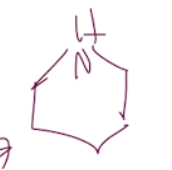
Piperadine
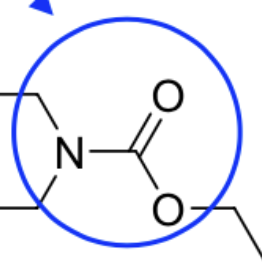
Carbomate
Fexofenadine
2nd Generation, H1, Non-sedating antihistamine
Blockade of hERG K+ channels
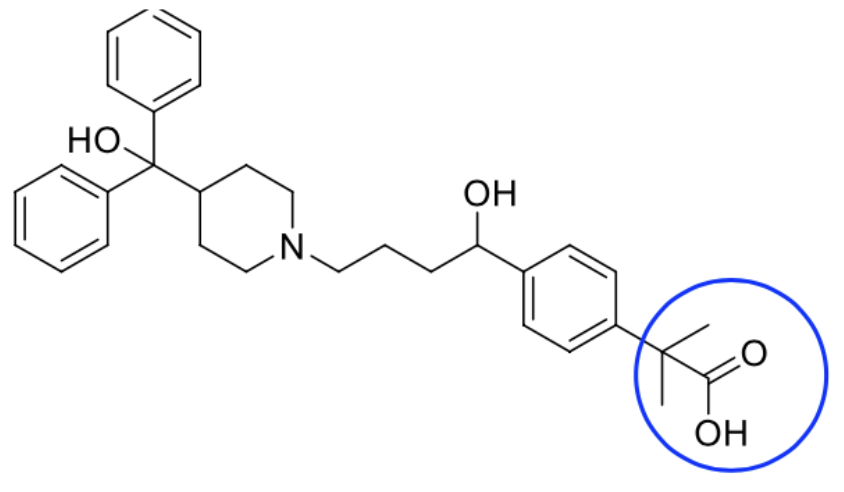
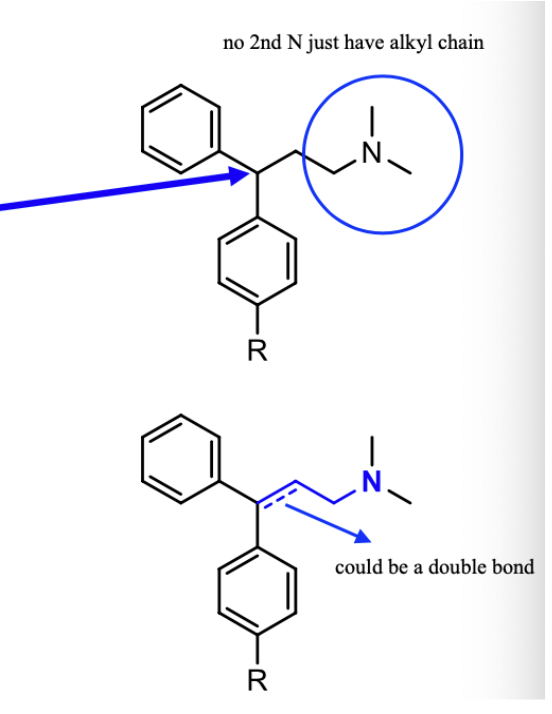
LOOK FOR THE BLUE CIRCLED STRUCTURE FOR DRUGS ENDING IN “ine”
Terfenadine, Astemizole
Life threatening hERG K+ ion channel
Not marketed
Loratadine, Desloratadine
2nd Generation, H1, Non-sedating antihistamine
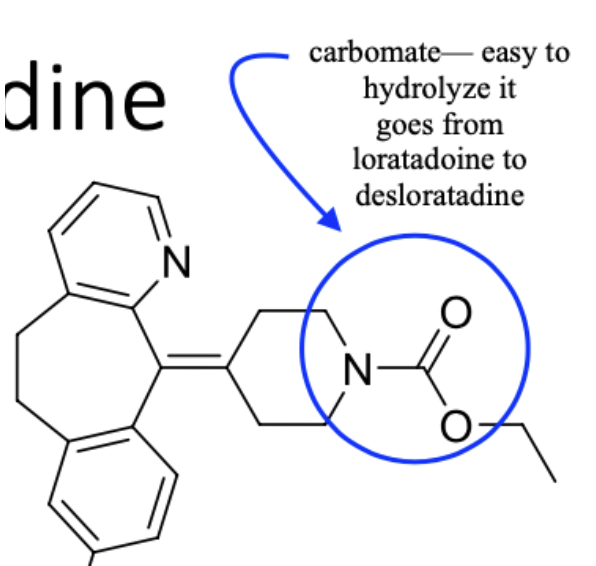
Cetirizine
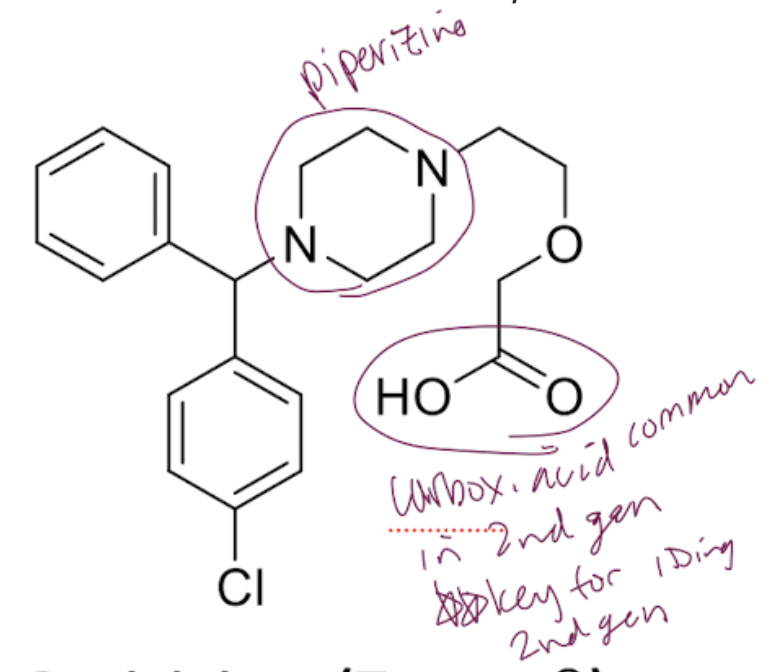
