Bio98 Lecture 14 TCA Cycle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Know the different reactions and enzymes in the TCA cycle (substrates mnemonic)
Please Can I Keep Selling Sex for Money, Officer?:
Pyruvate, Citrate, Isocitrate, α-Ketoglutarate, Succinyl-CoA, Succinate, Fumarate, Malate, Oxaloacetate
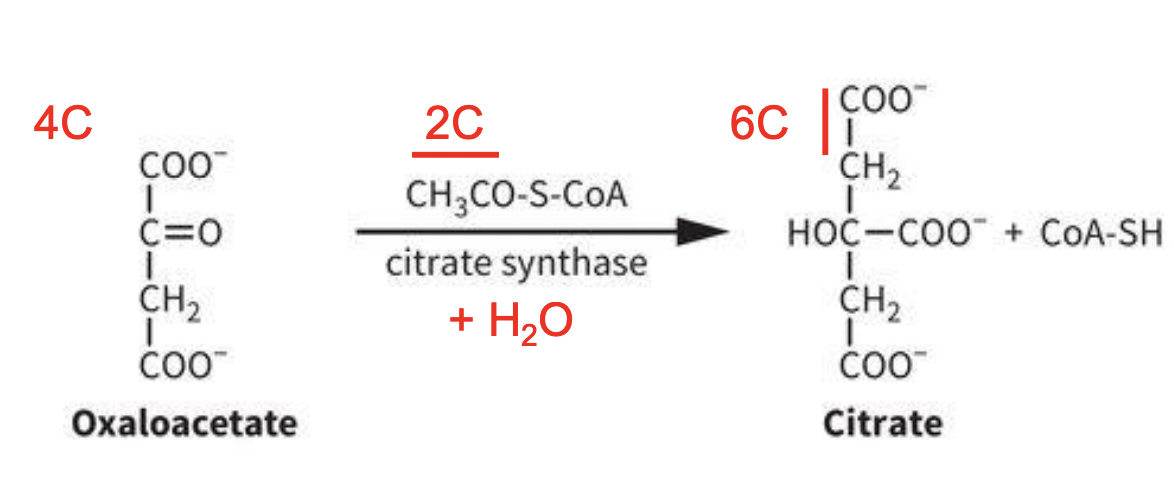
TCA Rxn 1: Acetyl-CoA Condensation w/ OAA
IRREVERISIBLE RXN: Aldol condensation (H2O release).
Oxaloacetate/OAA (4C) + acetyl-CoA (2C) → regenerates free CoA and Citrate (6C)
Enzyme: carried out by citrate synthase + release of H2O
Acetyl-CoA forms the enolate
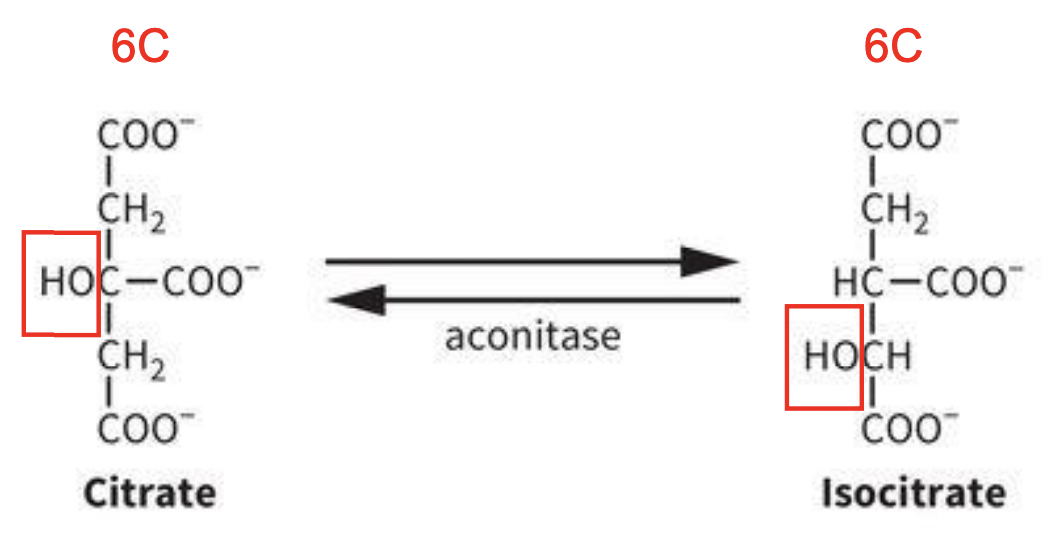
TCA Rxn 2: Isomerization of Citrate
REVERSIBLE RXN:
COMBINED DEHYDRATION-HDYRATION RXN: isomerizes tertiary alcohol citrate to secondary alcohol isocitrate
-Citrate (prochiral) turns into isocitrate (stereospecific rxn produces only one isomer) through aconitase (enzyme); basically just relocates the OH in diff positions
