B1.1: Carbohydrates and LIpids IBDP Biology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Chemical properties of carbon atom
-Carbon has 4 valencies, can form 4 single bonds or 2 double bonds or both single and double
- covalent bonds with other compounds
-Covalent bonds formed by carbon atom can spread apart to form a tetrahedral shape
-there can be branced or unbranced chains formed
- formation of single or multiple rings
what are macromolecules
large molecules formed from a lagre number of atoms
what are monomers
Subunits of polymers, which may be identical or of different types
what are polymers
long chain of monomers used to form macromolecules
examples/ classes of macromolecules
polysaccharides (ex: cellulose) , poplypeptides(proteins) and nucleic acids(DNA)
polymers can turn to monomers by which reaction
hydrolysis
what is hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
-Water molecules are split to provide the -H and -OH groups that are incorporated to produce monomers,
hence the name of this type of reaction.
which elements do carbohydrates contain
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What are monosaccharides?
simple sugars
have 3-7 carbon atoms
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose (hexose sugar), ribose (pentose sugar), fructose
how are monosaccharides linked
by condensation reactions to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
properties of monosacchride (ex:glucose)
-soluble and small
-easily transported
-circulates in blodd, dissolved in plasma
- chemically stable
-if stored in large quantities can cause osmotic problems
-yields energy when oxidised
Oligosaccharides
2-8 units of carbohydrates
Polysaccharides
9 or more units of carbohydrates
examples of polysacchardies
starch, glycogen, cellulose
why are polysaccharides used as enegry stores
compact nature of starch in plants and glycogen in animals due to coiling and branching during polymerization
-the relative insolubility of these compounds due to large molecular size and the relative ease of adding or removing alpha-glucose monomers by condensation and hydrolysis to build or mobilize energy stores.
what are the bonds formed in polysaccharides
1-4 glycodisc bonds and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
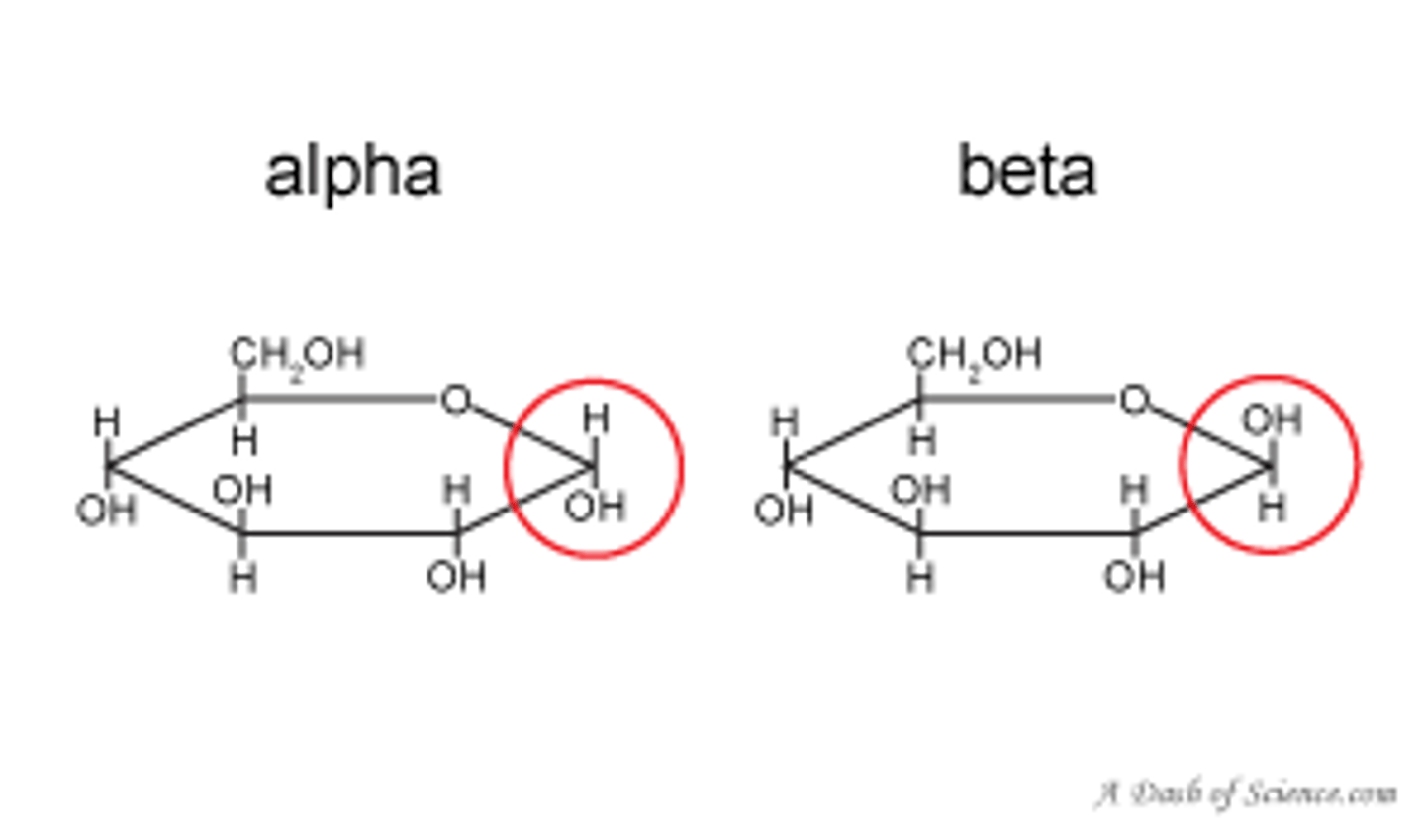
alpha and beta glucose
Alpha: hydroxyl group of carbon-1 is below the plane of ring
Beta: hydroxyl group of carbon-1 is above the ring
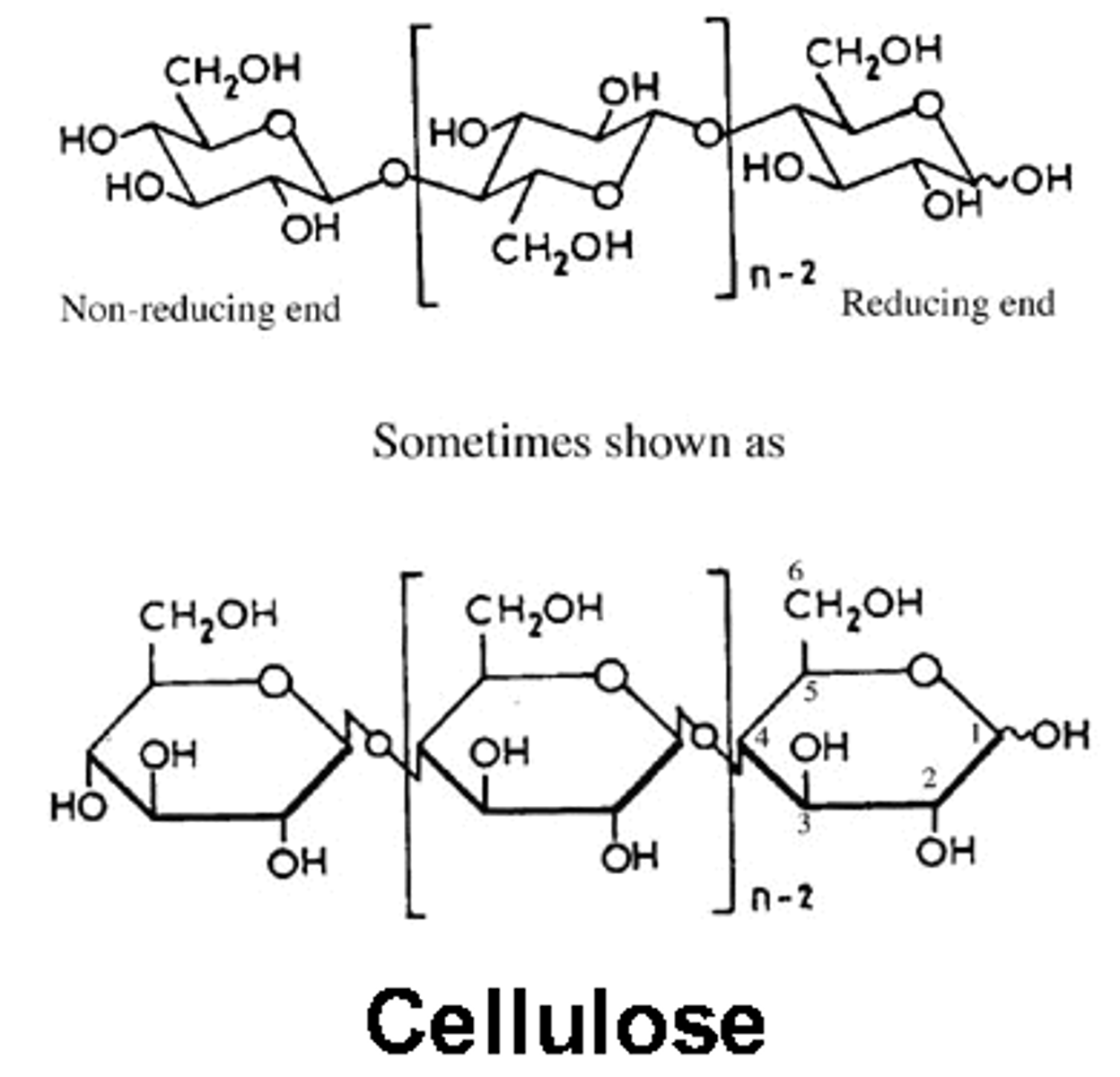
Structure of cellulose
-alternating orientation of beta-glucose monomers
-giving straight chains that can be grouped in bundles and cross-linked with hydrogen bonds.
