Aromatic Compounds 17.1, 17.3-17.4, 17.8
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
aromatic
a compound containing a planar ring of continuously overlapping p orbitals with 4n + 2 𝜋 electrons
double, single
a benzene ring is comprised of alternating _____ and _____ bonds
resonance structures
is the exchange of alternating double and single bonds in an aromatic ring an equilibrium process or are they resonance structures
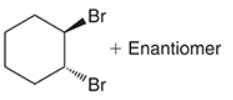
predict the product of this RXN
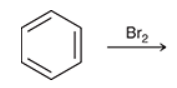
no reaction
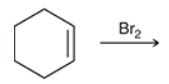
predict the product of this RXN
stability
aromatic rings exhibit a special/unusual _____ that would be lost if an addition reaction were to occur
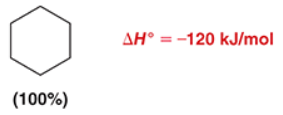
predict the product of this RXN
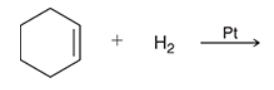
3, hydrogen, cyclohexane
benzene is generally stable to hydrogenation under standard conditions but under forcing conditions (high pressure/temp.), benzene also undergoes hydrogenation and reacts with _ equivalents of molecular ______ to form __________
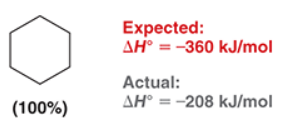
predict the product of this RXN
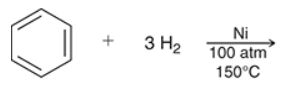
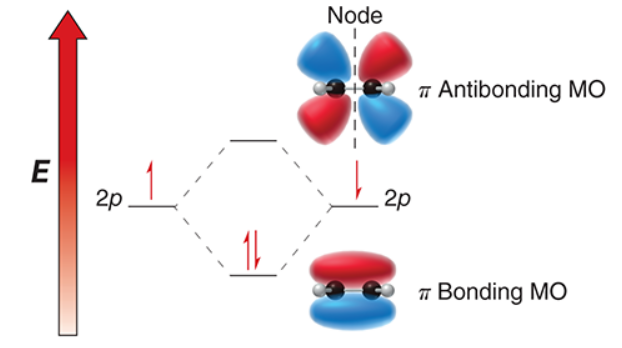
bonding, antibonding
the lower energy MO is the ______ MO while the higher energy MO is the ______ MO (antibonding/bonding)
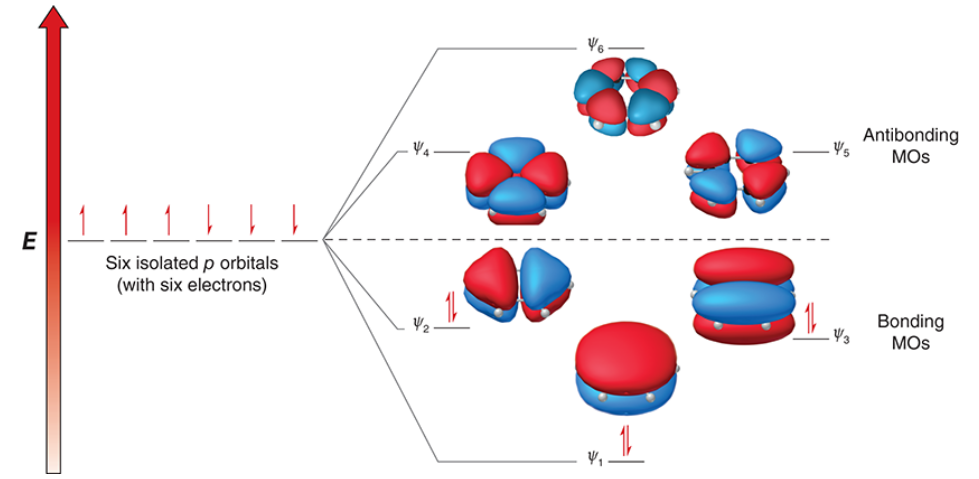
6
benzene is comprised of _ overlapping p orbitals which are replaced with the same number of MOs
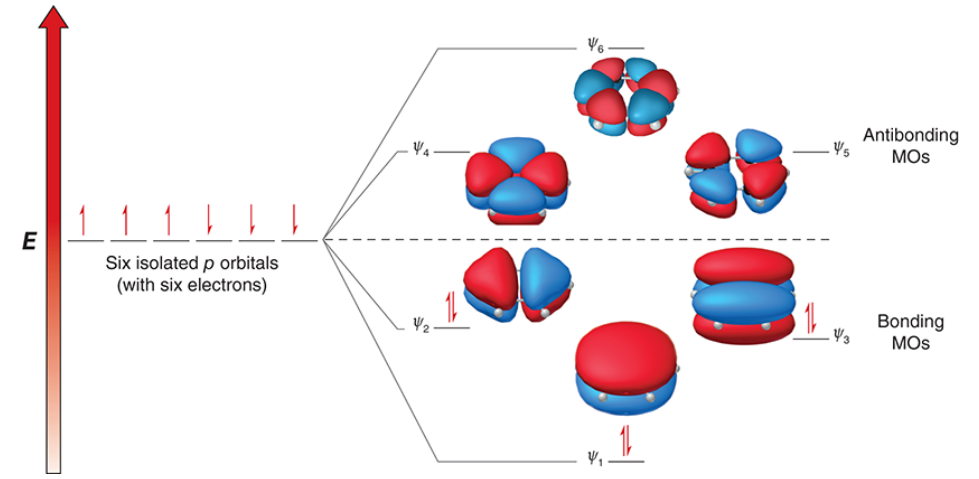
2, 6, 6, lower, closed
