Physical properties of period 3 elements
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
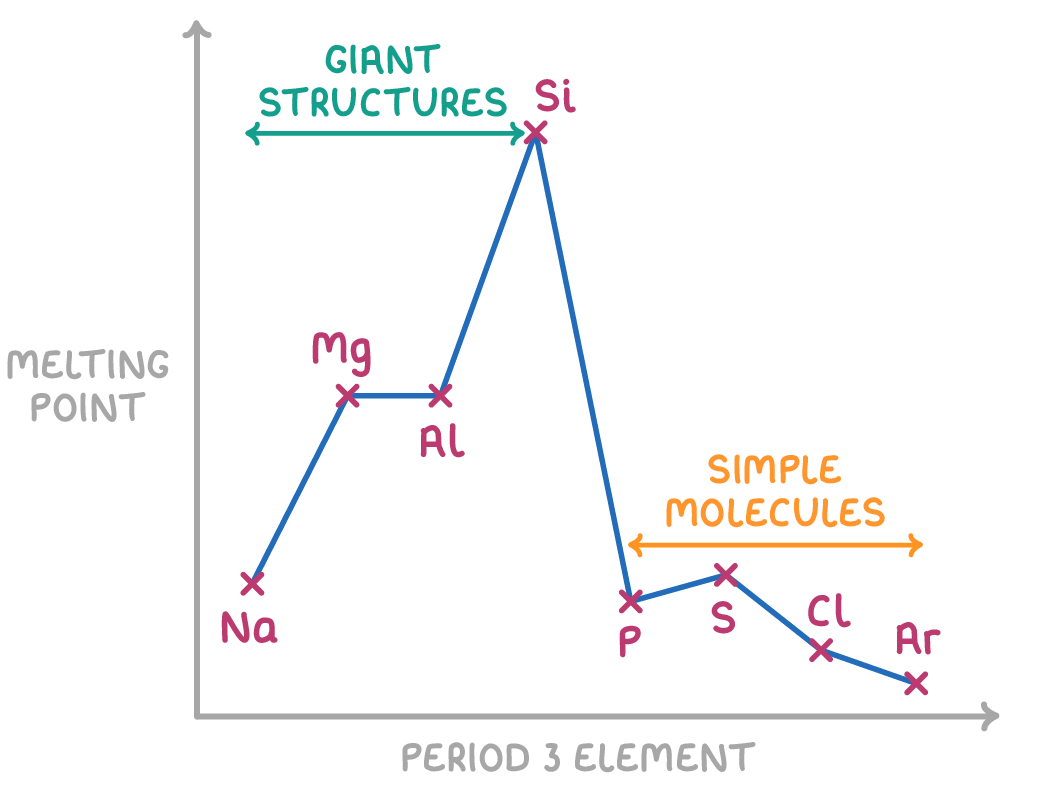
Which of the period 3 substances form giant covalent lattices?
Silicon
Which of the following period 3 substances form covalent bonds between their atoms?
Silicon
Phosphorus
Sulphur
Chlorine
Which trends are generally the case for all periods? (3)
Atomic radius decreases across each period.
First ionisation energy increases across each period
There is no clear upwards or downwards trend in melting point across a period
Magnesium is smaller than sodium because
there are more protons attracting the electrons towards the nucleus
Ionisation energy decreases between…
magnesium and aluminium
phosphorus and sulfur.
The explanation for the dip between phosphorus and sulfur is that, as we move from Group 5 to Group 6, there is some repulsion between electrons which are…
paired or in the same orbital
Across a period, the general trend is for first ionisation energy to…
increase
Across Period 3, shielding...
stays roughly the same
The 1st ionisation energy across Period 3 generally…
increases
Explain why the first ionisation energy of aluminium is less than magnesium.
The outermost electron of aluminium is in a p orbital whilst magnesium's is in an s orbital.
Electrons in the s orbital repel, and shield, the electrons in the p orbital, to some extent.
This means less energy is required to remove the first electron in the p orbital of aluminium.
Therefore, aluminium has a lower first ionisation energy.
Explain why the first ionisation energy of sulphur is less than phosphorus.
Phosphorus has only 1 electron in each of its p orbitals.
Sulphur has 2 electrons in one of its p orbitals, causing increased electron repulsion.
This means less energy is required to remove an electron from sulphur.
Therefore, sulphur has a lower first ionisation energy than phosphorus.
trend in melting point across period 3