- all are 1-4 glycosidic bonds, unbranched chain
-strong tensile strength (prevents plant cells from bursting)
what are 2 forms of starch
amylose and amylopectin
What is amylose and amylopectin?
-amylose is a linear polysaccharide, with a 1 → 4 α(alpha)-linkage
- amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide, has both 1 → 4 and 1 → 6 α -linkages.
Glycoproteins
poplypeptides with carbohydrate attached (mostly an oligosaccharide)
Role of glycoproteins
By displaying distictive glycoproteins, cells allow other cells to recognise them
-cell-to-cell recognisition (helps with organisation of tissues, allow foreign substances to be identified)
Examples of glycoproteins
ABO antigens in RBC
why glycoprotein O does not cause rejection for blood donation
it has same strcture as A and B but with one less monosaccharide
Lipids
substances that dissolve in non-polar solvents (lipids are hydrophobic)
examples of lipids
fats,oils, waxes, steroids
Importance of lipids
Storage, insulation, protection
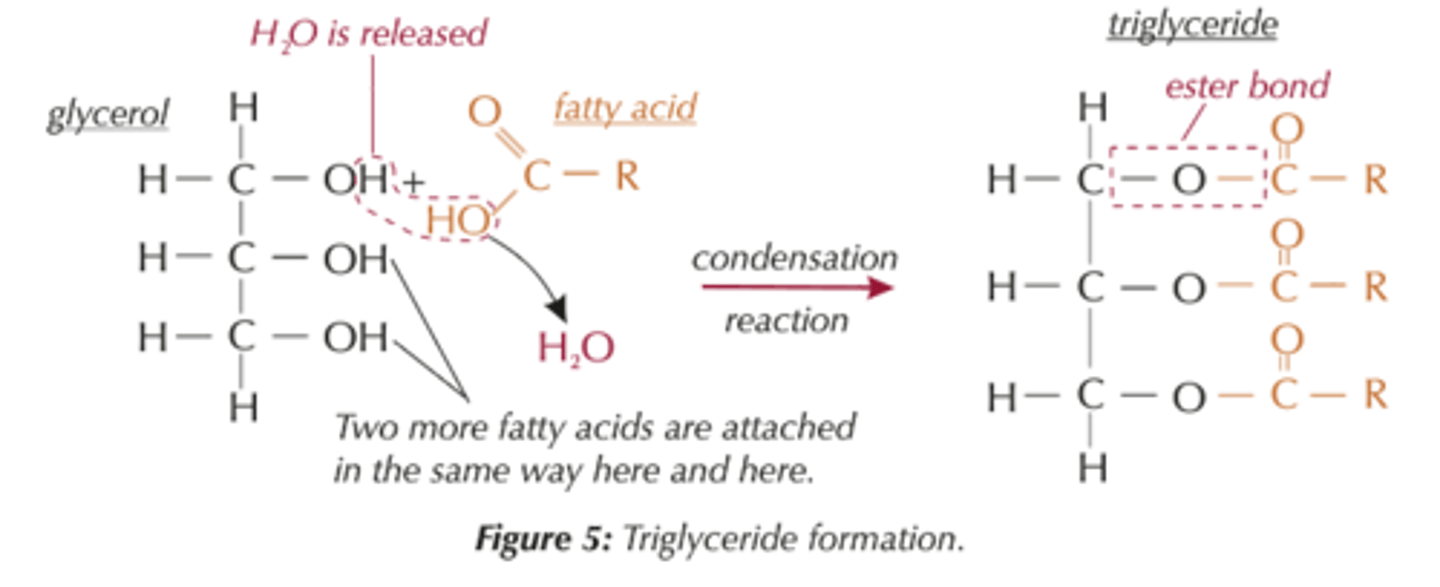
Formation of triglycerides
by condensation reactions, One glycerol molecule can link three fatty acid molecules , 3 water molecules produced
Different types of fatty acids
-saturated(Carbon Carbon single bonds)
- unsaturated- monounsaturated(1 Carbon Carbon double bond)
-and polyunsaturated(more than 1 Carbon Carbon double bond)
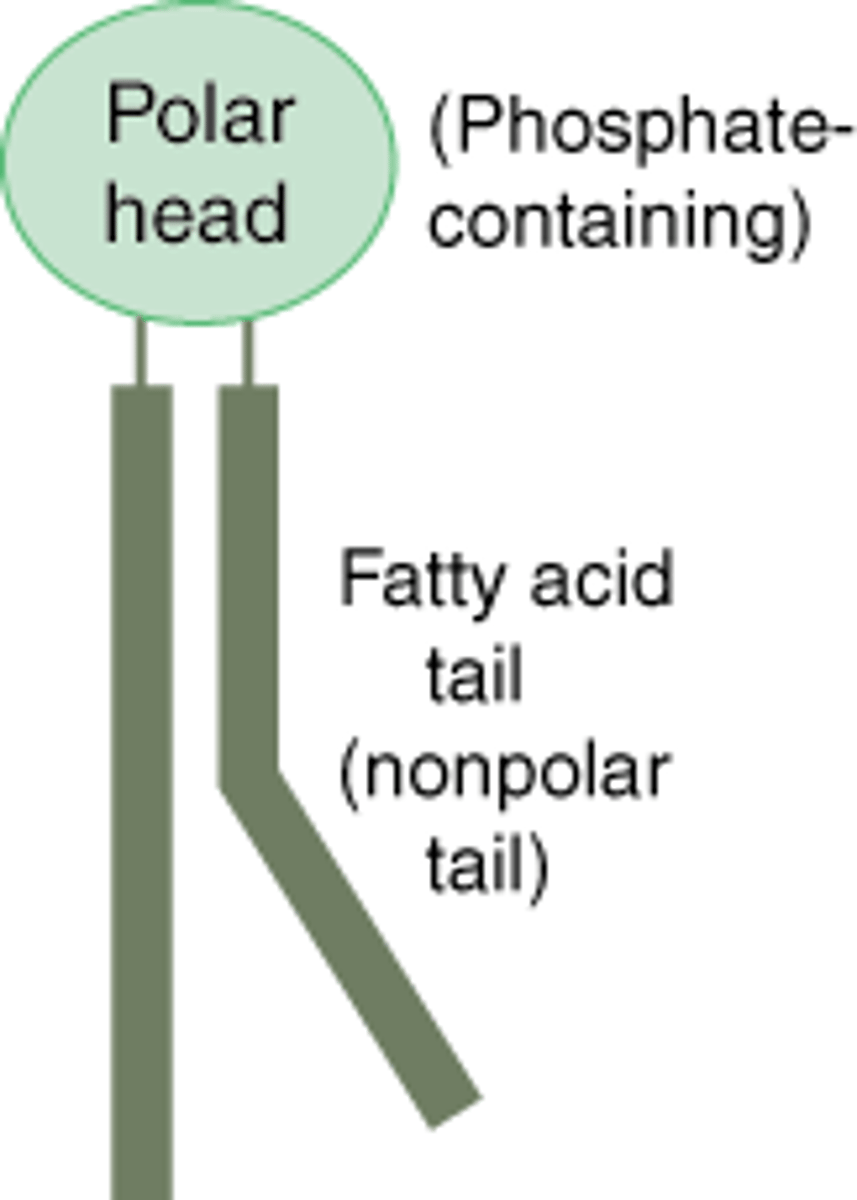
Fetaures of phospholipids
-stable structures
-basis of cell membrane
-Amphipathic (hydrophilic and hydrophobic)