3 of the 6 MOs in benzene are bonding MOs, and the other 3 are antibonding MOs
since each MO can contain _ electrons, the 3 bonding MOs can collectively accommodate up to _ π electrons
by occupying the bonding MOs, all _ electrons achieve a _____ (higher/lower) energy state and are delocalized
since the bonding MOs are filled with paired electrons while the antibonding MOs are empty, benzene is said to have a _____-shell electron configuration which is the source of the stabilization energy associated with benzene
bonding, antibonding, closed
since the ______ MOs are filled with paired electrons while the ______ MOs are empty, benzene is said to have a _____-shell electron configuration which is the source of the stabilization energy associated with benzene
the number of π electrons in the ring
on top of the presence of a fully conjugated ring of π electrons, what else is also an important requirement for aromaticity?
odd, 3
is an even or odd number of pairs of π electrons required for aromaticity? how many?
6, 3
benzene has a total of _ π electrons, or _ electron pairs
Huckel’s rule
the requirement for an odd number of π electron pairs in order for a compound to be aromatic
unstable
is an open-shell configuration stable or unstable?
stable
is a closed-shell configuration stable or unstable?
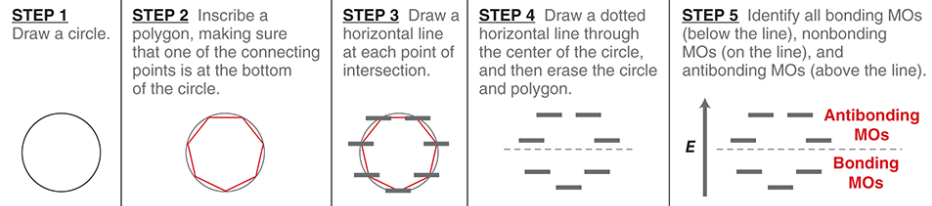
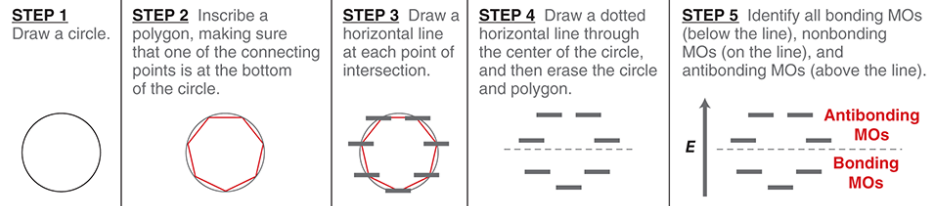
Frost circle
a simple method for drawing the relative energy levels of the MOs for a ring assembled from continuously overlapping p orbitals
odd
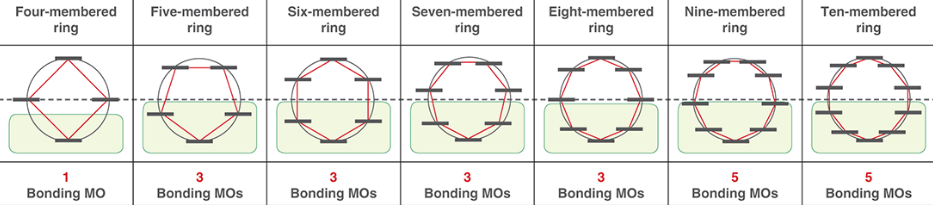
is the number of bonding MOs always even or odd?