hydroxyzine oxidized to make this
2nd gen
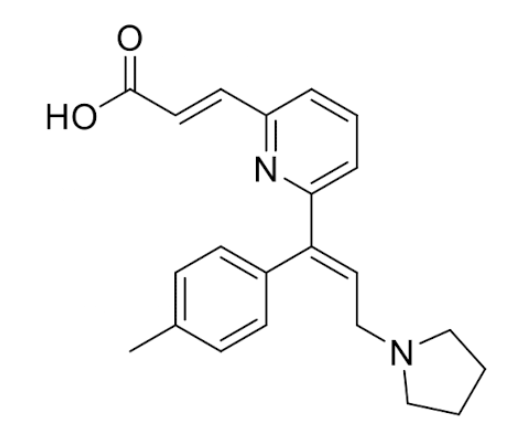
Acrivastine
Second gen non-sedating antihistamine: notice constrained amine
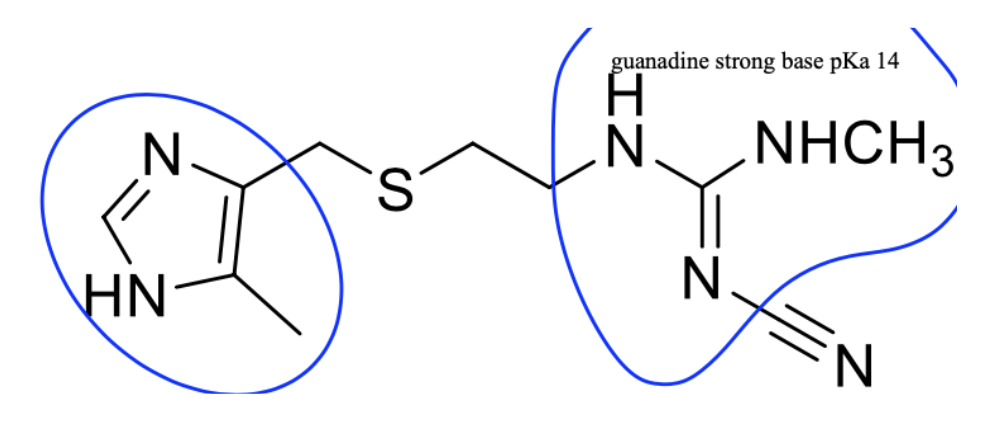
H2 antagonists (ex: Cimetidine)
Imidazole ring like histamine (causes increases side effects)
4 atom side chain includes sulfur
EWG Substituted guanidine
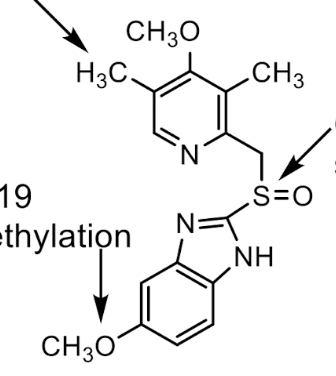
PPIs (ex: Omeprazole)
Metabolized by CYP 2C19
Isomers metabolized unequally in patient populations — Use of S isomer (Esomeprazole) provides greater bioavailability in extensive metabolizers