Fluoroacetate (1080) poison
Fluorocitrate is a suicide substrate for aconitase ; Australian “poison peas”
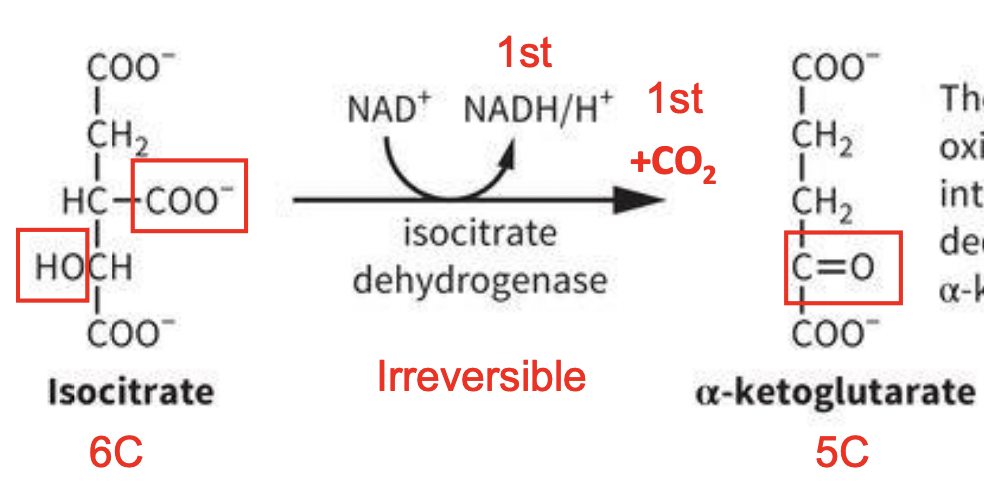
TCA Rxn 3: Oxidation of isocitrate to α-KG
IRREVERSIBLE RXN:
Summary: the secondary alcohol in isocitrate (6C) is oxidized (dehydrogenated) to give the intermediate oxalosucciante, which decarboxylates to give α-KG or α-ketoglutarate (5C)
-carried out by ISOCITRATE DEHYDROGENASE (IDH)
-uses NAD+ to release 1st NADH/H+ & 1st CO2 released
removal of a CO2 (decarboxylation rxn)
-regulated by substrate availability and product inhibition
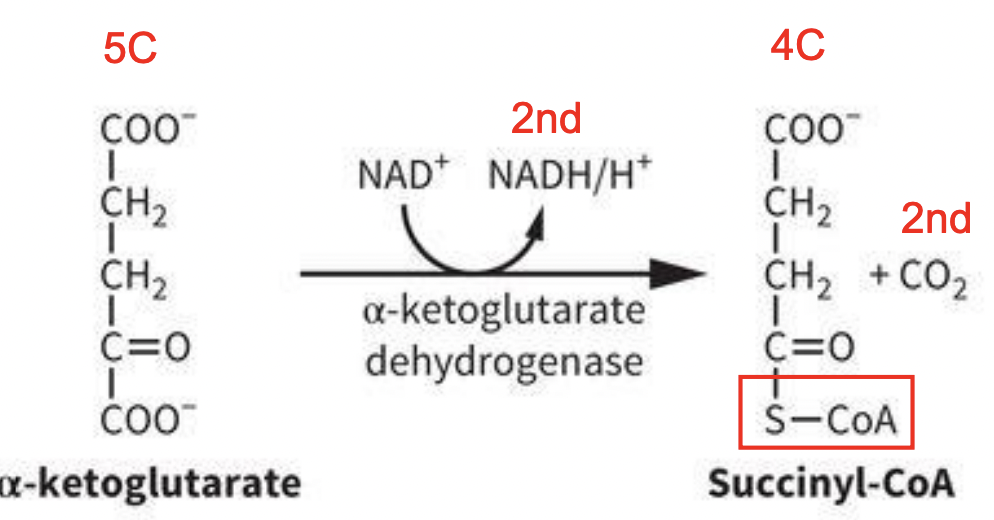
TCA Rxn 4: α-KG oxidative decarb. to succinyl-CoA
IRREVERSIBLE RXN:
Summary: α-ketoglutarate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation, a concerted rxn in which the carboxyl group closest to the carbonyl is lost as CO2 and succinyl-CoA is formed.