5
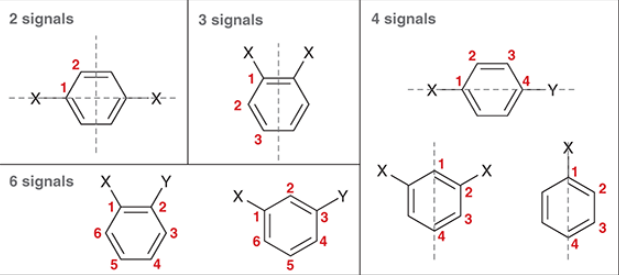
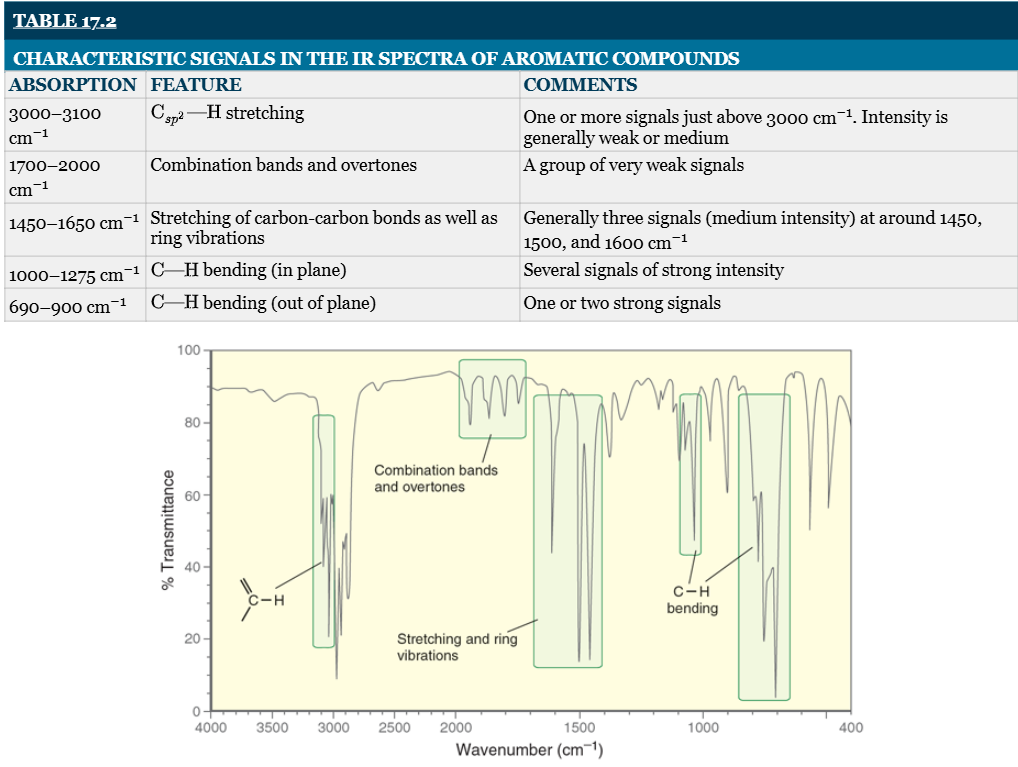
benzene derivatives generally produce signals in _ characteristic regions of an IR Spectrum
6.5, 8
in an H NMR spectrum, signals that indicate an aromatic ring appear between ___ to ___ ppm
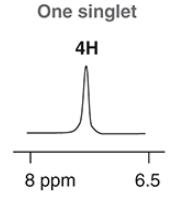
singlet, 4
a benzene ring with 2 of the same substituents across each other will have a ________ signal(s), and a signal will have an integration of _ H
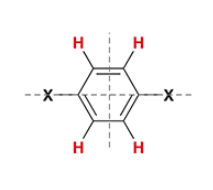
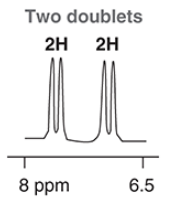
doublet of doublet, 2
a benzene ring with 2 different substituents across each other will have a ________ signal(s), and a signal will have an integration of _ H
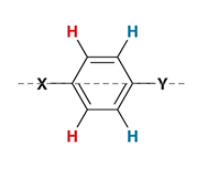
100, 150
the carbon atoms of aromatic rings typically produce signals in the range of ___ to ___ ppm in a C NMR spectrum