Formation of phospholipids
two fatty acid molecules and one phosphate group. Phosphate grop is hydrophilic so phospholipids are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
Where are lipids stored
In adipose tissue, ommediately beneath the skin and also around some organs
general formula for fatty acid
CH3(CH2)nCOOH
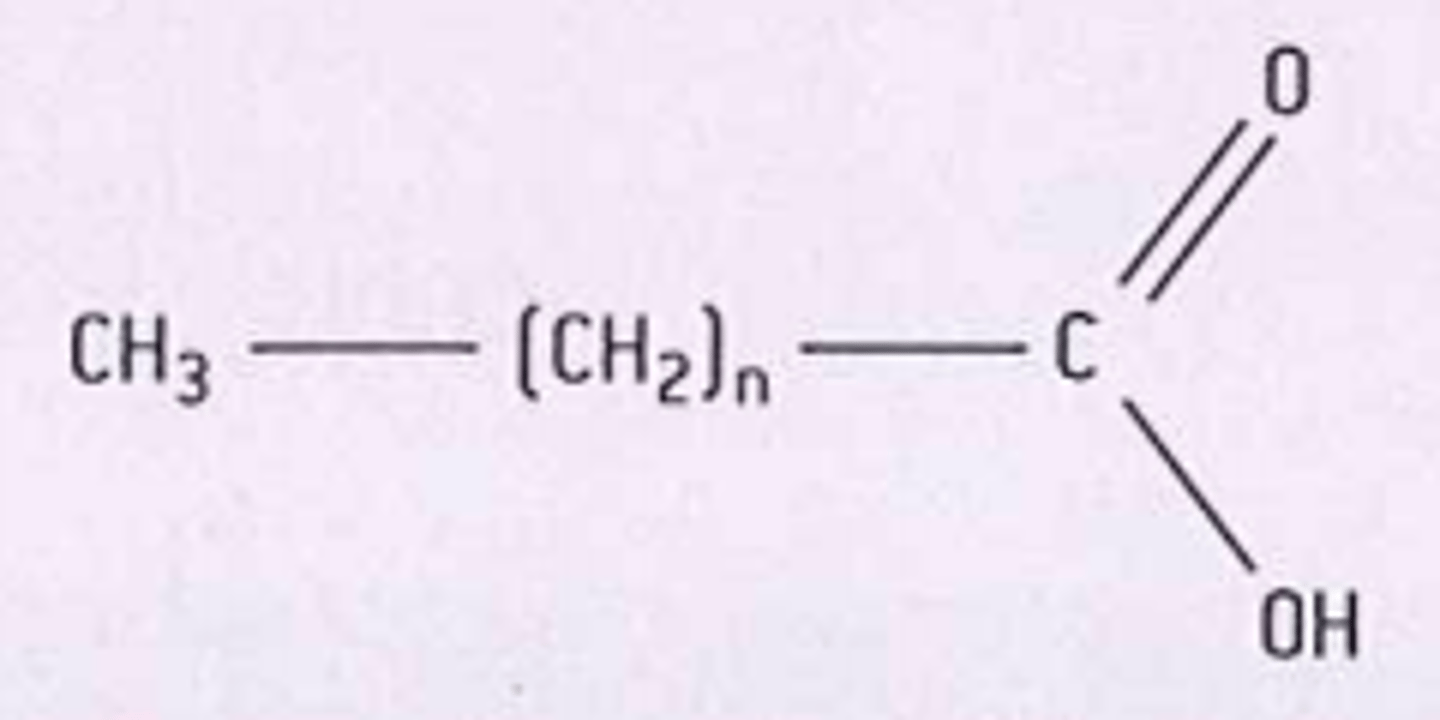
what are cis fatty acids
has both hydrogen atoms located on the same side
what are trans fatty acids
trans fatty acid has the two hydrogen atoms on opposite sides.
double carbon (C=C) bonds and how this affects melting point
The intermolecular interactions are much weaker than saturated molecules. As a result, the melting points are much lower for unsaturated fatty acids.