-1) α-ketoglutarate (5C) undergoes oxidative decarboxylation bc of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase ( KGDH enzyme) → NAD+ is required = release of 2nd NADH/H+
-2) Succinyl-CoA (4C) and 2nd CO2 made
Nomenclature: α-KG is oxidized, NAD+ is reduced. When something is oxidized, something else is reduced
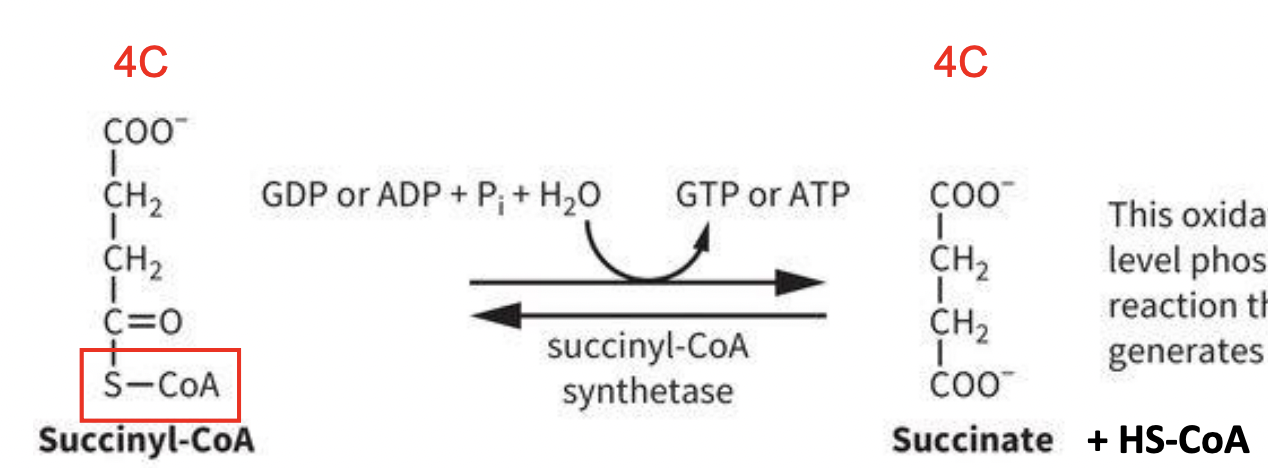
TCA Rxn 5: Succinyl-CoA to succinate
REVERSIBLE RXN:
-oxidation & substrate level phosphorylation rxn; rxn that directly generates ATP or GTP.
-Thioester provides energy for phosphorylation.
since GDP/ADP are getting phosphorylated (ie the substrate) rather than protein, that’s termed as substrate level phosphorylation.
-1) Succinyl-CoA (4C) undergoes rxn bc of succiynl-CoA synthetase (enzyme); GDP or ADP + Pi + H2O make GTP or ATP
-2) Succinate(4C) + HS-CoA are also made
TCA Rxn 6: Oxidation of succinate to fumarate
REVERSIBLE RXN: (THE ARROW SHOULD BE REVERSIBLE)
Summary: in this oxidation, e-s from succinate are transferred to FAD to form the trans dioic acid fumarate
-1) Succinate (4C) undergoes rxn bc of succinate dehydrogenase; FAD accepts electrons, gets reduced, oxidizes C-C bonds, and makes FADH2
-2) Fumarate (4C) gets made
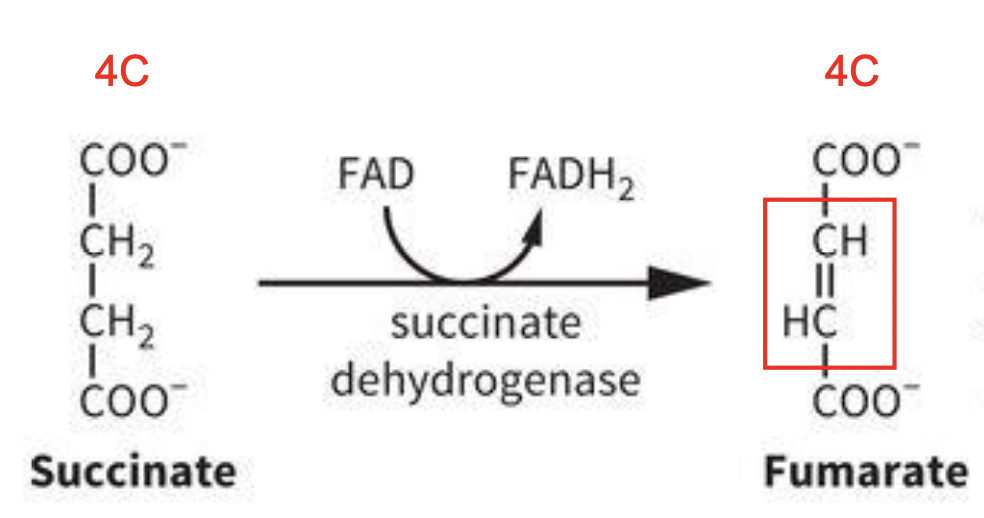
-All the other TCA enzymes are soluble in matrix but his onte is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane (close to ETC)
TCA Rxn 7: Hydration of fumarate to malate
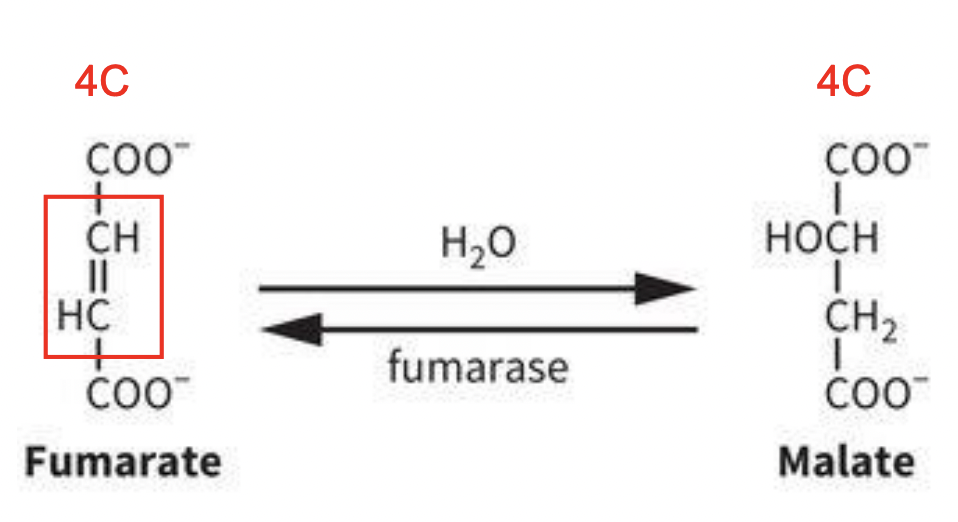
REVERSIBLE RXN:
Summary: the alkene moiety of fumarate is hdyrated to form the secondary alcohol in malate
Fumarate (4C) undergoes hydration (H2O) + fumarase (enzyme) = Malate (4C)
Fumarase Deficiency
-Autosomal recessive, leads to physical and neurological abnormalities 1:400 million chance in “the wild”
-Super rare, ~100 cases total worldwide, almost entirely within the FLDS community Genetic disorders impacting central metabolism (TCA) are extremely rare because of its importance to life
TCA Rxn 8: Oxidation of Malate to Oxaloacetate
REVERSIBLE RXN:
Summary: the hydroxyl group of malate is oxidized to the carbonyl of oxaloacetate. The e-s are harvested to NAD+ in the process.
-1) Malate (4C) undergoes rxn bc of malate dehydrogenase & NAD+ → release of 3rd NADH/H+
-2) Makes low oxaloacetate (4C)
Which are the irreversible steps? Do they have neg. or positive ΔG?
Rxn 1 (citrate synthase), 3 (IDH), 4 (KGDH); have largest negative overall ΔG
TCA Recap and Final Numbers
• Overall, we have produced:
• 3 NADH
• 1 FADH2
• 1 ATP (or GTP)
• 2 CO2
• Per molecule of glucose, TCA makes:
• 6 NADH
• 2 FADH2
• 2 ATP (or GTP)
Glycolyiss + PDH + TCA total
TOTAL: 4xATP + 10xNADH + 2xFADH2 per glucose up to this point
-Glycolysis- Net 2xATP + 2Xs Pyruvate + 2xNADH per glucose (uses 2 ATP but generates 4)
-PDH- 1xNADH per pyruvate (2x per glucose)
-TCA- 1xATP + 3xNADH + 1xFADH2 per acetyl-CoA (2x per glucose)
Anaplerotic rxn or “anaplerosis”
Molecules that are synthesized out of the TCA cycle can often be converted back into TCA intermediates
In pancreatic cancer cells, glutamine provides nearly all the carbon that goes through the TCA cycle