Triglycerides in adipose tissues
-energy storage cause they are chemically stable so enegry is not lost over time
-thermal insulation
-immisible with water so forms droplets in cytoplsm to avoid osmotic effects
-more energy than carbohydrates
-poor conductors of heat
-liquid at body temp, shock absorber
Steroids
4 fused ring of carbon atoms, hydrophobic so can pass through phospholipid bilayerand can enter or leave cells easily
strcture of steroids
3 cyclohexane rings, 1 cyclopentane ring
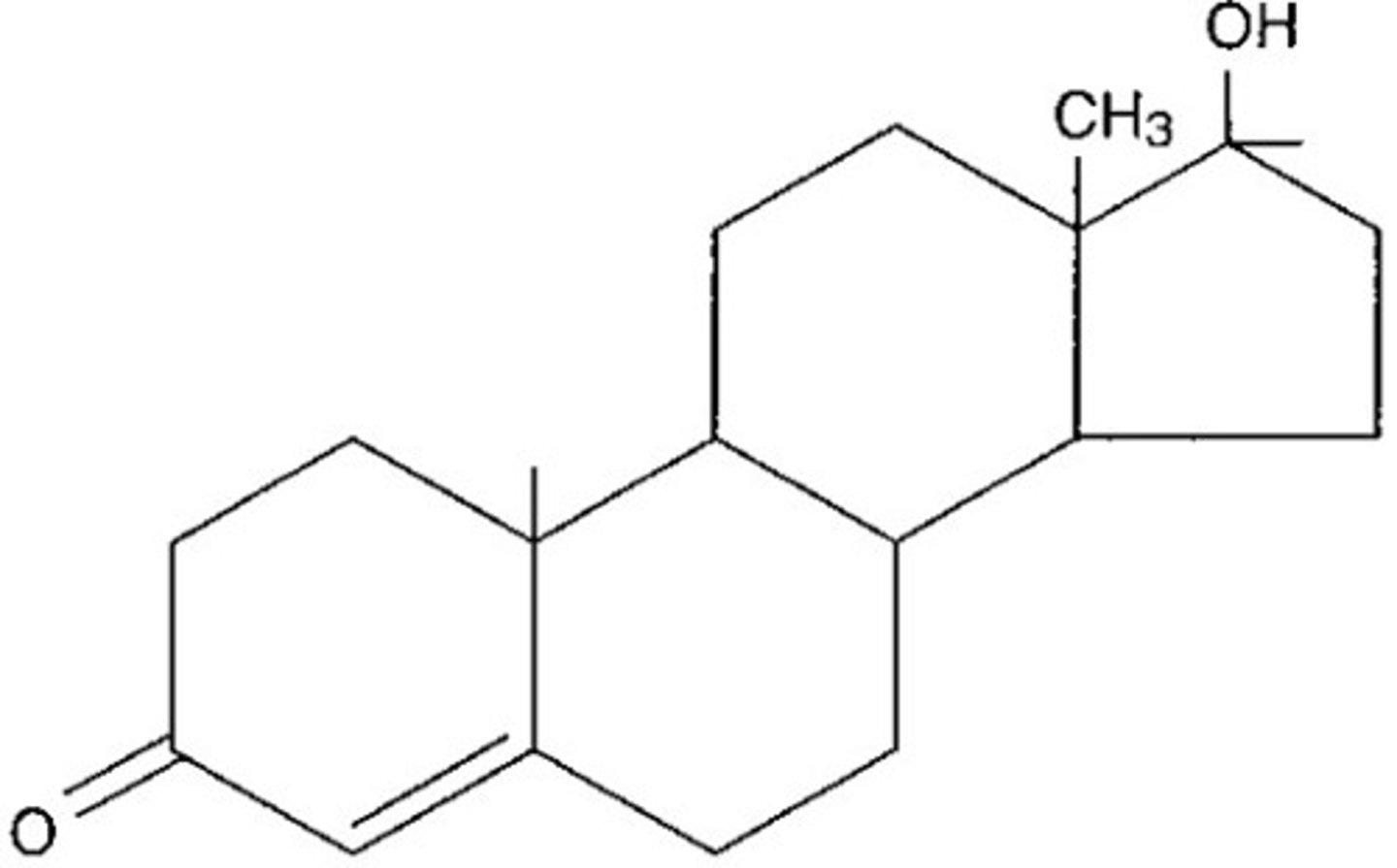
examples of steroids
oestradiol and testosterone